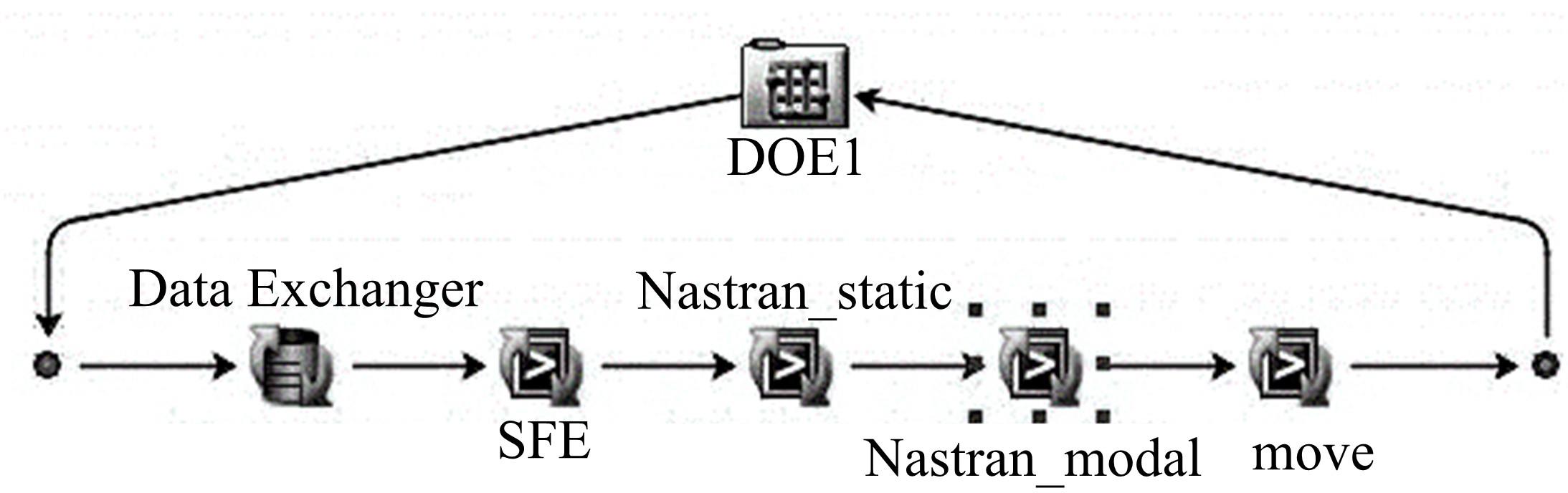
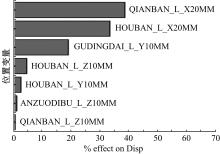
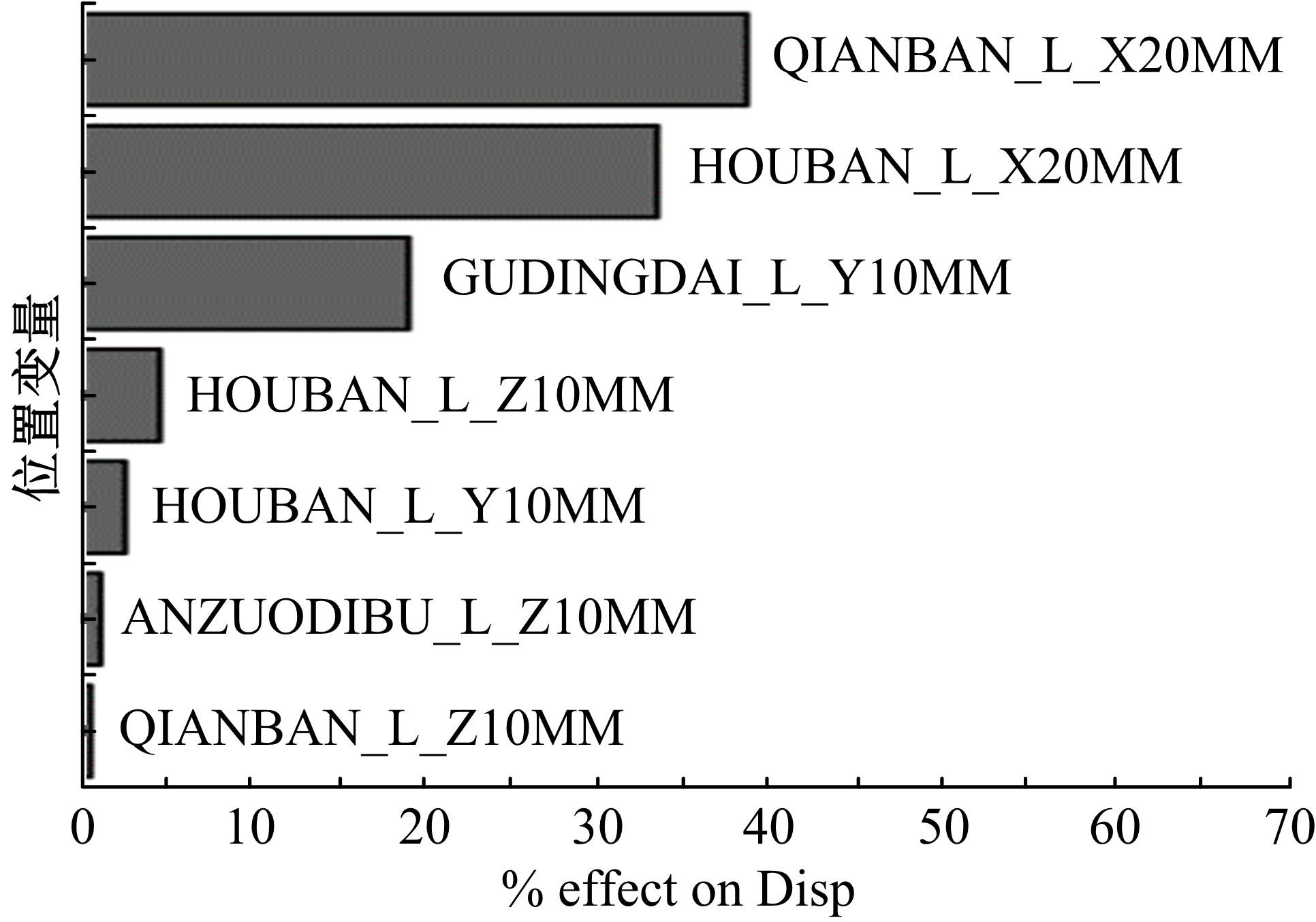
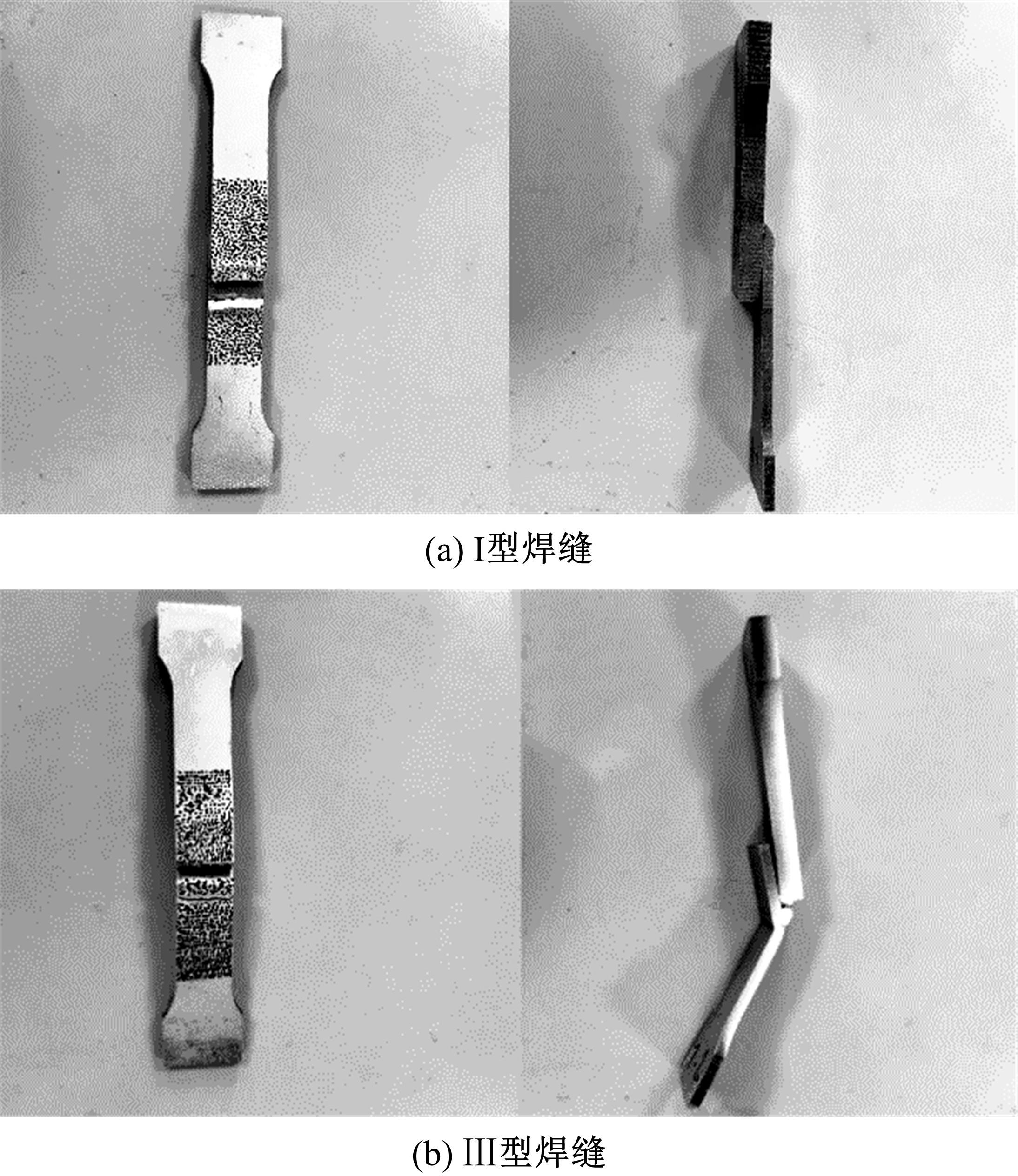
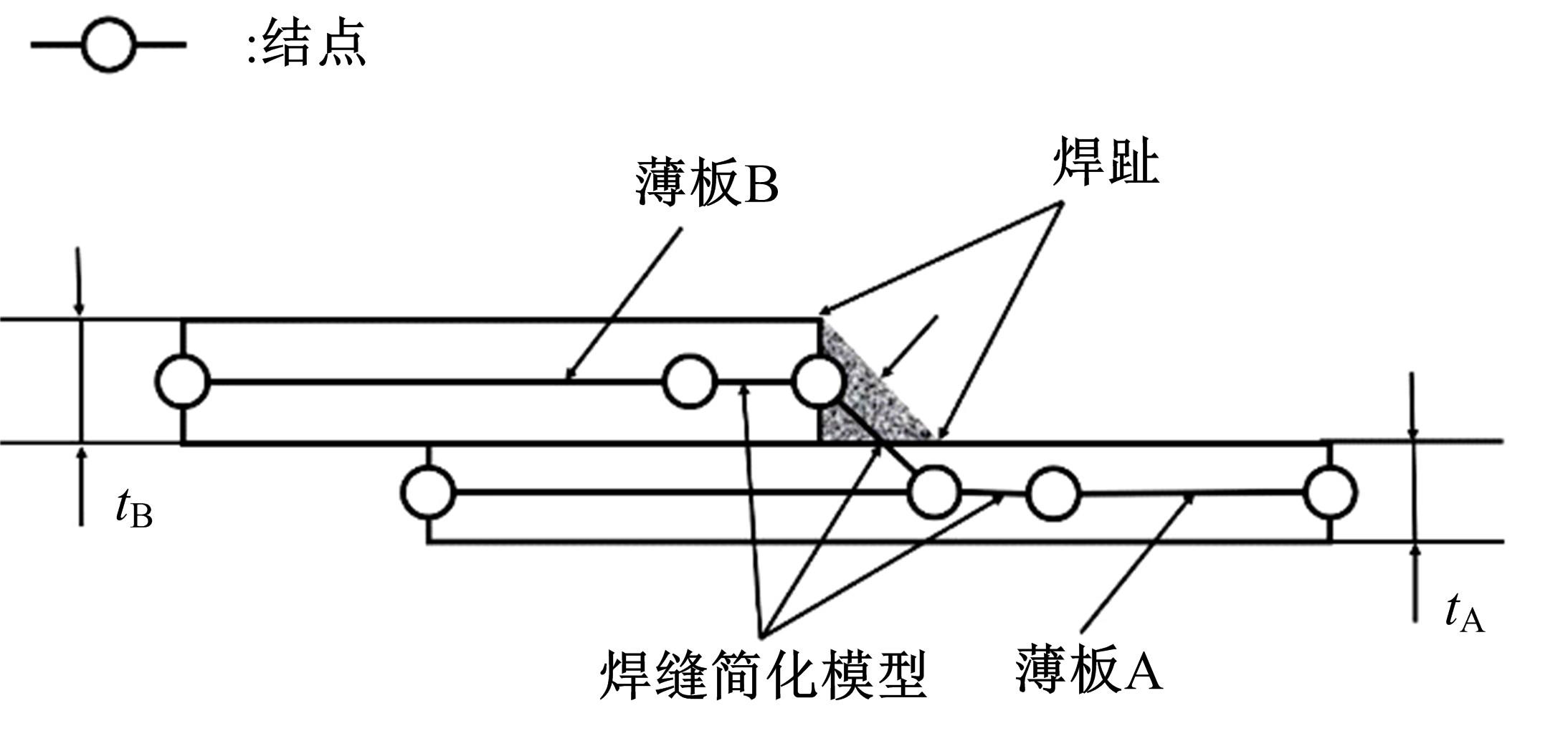
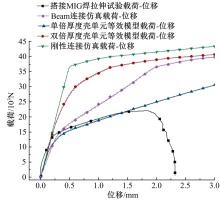
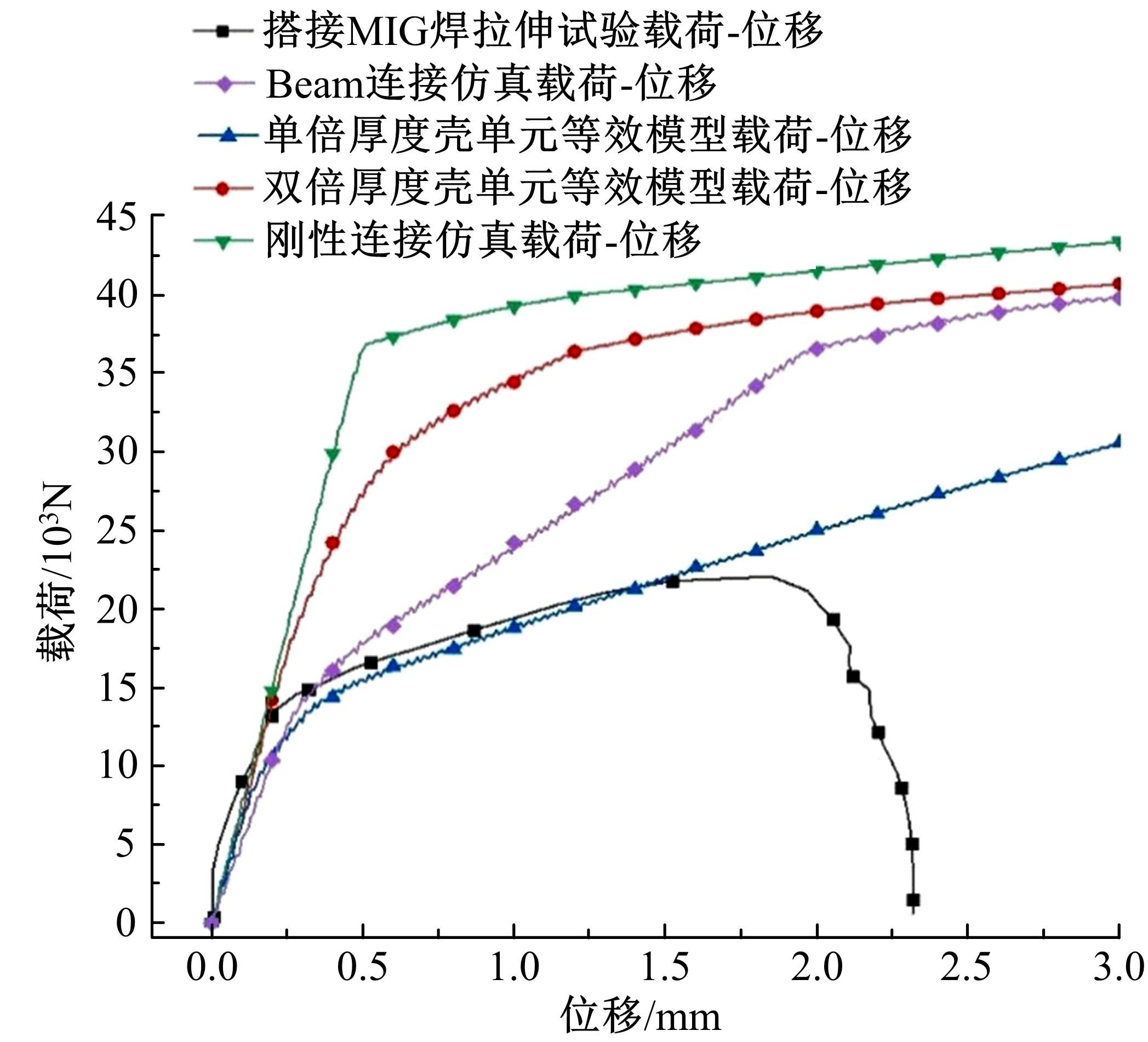
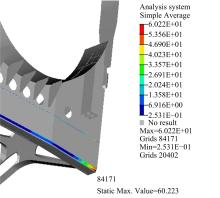
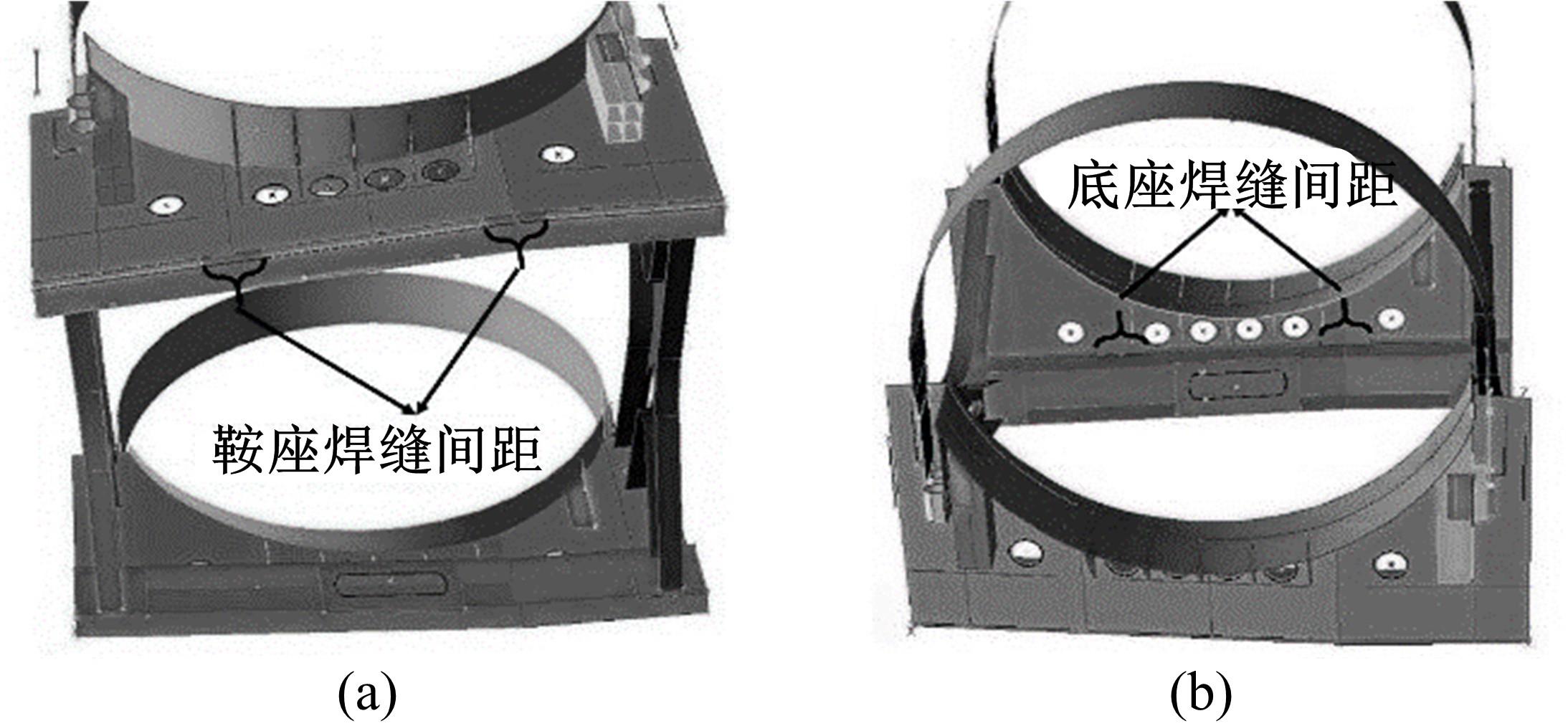
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1282-1288.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210920
Influence of lap welds on the lightweight design of welded aluminum structures
Xin CHEN1( ),Guan-chen ZHANG1,Kang-ming ZHAO1,Jia-ning WANG1,Li-fei YANG1,De-rong SITU2
),Guan-chen ZHANG1,Kang-ming ZHAO1,Jia-ning WANG1,Li-fei YANG1,De-rong SITU2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automobile Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Mechanical and Traffic Engineering,Guangxi University of Science and Technology,Liuzhou 545006,China
CLC Number:
- U46
