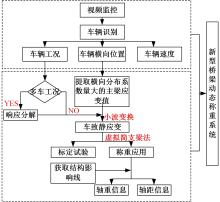
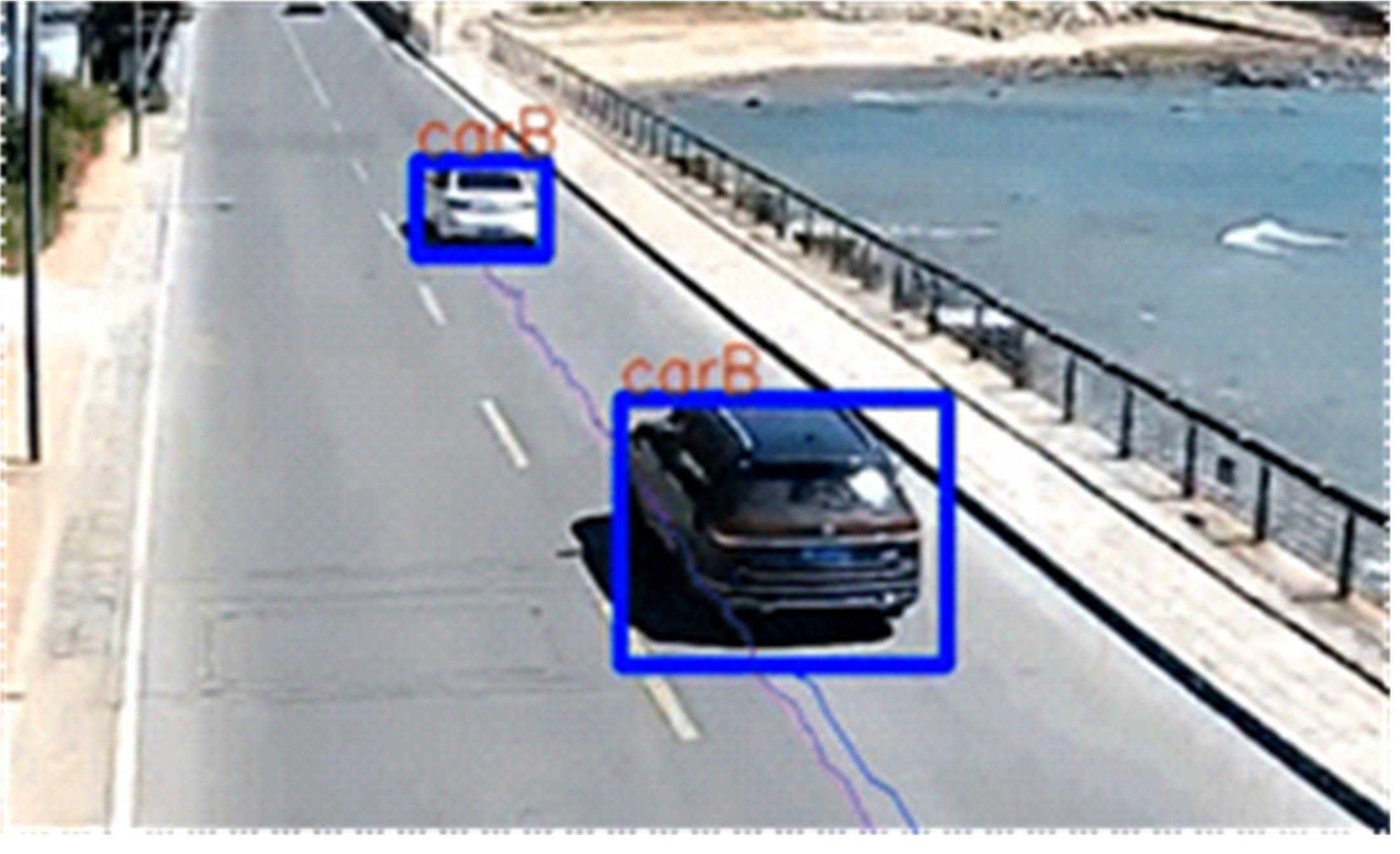
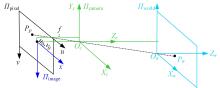
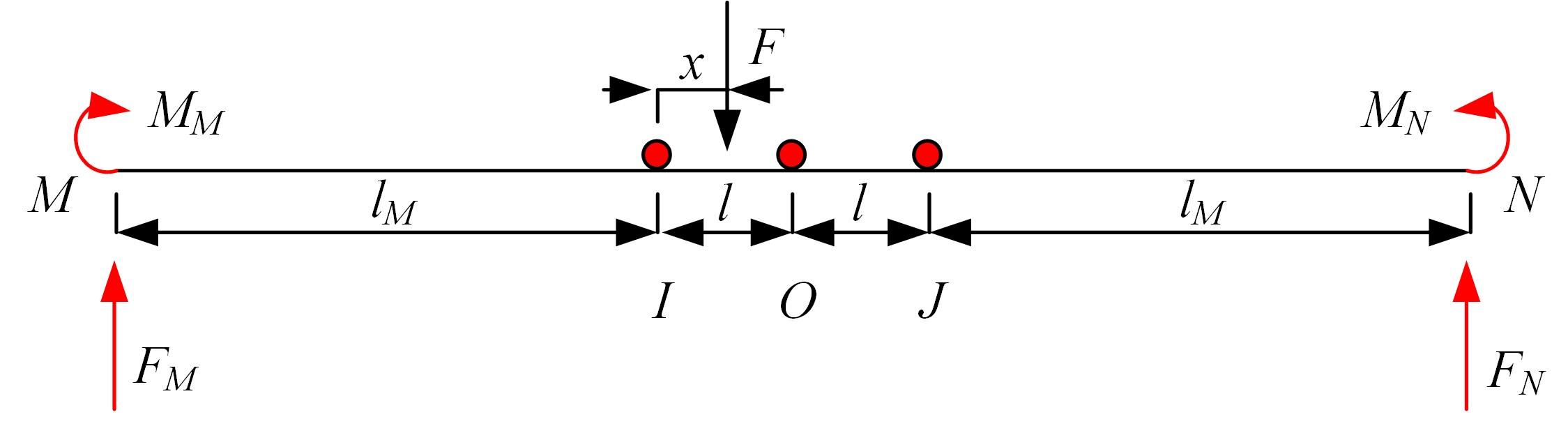
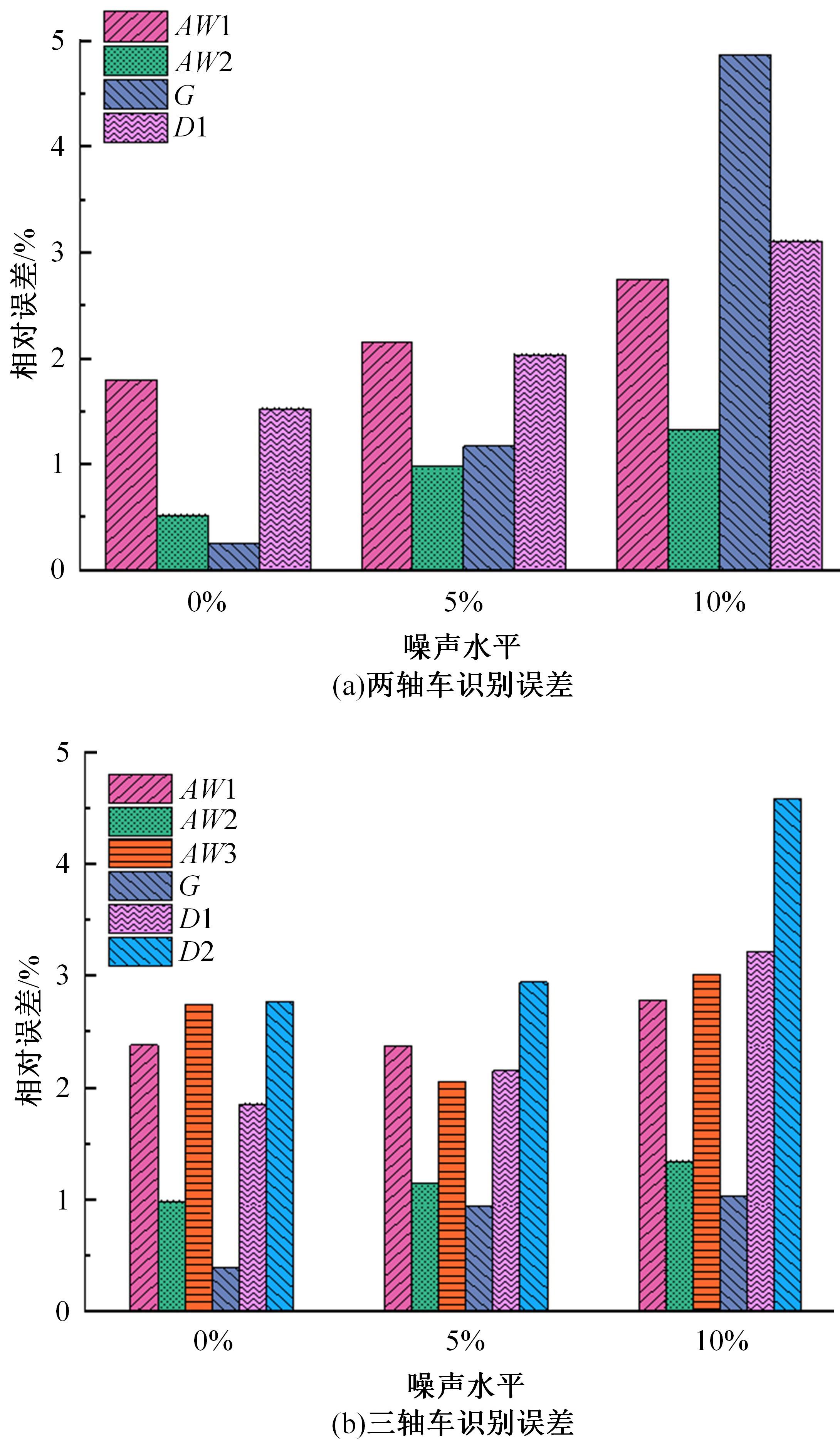
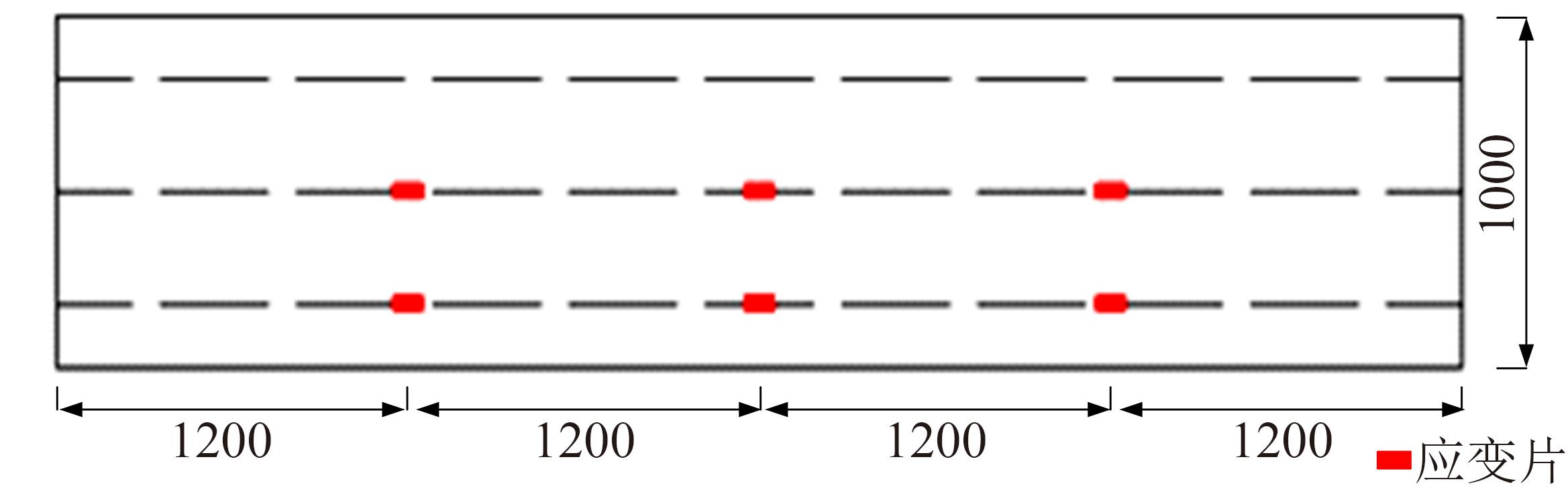
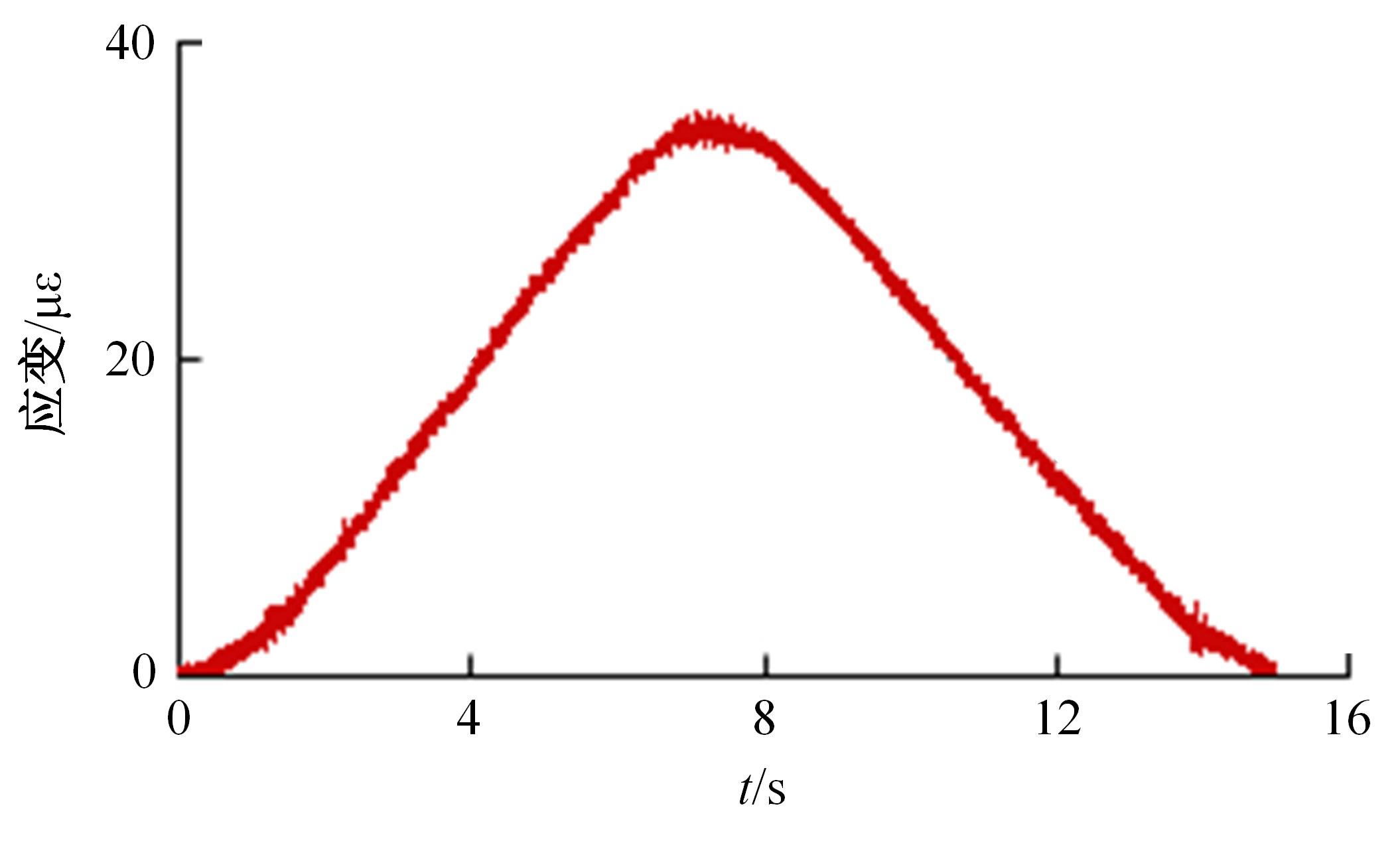
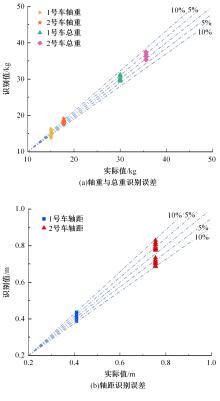
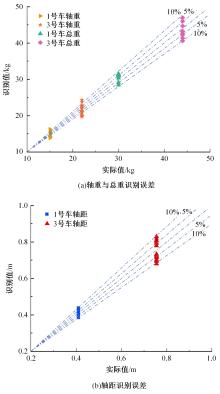
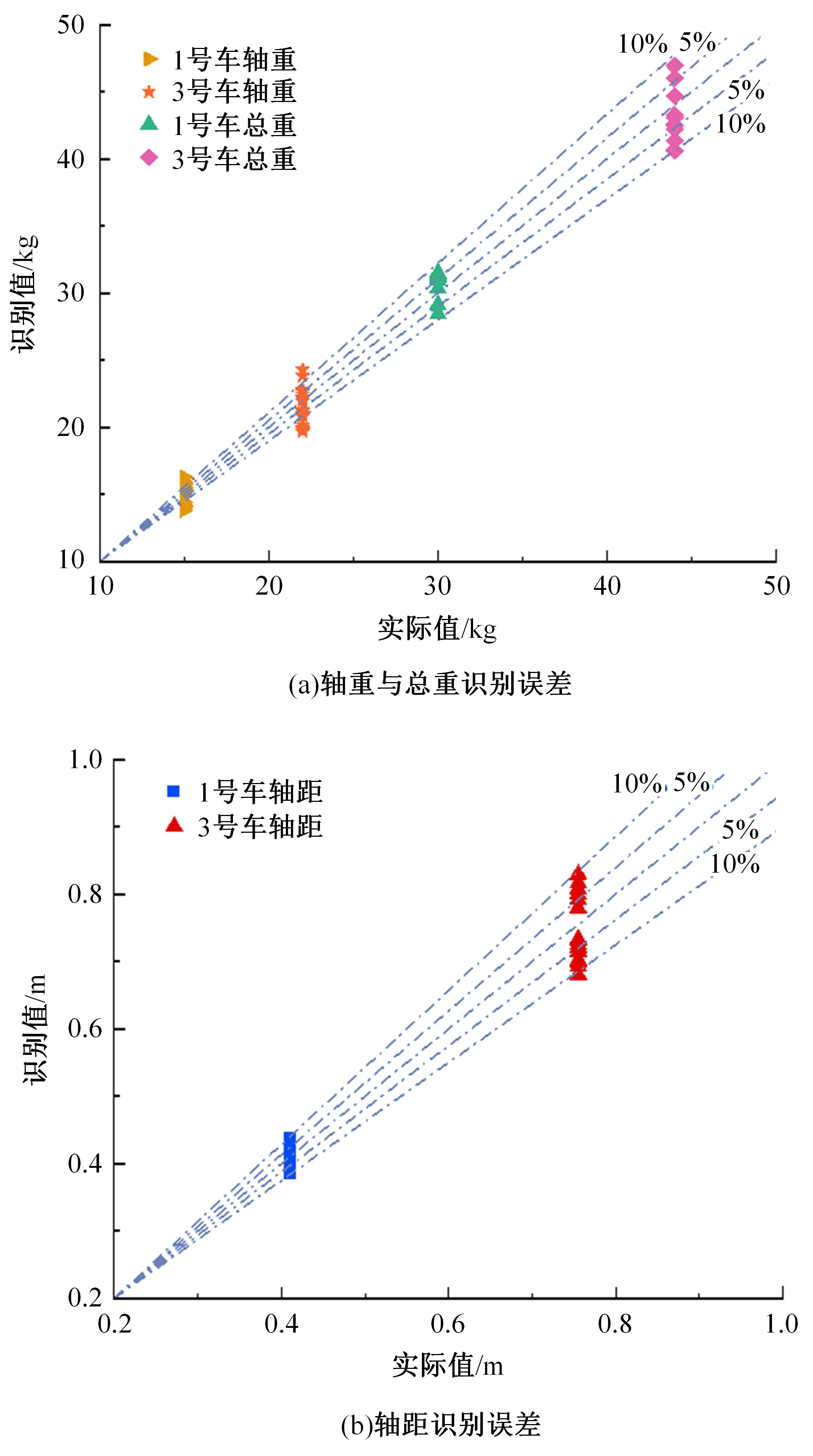
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 188-197.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230135
Bridge weigh-in-motion combined with machine version
Guan-xu LONG1,2( ),Xiu-shi ZHANG3,Gong-feng XIN1,2,Tao WANG3(
),Xiu-shi ZHANG3,Gong-feng XIN1,2,Tao WANG3( ),Gan YANG3
),Gan YANG3
- 1.Innovation Research Institute,Shandong Hi-Speed Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Jinan 250101,China
2.School of Highway,Chang'an University Xi'an 710064,China
3.Shandong Key Laboratory of Highway Technology and Safety Assessment,Jinan 250101,China
CLC Number:
- U446.2
| 1 | 何维. 公路桥梁动态称重关键技术研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院, 2019. |
| He Wei. Study of key technologies for highway bridge weigh-in-motion[D]. Changsha: College of Civil Engineering,Hunan University, 2019. | |
| 2 | 任伟新, 左小晗, 王宁波, 等. 非路面式桥梁动态称重研究综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2014, 27(7): 45-53. |
