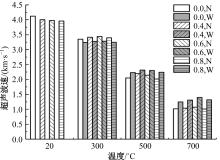
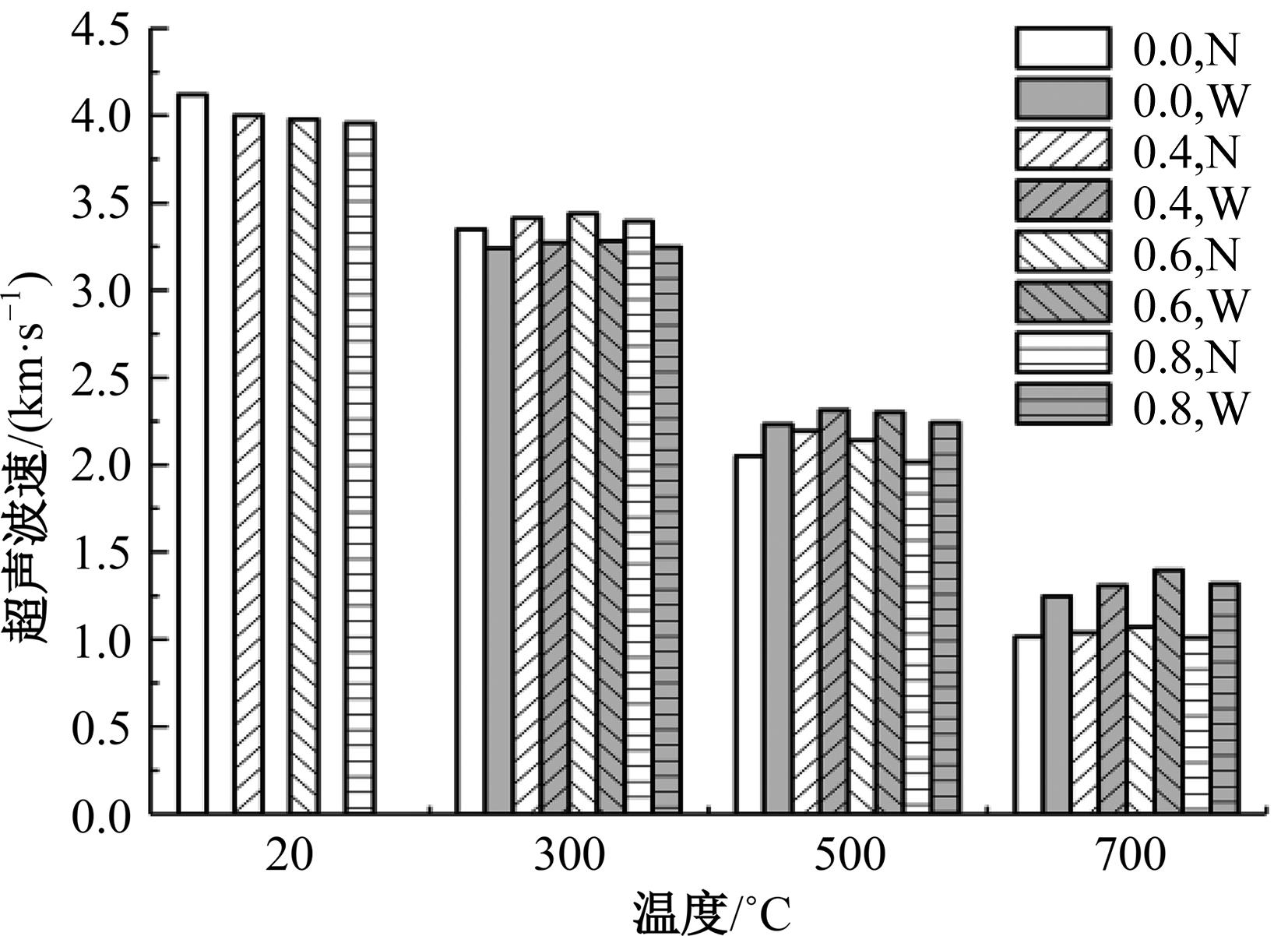
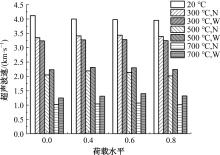
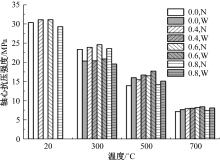
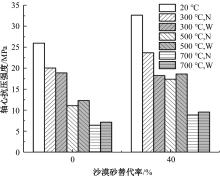
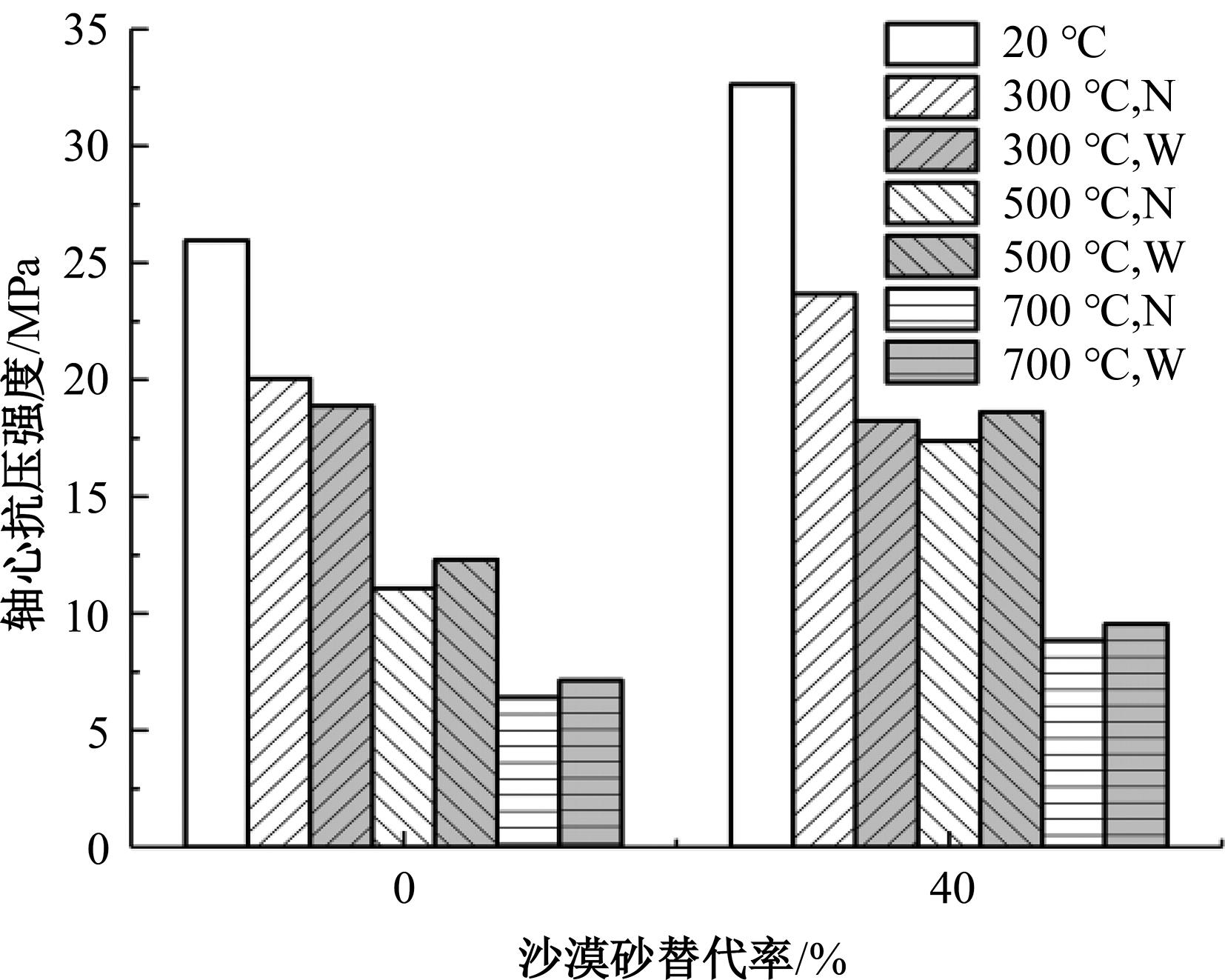
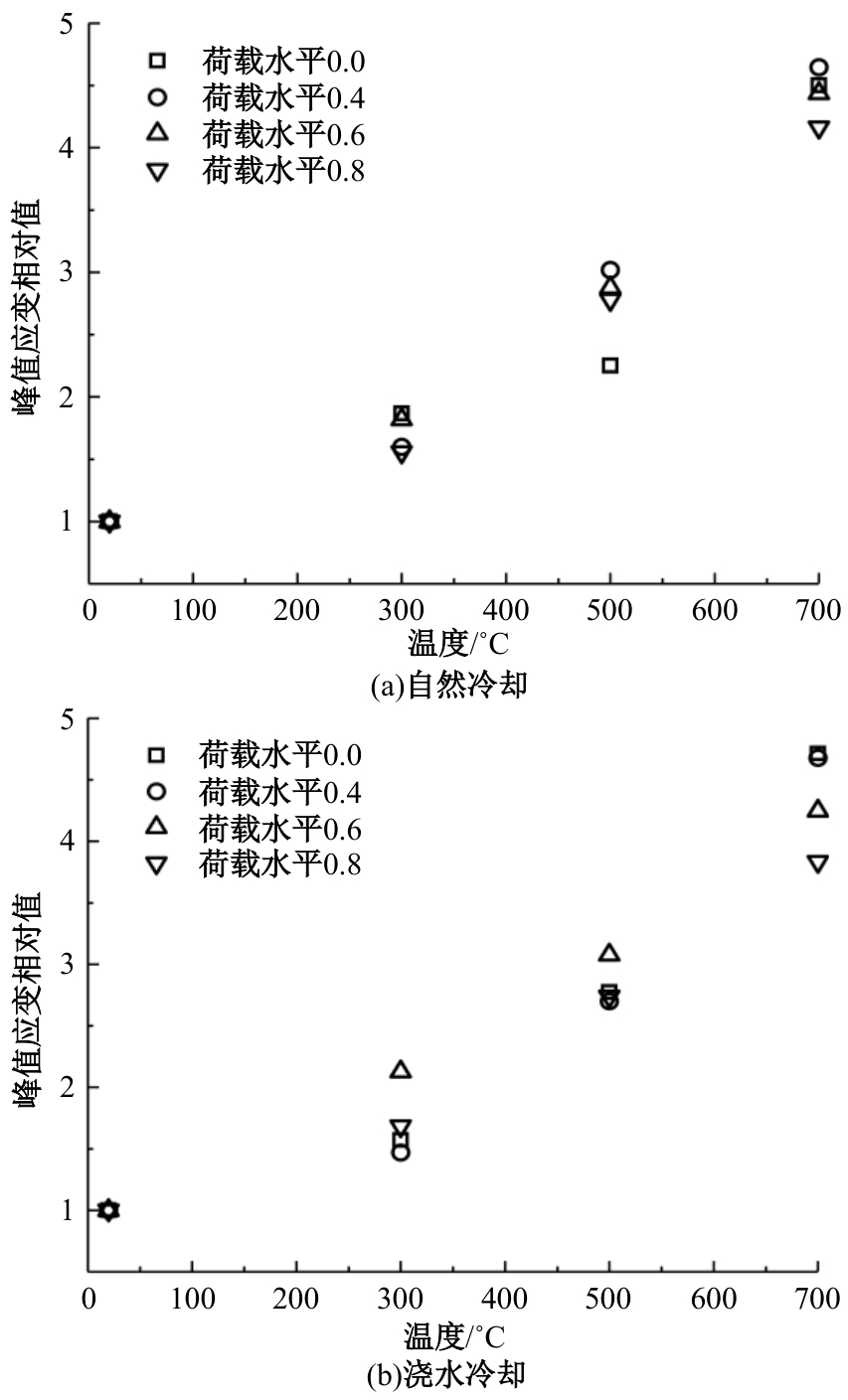
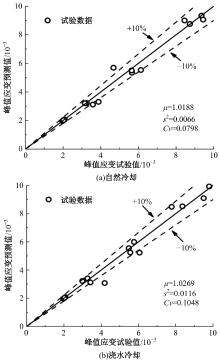
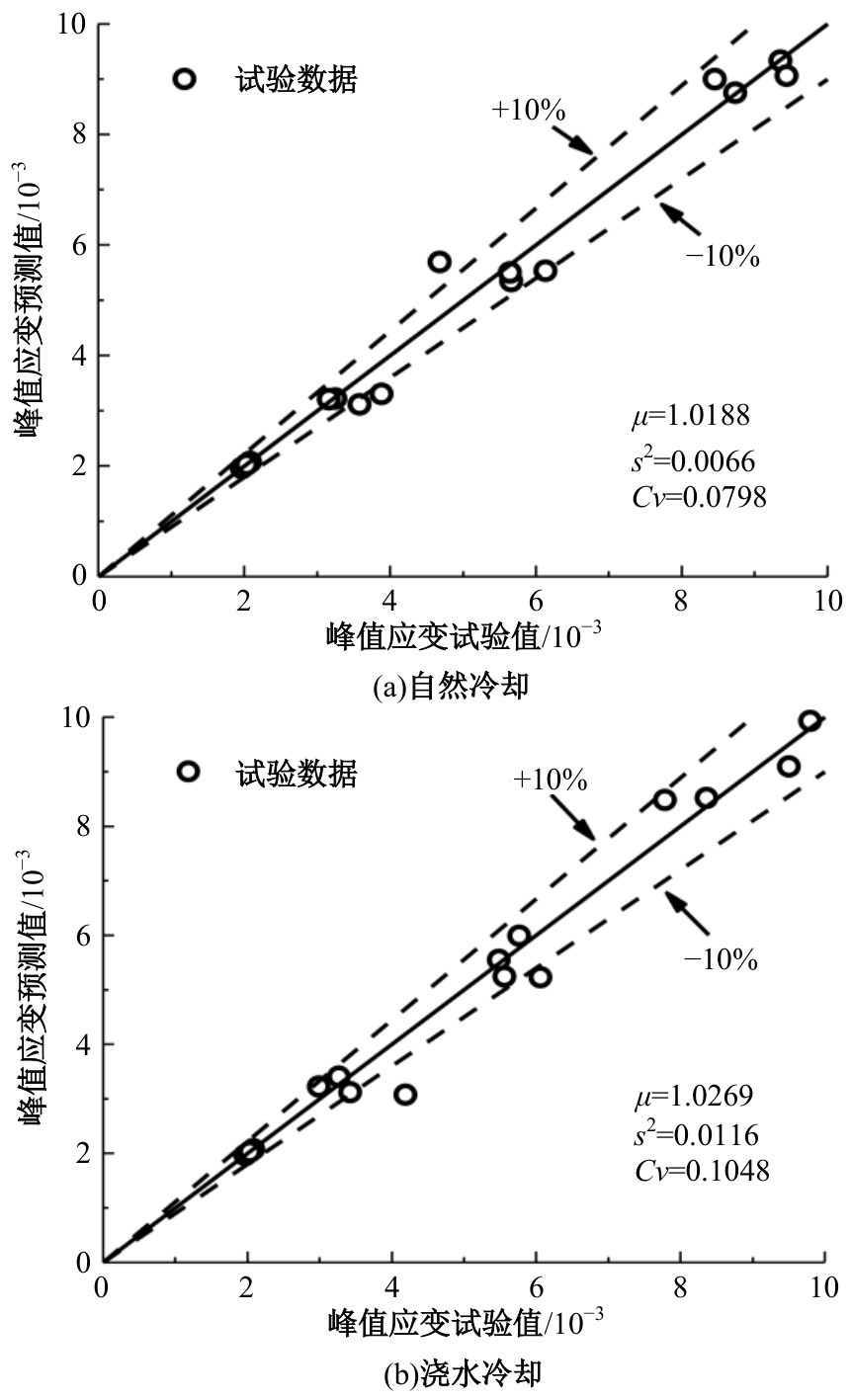
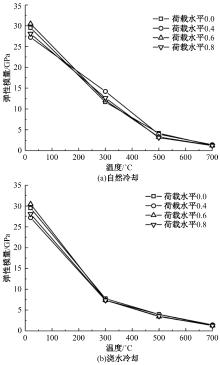
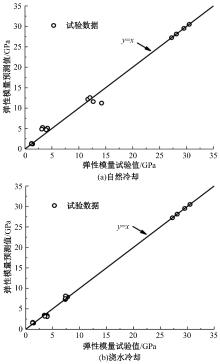
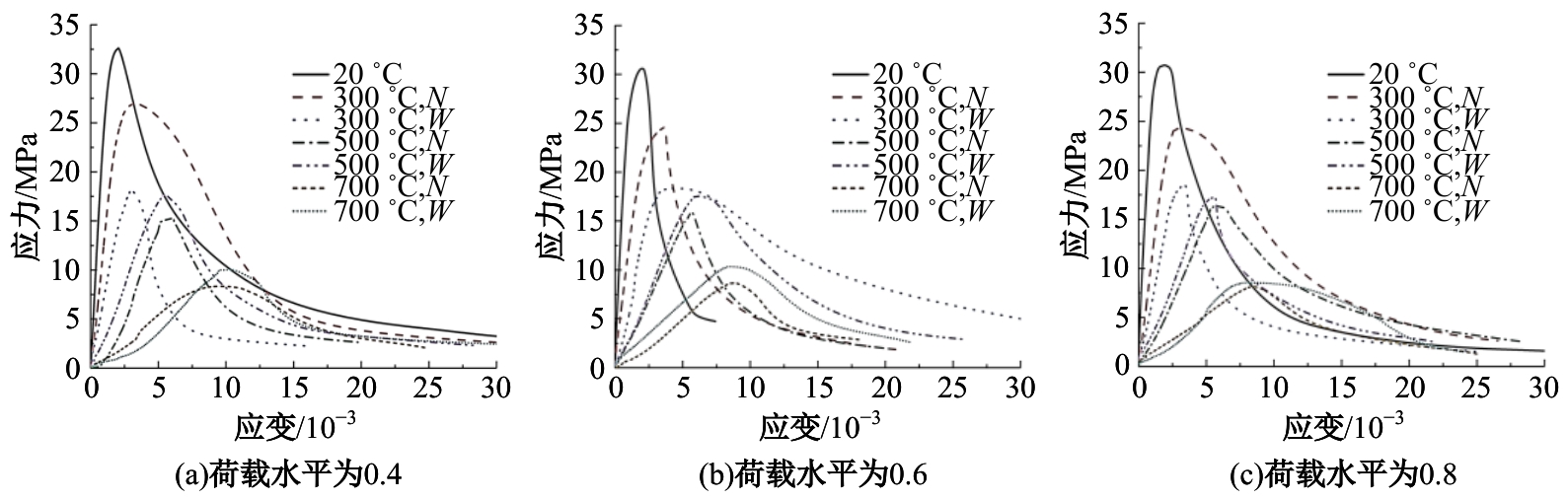
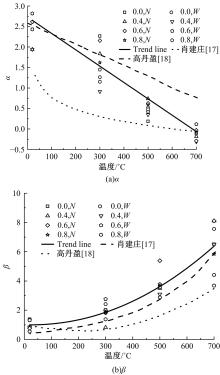
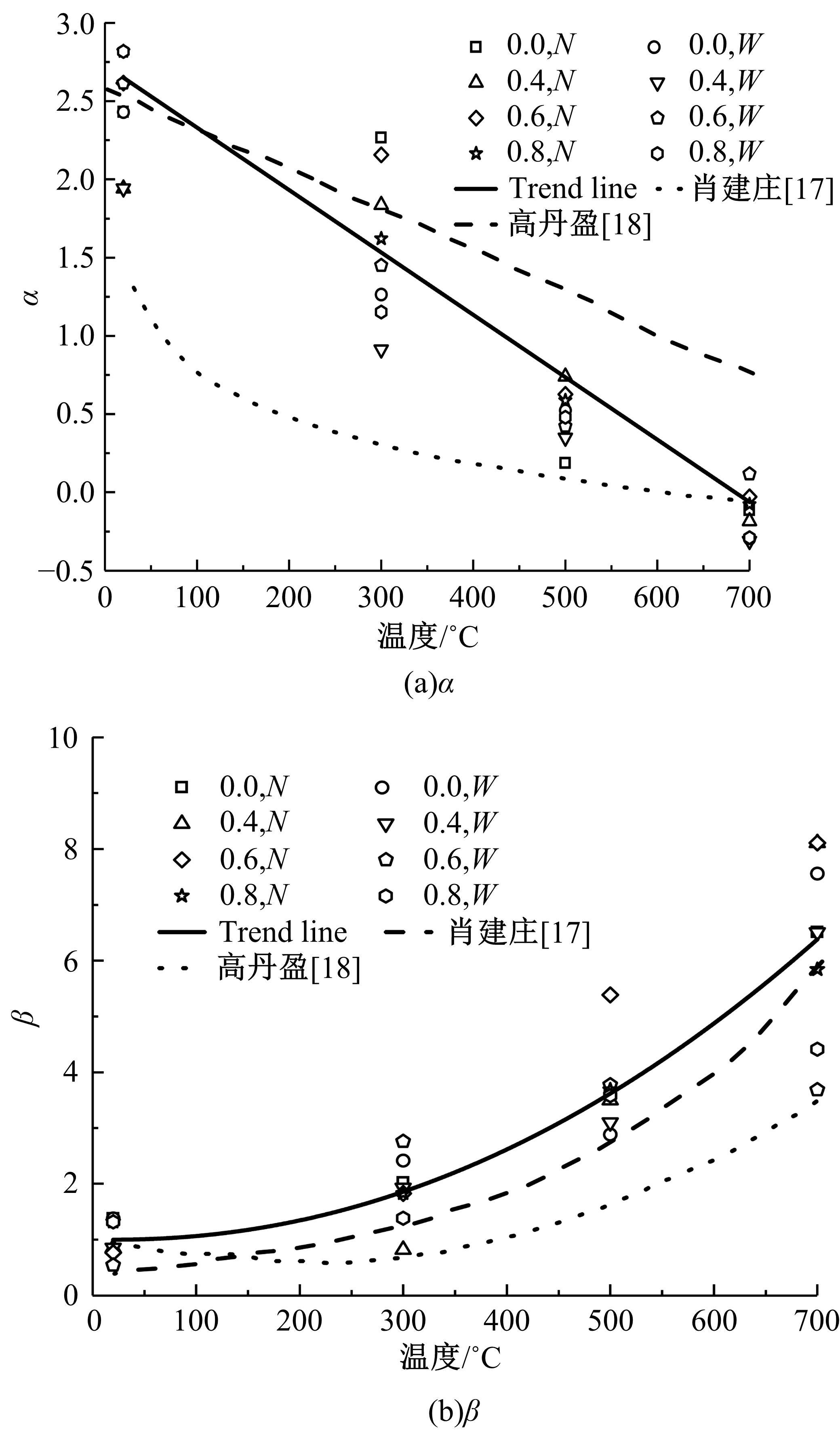
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2609-2619.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221408
Influence of loading and high temperature on uniaxial compressive properties of desert sand concrete
Hai-feng LIU( ),Ren-guang TAO,Jia-ling CHE,Wei-wu YANG,Li-chen ZHU
),Ren-guang TAO,Jia-ling CHE,Wei-wu YANG,Li-chen ZHU
- School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering,Ningxia University,Yinchuan 750021,China
CLC Number:
- TU528
| 1 | Liu H F, Ma J R, Wang Y Y, et al. Influence of desert sand on the mechanical properties of concrete subjected to impact loading[J]. Acta mechanica Solida Sinica, 2017, 30:583-595. |
| 2 | Luo F J, He L, Pan Z, et al. Effect of very fine particles on workability and strength of concrete made with dune sand[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 47: 131-137. |
| 3 | Bosco E, Claessens R J M A, Suiker A S J. Multi-scale prediction of chemo-mechanical properties of concrete materials through asymptotic homogenization[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 128:No.105929. |
| 4 | Wei D, Shen X D, Xue H J, et al. Research on the freeze-thaw cyclic test and damage model of aeolian sand lightweight aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 123: 792-799. |
| 5 | Liu H F, Ma Y C, Ma J R, et al. Frost resistance of desert sand concrete[J].Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021,2021(Pt.9): No.6620058. |
| 6 | 杜红秀,樊亚男.基于X-CT C60高性能混凝土高温细观结构损伤研究[J].建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(1): 210- 215. |
| Du Hong-xiu, Fan Ya-nan. Study on meso-structure damage of C60 high performance concrete at high temperature based on X-CT[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2020,23 (1) : 210-215. | |
| 7 | Wang L, Zhao Y R, Xing Y M. Investigating high temperature deformation evolution of concrete under sustained loading using DIC technology and a temperature mechanical coupled damage constitutive model[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 324: No.126638. |
| 8 | Fan K J, Li J B, Yu M, et al. Compressive stress-strain relationship for stressed concrete at high temperature[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2022, 130: No.103576. |
| 9 | 车佳玲,王俊,刘海峰,等.沙漠砂制备高韧性水泥基复合材料在不同环境下的自愈合性能[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(8): 2277-2286. |
| Che Jia-ling, Wang Jun, Liu Hai-feng, et al. Self- -healing prop-erties with different environments of ECC prepared with desert sand[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8):2277-2286. | |
