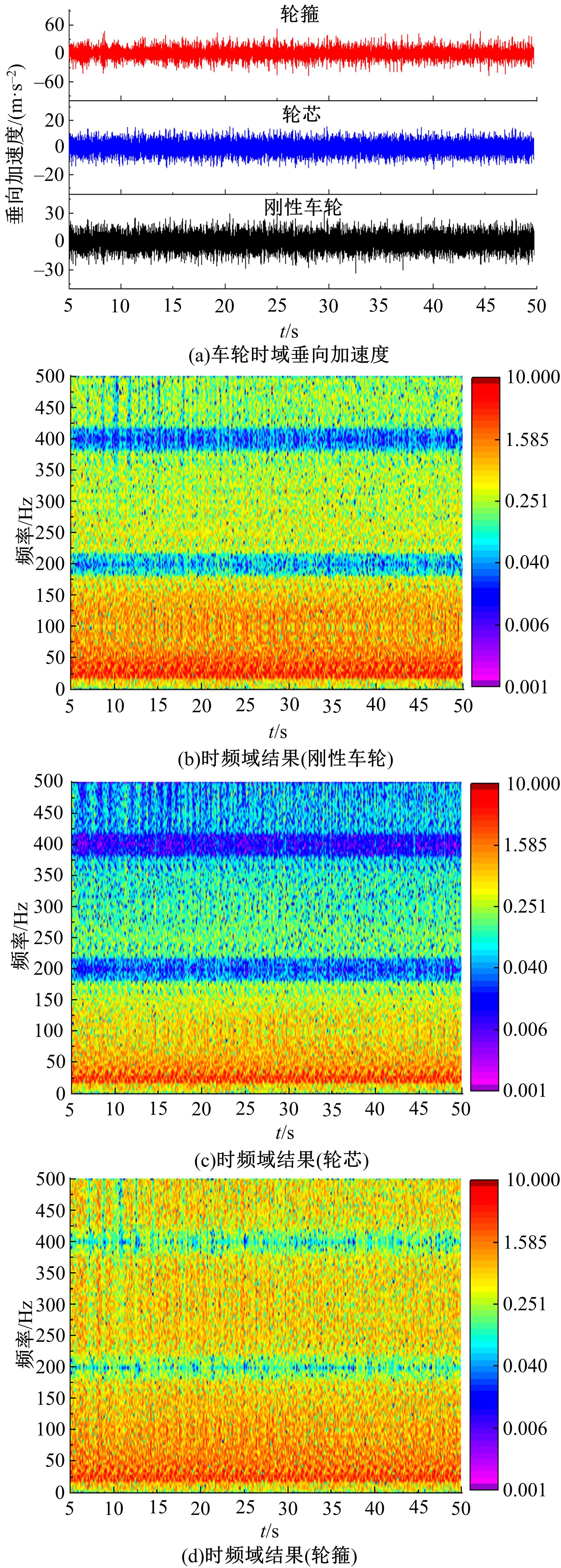
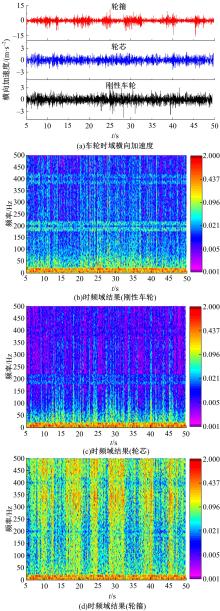
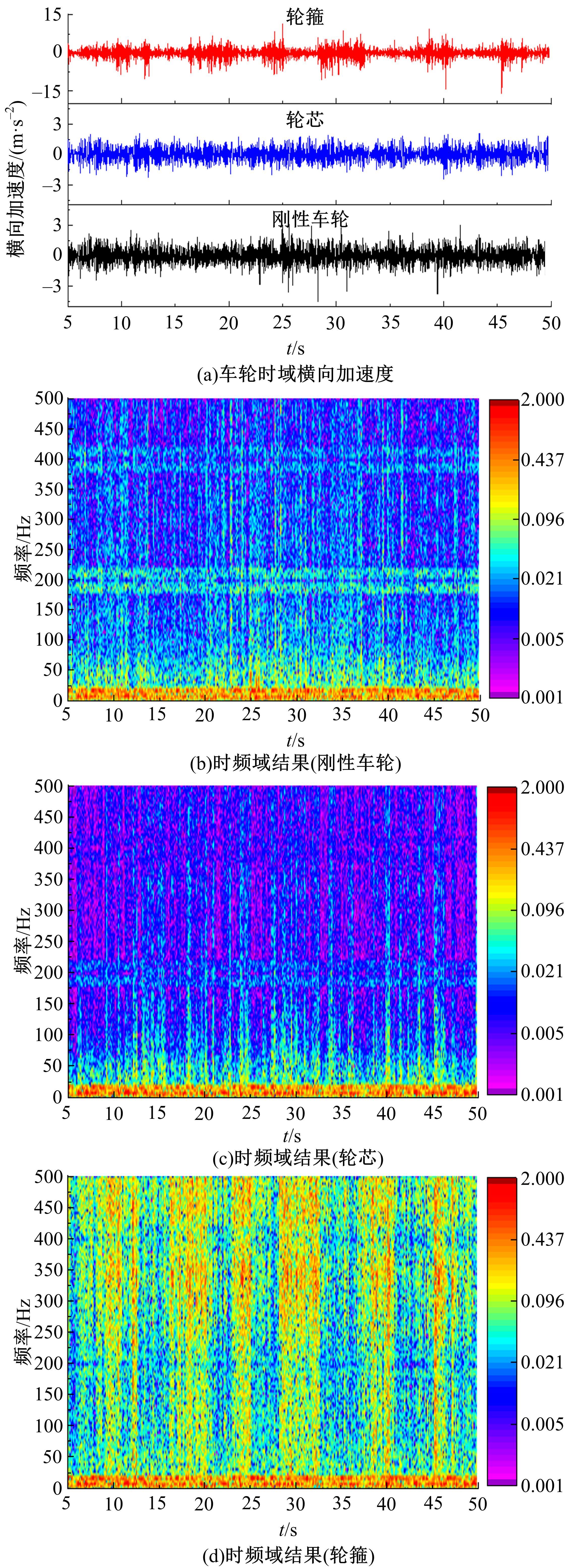
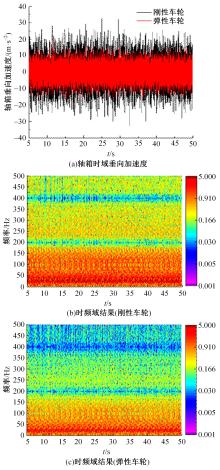
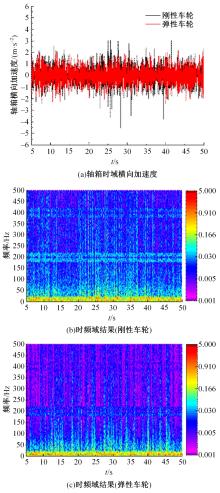
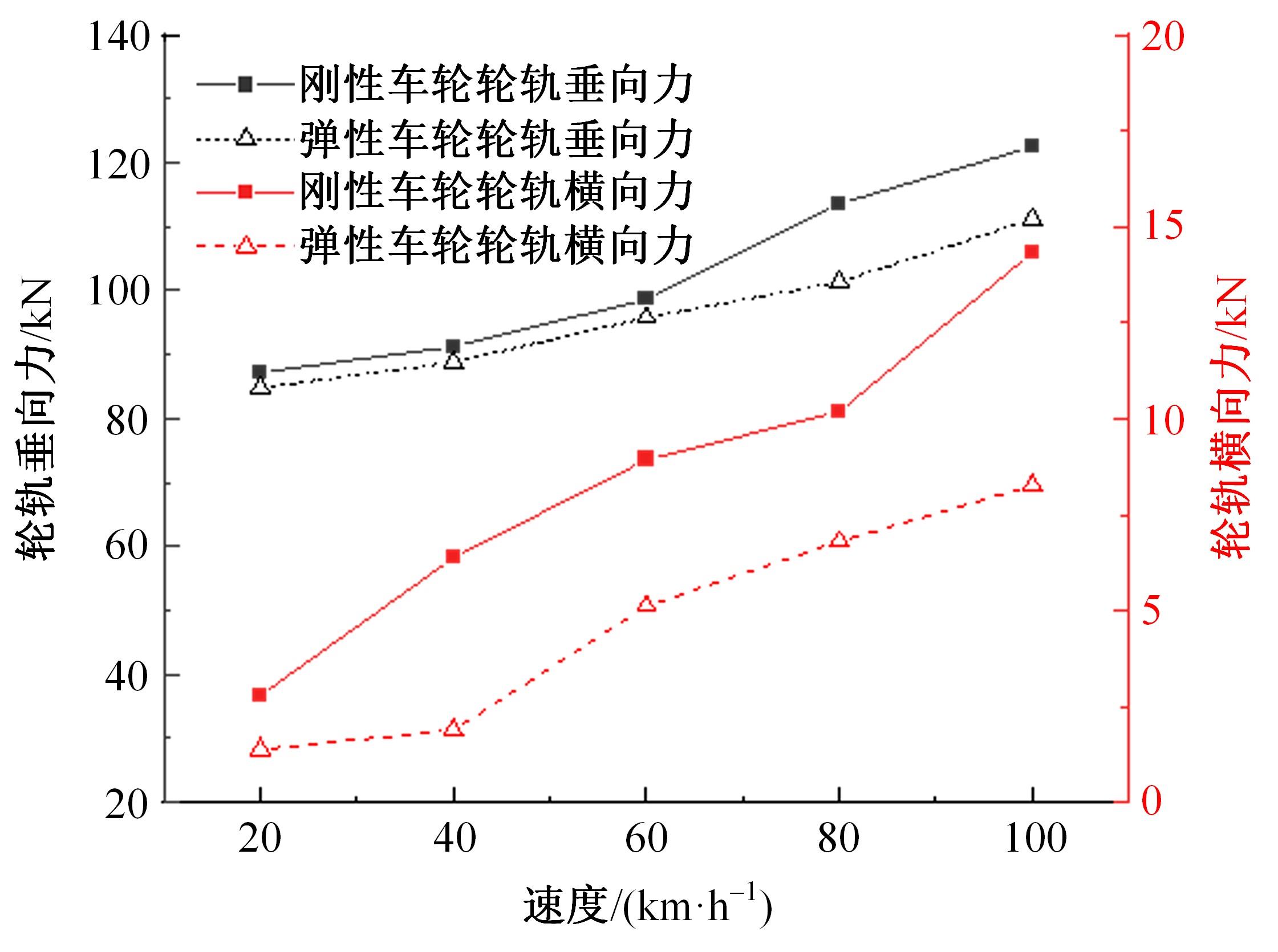
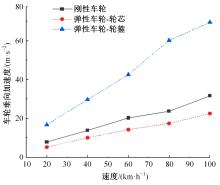
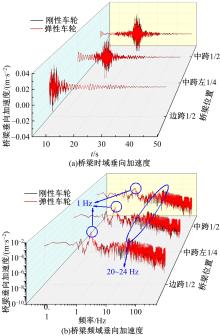
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2519-2532.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211258
Previous Articles Next Articles
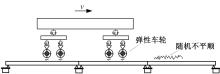
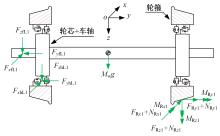
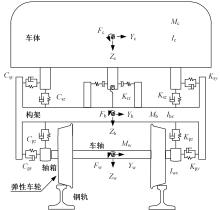
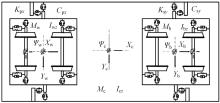
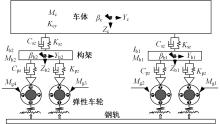
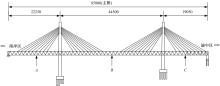
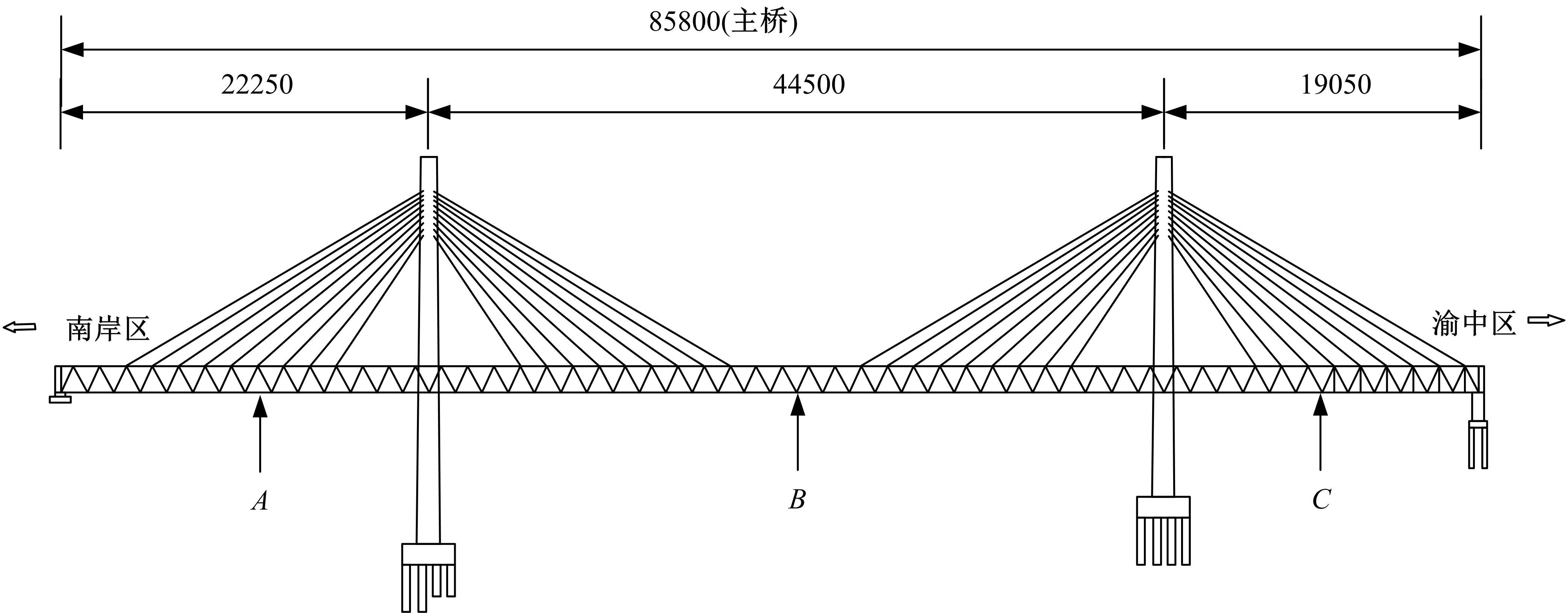
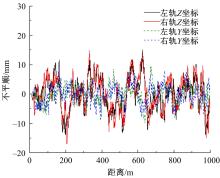
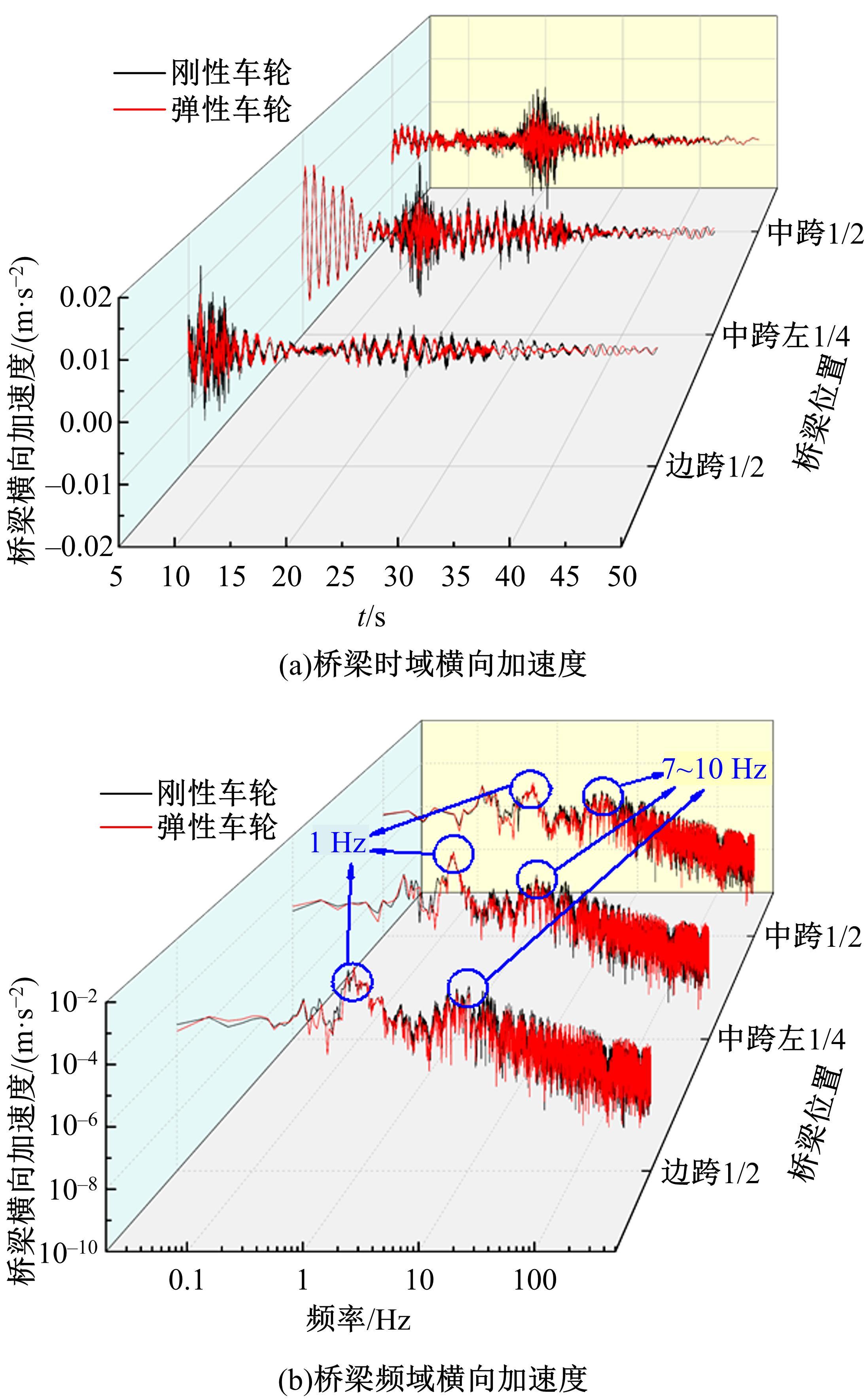
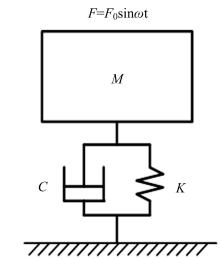
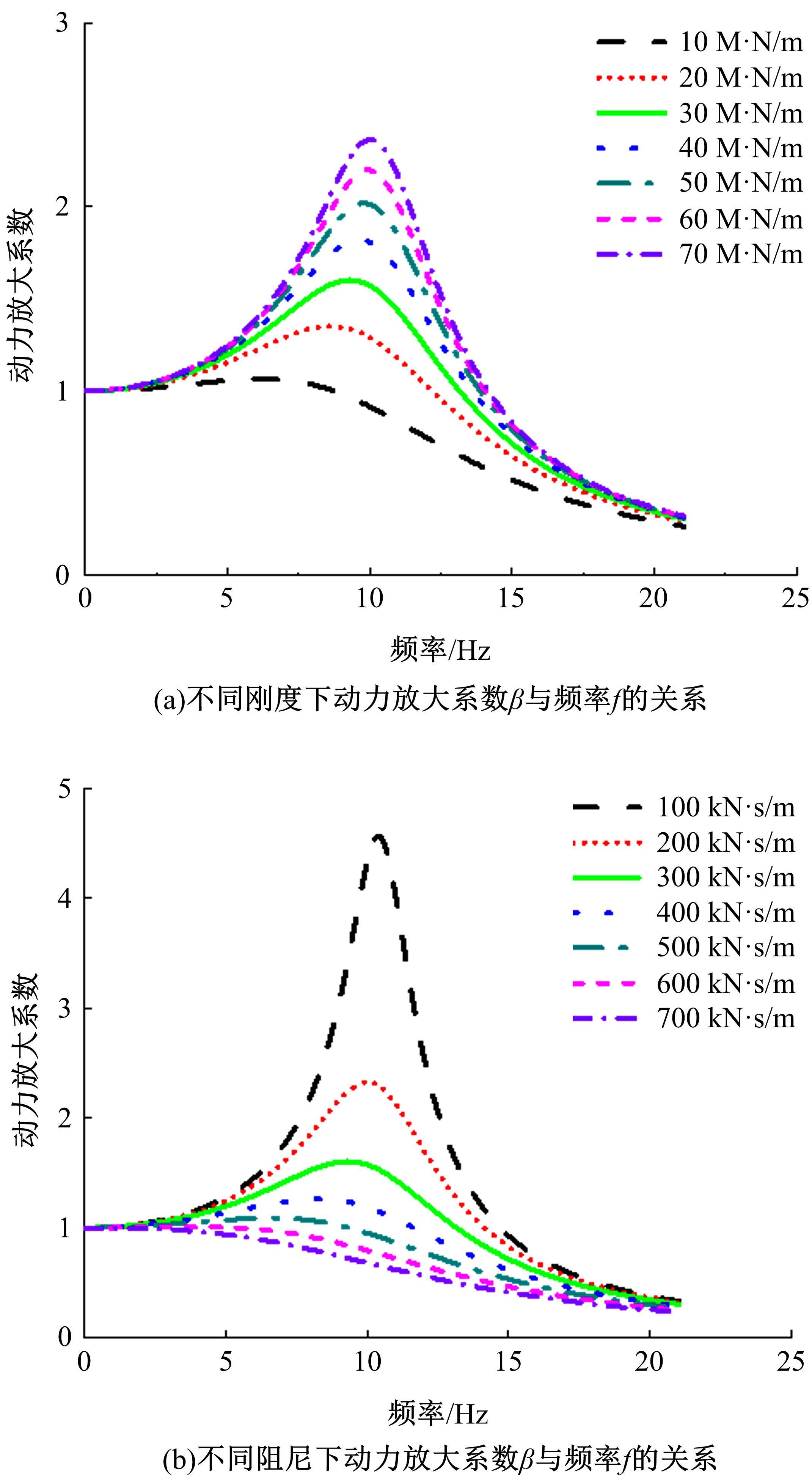
Suppression characteristics of vehicle⁃bridge coupling vibration of long⁃span cable⁃stayed bridge with resilient wheels
- Mechatronics and Vehicle Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
CLC Number:
- U24
| 1 | Bouvet P, V'meent N, Coblentz A, et al. Optimization of resilient wheels for rolling noise control[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1996, 1993(1): 253-260. |
