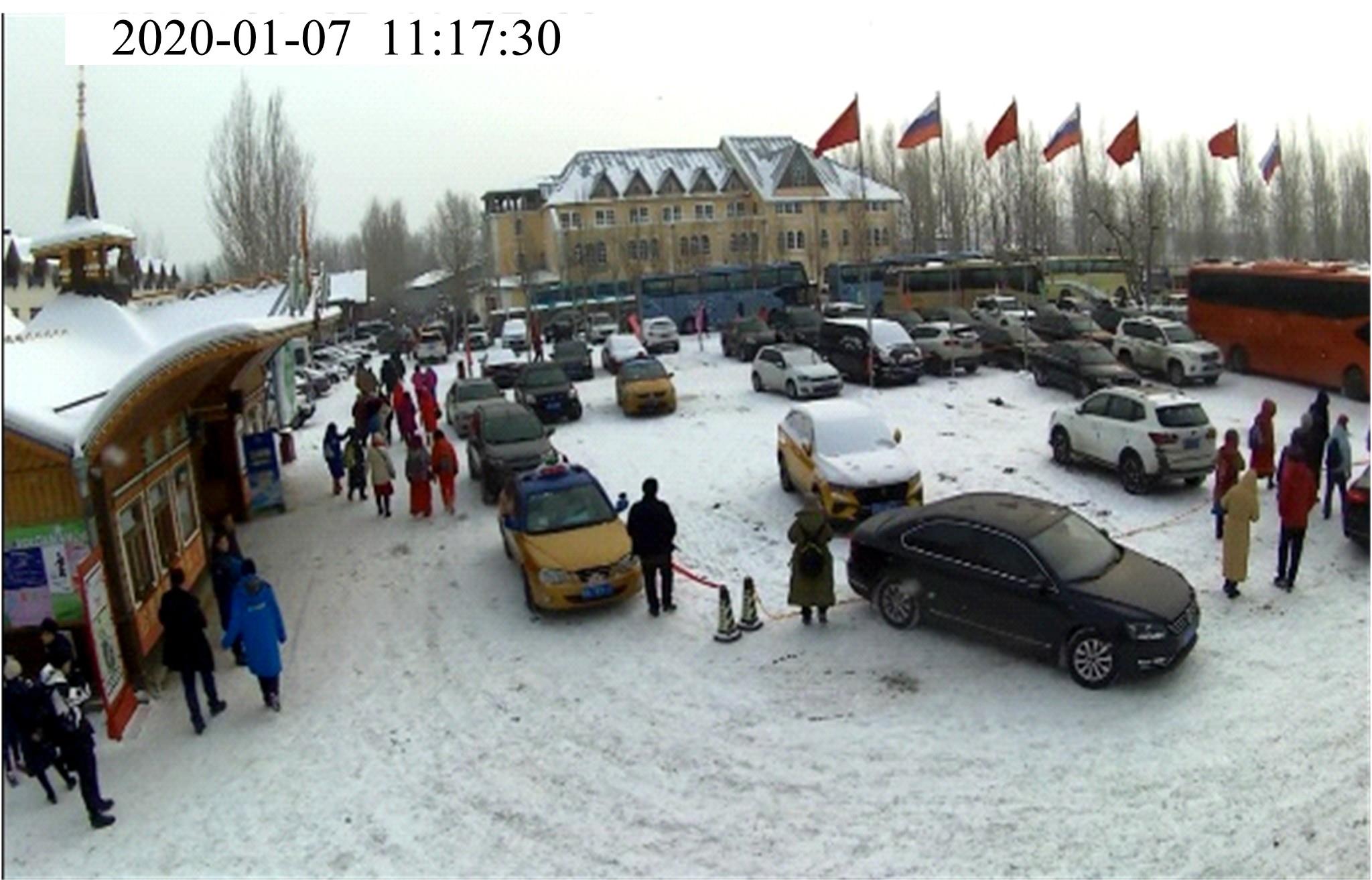
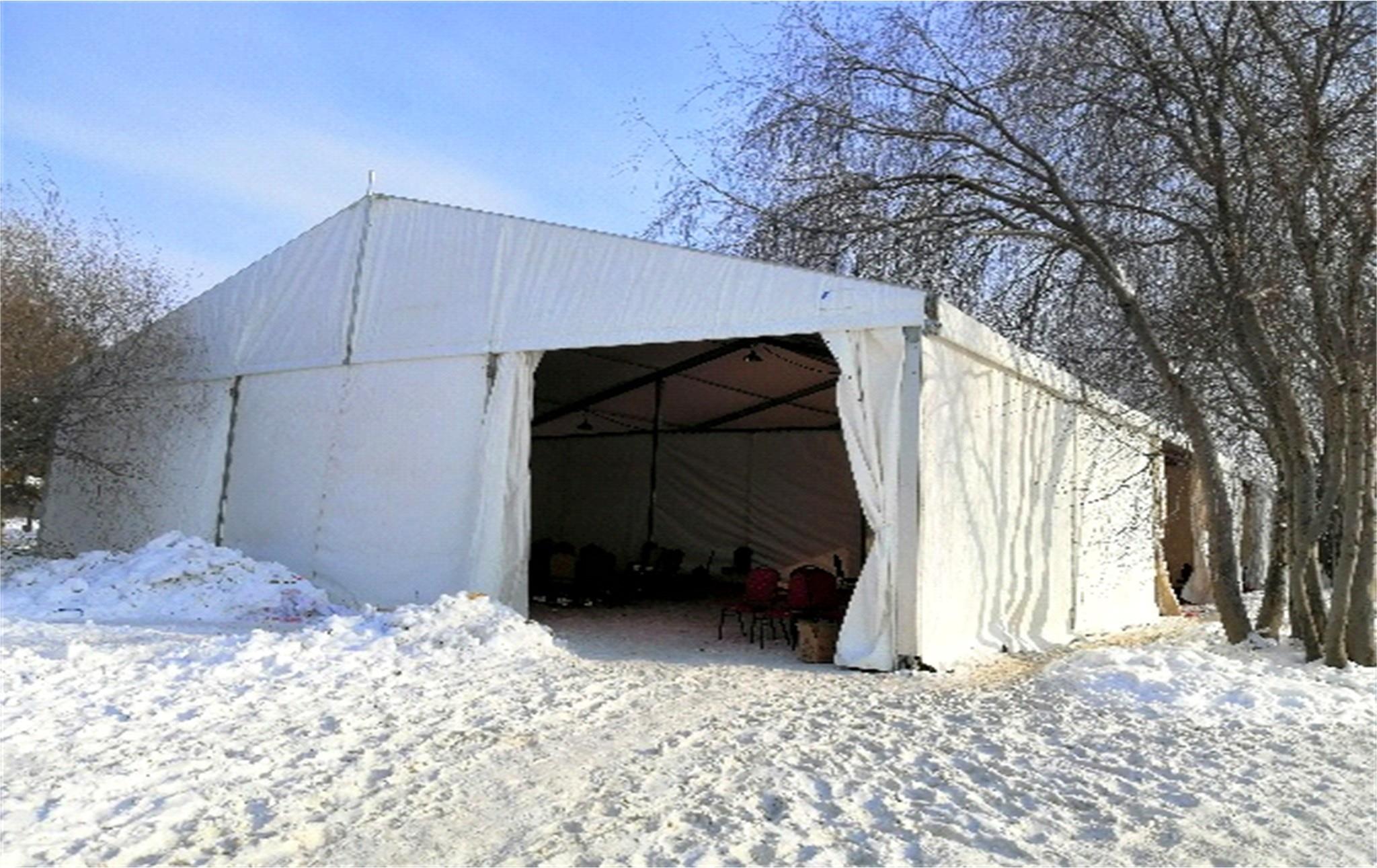
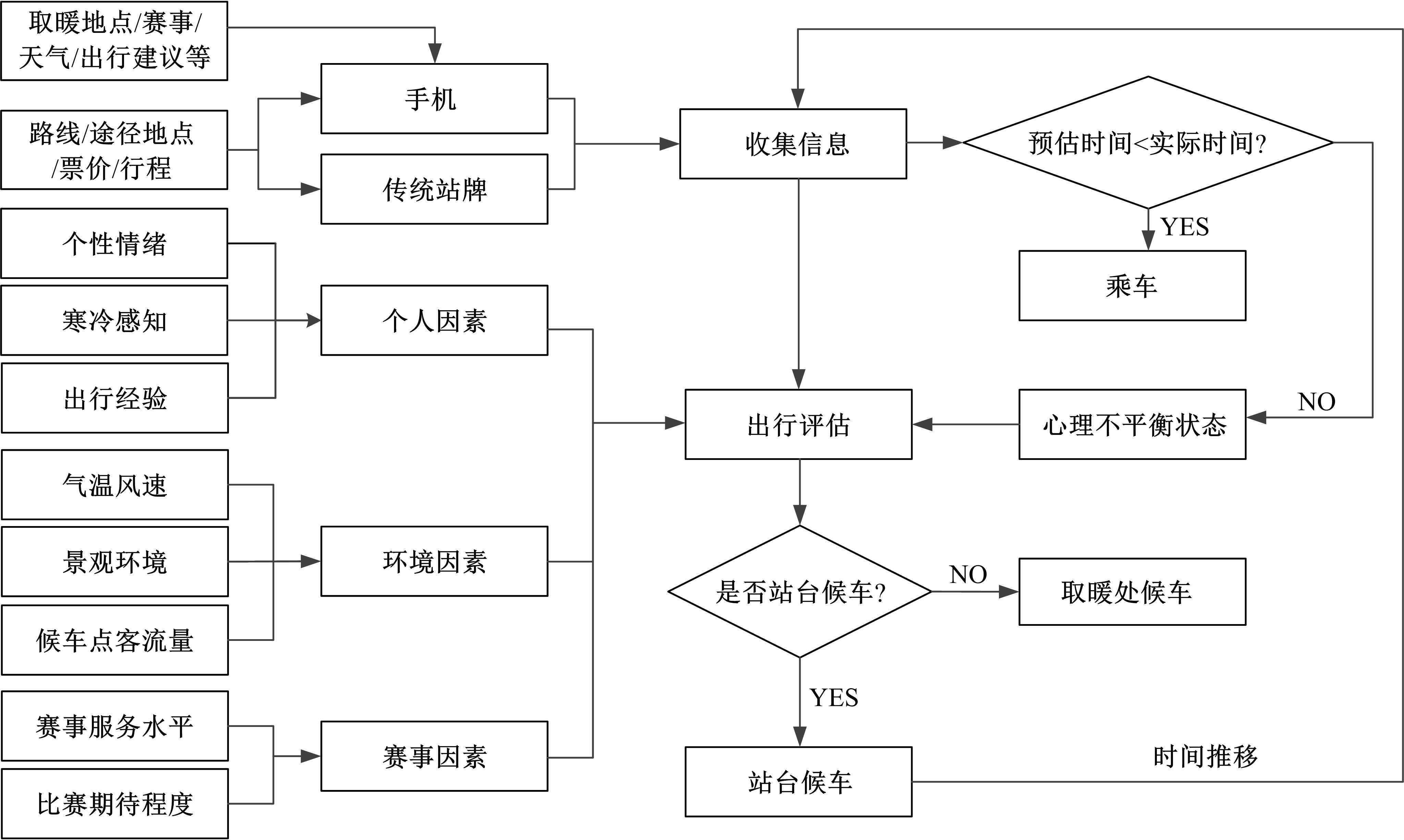
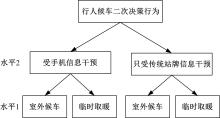
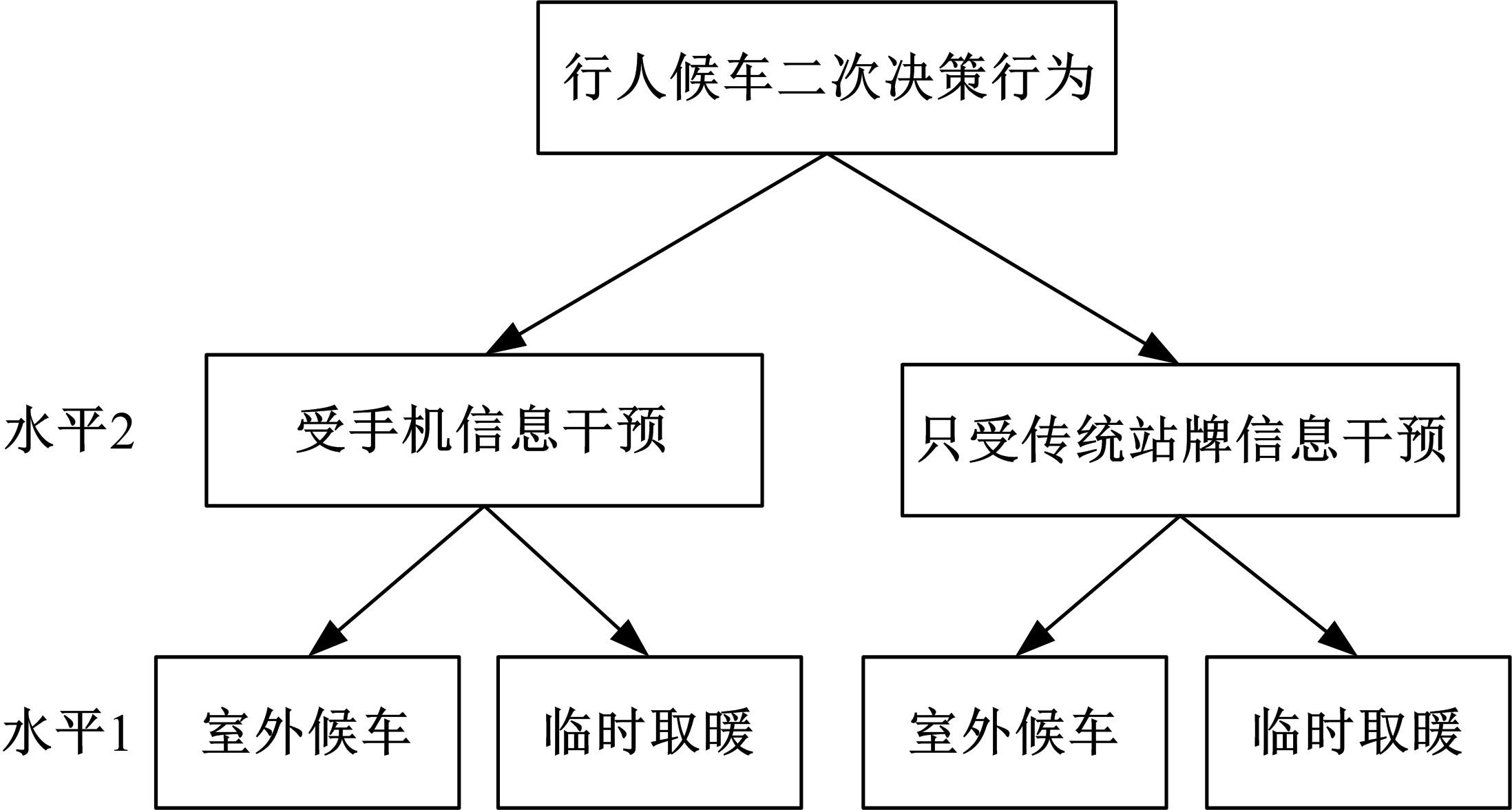
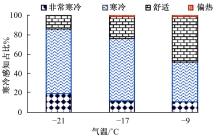
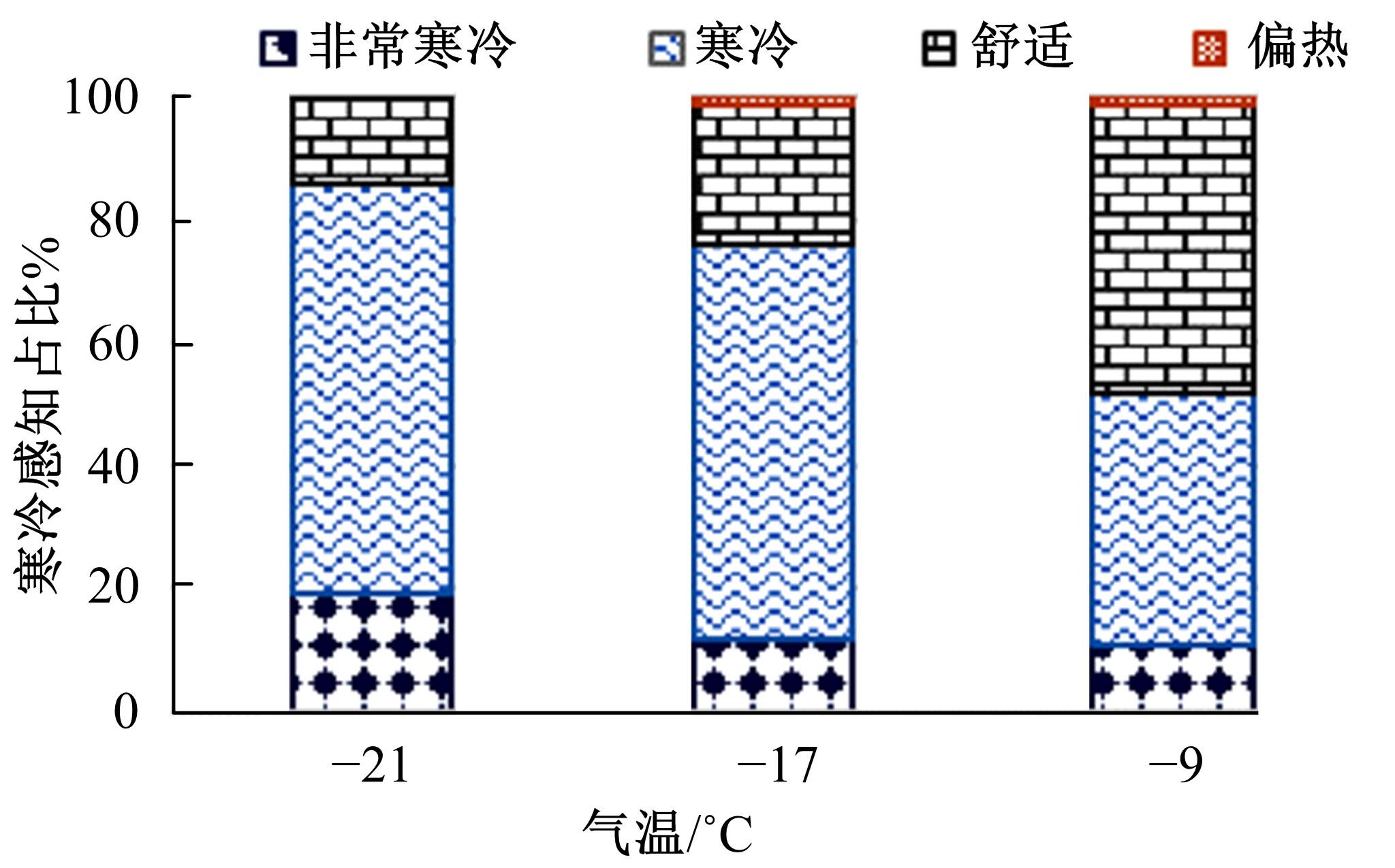
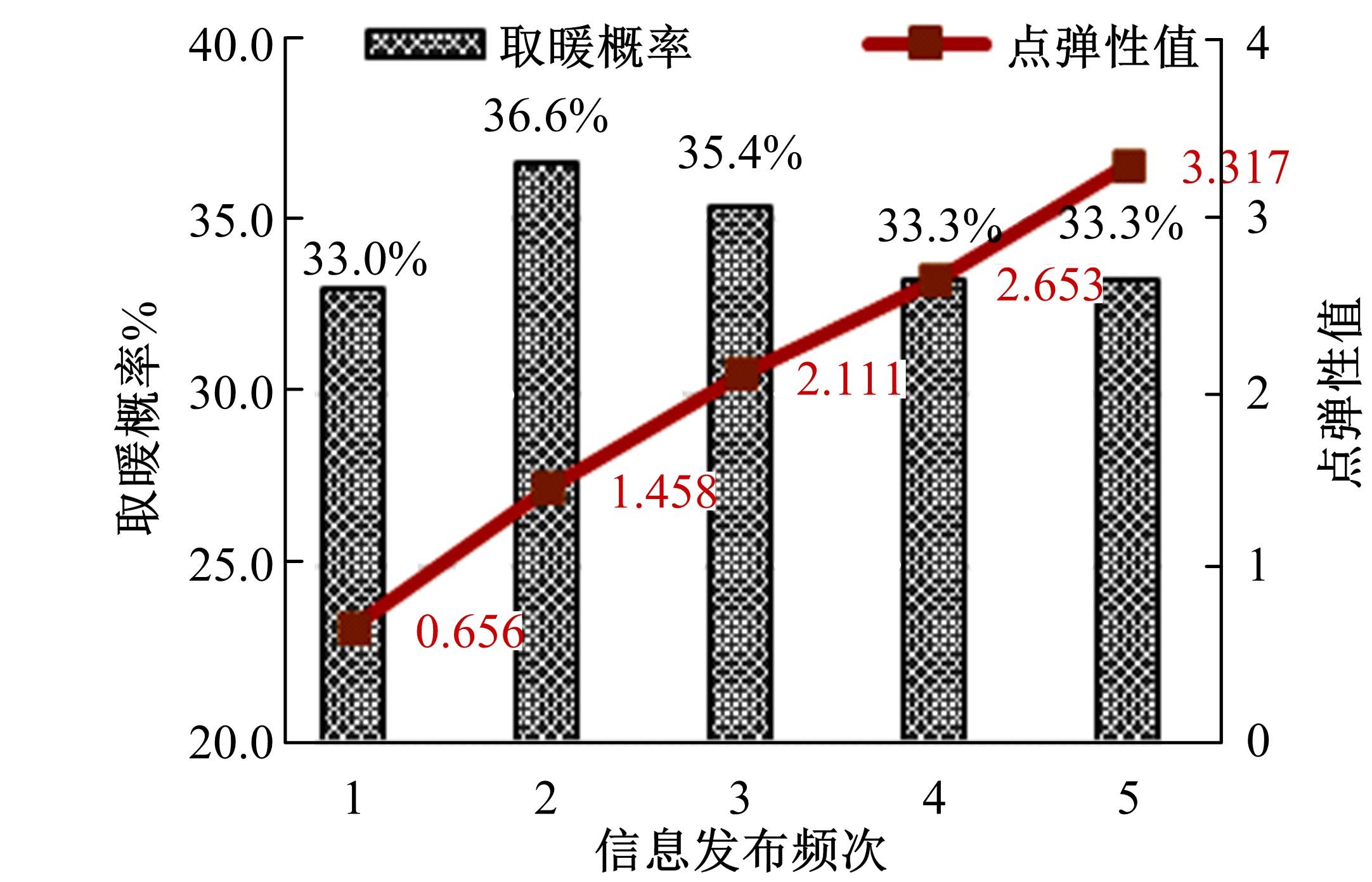
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 132-140.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210517
Decision⁃making behavior of pedestrians in cold competition area under the intervention of mobile information
Wen-bo HUANG1( ),Yan-yan CHEN1(
),Yan-yan CHEN1( ),Shu-shan CHAI2
),Shu-shan CHAI2
- 1.College of Metropolitan Transportation,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
2.Research Institute for Road Safety of MPS,Beijing 100062,China
CLC Number:
- U491.4
| 1 | Deng Y, Cao B, Yang H, et al. Effects of local body heating on thermal comfort for audiences in open-air venues in 2022 Winter Olympics[J]. Building and Environment, 2019, 165: No.106363. |
