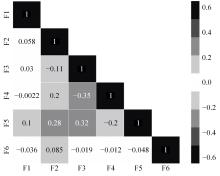
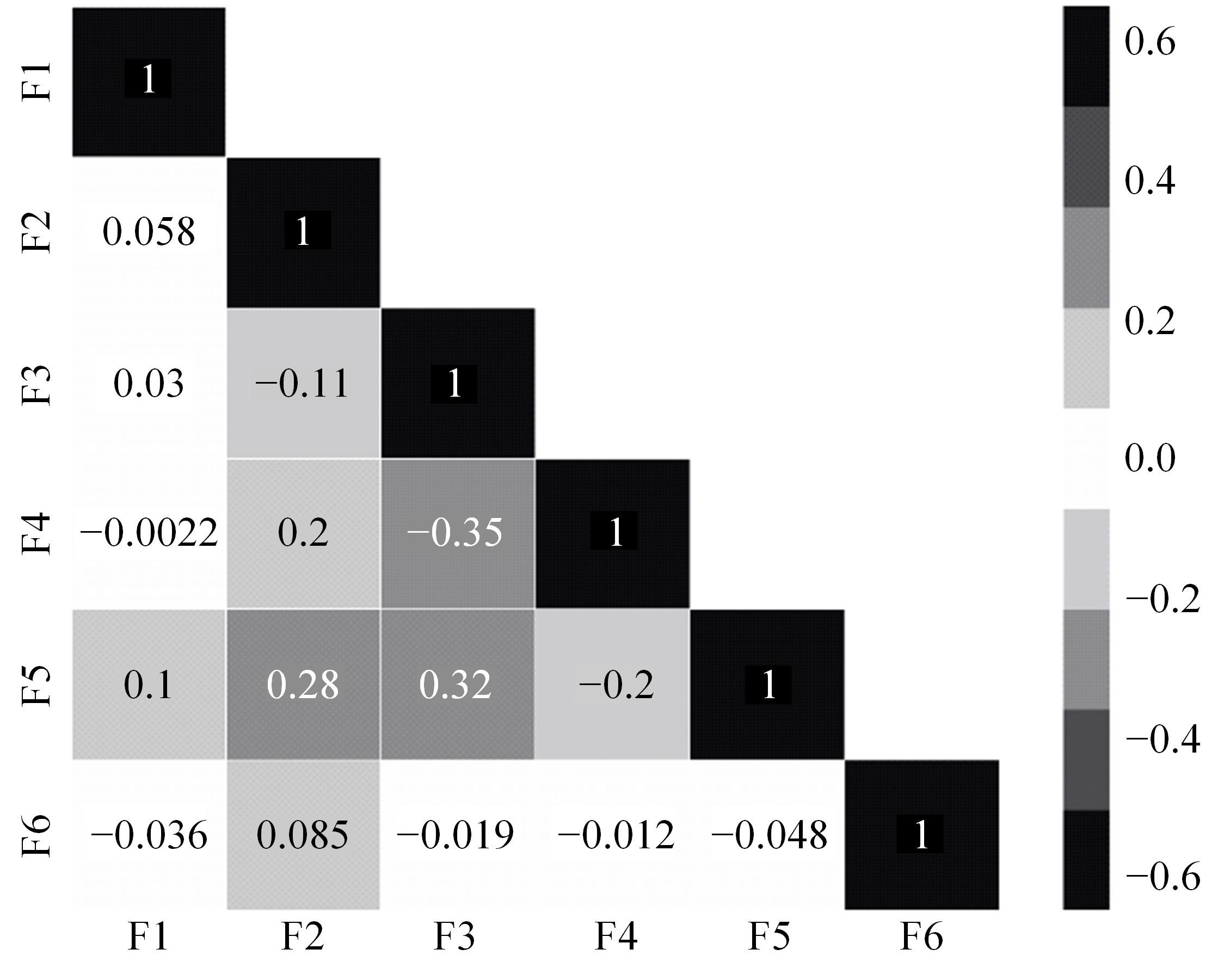
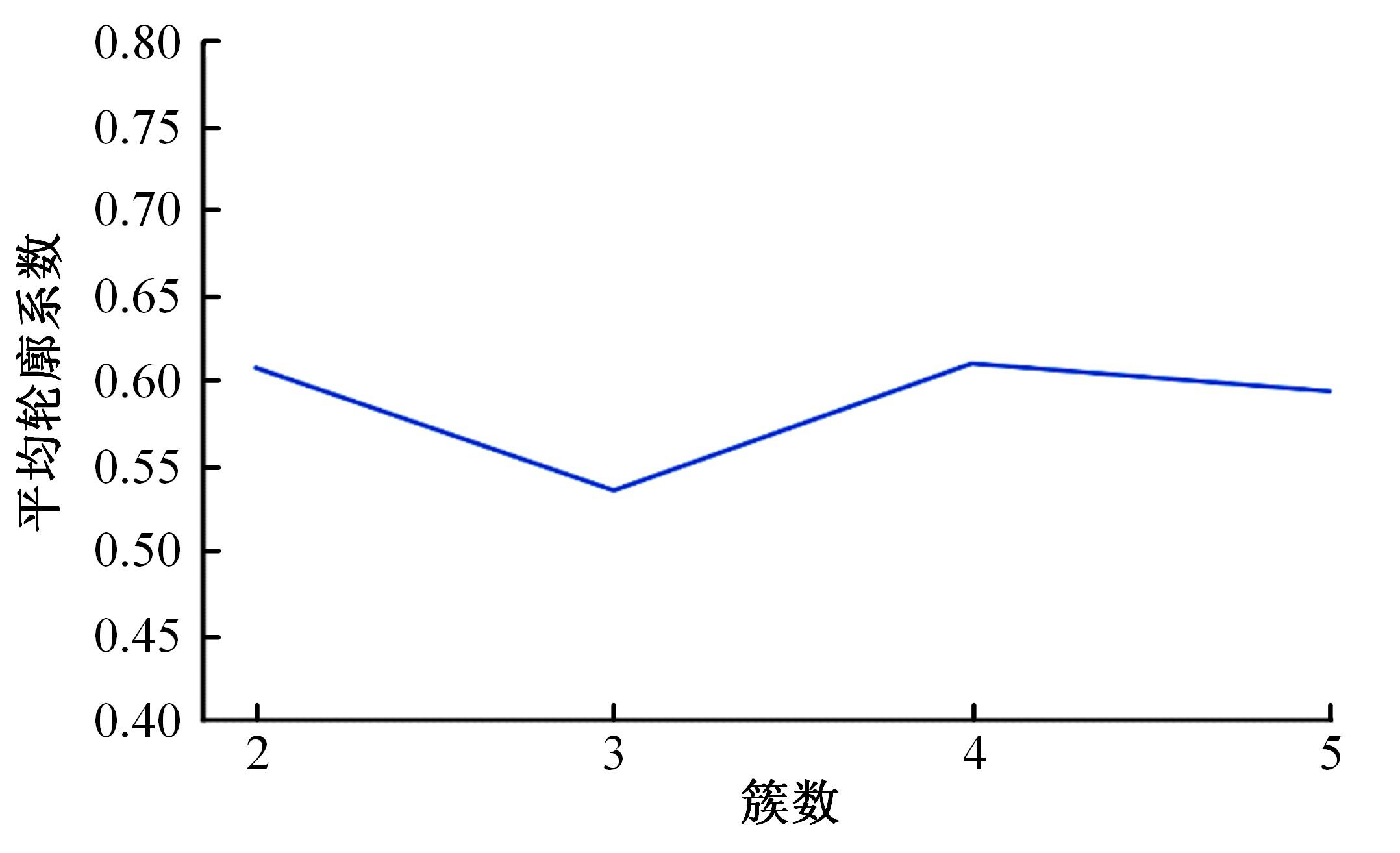
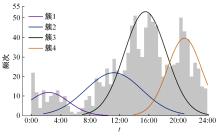
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2193-2200.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211130
Electric vehicle charging load forecasting method based on user portrait
Xue-jin HUANG1,2( ),Jin-xing ZHONG1,Jing-yu LU2,Ji ZHAO3,Wei XIAO3,Xin-mei YUAN2(
),Jin-xing ZHONG1,Jing-yu LU2,Ji ZHAO3,Wei XIAO3,Xin-mei YUAN2( )
)
- 1.Dongguan Power Supply Bureau,Guangdong Power Grid Corporation,Dongguan 523000,China
2.College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Sichuan Energy Internet Research Institute,Tsinghua University,Chengdu 610042,China
CLC Number:
- TM92
| 1 | 贾东明. 规模化电动汽车充电对配电网的影响及有序充电研究[D]. 保定:华北电力大学电气与电子工程学院, 2015. |
| Jia Dong-ming. Studies on the impacts of Large-scale vehicles charging on the power distribution network and coordinated charging[D]. Baoding: College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, North China Electric Power University, 2015. | |
| 2 | 张玮,张树培,罗江鹏,等.电动汽车充电桩排队服务动态优化模型[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022,52(5): 1045-1051. |
| Zhang Wei, Zhang Shu-pei, Luo Jiang-peng, et al. Dynamic optimization model of queuing service forelectric vehicle charging piles[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2022,52(5): 1045-1051. | |
| 3 | 和敬涵, 谢毓毓, 叶豪东, 等. 电动汽车充电模式对主动配电网的影响[J]. 电力建设, 2015,36(1):97-102. |
| He Jing-han, Xie Yu-yu, Ye Hao-dong, et al. Influence of electric vehicles charging modes on active network distribution[J].Electic Power Construction, 2015, 36(1): 97-102. | |
| 4 | 闫云娟,查伟雄,石俊刚,等.具有随机充电需求的混合动态网络平衡模型[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2022, 52(1): 136-143. |