| 2 | Makoto I I. 弹性车轮对轨道动态性能的作用[J]. 国外铁道车辆, 1998(6): 34-40. |
| Makoto I I. The effect of elastic wheels on track dynamic performance[J]. Foreign Railway Vehicles, 1998(6): 34-40. | |
| 3 | Remington P J. Wheel/rail rolling noise, I: theoretical analysis[J]. Acoust Soc Am, 1987, 81(6): 1805-1823. |
| 4 | 黄彪, 戚援, 杜利清. 弹性车轮非线性有限元分析及疲劳强度校核[J]. 轨道交通装备与技术, 2014(2): 44-47. |
| Huang Biao, Qi Yuan, Du Li-qing. Nonlinear finite element analysis and fatigue strength check of elastic wheels[J]. Rail Transportation Equipment and Technology, 2014(2): 44-47. | |
| 5 | 戚援, 侯传伦, 杜利清, 等. 低地板车辆用块式橡胶弹性车轮的研制[C]∥第十七届中国科协年会, 广州, 2015: No.6. |
| 6 | Cigada A, Manzoni S, Vanali M. Geometry effects on the vibro-acoustic behavior of railway resilient wheels[J]. Vibration Control, 2011, 17(12): No.1761. |
| 7 | Lopez I, Vera E, Busturia J M, et al. Theoretical and experimental analysis of ring damped railway wheels[C]∥In Proceedings of the ISMA21 Conference, Leuven, Belgium, 1996: 787-794. |
| 8 | 张乐. 弹性车轮结构刚度和强度研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学机械工程学院, 2014. |
| Zhang Le. Research on stiffness and strength of elastic wheel structure[D]. Chengdu: College of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| 9 | 邢璐璐, 李芾, 付政波. 弹性车轮车辆临界速度及曲线通过性能分析[J]. 电力机车与城轨车辆, 2012, 35(1): 25-28. |