| Ren Wei-xin, Zuo Xiao-han, Wang Ning-bo, et al. Review of non-pavement bridge weigh-in-motion[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2014, 27(7): 45-53. | |
| 3 | Moses F. Weigh-in-motion system using instrumented bridges[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 1979, 105(3): 233-249. |
| 4 | O'Brien E J, Quilligan M J, Karoumi R. Calculating an influence line from direct measurements[J]. Bridge Engineering, 2006, 159(1): 31-34. |
| 5 | 邓露, 施海, 何维, 等. 基于虚拟简支梁法的桥梁动态称重研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(15): 209-215. |
| Deng Lu, Shi Hai, He Wei,et al. Vehicles' BWIM based on virtual simply-supported beam method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2018,37(15):209-215. | |
| 6 | 施海. 基于虚拟简支梁法的桥梁动态称重研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院, 2017. |
| Shi Hai. Bridge weigh-in-motion based on the virtual simply-supported beam method[D]. Changsha: College of Civil Engineering,Hunan University, 2017. | |
| 7 | Deng L, He W, Yu Y, et al. Equivalent shear force method for detecting the speed and axles of moving vehicles on bridges [J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2018, 23(8): No.04018057. |
| 8 | He W, Deng L, Shi H, et al. Novel virtual simply supported beam method for detecting the speed and axles of moving vehicles on bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 22(4): No.04016141. |
