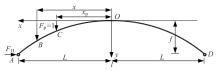
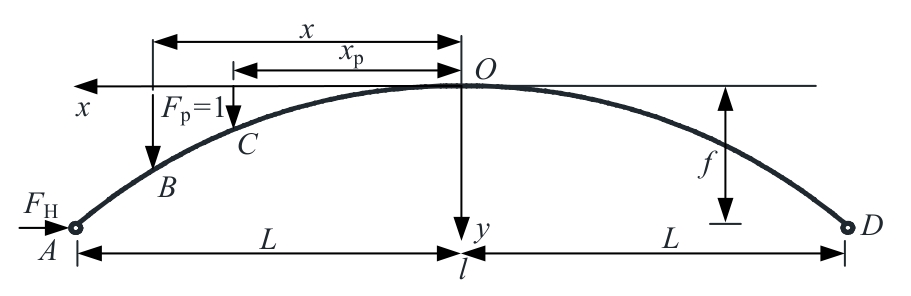
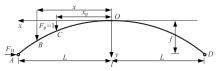
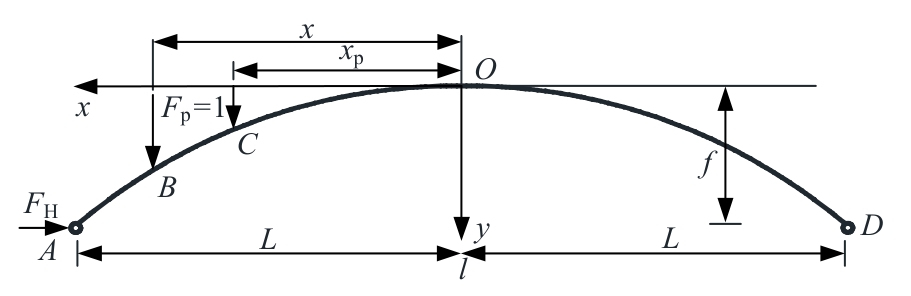
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 664-672.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230086
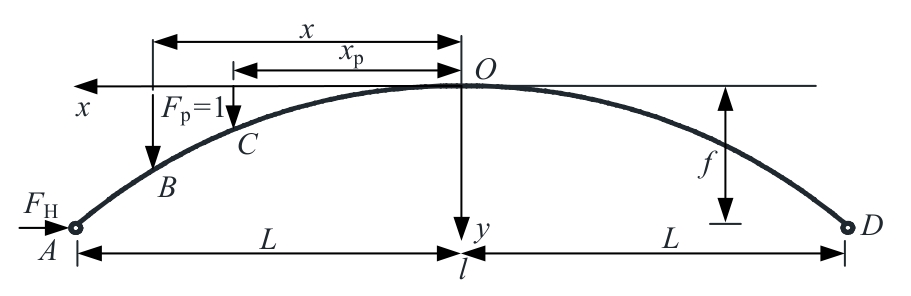
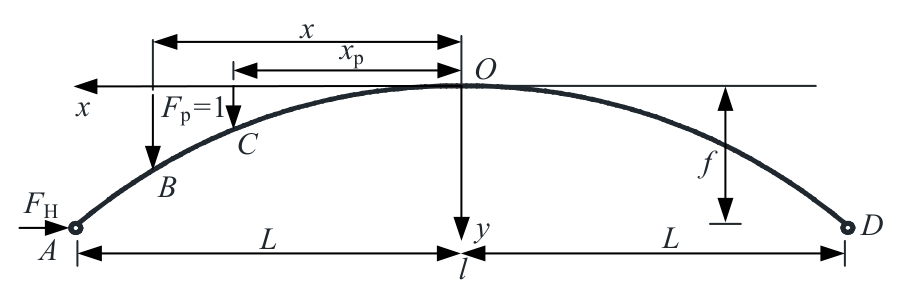
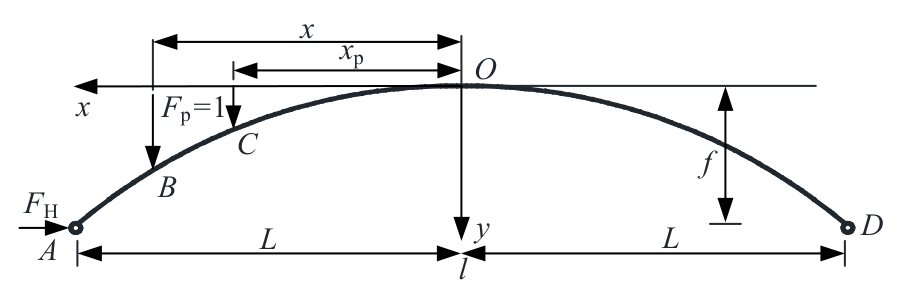
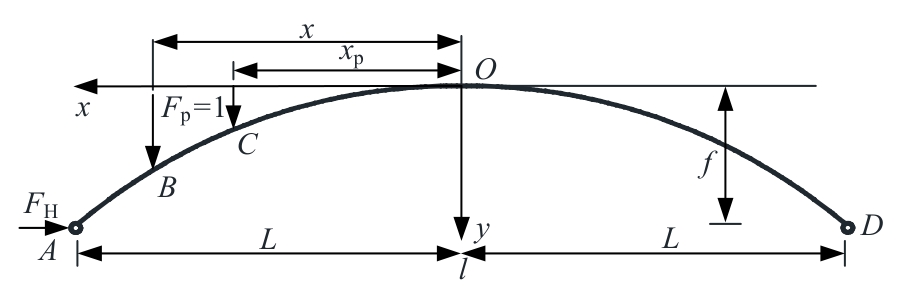
Analytical solution of thrust influence line of variable section two-hinged arch and application of damage identification
Yu ZHOU1,2,3( ),Meng LI2,3,Sheng-kui DI1,Xian-zeng SHI2,Dong CHEN2
),Meng LI2,3,Sheng-kui DI1,Xian-zeng SHI2,Dong CHEN2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Anhui Jianzhu University,Hefei 230601,China
3.National and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Building Health Monitoring and Disaster Prevention Technology,Anhui Jianzhu University,Hefei 230601,China
CLC Number:
- TU311
| 1 | Cocchetti G, Rizzi E. Least-thickness symmetric circular masonry arch of maximum horizontal thrust[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 91(6): 2617-2639. |
| 2 | 蒋伟, 吕大刚. 混凝土两铰圆弧拱的面内徐变稳定性[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(2): 186-189. |
| Jiang Wei, Da-gang Lyu. In-plane creep buckling of pin-ended concrete circle arches[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(2): 186-189. | |
| 3 | 谢旭, 李辉, 黄剑源. 大跨度两铰钢拱桥面内稳定分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2004, 37(8): 43-49. |
| Xie Xu, Li Hui, Huang Jian-yuan. Study on in-plane stability of long-span two-hingedsteelarchbridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2004, 37(8): 43-49. | |
| 4 | 周宇, 狄生奎, 李喜梅, 等. 基于弹性约束梁应变影响线曲率的桥梁结构损伤识别[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2021, 29(4): 901-914. |
| Zhou Yu, Di Sheng-kui, Li Xi-mei, et al. Damage identification of bridge structural based on strain influence line curvature of elastic restrained beam[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2021, 29(4): 901-914. | |
| 5 | 王宁波, 左晴, 李靖, 等. 基于当前多影响线信息的超静定梁损伤识别方法[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 52(9): 3284-3294. |
| Wang Ning-bo, Zuo Qing, Li Jing, et al. Damage detection method for statically indeterminate bridge based on multi-influence line information in current state[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(9): 3284-3294. | |
| 6 | 贺文宇, 武骥元, 任伟新. 基于车致桥梁响应和L1正则化的损伤识别研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(4): 61-70. |
| He Wen-yu, Wu Ji-yuan, Ren Wei-xin. Bridge damage detection based on the moving-vehicle-induced response and L1 regularization[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(4): 61-70. | |
| 7 | Zheng X, Yi T H, Yang D H, et al. Stiffness estimation of girder bridges using influence lines identified from vehicle-induced structural responses[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics-ASCE, 2021, 147(8): 4021042. |