| 1 | Palani P K, Murugan N. Selection of parameters of pulsed current gas metal arc welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2006,172(1):1-10. |
| 2 | Kah P, Hiltunen E, Martikainen J. Sensing in aluminum alloy welding[J]. Adv Mater Res-Switz, 2014, 849: 291-287. |
| 3 | 吕天佟, 王登峰, 王传青. 隐式参数化白车身多目标协同优化设计[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2019, 39(5): 447-453. |
| Lv Tian-tong, Wang Deng-feng, Wang Chuan-qing. Multi-objective lightweight collaborative optimization and design for latent parametric BIW structure[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2019, 39(5): 447-453. | |
| 4 | 陈鑫, 胡翠松, 宁厚于, 等. SUV白车身隐式参数化建模及多性能优化轻量化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(6): 1780-1785. |
| Chen Xin, Hu Cui-song, Ning Hou-yu, et al. Implicit parameterization modeling and multi-performance lightweight optimization for SUV body-in-white[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1780-1785. | |
| 5 | Hilmann J, Paas M, Haenschke A, et al. Automatic concept model generation for optimisation and robust design of passenger cars[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2007, 38(11/12): 795-801. |
| 6 | Rayamajhi M, Hunkeler S, Duddeck F. Geometrical compatibility in structural shape optimisation for crashworthiness[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2014, 19(1): 42-56. |
| 7 | Shi Y, Lin Z, Zhu P, et al. Impact modeling of the weld line of tailor-welded blank[J]. Mater Design, 2008, 29(1): 232-238. |
| 8 | Xu F, Tian X, Li G. Experimental study on crashworthiness of functionally graded thickness thin-walled tubular structures[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2015, 55(7): 1339-1352. |
| 9 | 唐辉, 门永新, 毛雪峰, 等. 基于隐式参数化的车身概念开发[J]. 汽车工程, 2014, 36(10): 1248-1253. |
| Tang Hui, Yong-xin Men, Mao Xue-feng,et al.Concept development of vehicle body based on implicit parametric technology[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2014, 36(10): 1248-1253. | |
| 10 | . 燃气汽车专用装置的安装要求中气瓶安装强度试验方法的应用 [S]. |
| 11 | 宋康, 陈潇凯, 林逸. 汽车行驶动力学性能的多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2):352-357. |