| Xing Lu-lu, Li Fu, Fu Zheng-bo. Analysis of the critical speed and curve passing performance of flexible wheel vehicles[J]. Electric Locomotives and Urban Rail Vehicles, 2012, 35(1): 25-28. | |
| 10 | 孙明昌, 曾京, 徐志胜. 弹性轮对车辆-轨道垂向耦合系统动力学研究[J]. 铁道车辆, 2003(1):15-20. |
| Sun Ming-chang, Zeng Jing, Xu Zhi-sheng. Dynamics study of elastic wheelset vehicle-track vertical coupling system[J]. Railway Vehicle, 2003(1):15-20. | |
| 11 | 文娟. 弹性车轮动力学性能及纵向振动研究[D].西南交通大学机械工程学院, 2016. |
| Wen Juan. Research on dynamic performance and longitudinal vibration of elastic wheel[D]. Chengdu: College of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 12 | 杨阳, 丁军君, 李芾, 等. 弹性车轮等效刚度对车辆动力学性能的影响[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2018, 39(3): 63-70. |
| Yang Yang, Ding Jun-jun, Li Fu, et al. The effect of the equivalent stiffness of elastic wheels on vehicle dynamics[J]. China Railway Science, 2018, 39(3): 63-70. | |
| 13 | 郭文浩, 池茂儒, 杨飞, 等. 弹性轮对对轮轨动作用力的影响[J]. 机械, 2011, 38(9):1-7. |
| Guo Wen-hao, Chi Mao-ru, Yang Fei, et al. The effect of elastic wheel pair on wheel-rail action force[J]. Machinery, 2011, 38(9):1-7. | |
| 14 | 刘玉霞, 韩健, 周信, 等. 弹性车轮减振降噪特性分析[J]. 铁道学报, 2015, 37(6): 48-53. |
| Liu Yu-xia, Han Jian, Zhou Xin, et al. Analysis of vibration and noise reduction characteristics of elastic wheels[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(6):48-53. | |
| 15 | 周信. 地铁弹性车轮的减振降噪及动态特性研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学机械工程学院, 2019. |
