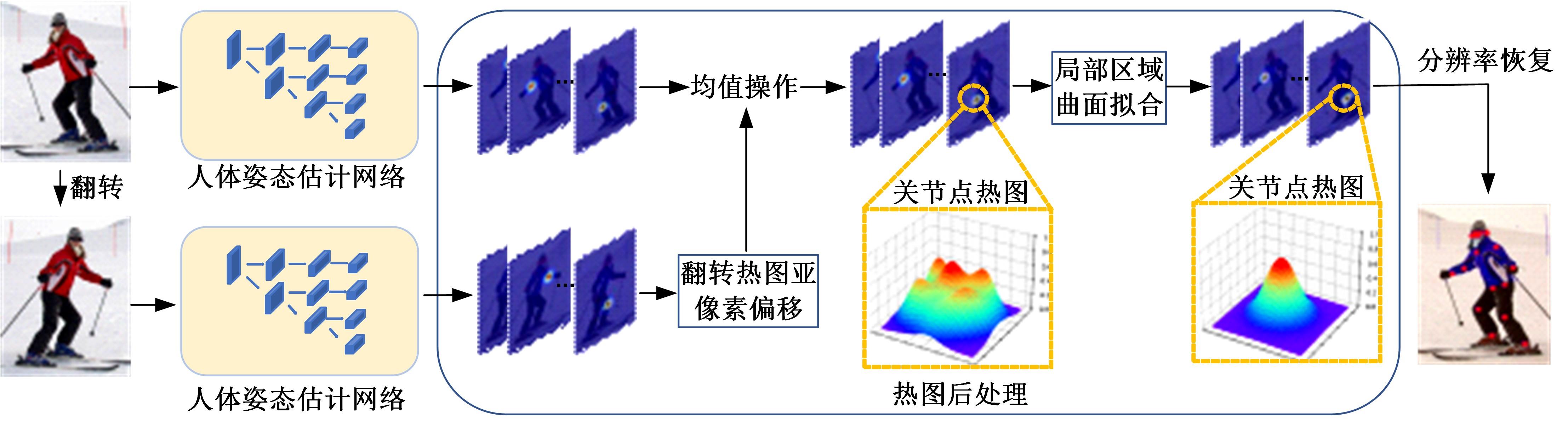
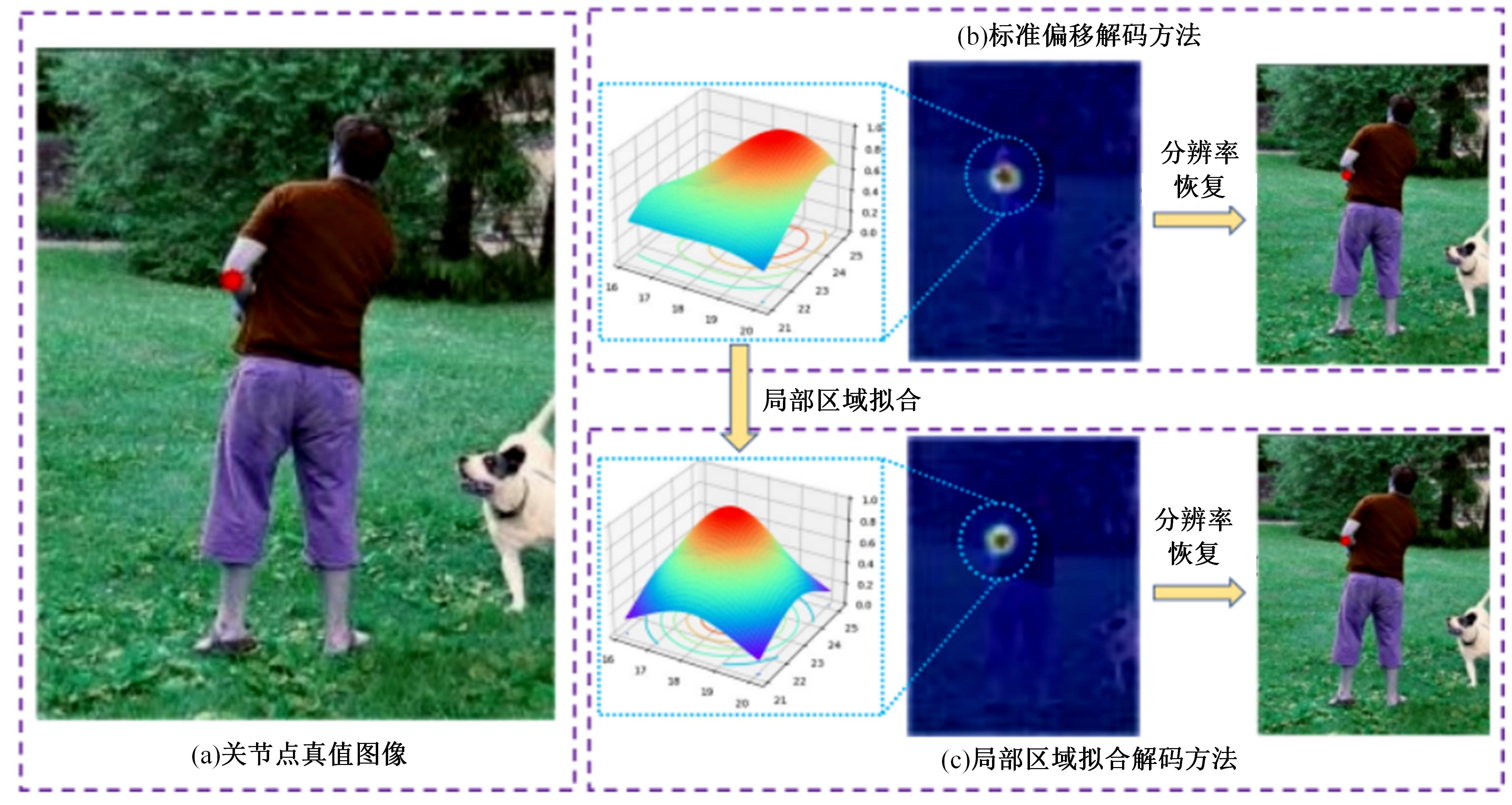
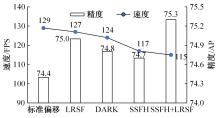
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 1385-1392.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230268
Postprocessing of human pose heatmap based on sub⁃pixel location
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Electronics and Information Engineering,Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology,Harbin 150022,China
CLC Number:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Islam M U, Mahmud H, Ashraf F B, et al. Yoga posture recognition by detecting human joint points in real time using microsoft kinect[C]∥ IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference (R10-HTC), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017: 668-673. |
| 2 | 李贻斌, 郭佳旻, 张勤. 人体步态识别方法与技术[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 1-18. |
| Li Yi-bin, Guo Jia-min, Zhang Qin. Methods and technologies of human gait recognition[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 1-18. | |
| 3 | 田皓宇, 马昕, 李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| Tian Hao-yu, Ma Xin, Li Yi-bin. Skeleton-based abnormal gait recognition: a survey[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. | |
| 4 | Tang S, Andriluka M, Andres B, et al. Multiple people tracking by lifted multicut and person re-identification[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hololulu, USA, 2017: 3539-3548. |
| 5 | 侯春萍, 杨庆元, 黄美艳, 等. 基于语义耦合和身份一致性的跨模态行人重识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(12): 2954-2963. |
| Hou Chun-ping, Yang Qing-yuan, Huang Mei-yan, et al. Cross⁃modality person re-identification based on semantic coupling and identity-consistence constraint[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2954-2963. | |
| 6 | Cheng Y, Yi P, Liu R, et al. Human-robot interaction method combining human pose estimation and motion intention recognition[C]∥ IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design, Dalian, China, 2021: 958-963. |
| 7 | Toshev A, Szegedy C. Deeppose: human pose estimation via deep neural networks[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 1653-1660. |
| 8 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 5693-5703. |
| 9 | Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y. Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking[C]∥ Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munichi, Germany, 2018: 466-481. |
| 10 | Huang J, Zhu Z, Guo F, et al. The devil is in the details: delving into unbiased data processing for human pose estimation[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5700-5709. |
| 11 | Zhang F, Zhu X, Dai H, et al. Distribution-aware coordinate representation for human pose estimation[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 7093-7102. |
| 12 | Newell A, Yang K, Deng J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥ Computer Vision-ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 483-499. |
| 13 | Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, et al. Microsoft coco: common objects in context[C]∥ Computer Vision⁃ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740-755. |