| 2 | 张越. 基于ACP方法的城市轨道交通枢纽应急疏散若干问题研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院, 2013. |
| Zhang Yue. Several problems of urban rail transit hub emergency evacuation based on ACP approach[D]. Beijing: College of Electronical and Information Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 3 | 孙祥龙, 冯树民, 吴海月. 站台环境与候车行为对感知候车时间的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(2):186-190. |
| Sun Xiang-long, Feng Shu-min, Wu Hai-yue. Influence of stop environment and waiting behavior on perceived waiting time[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(2):186-190. | |
| 4 | Wang P C, Hsu Y T, Hsu C W. Analysis of waiting time perception of bus passengers provided with mobile service[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2021, 145(6):319-336. |
| 5 | 马卫武, 刘小燕, 李立清. 铁路客运站旅客候车时间研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2009, 31(5):104-107. |
| Ma Wei-wu, Liu Xiao-yan, Li Li-qing. Research of waiting time of passengers at railway stations[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2009, 31(5):104-107. | |
| 6 | Lu Hui, Peter Burge, Chris Heywood, et al. The impact of real-time information on passengers' value of bus waiting time[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2018, 31:18-34. |
| 7 | Věra K, Prague U. Combined restraint and cold stress in rats: effects on memory processing in passive avoidance task and on plasma levels of ACTH and corticosterone[J]. Behavioural Brain Research, 2003, 142(1/2):143-149. |
| 8 | Long W B, Edlich R F, Winters K L, et al. Cold injuries[J]. J Long Term Eff Med Implants, 2005, 15(1):67-78. |
| 9 | Reed H L, Reedy K R, Palinkas L A, et al. Impairment in cognitive and exercise performance during prolonged antarctic residence: effect of thyroxine supplementation in the polar triiodothyronine syndrome[J]. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2001, 86(1):110-116. |