| Zhou Xin. Research on vibration and noise reduction and dynamic characteristics of subway elastic wheels[D]. Chengdu: College of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 16 | Han J, He Y, Xiao X, et al. Effect of control measures on wheel/rail noise when the vehicle curves[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(11): No.1144. |
| 17 | 张小强, 黄振兴, 侯传伦. 弹性车轮在地铁车辆上的应用及分析[J]. 机车车辆工艺, 2020(3): 11-15. |
| Zhang Xiao-qiang, Huang Zhen-xing, Hou Chuan-lun. Application and analysis of elastic wheels on metro vehicles[J]. Locomotive and Rolling Stock Technology, 2020(3): 11-15. | |
| 18 | Claus H, Schiehlen W. Dynamic stability and random vibrations of rigid and elastic wheelsets[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2004, 36(2-4): 299-311. |
| 19 | Arai H. On the acoustic and dynamic characteristics of resilient wheel:1st report, comparison with various types of wheels[J]. Transactions of the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers C, 1983, 49: 543-552. |
| 20 | 李小珍, 强士中, 沈锐利. 高速列车-大跨度钢斜拉桥空间耦合振动响应研究[J]. 桥梁建设, 1998(4):67-70. |
| Li Xiao-zhen, Qiang Shi-zhong, Shen Rui-li. Research on spatial coupling vibration response of high-speed train and long-span steel cable-stayed bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 1998(4): 67-70. | |
