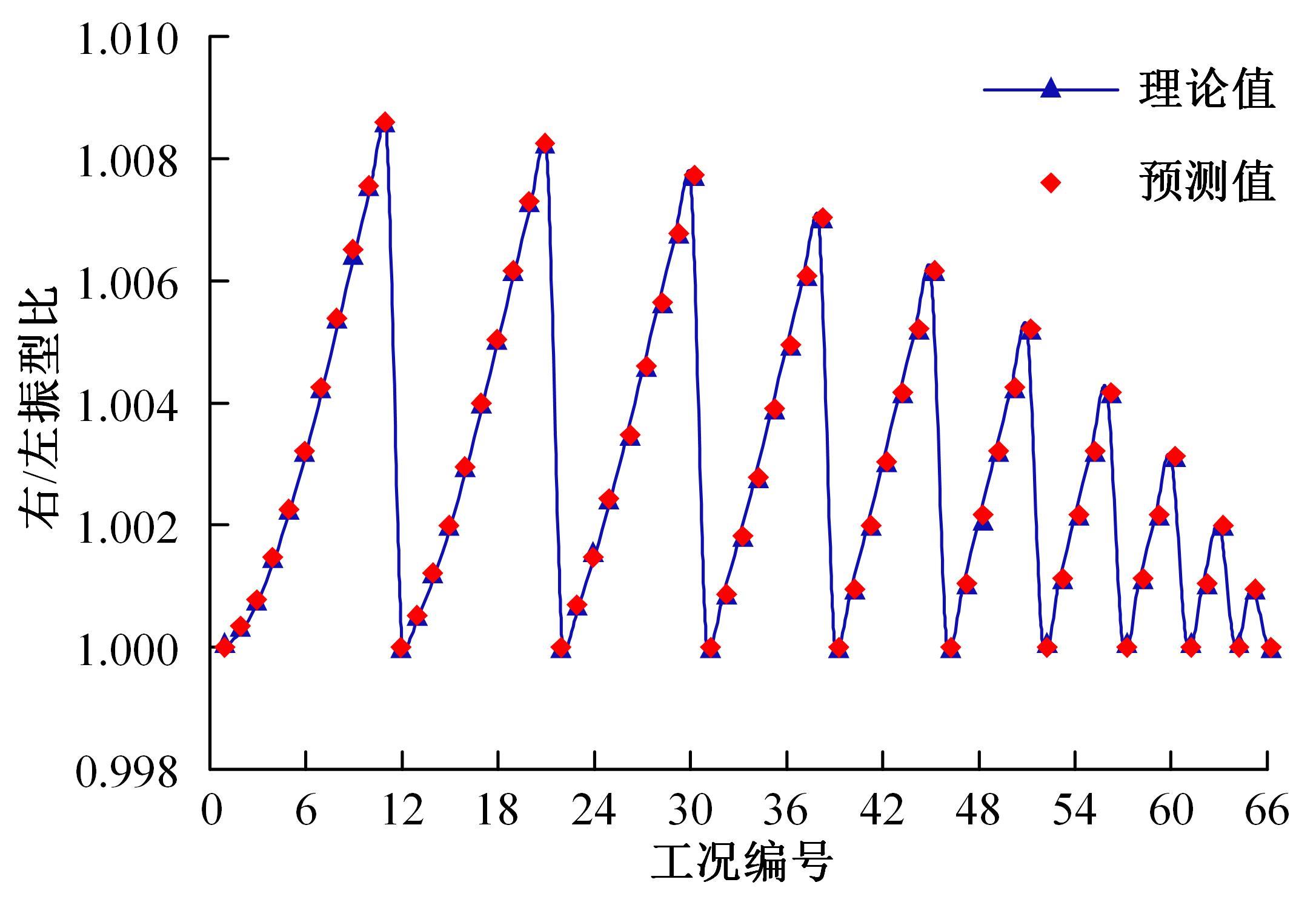
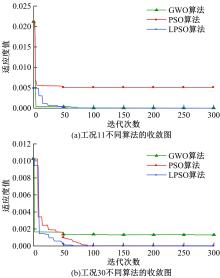
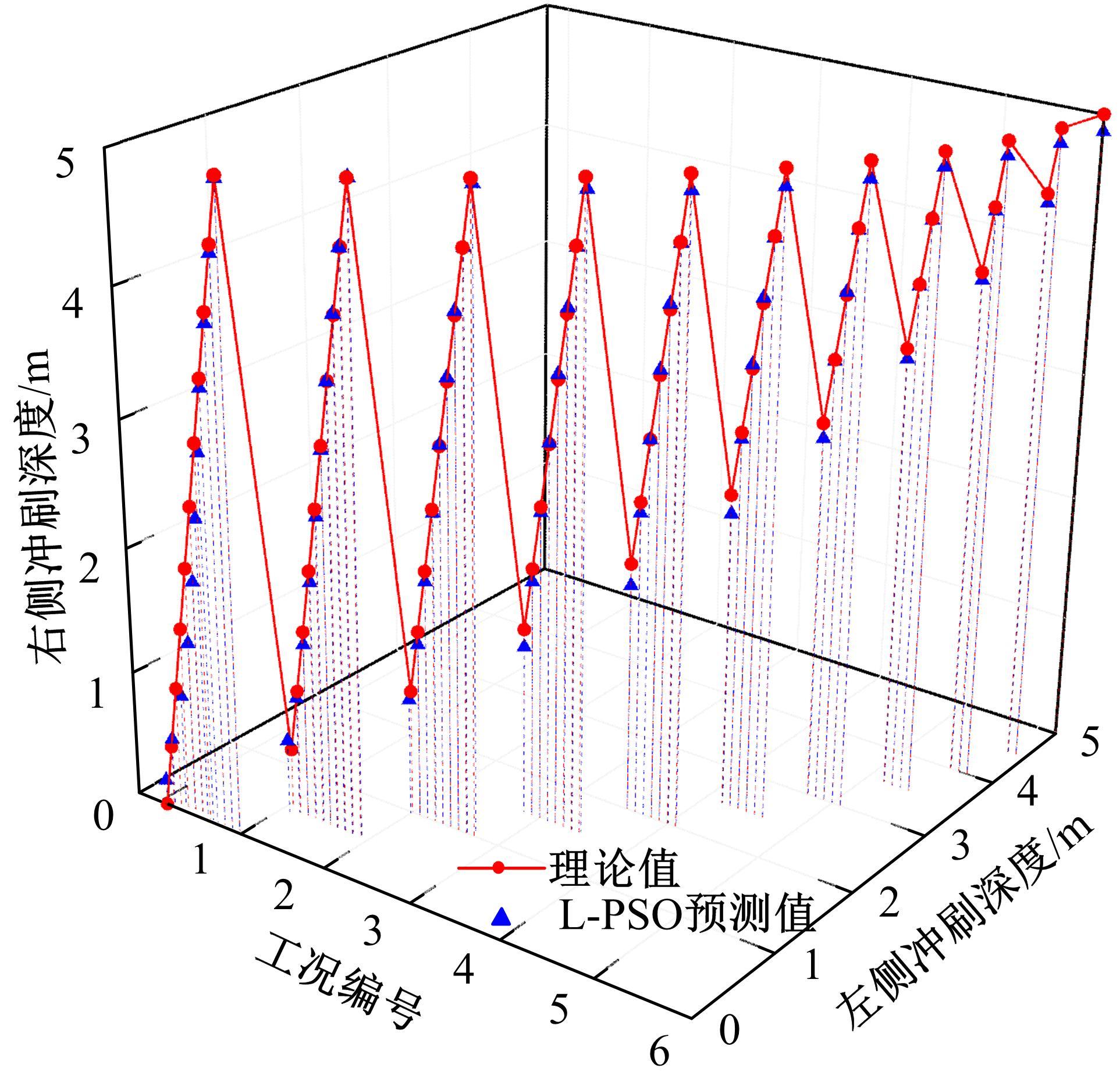
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1592-1600.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230145
Bridge scour depth identification based on dynamic characteristics and improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
Guo-jin TAN1( ),Qing-wen KONG1,Xin HE1(
),Qing-wen KONG1,Xin HE1( ),Pan ZHANG2,Run-chao YANG3,Yang-jun CHAO4,Zhong YANG4
),Pan ZHANG2,Run-chao YANG3,Yang-jun CHAO4,Zhong YANG4
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Changchun Construction Project Safety Supervision Station,Changchun 130012,China
3.Jilin Provincial Highway Administration,Changchun 130021,China
4.Jilin Traffic Planning and Design Institute,Changchun 130021,China
CLC Number:
- U446
| 1 | 熊文, 魏乐永, 张学峰, 等. 大跨度缆索支承桥梁基础冲刷动力识别方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(3): 92-98. |
| Xiong Wen, Wei Le-yong, Zhang Xue-feng, et al. Dynamic-based bridge scour identification of super-span cable-supported bridges[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(3): 92-98. | |
| 2 | Lu J Y, Shi Z Z, Hong J H, et al. Temporal variation of scour depth at nonuniform cylindrical piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2011, 137(1): 45-56. |
| 3 | Bao T, Liu Z, Bird K. Influence of soil characteristics on natural frequency-based bridge scour detection[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 446(1): 195-210. |
| 4 | 张佰战, 李付军. 桥墩局部冲刷计算研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(2): 48-51. |
| Zhang Bai-zhan, Li Fu-jun. Bridge pier local scour calculation[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(2): 48-51. | |
| 5 | 詹义正, 王军, 谈广鸣, 等. 桥墩局部冲刷的试验研究[J]. 武汉大学学报, 2006, 39(6): 3-4. |
| Zhan Yi-zheng, Wang Jun, Tan Guang-ming, et al. Experimental study on bridge pier local scour[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2006, 39(6): 3-4. | |