| Song Kang, Chen Xiao-kai, Lin Yi. Multi-objective optimization of vehicle ride dynamic behaviors[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 352-357. | |
| 12 | . 钢结构焊接规范 [S]. |
| 13 | . 焊接接头拉伸试验方法 [S]. |
| 14 | . 金属材料焊缝破坏性试验 十字接头和搭接接头拉伸试验方法 [S]. |
| 15 | Fermer M, Svensson H.Industrial experiences of FE-based fatigue life predictions of welded automotive structures[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, 2001, 24(7): 489-500. |
| 16 | 陈军, 成艾国, 陈涛, 等. Beam与Solid两种点焊模拟方法对比研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2012, 23(19): 2388-2392. |
| Chen Jun, Cheng Ai-guo, Chen Tao, et al. Comparative study of spot weld simulation method between beam and solid[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 23(19): 2388-2392. | |
| 17 | Lin S H, Pan J, Tyan T, et al. A general failure criterion for spot welds under combined loading conditions[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40(21): 5539-5564. |
| [1] | Lei CHEN,Yang WANG,Zhi-sheng DONG,Ya-qi SONG. A vehicle agility control strategy based on steering intent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [2] | Shao-hua WANG,Kun CHU,De-hua SHI,Chun-fang YIN,Chun LI. Robust compound coordinated control of HEV based on finite⁃time extended state observation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [3] | Xiao-bo CHEN,Ling CHEN. Variational Bayesian cooperative target tracking with unknown localization noise statistics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
| [4] | Hai-bo LONG,Jia-qi YANG,Liang YIN,Xue-yu ZHAO,Zi-quan XIANG. Multi-objective decision-making on emergency material distribution under uncertain demand based on robust optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1078-1084. |
| [5] | Rui ZHAO,Yun LI,Hong-yu HU,Zhen-hai GAO. Vehicle collision warning method at intersection based on V2I communication [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [6] | Hong-bo YANG,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Nian-cheng