| 9 | 韩万水, 李彦伟, 乔磊, 等. 基于车-桥耦合振动理论的移动荷载识别[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(1): 74-86. |
| Han Wan-shui, Li Yan-wei, Qiao Lei, et al. Moving load identification based on vehicle bridge coupling vibration theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(1): 74-86. | |
| 10 | 张青霞. 基于虚拟变形法的动态荷载与结构损伤识别方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2010. |
| Zhang Qing-xia. Dynamic load and structural damage identification using virtual distortion method[D]. Harbin: School of Civil Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,2010. | |
| 11 | Yang G, Wang P, Han W S, et al. Automatic generation of fine-grained traffic load spectrum via fusion of weigh-in-motion and vehicle spatial-temporal information[J]. Computer-aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2022, 37(4):485-499. |
| 12 | 夏烨, 简旭东, 邓露, 等. 交通视频辅助的桥梁动态称重方法研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(12): 104-114. |
| Xia Ye, Jian Xu-Dong, Deng Lu, et al. Research on traffic-video-aided bridge weigh-in-motion approach[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2021, 34(12):104-114. | |
| 13 | 余婷. 基于影响线的桥梁快速安全评定方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学土木工程学院, 2019. |
| Yu Ting. Rapid assessment method of bridge safety condition based on influence line[D]. Nanjing: School of Civil Engineering,Southeast University, 2019. | |
| 14 | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of IEEE, 1998, 86(11):2278-2324. |
| 15 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥ International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA,2012:1097-1105. |
| 16 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J/OL]. arXiv e-prints, 2014. |
| 17 | Girshick R B, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus,USA, 2014: 580-587. |
| 18 | Girshick R. Fast RCNN[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Cambridge, USA, 2015: 1440-1448. |
| 19 | Redmon J, Farhadi A.YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J/OL].[2018-12-10]. . |
| 20 | 杨干, 韩万水, 张书颖. 基于多源信息融合的交通荷载重构方法研究[C]∥世界交通运输大会论文集, 中国,武汉,2022: 421-426. |
| Yang Gan, Han Wan-shui, Zhang Shu-ying. Research on traffic load reconstruction method based on multi-source information fusion[C]∥Proceedings of 2022 World Transport Convention, Wuhan, China, 2022: 421-426. | |
| 21 | 韩万水, 陈艾荣. 随机车流下的风-汽车-桥梁系统空间耦合振动研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008(9):97-102. |
| Han Wan-shui, Chen Ai-rong. Three-dimensional coupling vibration of wind-vehicle-bridge systems under random traffic flow[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2008(9):97-102. | |