| 6 | Hong J H, Guo W D, Chiew Y M, et al. A new practical method to simulate flood-induced bridge pier scour—a case study of mingchu bridge piers on the cho-shui river[J]. Water, 2016, 8(6): 238. |
| 7 | Deng L, Cai C S. Bridge scour: prediction, modeling, monitoring and countermeasures-review[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design & Construction, 2010, 15(2): 125-134. |
| 8 | Zounemat-Kermani A, Beheshti A, Ataie-Ashtiani B. Estimation of current-induced scour depth around pile groups using neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2009, 9(2): 746-755. |
| 9 | 熊文, 张愉, 李飞泉, 等. 基于时频分析与神经网络的桥梁冲刷动力评估[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版, 2020, 53(4): 397-404. |
| Xiong Wen, Zhang Yu, Li Fei-quan, et al. Dynamic assessment of bridge scour based on time-frequency analysis and neural network[J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology), 2020, 53(4): 397-404. | |
| 10 | 张效忠, 孙延华, 孙国民. 基于支持向量机的桥梁冲刷深度识别方法研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2016, 14(3): 206-210. |
| Zhang Xiao-zhong, Sun Yan-hua, Sun Guo-min. Identification method of scour depth for bridge based on ERA and SVM[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2016, 14(3): 206-210. | |
| 11 | Ju S H. Determination of scoured bridge natural frequencies with soil-structure interaction[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 55: 247-254. |
| 12 | Kong X, Cai C S. Scour effect on bridge and vehicle responses under bridge-vehicle-wave interaction[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(4): No.04015083. |
| 13 | 熊文, 邹晨, 叶见曙. 基于动力特性识别的桥墩冲刷状态分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(5): 89-96. |
| Xiong Wen, Zou Chen, Ye Jian-shu. Condition assessment of bridge scour by tracing dynamic performances of bridges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(5): 89-96. | |
| 14 | 于繁华, 刘寒冰. 基于支持向量机和粒子群算法的结构损伤识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008, 38(2): 434-439. |
| Yu Fan-hua, Liu Han-bing. Structural damage identification by support vector machine and particle swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2008, 38(2): 434-439. | |