| 21 | Zhai W M. Two simple fast integration methods for large-scale dynamic problems in engineering[J]. International Yournal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1996, 39(24): 4199-4214. |
| 22 | 陈兆玮. 高速铁路桥墩沉降对行车性能影响的研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学机械工程学院, 2017. |
| Chen Zhao-wei. Influence of pier settlement on dynamic performance of running trains in high-speed railway[D]. Chengdu: College of Mechanical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. | |
| 23 | 向波, 周逸, 陈县伟. 东水门长江大桥动力特性监测系统研究[J]. 西部交通科技, 2015(11): 46-50. |
| Xiang Bo, Zhou Yi, Chen Xian-wei. Research on the dynamic characteristics monitoring system of dongshuimen yangtze river bridge[J]. Western Transportation Science and Technology, 2015(11): 46-50. | |
| 24 | 袁万城, 崔飞, 张启伟. 桥梁健康监测与状态评估的研究现状与发展[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 1999(2): 59-63. |
| Yuan Wan-cheng, Cui Fei, Zhang Qi-wei. Research status and development of bridge health monitoring and condition assessment[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science Edition), 1999(2): 59-63. | |
| 25 | 杨学志, 严普强, 张锻, 等. DP传感器研究及桥梁自振特性测试[J]. 振动.测试与诊断, 1997(2):53-58. |
| Yang Xue-zhi, Yan Pu-qiang, Zhang Duan, et al. DP sensor research and bridge natural vibration characteristics test[J]. Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis, 1997(2): 53-58. | |