| 14 | Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler P, et al. 2d human pose estimation: new benchmark and state of the art analysis[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 3686-3693. |
| 15 | Yang Y, Ramanan D. Articulated pose estimation with flexible mixtures-of-parts[C]∥ CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, USA, 2011: 1385-1392. |
| [1] | Jing-hong LIU,An-ping DENG,Qi-qi CHEN,Jia-qi PENG,Yu-jia ZUO. Anchor⁃free target tracking algorithm based on multiple attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
| [2] | Kan WANG,Hang SU,Hao ZENG,Jian QIN. Deep target tracking using augmented apparent information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2676-2684. |
| [3] | Jie CAO,Xue QU,Xiao-xu LI. Few⁃shot image classification method based on sliding feature vectors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [4] | Tao XU,Ke MA,Cai-hua LIU. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [5] | Hong-wei ZHAO,Ming-zhao LI,Jing LIU,Huang-shui HU,Dan WANG,Xue-bai ZANG. Scene classification based on degree of naturalness and visual feature channels [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [6] | CHE Xiang-jiu, WANG Li, GUO Xiao-xin. Improved boundary detection based on multi-scale cues fusion [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
| [7] | XU Yan-yan, CHEN Hui, LIU Jia-ju, YUAN Jin-zhao. Cell processor stereo matching parallel computation [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 952-958. |
| [8] | ZHANG Bao-hua, HUANG Wen-qian, LI Jiang-bo, ZHAO Chun-jiang, LIU Cheng-liang, HUANG Dan-feng. Online sorting of irregular potatoes based on I-RELIEF and SVM method [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1811-1817. |
| [9] | YANG Yan, LIU Sa, LIAN Shi-bin, ZHU Xiao-dong. Analysis of fruit tree pests morphological characteristics based on computer vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(增刊1): 235-238. |
| [10] | SHANG Fei, MA Jun-Xiao, YAO Li, TIAN Di, QIU Chun-Ling. Multifeature fusion based method for monitoring working status of instruments [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(02): 545-0548. |
| [11] | GE Liang, ZHU Qing-sheng, FU Si-si, LUO Da-jiang, LIU Jin-feng. Improved image dense stereo matching algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(01): 212-0217. |
| [12] |
GUAN Xin, JIA Xin, GAO Zhen-hai .
Adaptive threshold algorithm based on contrast-regional homogeneity analysis of lane image [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(04): 758-763. |
| [13] | Wan Peng,Sun Yu,Sun Yong-hai . Recognition method of rice kernel shape based on computer vision [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2008, 38(02): 489-0492. |
| [14] | Tian Jian, Li Jiang, Li Yaqiao. Calibration technique of photogrammetry of traffic accident scene [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2006, 36(增刊1): 136-0139. |
| [15] | GUAN Xin, DONG Yin-ping, GAO Zhen-hai. LMedSquare based road curve fitting algorithm [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2004, (2): 194-197. |
|
||