| 15 | 王学武, 严益鑫, 丁冬雁, 等. 基于Lévy-PSO算法的焊接机器人避障路径规划[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2016, 50(10): 1517-1520. |
| Wang Xue-wu, Yan Yi-xin, Ding Dong-yan, et al. Collision free path planning for welding robot based on Lévy-PSO[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2016, 50(10): 1517-1520. | |
| 16 | 孟宪猛, 蔡翠翠. 基于精英反向学习和Lévy飞行的鲸鱼优化算法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(20): 82-87. |
| Meng Xian-meng, Cai Cui-cui. Whale optimization algorithm based on elite reverse learning and Lévy flight[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(20): 82-87. | |
| 17 | API. Recommended Practice for Planning, Designing and Constructing Fixed Offshore Platforms-Working Stress Design[M]. 20th ed. Washington DC: API, 2000. |
| 18 | Meidani K, Mirjalili S, Barati F A, et al. Grey Wolf Optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| [1] | Hui JIANG,Xin LI,Xiao-yu BAI. Review on development of bridge seismic structural systems: from ductility to resilience [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [2] | Yue ZHANG,Chuan-sen LIU,Fei SONG. Influence of abutment back wall on continuous girder bridge's seismic fragility [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [3] | Shu-wei LAN,Dong-hua ZHOU,Xu CHEN,Nan-ming MO. Practical calculation method for the critical bearing capacity of double column bridge with high piers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [4] | Qi-kai SUN,Nan ZHANG,Xiao LIU,Zi-ji ZHOU. Dynamic reduction coefficients of steel⁃concrete composite beam based on Timoshenko beam theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
| [5] | Rang-lin FAN,Zi-jian LIU,Fu-liang MA,Quan-fa WU. Mid⁃high⁃frequency active and passive dynamic characteristics of active hydraulic mounts with oscillating coil actuator [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 50-60. |
| [6] | Hua-wen YE,Zhi-chao DUAN,Ji-lin LIU,Yu ZHOU,Bing HAN. Wheel⁃load diffusion effect on orthotropic steel⁃concrete composite bridge deck [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1808-1816. |