| 26 | 严普强, 乔陶鹏. 工程中的低频振动测量与其传感器[J]. 振动.测试与诊断, 2002(4): 39-75. |
| Yan Pu-qiang, Qiao Tao-peng. Low-frequency vibration measurement and its sensors in engineering[J]. Vibration, Testing and Diagnsis, 2002(4): 39-75. | |
| 27 | 翟婉明. 车辆-轨道耦合动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. |
| 28 | Sato Y. Study on high-frequency vibration in track operation with high-speed trains[J]. Quarterly Report of RTRI, 1997, 18(3): 109-114. |
| 29 | 杨阳, 李芾, 戚壮, 等. 弹性车轮动力学复合模型及其性能研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2015, 36(4): 93-100. |
| Yang Yang, Li Fu, Qi Zhuang, et al. Composite model of elastic wheel dynamics and its performance research[J]. China Railway Science, 2015, 36(4): 93-100. | |
| 30 | Claus H, Len W S. Dynamic stability and random vibrations of rigid and elastic wheelsets[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2004, (36): 299-311. |
| [1] | Shu-pei ZHANG,Ming-yue XIA,Wei ZHANG,Zhao CHEN,Yi-xiang CHEN. Impact dynamic modeling and simulation for ball joint with clearance considering nonlinear stiffness [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2227-2235. |
| [2] | Hui CHEN,Ya-jun SHAO. Measurement method of pavement surface spectrum with multi⁃sensor coupling based on inertial benchmark [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2254-2262. |
