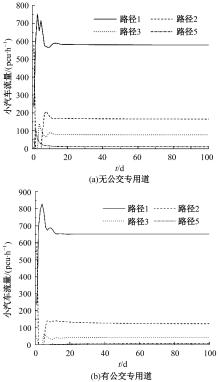
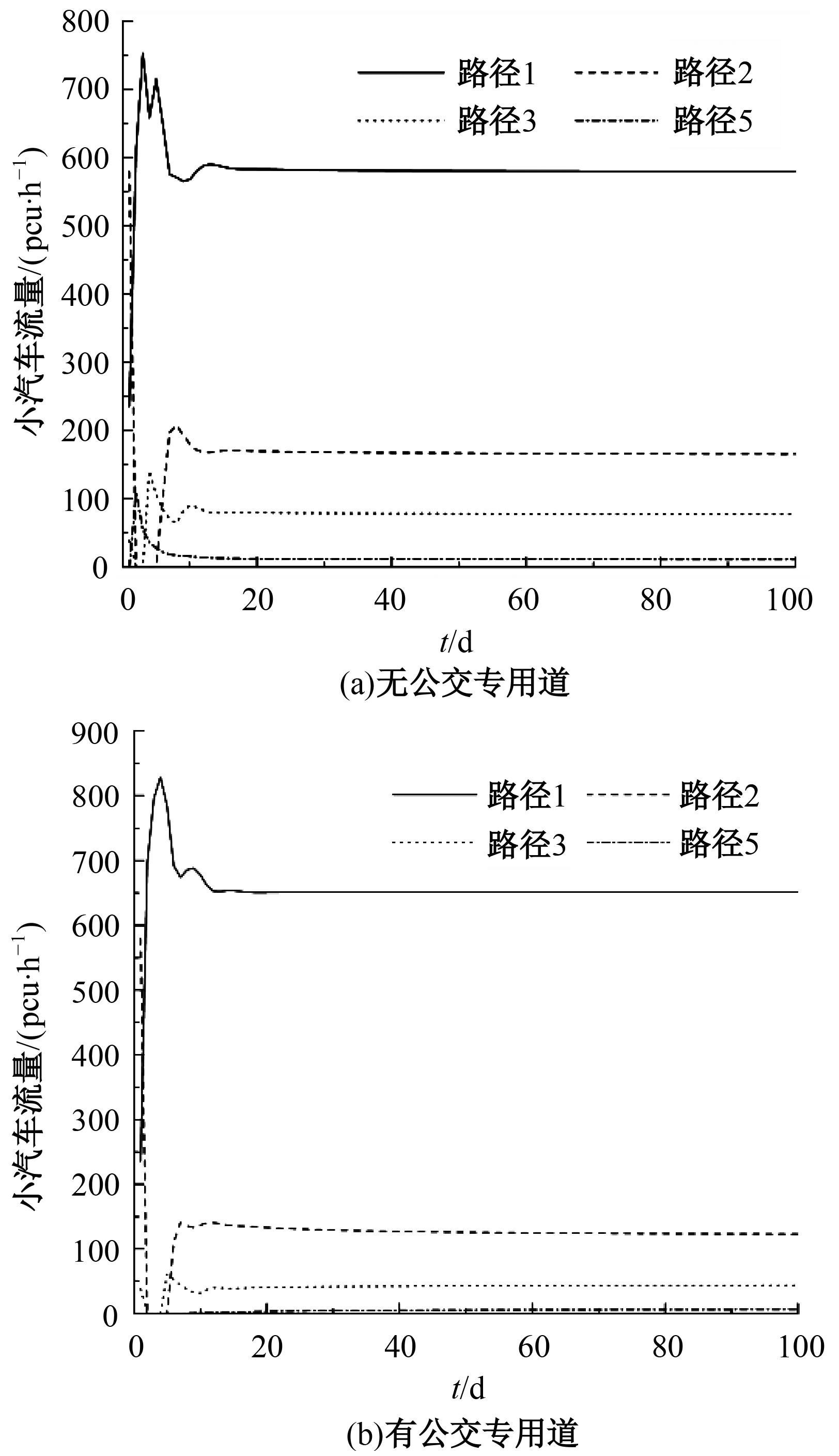
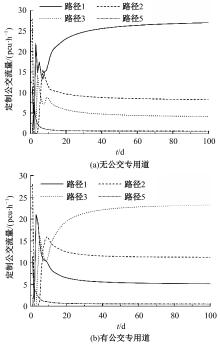
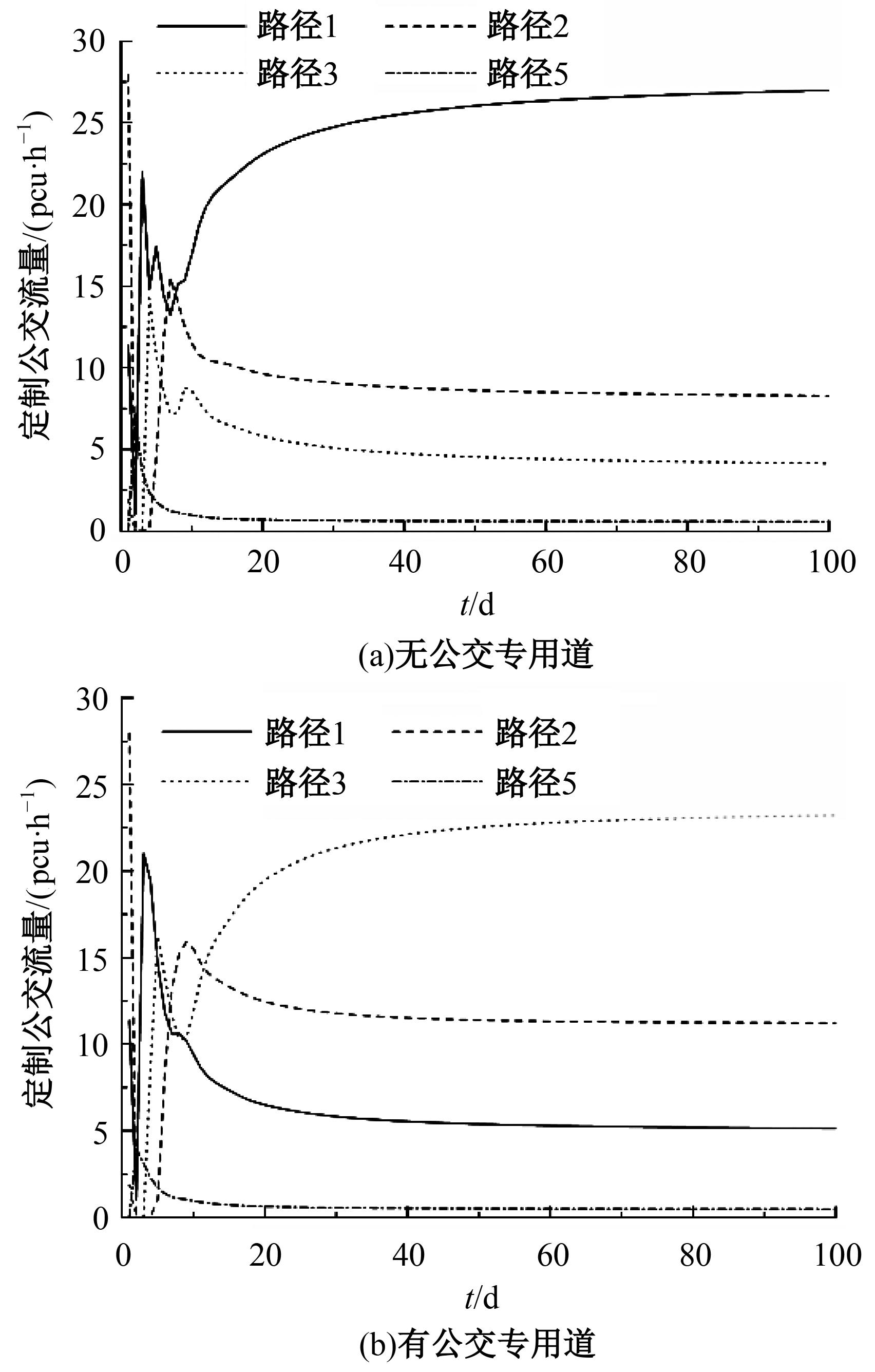
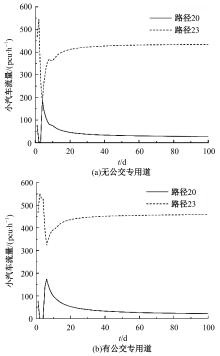
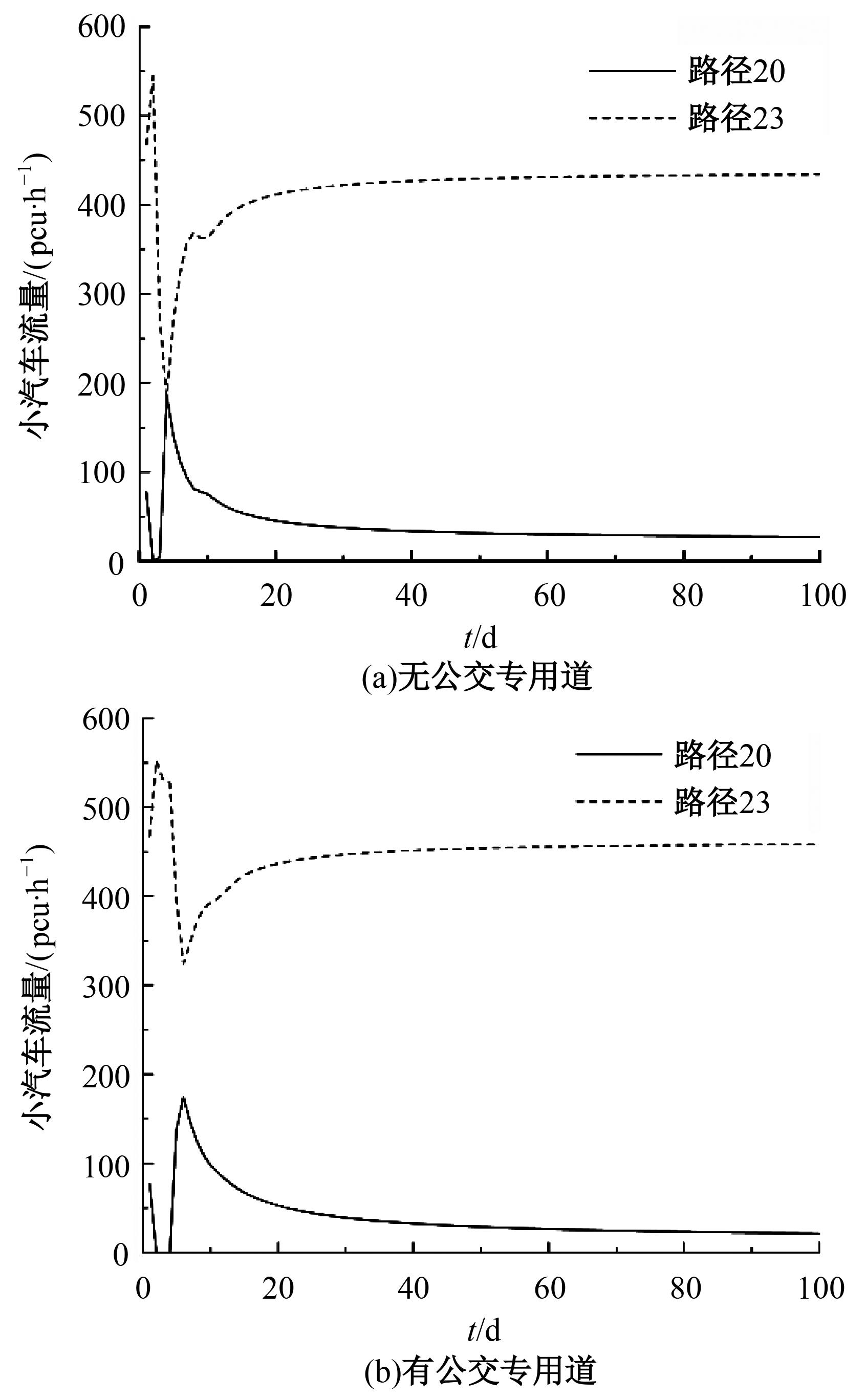
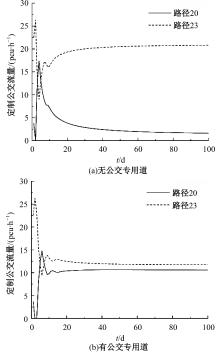
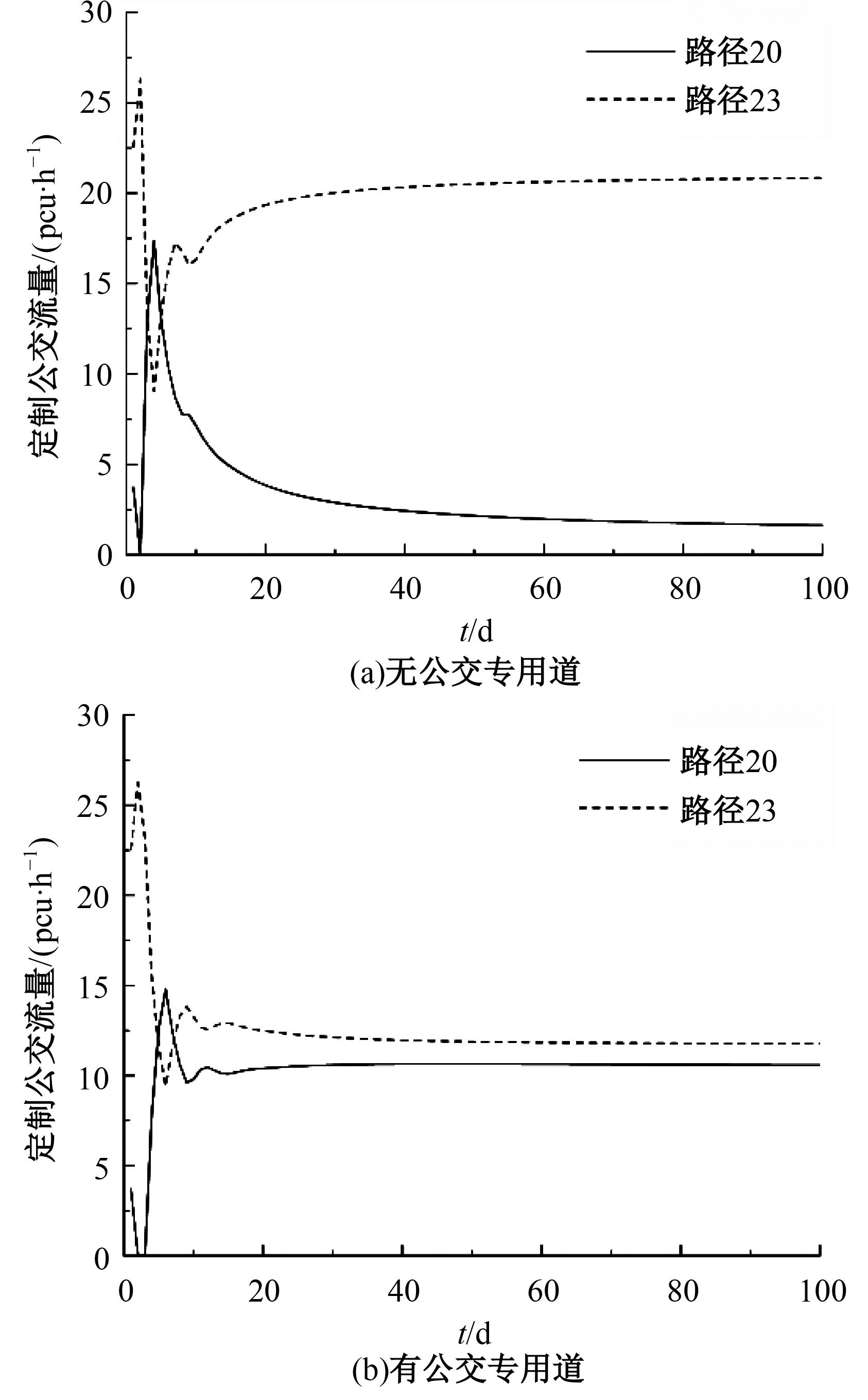
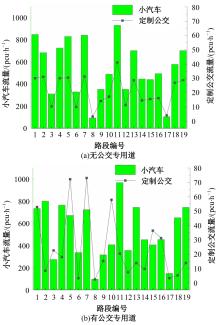
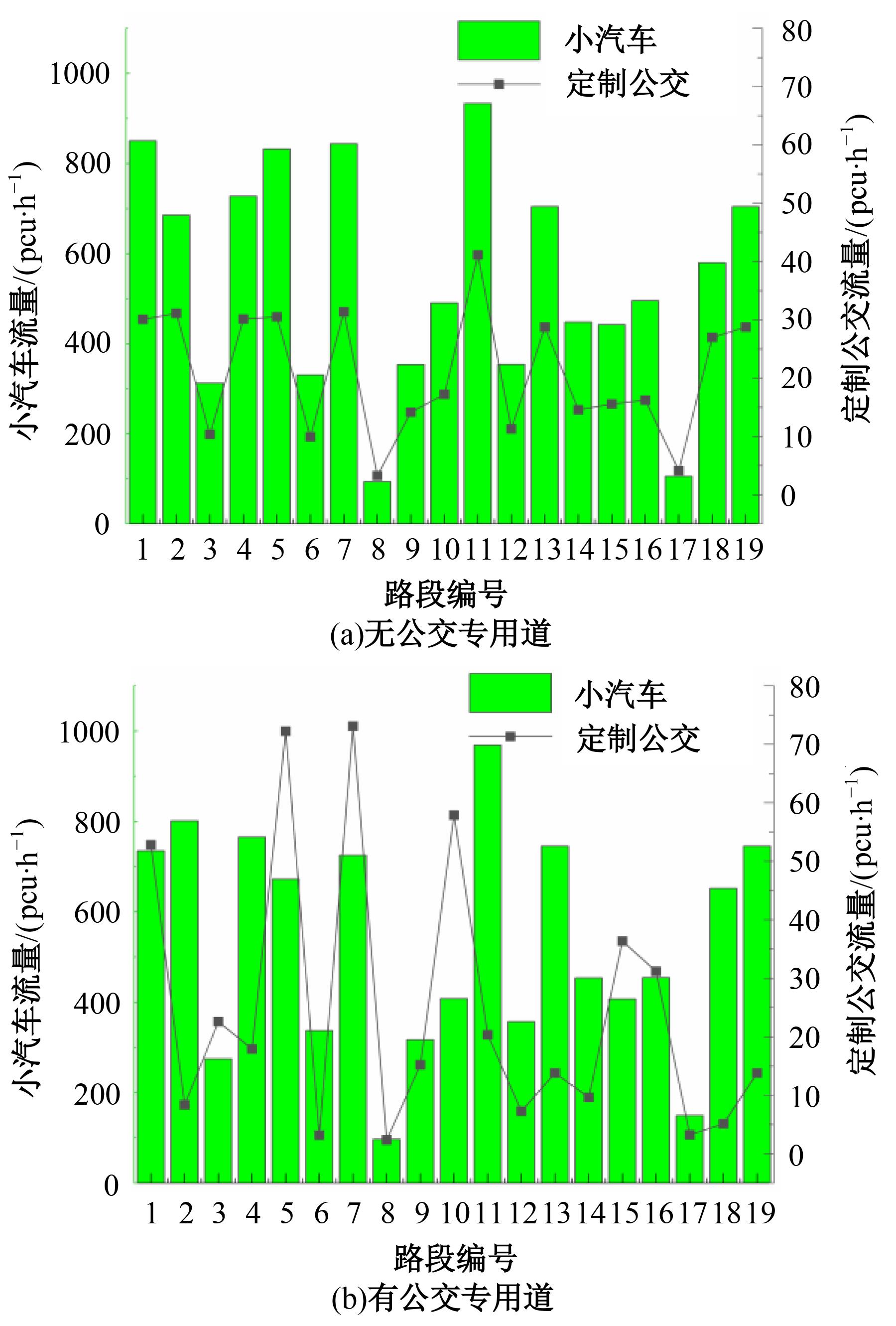
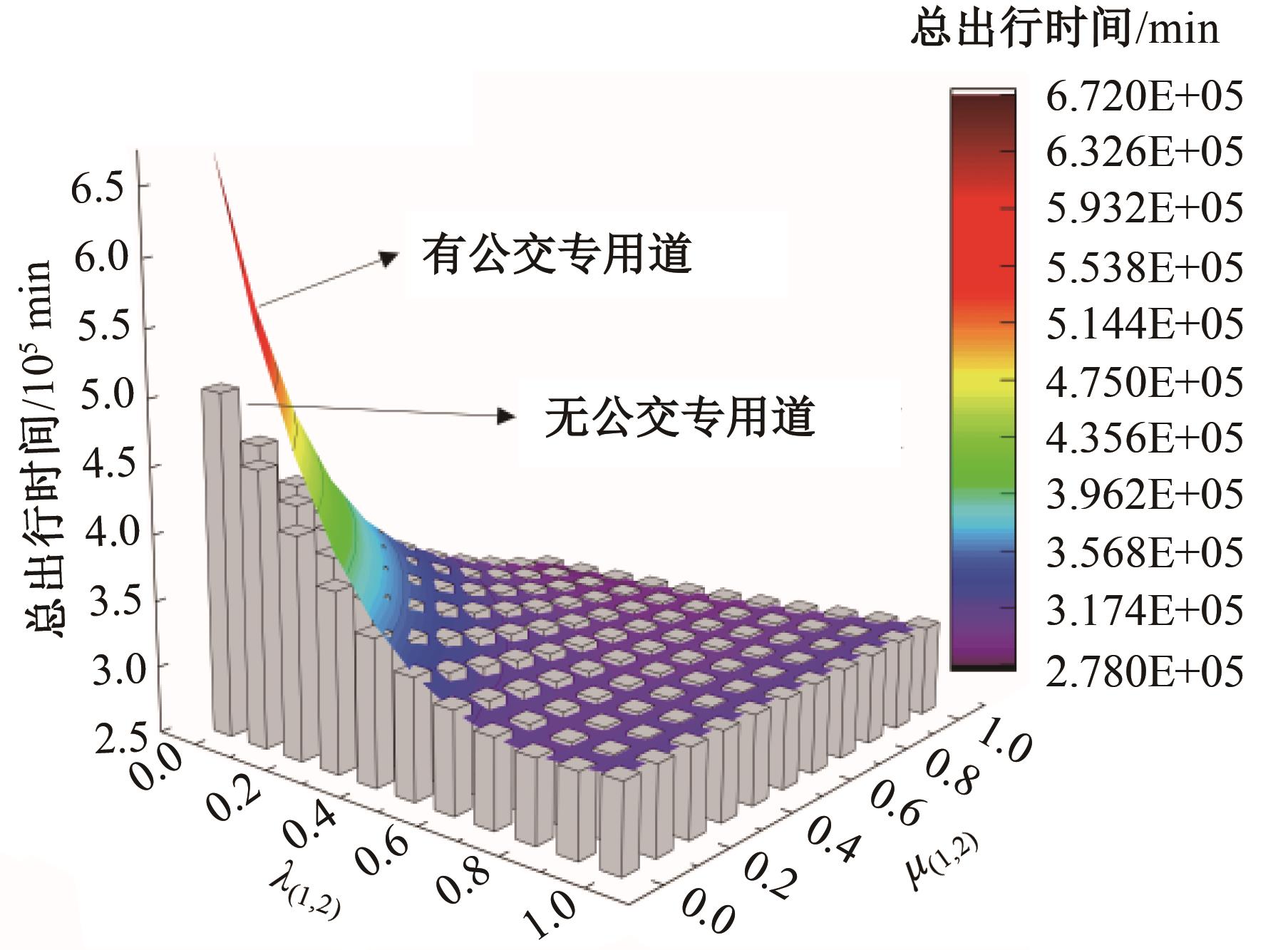
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3209-3219.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221644
Previous Articles Next Articles
Day-to-day equilibrium model of mixed traffic flow considering customized bus and exclusive bus lane
Yu-lin CHANG1,2,3( ),Yi-jie WANG1,Jian WANG4,Chao SUN1,2(
),Yi-jie WANG1,Jian WANG4,Chao SUN1,2( ),Peng ZHANG1,Wen-qian XU1
),Peng ZHANG1,Wen-qian XU1
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.College of Automotive Engineering,Nantong Institute of Technology,Nantong 226002,China
3.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