| Yan Yun-juan, Zha Wei-xiong, Shi Jun-gang, et al. Mixed network equilibrium model with stochastic charging demand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 136-143. | |
| 5 | 胡泽春, 宋永华, 徐智威, 等. 电动汽车接入电网的影响与利用[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(4): 1-10. |
| Hu Ze-chun, Song Yong-hua, Xu Zhi-wei, et al. Impacts and utilization of electric vehicles integration into power systems[J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2012, 32(4): 1-10. | |
| 6 | 朱慧婷, 杨雪, 陈友媛. 电动汽车充电负荷预测方法综述[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2016, 14(5): 44-47. |
| Zhu Hui-ting, Yang-xue, Chen You-yuan, et al. Overview of the charging load forecasting methods of plug-in electric vehicles[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2016, 14(5):44-47. | |
| 7 | 张谦, 王众, 谭维玉, 等. 基于MDP随机路径模拟的电动汽车充电负荷时空分布预测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42(20): 59-66. |
| Zhang Qian, Wang Zhong, Tan Wei-yu, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution prediction of charging lord for electric vehicle based on MDP random path simulation[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(20): 59-66. | |
| 8 | Wang D, Guan X, Wu J, et al. Analysis of multi-location PEV charging behaviors based on trip chain generation[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering, New Taipei, China, 2014: 14692218. |
| 9 | 陈丽丹, 聂涌泉, 钟庆. 基于出行链的电动汽车充电负荷预测模型[J]. 电工技术学报, 2015, 30(4): 216-225. |
| Chen Li-dan, Nie Yong-quan, Zhong Qing, et al. A model for electric vehicle charging load forecasting based on trip chains[J].Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2015, 30(4): 216-225. | |
| 10 | Bae S, Kwasinski A. Spatial and temporal model of electric vehicle charging demand[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2012,3(1): 394-403. |
| 11 | 余孟杰. 产品研发中用户画像的数据模建——从具象到抽象[J]. 设计艺术研究, 2014,4(6):60-64. |