| [3] | Ping-yi LIU,Xiao-ting LI,Ruo-lin GAO,Hai-tao LI,Wen-jun WEI,Ya WANG. Design and experiment of tilt-driving mechanism for the vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [4] | Xue-jin HUANG,Jin-xing ZHONG,Jing-yu LU,Ji ZHAO,Wei XIAO,Xin-mei YUAN. Electric vehicle charging load forecasting method based on user portrait [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2193-2200. |
| [5] | Zheng-wei GU,Pan ZHANG,Dong-ye LYU,Chun-li WU,Zhong YANG,Guo-jin TAN,Xiao-ming HUANG. Earthquake⁃induced residual displacement analysis of simply supported beam bridge based on numerical simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1711-1718. |
| [6] | Xin CHEN,Guan-chen ZHANG,Kang-ming ZHAO,Jia-ning WANG,Li-fei YANG,De-rong SITU. Influence of lap welds on the lightweight design of welded aluminum structures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [7] | Yong ZHANG,Feng-zhao MAO,Shui-chang LIU,Qing-yu WANG,Shen-gong PAN,Guang-sheng ZENG. Optimization on distortion grid of vehicle external flow field based on Laplacian Algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [8] | Shao-hua WANG,Kun CHU,De-hua SHI,Chun-fang YIN,Chun LI. Robust compound coordinated control of HEV based on finite⁃time extended state observation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [9] | Lei CHEN,Yang WANG,Zhi-sheng DONG,Ya-qi SONG. A vehicle agility control strategy based on steering intent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [10] | Yan-li YIN,Xue-jiang HUANG,Xiao-liang PAN,Li-tuan WANG,Sen ZHAN,Xin-xin ZHANG. Hierarchical control of hybrid electric vehicle platooning based on PID and Q⁃Learning algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [11] | Gui-shen YU,Xin CHEN,Zi-tao WU,Yi-xiong CHEN,Guan-chen ZHANG. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of probeless friction stir spot welding joint in AA6061⁃T6 aluminum thin plate [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [12] | Yan-tao TIAN,Xing HUANG,Hui-qiu LU,Kai-ge WANG,Fu-qiang XU. Multi⁃mode behavior trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicle based on attention and depth interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [13] | Hong-bo YANG,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Nian-cheng GUO,Yan-yan ZHAO. Multi⁃objective optimization of macro parameters of helical gear based on NSGA⁃Ⅱ [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [14] | Rui ZHAO,Yun LI,Hong-yu HU,Zhen-hai GAO. Vehicle collision warning method at intersection based on V2I communication [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [15] | Xiao-bo CHEN,Ling CHEN. Variational Bayesian cooperative target tracking with unknown localization noise statistics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
|