| 8 | 周宇, 狄生奎, 项长生, 等. 基于弹性约束支承梁转角影响线的梁结构损伤诊断[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 54(5): 879-888. |
| Zhou Yu, Di Sheng-kui, Xiang Chang-sheng, et al. Beam structure damage detection based on rotational-angleinfluence-lines of elastic-constrained-support beam[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2020, 54(5): 879-888. | |
| 9 | Zheng X, Yi T H, Zhong J W, et al. Rapid evaluation of load-carrying capacity of long-span bridges using limited testing vehicles[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2022, 27(4): 0001838. |
| 10 | Wang N B, Shen W, Guo C R, et al. Moving load test-based rapid bridge capacity evaluation through actual influence line[J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 252: 113630. |
| 11 | 王立宪, 周宇, 狄生奎, 等. 考虑边界非理想的铁路桥梁挠度影响线分析与损伤识别[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2020, 52(3): 123-132. |
| Wang Li-xian, Zhou Yu, Di Sheng-kui, et al. Influence line analysis and damage detection of railway bridgedeflection with non-ideal boundaries[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2020, 52(3): 123-132. | |
| 12 | 胡常福, 雷亮亮, 陈海龙, 等. 等截面抛物线拱桥内力实用解析解研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2011, 8(5): 12-18. |
| Hu Chang-fu, Lei Liang-liang, Chen Hai-long, et al. Research on practical analytic solution of parabolic arch bridges with uniform section[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2011, 8(5): 12-18. | |
| 13 | 杨雨厚, 刘来君, 孙维刚, 等. 等截面抛物线无铰拱挠度影响线实用解析解[J]. 计算力学学报, 2017, 34(4): 480-486. |
| Yang Yu-hou, Liu Lai-jun, Sun Wei-gang,et al. Practical analytical solution of deflection influence line of clamped parabolic arch bridges with uniform section[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2017, 34(4): 480-486. | |
| 14 | 周宇, 许成超, 赵青, 等. 变截面悬链线无铰拱应变影响线的解析解[J]. 计算力学学报, 2022, 39(5): 551-556. |
| Zhou Yu, Xu Cheng-chao, Zhao Qing,et al. Practical analytical expression to strain influence line of varying cross section catenary fixed arch[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2022, 39(5): 551-556. | |
| 15 | 胡常福, 陆小雨, 甘慧慧, 等. 基于近似积分的悬链线拱实用解析解[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 46(3): 1058-1065. |
| Hu Chang-fu, Lu Xiao-yu, Gan Hui-hui,et al. Practical analytical solution of catenary arch based on approximate integration method[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(3): 1058-1065. | |
| 16 | 胡常福, 何兵兵, 石萃佳, 等. 复杂轴线拱结构实用解析解研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 49(1): 217-225. |
| Hu Chang-fu, He Bing-bing, Shi Cui-jia,et al. Research on approximate analytical solution of arch structure with complex arch axis[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(1): 217-225. |
| [1] | Hao JIANG,Zheng-wen ZHAO. Experiment on shear performance of RC beams strengthened with basalt fiber grid cement-based composites [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 211-220. |
