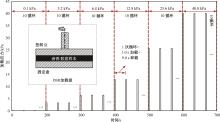
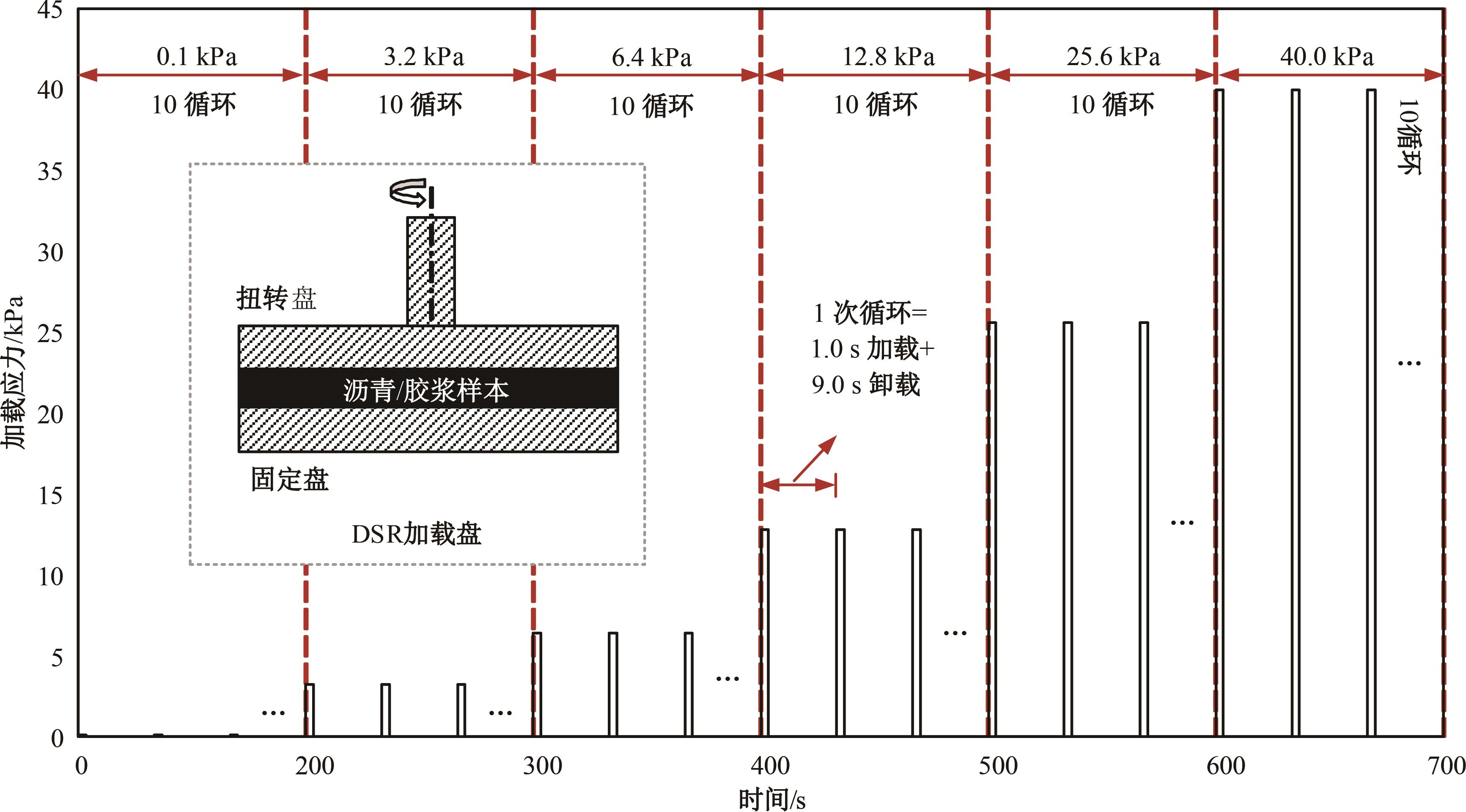
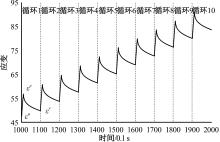
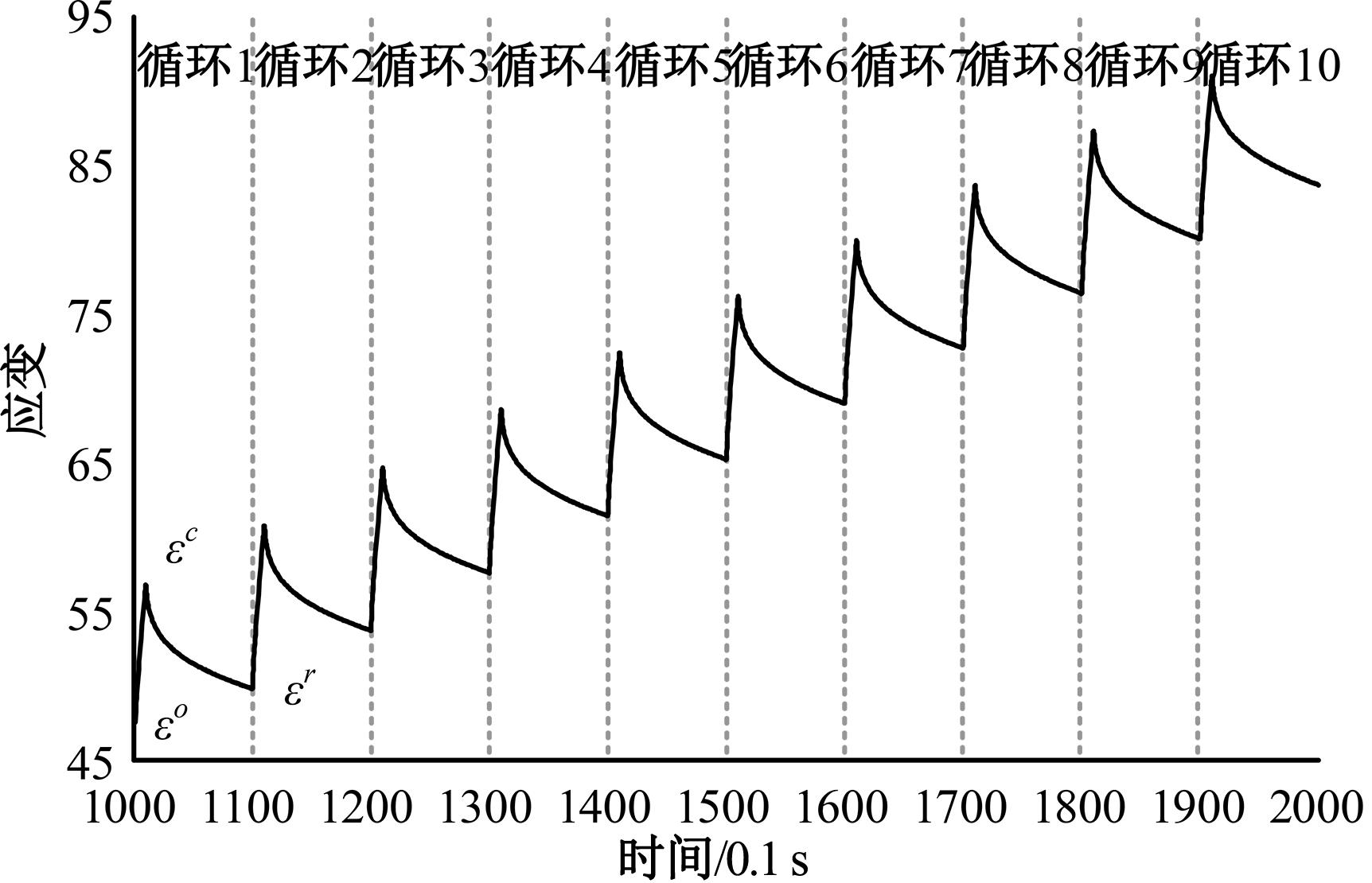
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3244-3254.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230073
Evaluation of high-temperature rheological properties of asphalt mastic and its filler stiffening effect
Song LI1,2( ),Xing-xing SHI1,3,Chun-di SI1,2,Ji-wang JIANG4,Bin-shuo BAO5
),Xing-xing SHI1,3,Chun-di SI1,2,Ji-wang JIANG4,Bin-shuo BAO5
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Behavior and System Safety of Traffic Engineering Structures,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
3.School of Civil Engineering,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
4.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211102,China
5.School of Management,Shijiazhuang Tiedao University,Shijiazhuang 050043,China
CLC Number:
- U416
| 1 | You T, Kim Y R, Rami K Z, et al. Multiscale modeling of asphaltic pavements: comparison with field performance and parametric analysis of design variables[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 2018, 144(2): No.04018012. |
| 2 | 董伟智, 张爽, 朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| Dong Wei-zhi, Zhang Shuang, Zhu Fu. Evaluation of pavement performance of asphalt mixture based on extension analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. | |
