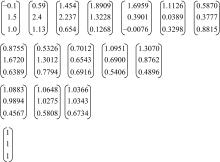
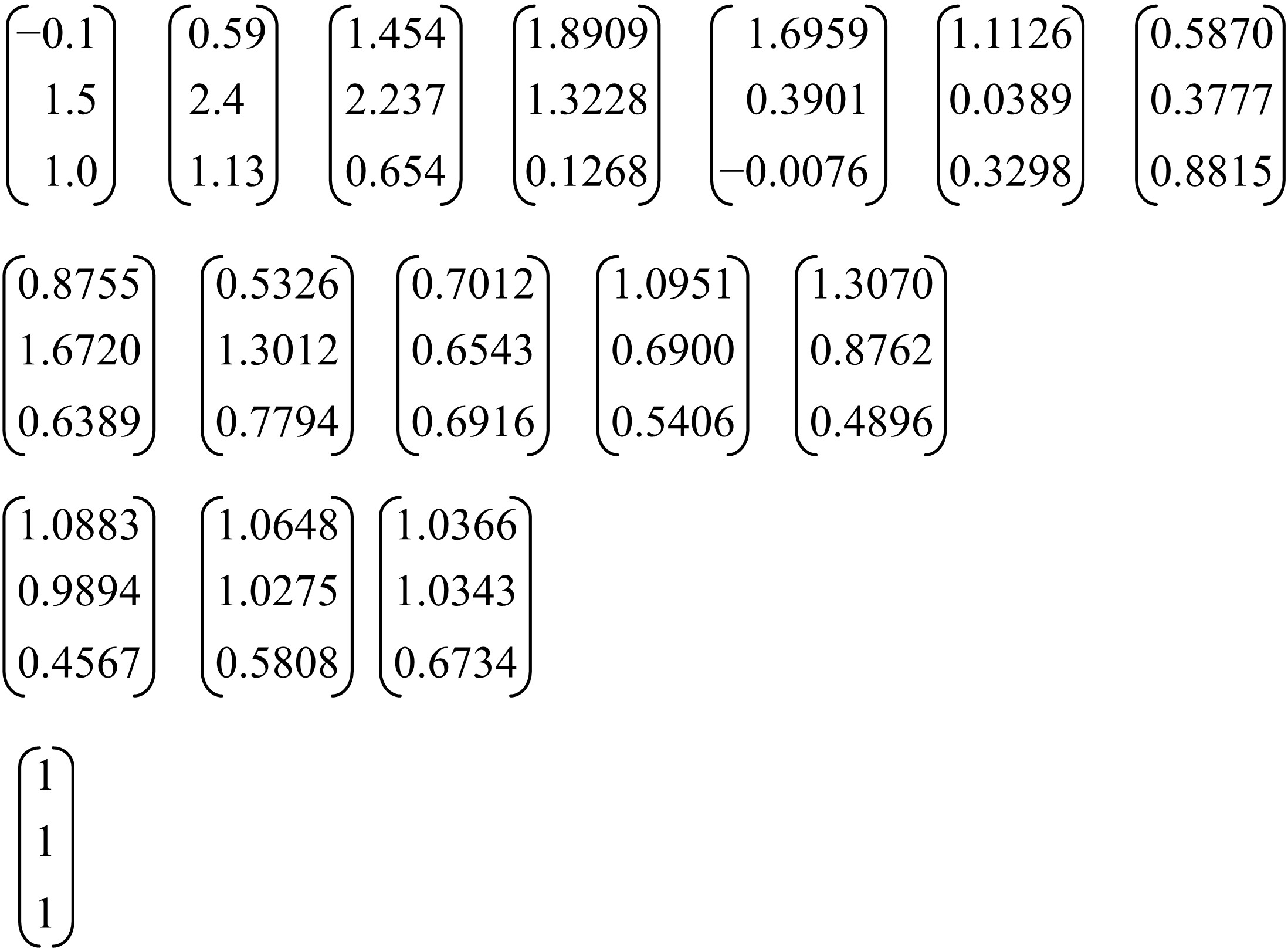
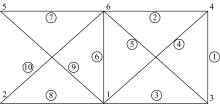
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 472-477.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191183
First and second⁃order sensitivity method of structure static displacement
Kai MA1( ),Bang-hui LI1,Kun YANG2(
),Bang-hui LI1,Kun YANG2( ),Qiao-ling LIU1
),Qiao-ling LIU1
- 1.College of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Basic Education College of Aviation University of Air Force,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- O342
| 1 | Arora J. Servey of structural reanalysis techniques[J]. Journal of the Structural Division American Society of Civil Engineers, 1976, 102(4): 783-802. |
| 2 | Kirsch U, Rubinstein M F. Structural reanalysis by iteration[J]. Computers and Structures, 1972, 2(4): 497-510. |
| 3 | Wang H, Li E, Li G. A parallel reanalysis method based on approximate inverse matrix for complex engineering problems[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2013, 135(8): 081001. |
| 4 | 王琥, 种浩, 高国强, 等. 重分析方法研究进展及展望[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(5): 1-16. |
| Wang Hu, Chong Hao, Gao Guo-qiang, et al. Review of advances and outlook in reanalysis methods[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(5): 1-16. | |
| 5 | Kirsch U. Implementation of combined approximations instructural optimization[J]. Computers and Structures, 2000, 78(1-3): 449-457. |
| 6 | Kirsch U. Approximate vibration reanalysis of structures[J]. AIAA Journal, 2003, 41(3): 504-511. |
| 7 | Kirsch U. A unified reanalysis approach for structural analysis design and optimization[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2003, 25(2): 67-85. |
| 8 | Zuo W, Yu Z, Zhao S, et al. A hybrid fox and Kirsch's reduced basis method for structural static reanalysis[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2012, 46(2): 261-272. |
| 9 | Sun R, Liu D, Xu T, et al. New adaptive technique of Kirsch method for structural reanalysis[J]. AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(3): 486-495. |
| 10 | 刘寒冰, 陈塑寰. 结构动特性灵敏度分析的边界元摄动法[J]. 振动与冲击, 1993, 12(3): 25-30. |
| Liu Han-bing, Chen Su-huan. Boundary element perturbation method for shape design sensitivity analysis of structural dynamic character[J],Journal of Vibration and Shock, 1993, 12(3): 25-30. | |
| 11 | Kirsch U. Approximate vibration reanalysis of structures[J]. AIAA Journal, 2003, 41(3): 504-511. |
| 12 | Lederer C, Altstadt S, Andriamonje S. An efficient reanalysis methodology for probabilistic vibration of largescale structures[J]. Journalof Mechanical Design, 2009, 131(5): 051007. |
| 13 | Xu T, Guo G, Zhang H. Vibration reanalysis using frequency-shift combined approximations[J]. Structural and Multi-disciplinary Optimization, 2011, 44(2): 235-246. |