4.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| [1] | 卢文慧. 基于多视角的城市交通拥堵问题研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2019. |
| Lu Wen-hui. A multi-perspective study of urban traffic congestion[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2019. | |
| [2] | 李彬. 定制公交与定制公交客车的研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学汽车学院, 2013. |
| Li Bin. The study of customized city bus service[D]. Xi'an: School of Automobile, Chang'an University, 2013. | |
| [3] | Liu K J, Liu J M, Zhang J W. Heuristic approach for the multiobjective optimization of the customized bus scheduling problem[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2022, 16(3): 277-291. |
| [4] | 沈旻宇. 随机用户均衡下考虑学习行为的逐日动态模型研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2016. |
| Shen Min-yu. Day-to-day flow dynamics with user learning under stochastic user equilibrium[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| [5] | Zhou B, Xu M, Meng Q, et al. A day-to-day route flow evolution process towards the mixed equilibria[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2017, 82: 210-228. |
| [6] | Zhang C, Liu T L, Huang H J, et al. A cumulative prospect theory approach to commuters' day-to-day route-choice modeling with friends' travel information[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 86: 527-548. |
| [7] | 尹子坤, 关宏志, 李涛. 逐日路径演化中出行者信息偏好的实验分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. |
| Yin Zi-kun, Guan Hong-zhi, Li Tao. Experimental analysis of diver's information preference under day-to-day traffic dynamics[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2017, 17(4): 234-240. | |
| [8] | Lou X M, Cheng L, Chu Z M. Modelling travellers' en-route path switching in a day-to-day dynamical system[J]. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, 2017, 5(1): 15-37. |
| [9] | 刘诗序, 王智煜, 关宏志, 等. 不同信息下的逐日路径选择行为实验与模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(6): 106-113. |
| Liu Shi-xu, Wang Zhi-yu, Guan Hong-zhi, et al. Experiment and model of day-to-day route-choice behavior under different information[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(6): 106-113. | |