| 22 | 韩万水, 马麟, 汪炳, 等. 随机车流-桥梁系统耦合振动精细化分析与动态可视化[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(4):78-87. |
| Han Wan-shui, Ma Lin, Wang Bing, et al. Refinement analysis and dynamic visualization of traffic-bridge coupling vibration system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2013,26(4):78-87. | |
| 23 | 邓露, 何维, 俞扬, 等. 公路车-桥耦合振动的理论和应用研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(7):38-54. |
| Deng Lu, He Wei, Yu Yang, et al. Research progress in theory and applications of highway vehicle-bridge coupling vibration[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018,31(7):38-54. | |
| 24 | . Mechanical vibration-road surface profiles-reporting of measured data [S]. |
| [1] | Guo-jin TAN,Ji OU,Yong-ming AI,Run-chao YANG. Bridge crack image segmentation method based on improved DeepLabv3+ model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 173-179. |
| [2] | Ran AN,You-zhi WANG. Shear properties of shear stud connectors under combined tension and shear loading [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2554-2562. |
| [3] | Xin-dai ZUO,Jin-quan ZHANG,Shang-chuan ZHAO. Fatigue stiffness degradation and life prediction method of in⁃service concrete T⁃beams [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2563-2572. |
| [4] | Zheng-wei GU,Pan ZHANG,Dong-ye LYU,Chun-li WU,Zhong YANG,Guo-jin TAN,Xiao-ming HUANG. Earthquake⁃induced residual displacement analysis of simply supported beam bridge based on numerical simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1711-1718. |
| [5] | Chun-li WU,Shi-ming HUANG,Kui LI,Zheng-wei GU,Xiao-ming HUANG,Bing-tao ZHANG,Run-chao YANG. Analysis of pier action effect under flood based on numerical simulation and statistical analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [6] | Guo-jin TAN,Qing-wen KONG,Xin HE,Pan ZHANG,Run-chao YANG,Yang-jun CHAO,Zhong YANG. Bridge scour depth identification based on dynamic characteristics and improved particle swarm optimization algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [7] | Hui JIANG,Xin LI,Xiao-yu BAI. Review on development of bridge seismic structural systems: from ductility to resilience [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [8] | Feng WANG,Shuang-rui LIU,Jia-ying WANG,Jia-ling SONG,Jun WANG,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Xiao-ming HUANG. Size and shape effects of wind drag coefficients for porous structures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1677-1685. |
| [9] | Jun WANG,Jia-wu LI,Feng WANG,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Xiao-ming HUANG. Wind speed distribution in simplified U⁃shaped valley and its effect on buffeting response of long⁃span suspension bridge [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. |
| [10] | Hua WANG,Long-lin WANG,Zi-mo ZHANG,Xin HE. Safety early warning technology of continuous rigid frame bridges based on crack width variation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1650-1657. |
| [11] | Yu FENG,Jian-ming HAO,Feng WANF,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Xiao-ming HUANG. Analysis of transient wind⁃induced response of long⁃span bridge under nonstationary wind field [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1638-1649. |
| [12] | Ye YUAN. Natural frequency analysis of beam bridge structure under temperature and vehicle action [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1702-1710. |
| [13] | Zi-yu LIU,Shi-tong CHEN,Mo-mo ZHI,Xiao-ming HUANG,Zhe-xin CHEN. Ultimate bearing capacity of temporary⁃permanent conversion rush⁃repair steel pier for emergency use [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1601-1611. |
| [14] | Yue ZHANG,Chuan-sen LIU,Fei SONG. Influence of abutment back wall on continuous girder bridge's seismic fragility [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [15] | Shu-wei LAN,Dong-hua ZHOU,Xu CHEN,Nan-ming MO. Practical calculation method for the critical bearing capacity of double column bridge with high piers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
|
||