| [7] | Li-feng WANG,Zi-wang XIAO,Sai-sai YU. New risk analysis method based on Bayesian network for hanging basker system of multi-tower cable-stayed bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(4): 865-873. |
| [8] | Yan-ling ZHANG,Can WANG,Xu ZHANG,Ang-yang WANG,Yun-sheng LI. Human⁃induced vibration analysis and pedestrian comfort evaluation for suspension footbridge with different hunger systems [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2644-2652. |
| [9] | Chang-jun ZHONG,Zhong-bin WANG,Chen-yang LIU. Influencing factors and structural optimization of main cable saddle bearing capacity of suspension bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2068-2078. |
| [10] | Wei CHEN,Tian-bao WAN,Zhong-bin WANG,Xuan LI,Rui-li SHEN. Design and performance of internal air supply conduit for dehumidification in main cables of suspension bridges [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1749-1755. |
| [11] | Shu-lun GUO,Tie-yi ZHONG,Zhi-gang YAN. Calculation method of buffeting response for stay cables of long⁃span cable⁃stayed bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1756-1762. |
| [12] | Kai GAO,Gang LIU. Effective strength improvement of global critical strength branch and bound method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 597-603. |
| [13] | Xiao-tao LI,Jin-peng REN,Xiao-xu LI,Hang YANG. Mechanism of a linear actuator driven by dual piezoelectric oscillators in inverse mode [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 468-471. |
| [14] | Ya-feng GONG,Jia-xiang SONG,Guo-jin TAN,Hai-peng BI,Yang LIU,Cheng-xin SHAN. Multi⁃vehicle bridge weigh⁃in⁃motion algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 583-596. |
| [15] | Qing-wen KONG,Guo-jin TAN,Long-lin WANG,Yong WANG,Zhi-gang WEI,Han-bing LIU. Analysis of free vibration characteristics of cracked box girder bridge based on finite element method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 225-232. |
|
||