| [10] | 常玉林, 徐文倩, 孙超, 等. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| Chang Yu-lin, Xu Wen-qian, Sun Chao, et al. Day-to-day equilibrium of hybrid traffic considering obedience degree under internet of vehicles environment[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. | |
| [11] | Wu J, Ji Y, Sun X, et al. Guidance optimization of travelers' travel mode choice based on fuel tax rate and bus departure quantity in two-mode transportation system[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020(10): 1-10. |
| [12] | 寇钊. 双模式交通逐日演化模型和逐周干预策略研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2021. |
| Kou Zhao. Day-to-day traffic evolution model and week-to-week intervention strategies for bi-modal networks[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| [13] | Yao J, Shi F, Shi A, et al. Evaluation of exclusive bus lanes in a bi-modal degradable road network[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 60: 36-51. |
| [14] | Zheng F, Chen J, Wang H, et al. Developing a dynamic utilisation scheme for exclusive bus lanes on urban expressways: an enhanced CTM‐based approach versus a microsimulation‐based approach[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(12): 1657-1664. |
| [15] | 四兵锋, 钟鸣, 高自友. 城市混合交通条件下路段阻抗函数的研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2008, 35(1): 68-73. |
| Si Bing-feng, Zhong Ming, Gao Zi-you. A link resistance function of urban mixed traffic network[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2008, 35(1): 68-73. | |
| [16] | 陈旭, 陆丽丽, 曹祖平, 等. 道路阻抗函数研究综述[J].交通运输研究, 2020, 6(2): 30-39. |
| Chen Xu, Lu Li-li, Cao Zu-ping, et al. Review of studies on road impedance functions[J]. Transport Research, 2020, 6(2): 30-39. | |
| [17] | 陈芳, 龙建成. 基于双层规划的城市公交专用道优化设计[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 39(3): 296-302. |
| Chen Fang, Long Jian-cheng. Optimum design of city bus lane based on bi-level programming[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 39(3): 296-302. | |
| [18] | 四兵锋, 杨小宝, 高亮. 基于系统最优的城市公交专用道网络设计模型及算法[J]. 中国管理科学, 2016, 24(6): 106-114. |