| 10 | Zhang Q, Liu Q, Liu H F. Effect of desert sand on the uniaxial compressive properties of mortar after elevated temper-ature[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2021, 121: No.102962 |
| 11 | Shen Y J, Peng C, Han J S, et al. High temperature resistance of desert sand concrete: strength change and intrinsic mechanism[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 327: No.126948 |
| 12 | Kotsovos M, Michael D, Newman John B. Generalized stress-strain relations for concrete[J]. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, 1978, 12: 431-437. |
| 13 | 李卫, 过镇海. 高温下砼的强度和变形性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 1993, 14(1): 8-16. |
| Li Wei, Guo Zhen-hai. Experimental study on strength and deformation properties of concrete under high temperature[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 1993, 14(1): 8-16. | |
| 14 | 陈小龙. 高温后沙漠砂混凝土抗压强度试验研究及火灾评价[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学土木与水利工程学院, 2021. |
| Chen Xiao-long. Experimental study on compressive strength of desert sand concrete after high temperature and fire evalu-ation[D]. Yinchuan: School of Civil and Hydraulic Enginee-ring, Ningxia University, 2021. | |
| 15 | 刘宁. 沙漠砂混凝土高温后力学性能研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学土木与水利工程学院, 2018. |
| Liu Ning. Study on the mechanical behavior of desert sand concrete after high temperature[D].Yinchuan: School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Ningxia University, 2018. | |
| 16 | 过镇海. 混凝土的强度与本构关系[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2004. |
| 17 | 肖建庄, 王平, 谢猛, 等.矿渣高性能混凝土高温后受压本构关系试验[J].同济大学学报: 自然科学版,2003,31(2): 186-190. |
| Xiao Jian-zhuang, Wang Ping, Xie Meng, et al. Experiment on compressive constitutive relation of high performance slag concrete after high temperature[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2003, 31 (2): 186-190. | |
| 18 | 高丹盈,李晗.高温后纤维纳米混凝土单轴受压应力-应变关系[J].土木工程学报, 2015, 48(10): 10-20. |