| 14 | Gao G, Wang H, Li G. An adaptive time-based global method for dynamic reanalysis[J]. Structural and Multi-disciplinary Optimization, 2013, 48(2): 355-365. |
| [1] | Yi JIA,Ren-da ZHAO,Yong-bao WANG,Fu-hai LI. Sensitivity analysis of viscous damper parameters for multi⁃span and long⁃unit continuous girder bridges [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1871-1883. |
| [2] | CHEN Dong-hui, LYU Jian-hua, LONG Gang, ZHANG Yu-chen, CHANG Zhi-yong. Static rollover stability of semi-mounted agricultural machinery based on ADAMS [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1176-1183. |
| [3] | ZHANG Ze-xing, CHEN Guo-ying, ZONG Chang-fu. Objective evaluation indices of steering performance for EPS based on sensitivity analysis [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1043-1048. |
| [4] | KE Jun, CHENG Zhi-yong, SHI Wen-ku, SHI Teng, ZHANG Yi-jing, GUO Fu-xiang. Modal analysis and structure optimization of bus floor based on floor vibration control [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 719-725. |
| [5] | CHEN Shu-ming, PENG Deng-zhi, WANG Deng-feng, LIANG Jie. Structural-acoustic coupling and optimal experimental design for automotive interior low frequency noise [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1550-1556. |
| [6] | ZHAO Shi-jia, XU Tao, CHEN Wei, TAN Li-hui. Efficient approach for modal sensitivity analysis for near defective systems [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 497-499. |
| [7] | XU Tao, QIU Bing, CHENG Fei, JIN Yan-zhong, JIANG Yong-zhou, ZHAO Shi-jia. Structural reanalysis algorithm study of topological modifications based on even lines Epsilon accelerated method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 246-249. |
| [8] | ZHANG Ying-shuang, WANG Guo-qiang, WANG Ji-xin, HOU Xiao-ting, et al. Load spectrum compiling and fatigue life prediction of wheel loader axle shaft [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1646-1651. |
| [9] | LI Hong-Yan, WANG Yu-Xin, DUAN Chang-Chun. Impact of atmospheric circulation and its sensitivity analysis of Nenjiang river valley runoff [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(03): 879-0883. |
| [10] | GAO Jin, SONG Chuan-Xue. Influence of rubber bushing stiffness on suspension performance [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 324-0329. |
| [11] | GAO Shu-Na, DENG Zhao-Xiang, HU Yu-Mei. Optimization of car interior low frequency noise based on sensitivity analysis [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(05): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | WANG Xu,CHEN Yong-gang,YANG Yin-sheng . DEA-DA model with interval numbers and its sensitivity analysis [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2009, 39(03): 716-0720. |
| [13] | CHENG Yong-chun,TAN Guo-jin,LIU Han-bing,FU Cong . Damage identification of bridge structure based on statistical properties of eigen-solution [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 812-816. |
|
||