| Si Bing-feng, Yang Xiao-bao, Gao Liang. System optimization based bus-lane network design model and algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2016, 24(6): 106-114. | |
| [19] | 刘诗序, 陈文思, 池其源, 等. 弹性需求下的网络交通流逐日动态演化[J]. 物理学报, 2017, 66(6): 12-26. |
| Liu Shi-xu, Chen Wen-si, Chi Qi-yuan, et al. Day-to-day dynamical evolution of network traffic flow with elastic demand[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2017, 66(6): 12-26. | |
| [20] | . 城市道路工程设计规范 [S]. |
| [1] | Cheng-dong ZHOU,Fei SONG,Xiao-mei ZHAO,Jun-jie YAO. Congestion pricing model in multi-modal network based on doubly dynamical evolution [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1319-1327. |
| [2] | Yan-yan QIN,Teng-fei XIAO,Qin-zhong LUO,Bao-jie WANG. Car-following safety analysis and control strategy for foggy freeway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1241-1249. |
| [3] | Hao YUE,Xiao CHANG,Jian-ye LIU,Qiu-shi QU. Customized bus route optimization with vehicle window [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1266-1274. |
| [4] | Xian-min SONG,Tian-shu ZHAN,Hai-tao LI,Bo LIU,Yun-xiang ZHANG. Reservation and allocation model considering user cost and utilization of parking space [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1287-1297. |
| [5] | Yi-yong PAN,Xiang-yu XU. Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 947-953. |
| [6] | Yong-heng CHEN,Jia-wei YANG,Jing-yu SUN. Optimal trajectory control for connected left-turn vehicles at exit lane for left-turn intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 614-622. |
| [7] | Xi-zhen ZHOU,He GONG,Dun-dun LI,Yan-jie JI,Jie YAN. Nonlinear model for impact of built environment on curb parking spaces occupancy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [8] | Ya-qin QIN,Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE. Vehicle cooperative obstacle avoidance strategy driven by CLAM model and trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [9] | Ming-chen GU,Hui-yuan XIONG,Zeng-jun LIU,Qing-yu LUO,Hong LIU. Weight estimation model for trucks integrating multi-head attention mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2771-2780. |
| [10] | Wen-cai SUN,Xu-ge HU,Zhi-fa YANG,Fan-yu MENG,Wei SUN. Optimization of infrared-visible road target detection by fusing GPNet and image multiscale features [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2799-2806. |
| [11] | Hao YUE,Qi-yue ZHANG,Zi-yu YANG,Meng-jie REN,Xu ZHANG. Iterative weighted algorithms of static congestion traffic assignment considering spatial queuing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 136-145. |
| [12] | Hong-tao LI,Lin-hong WANG,Jun-da LI. Influence of lighting and speed limit on visual search ability at highway intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [13] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [14] | Zhen-liang LIU,Cun-bao ZHAO,Yun-peng WU,Mi-na MA,Long-shuang MA. Life⁃cycle seismic resilience assessment of highway bridge networks using data⁃driven method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [15] | Hong-fei JIA,Ying-jun XU,Li-li YANG,Nan WANG. League member selection and benefit distribution of commercial vehicles multi⁃modal transportation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
|