| Gao Dan-ying, Li Han. Uniaxial compressive stress-strain relationship of fiber reinforced nano-concrete after high temperature [J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 2015, 48 (10) : 10-20. | |
| 19 | 周星宇, 周济, 陈宗平.高温消防喷水冷却后混凝土应力-应变本构方程及剩余强度评估[J]. 工业建筑, 2022, 52(1): 194-199. |
| Zhou Xing-yu, Zhou Ji, Chen Zong-ping. Stress-strain constitutive equation and residual strength evaluation of concrete after high temperature fire sprinkler cooling[J]. Industrial Construction, 2022, 52 (1): 194-199. |
| [1] | Fang-cheng LIU,Jiang WANG,Meng-tao WU,Guo-bin BU,Jie HE. Stress⁃strain characteristics of geogrid reinforced rubber sand mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2542-2553. |
| [2] | Xin-yu LI,Xian-zhang LING,Na QU. Statistical damage model of frozen expansive soil considering temperature effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2339-2349. |
| [3] | Deng-feng WANG,Hong-li CHEN,Jing-xin NA,Xin CHEN. Failure comparison of single and double lap joints after high temperature aging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 346-354. |
| [4] | Guo⁃feng QIN,Jing⁃xin NA,Wen⁃long MU,Wei TAN,Jian⁃ze LUAN,Hao SHEN. Degradation failure of adhesively bonded CFRP/aluminum alloy subjected to high temperature environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1063-1071. |
| [5] | CHENG Yong-chun, BI Hai-peng, MA Gui-rong, GONG Ya-feng, TIAN Zhen-hong, LYU Ze-hua, XU Zhi-shu. Pavement performance of nano materials-basalt fiber compound modified asphalt binder [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 460-465. |
| [6] | DUAN Xing-wang,LIU Jian-sheng. Plasticity at elevated temperature and fracture character of 316LN steel [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 494-500. |
| [7] | YANG Ai-wu,ZHOU Jin,KONG Ling-wei. Experiment on mechanical properties of stabilized soft dredger fill [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 661-667. |
| [8] | ZANG Chuan-yi,GUO Wei,HU Qiang,HUANG Guo-feng,CHEN Xiao-zhou,JIA Xiao-peng. Morphology changes of synthetic and metastable regrown graphites [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(01): 87-0091. |
|
||