GUO,Yan-yan ZHAO. Multi⁃objective optimization of macro parameters of helical gear based on NSGA⁃Ⅱ [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [7] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Enhanced localization system based on camera and lane markings [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 663-673. |
| [8] | Bing ZHU,Tian-xin FAN,Jian ZHAO,Pei-xing ZHANG,Yu-hang SUN. Accelerate test method of automated driving system based on hazardous boundary search [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 704-712. |
| [9] | Ying HE,Jun-song FAN,Wei WANG,Geng SUN,Yan-heng LIU. Joint optimization of secure communication and trajectory planning in unmanned aerial vehicle air⁃to⁃ground [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 913-922. |
| [10] | Yan-tao TIAN,Fu-qiang XU,Kai-ge WANG,Zi-xu HAO. Expected trajectory prediction of vehicle considering surrounding vehicle information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [11] | Song GAO,Yu-qiong WANG,Yu-hai WANG,Yi XU,Ying-chao ZHOU,Peng-wei WANG. Longitudinal and lateral integrated feedback linearization control for intelligent vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 735-745. |
| [12] | Bo XIE,Rong GAO,Fu-qiang XU,Yan-tao TIAN. Stability control of human⁃vehicle shared steering system under low adhesion road conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 713-725. |
| [13] | Yan-tao TIAN,Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE. Deep reinforcement learning augmented decision⁃making model for intelligent driving vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [14] | Jian ZHANG,Jin-bo LIU,Yuan GAO,Meng-ke LIU,Zhen-hai GAO,Bin YANG. Localization algorithm of vehicular sensor based on multi⁃mode interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 772-780. |
| [15] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Wheel odometry error prediction model based on transformer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
|
||