| [2] | Yu-dai WANG,Bin WANG,Fu-sheng MIAO,Nan MA. Freezing and expansion response of lined channels under changes in hydrothermal coupling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 256-268. |
| [3] | Fang-fang WEI,Li-ping LI,Qing-peng XU,You-zheng ZHAO,Jing-jing YANG. Experiment on seismic behavior of fire-fired composite shear wall with double steel plates and infill concrete after reinforcement [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 230-244. |
| [4] | Wei-song YANG,An ZHANG,Wei-xiao XU,Hai-sheng LI,Ke DU. Seismic performance of stiffness enhanced metal coupling beam damper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2469-2483. |
| [5] | Jin-quan ZHAO,Long ZHOU,Yong-gang DING,Rong-ji ZHU. Experiment on anchoring performance of spiral stirrup-corrugated pipe grout splicing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2484-2494. |
| [6] | Qi-wu YAN,Zhong-liang ZOU. Hybrid algorithm for seismic energy-dissipated structures based on optimal placement of dampers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2267-2274. |
| [7] | Feng-guo JIANG,Yu-ming ZHOU,Li-li BAI,Shuang LIANG. Improved krill algorithm and its application in structural optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2256-2266. |
| [8] | Guang-tai ZHANG,Cheng-xiao ZHOU,Shi-tuo LIU. Restoring force model of fiber lithium slag concrete column in saline soil environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1944-1957. |
| [9] | Yan-song DIAO,Yi-jian REN,Yuan-qiang YANG,Ling-yun ZHAO,Xiu-li LIU,Yun LIU. Experimental on seismic performance of replaceable splicing steel beam-column joints with friction energy dissipation components [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1643-1656. |
| [10] | Xue-ping FAN,Yue-fei LIU. Bridge extreme stress dynamic prediction based on improved Gaussian mixed particle filter new algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | Yi-fan LIU,Zhi-wei MIAO,Chen SHEN,Xiang-dong GENG. Evaluation of mechanical properties of non-uniform corroded rebars based on Monte Carlo method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1007-1015. |
| [12] | Xue-ping FAN,Heng ZHOU,Yue-fei LIU. Time⁃variant reliability analysis of bridge members based on Gaussian Copula⁃Bayesian dynamic models [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 485-493. |
| [13] | Hai-xu YANG,Yue GUO,Hai-biao WANG,Yi HU. Bending performance of cold-formed thin-walled steel-glulam composite beams [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3513-3525. |
| [14] | Xue-ping FAN,Heng ZHOU,Yue-fei LIU. Multi⁃process Bayesian dynamic combinatorial prediction of time⁃variant reliability for bridges [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2332-2338. |
| [15] | Chen JIN,Meng-yuan ZENG,Di-fei WU. Damage identification of concrete pavement joint using vibration transmissibility [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1736-1745. |
|
||