| 10 | 关宏志. 非集计模型——交通行为分析的工具[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2004:5-35. |
| 11 | 张文会,秦佳琪,等. 考虑拥挤度的常规公交与地铁出行方式选择模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(1):200-205. |
| Zhang Wen-hui, Qin Jia-qi, et al. Travel choice between bus transit and subway considering crowding degree[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1):200-205. | |
| 12 | 赵顗, 陆建, 张文珺, 等. Logit模型下的道路拥堵收费策略改善效果分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(3): 80-85. |
| Zhao Yi, Lu Jian, Zhang Wen-jun, et al. Improvement effect analysis of congestion pricing using Logit model[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(3): 80-85. | |
| 13 | Horowitz J L. Reconsidering the multinomial probit model[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 1991, 25(6):433-438. |
| 14 | Ehrhart O. Dry wind chill effect and clothing [J]. Journal of Wilderness Medicine, 1991, 2(2): 102-109. |
| 15 | Koppelman F S, Wen C H. The paired combinatorial logit model: properties, estimation and application[J]. Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2000, 34(2):75-89. |
| [1] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [2] | Chao SUN,Hao-wei YIN,Wen-yun TANG,Zhao-ming CHU. Sensor deployment strategy and expansion inference of mobile phone data for traffic demand estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [3] | Hong-fei JIA,Ying-jun XU,Li-li YANG,Nan WANG. League member selection and benefit distribution of commercial vehicles multi⁃modal transportation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [4] | Xian-min SONG,Shu-tian YANG,Ming-xin LIU,Zhi-hui LI. Fluctuation characteristics and prediction method of bus travel time between stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [5] | Zhi ZHENG,Bo GENG,Fu-min WANG,Jun-hong DONG,Si-si WEI. Improvement of protective ability for existing low⁃grade concrete guardrail [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [6] | Wen-jing WU,Yong-bin ZHAN,Li-li YANG,Run-chao CHEN. Coordinated control method of variable speed limit in on⁃ramp area considering safety distance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [7] | Hong-fei JIA,Zi-han SHAO,Li-li YANG. Ride⁃sharing matching model and algorithm of online car⁃hailing under condition of uncertain destination [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [8] | Xing-hua LI,Fei-yu FENG,Cheng CHENG,Wei WANG,Peng-cheng TANG. Choice preference analysis and modeling of ridesplitting service [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [9] | Tian-jun FENG,Xue-lu SUN,Jia-sheng HUANG,Xiu-juan TIAN,Xian-min SONG. Two-phase signal intersection delay based on three crossing modes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [10] | Xian-tong LI,Wei QUAN,Hua WANG,Peng-cheng SUN,Peng-jin AN,Yong-xing MAN. Route travel time prediction on deep learning model through spatiotemporal features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [11] | Yi-ran WANG,Jing-xu CHEN,Yue-ping WANG,Jin-biao HUO,Zhi-yuan LIU. Instant demand⁃responsive scheme for customized bus considering service fairness [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2574-2581. |
| [12] | Yan-feng JIA,Da-yi QU,Lu LIN,Rong-han YAO,Xiao-long MA. Coordinated speed control of connected mixed traffic flow based on trajectory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| [13] | Da-wei ZHANG,Hai-tao ZHU. An optimization⁃based evacuation model considering pedestrian heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [14] | Chang-fu ZONG,Long WEN,Lei HE. Object detection based on Euclidean clustering algorithm with 3D laser scanner [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [15] | Liang JIANG,Yi HE. Risky driving behavior and influencing factors analysis for electric two⁃wheeler [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
|
||