| Yu Meng-jie. Data modeling of user portrayal in the product development: from concrete to abstract[J]. Design Research, 2014, 4(6): 60-64. | |
| 12 | 计智伟, 胡珉, 尹建新. 特征选择算法综述[J]. 电子设计工程, 2011(9): 52-57. |
| Ji Zhi-wei, Hu Min, Yin Jian-xin. A survey of feature selection algorithm[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2011(9): 52-57. | |
| 13 | 张剑峰. 基于分布式发电的配电网规划问题的分析[J]. 低碳世界, 2019, 9(11): 106-107. |
| Zhang Jian-feng. Analysis of distribution network planning based on distributed generation[J]. Low Carbon World, 2019, 9(11): 106-107. |
| [1] | Ping-yi LIU,Xiao-ting LI,Ruo-lin GAO,Hai-tao LI,Wen-jun WEI,Ya WANG. Design and experiment of tilt-driving mechanism for the vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [2] | Xin CHEN,Guan-chen ZHANG,Kang-ming ZHAO,Jia-ning WANG,Li-fei YANG,De-rong SITU. Influence of lap welds on the lightweight design of welded aluminum structures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [3] | Yong ZHANG,Feng-zhao MAO,Shui-chang LIU,Qing-yu WANG,Shen-gong PAN,Guang-sheng ZENG. Optimization on distortion grid of vehicle external flow field based on Laplacian Algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [4] | Shao-hua WANG,Kun CHU,De-hua SHI,Chun-fang YIN,Chun LI. Robust compound coordinated control of HEV based on finite⁃time extended state observation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [5] | Lei CHEN,Yang WANG,Zhi-sheng DONG,Ya-qi SONG. A vehicle agility control strategy based on steering intent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [6] | Yan-li YIN,Xue-jiang HUANG,Xiao-liang PAN,Li-tuan WANG,Sen ZHAN,Xin-xin ZHANG. Hierarchical control of hybrid electric vehicle platooning based on PID and Q⁃Learning algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [7] | Gui-shen YU,Xin CHEN,Zi-tao WU,Yi-xiong CHEN,Guan-chen ZHANG. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of probeless friction stir spot welding joint in AA6061⁃T6 aluminum thin plate [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [8] | Yan-tao TIAN,Xing HUANG,Hui-qiu LU,Kai-ge WANG,Fu-qiang XU. Multi⁃mode behavior trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicle based on attention and depth interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [9] | Hong-bo YANG,Wen-ku SHI,Zhi-yong CHEN,Nian-cheng GUO,Yan-yan ZHAO. Multi⁃objective optimization of macro parameters of helical gear based on NSGA⁃Ⅱ [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [10] | Rui ZHAO,Yun LI,Hong-yu HU,Zhen-hai GAO. Vehicle collision warning method at intersection based on V2I communication [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [11] | Xiao-bo CHEN,Ling CHEN. Variational Bayesian cooperative target tracking with unknown localization noise statistics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
| [12] | Yan-tao TIAN,Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE. Deep reinforcement learning augmented decision⁃making model for intelligent driving vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [13] | Jian ZHANG,Jin-bo LIU,Yuan GAO,Meng-ke LIU,Zhen-hai GAO,Bin YANG. Localization algorithm of vehicular sensor based on multi⁃mode interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 772-780. |
| [14] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Wheel odometry error prediction model based on transformer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [15] | Yan-ran LIU,Qing-yu MENG,Hong-yan GUO,Jia-lin LI. Vehicle trajectory prediction combined with high definition map in graph attention mode [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 792-801. |
|
||