| 3 | Guo M, Bhasin A, Tan Y. Effect of mineral fillers adsorption on rheological and chemical properties of asphalt binder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 141: 152-159. |
| 4 | Underwood B S, Kim Y R. Nonlinear viscoelastic analysis of asphalt cement and asphalt mastics[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2014, 16(6): 510-529. |
| 5 | 李震南, 申爱琴, 郭寅川, 等. 玄武岩纤维沥青胶浆及混合料的低温性能关联性[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(1): 146-152. |
| Li Zhen-nan, Shen Ai-qin, Guo Yin-chuan, et al. Low temperature performance correlation of basalt fiber asphalt mortar and mixture[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(1): 146-152. | |
| 6 | Diab A, You Z. Linear and nonlinear rheological properties of bituminous mastics under large amplitude oscillatory shear testing[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(3): No.04017303. |
| 7 | 李松. 沥青混合料高温蠕变性能的多尺度研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2020. |
| Li Song. Multi-scale study on creep property of asphalt mixture at high temperature[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation,Southeast University, 2020. | |
| 8 | 詹小丽, 张肖宁, 王端宜, 等. 基于DMA方法的沥青胶浆微观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(4): 916-920. |
| Zhan Xiao-li, Zhang Xiao-ning, Wang Duan-yi, et al. Microstructure of asphalt mastic using dynamic mechanical analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(4): 916-920. | |
| 9 | Cheng Y, Tao J, Jiao Y, et al. Influence of the properties of filler on high and medium temperature performances of asphalt mastic[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 118: 268-275. |
| 10 | Zhang J, Liu G, Hu Z, et al. Effects of temperature and loading frequency on asphalt and filler interaction ability[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 124: 1028-1037. |
| 11 | 付军, 熊定邦, 李忠杰, 等. 沥青混合料界面区微米划痕试验与参数分析[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(1): 78-84. |
| Fu Jun, Xiong Ding-bang, Li Zhong-jie, et al. Micro- scratch test and parameter analysis of asphalt mixture interfacial transition zone[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(1): 78-84. | |
| 12 | 熊锐, 乔宁, 褚辞, 等. 掺盐沥青胶浆低温流变及粘附特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 183-190. |
| Xiong Rui, Qiao Ning, Chu Ci, et al. Investigation on low-temperature rheology and adhesion properties of salt-doped asphalt mortar[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 183-190. | |
| 13 | Underwood B S, Kim Y R. Microstructural investigation of asphalt concrete for performing multiscale experimental studies[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2013, 14(5): 498-516. |
| 14 | Wang H, Liu X, Apostolidis P, et al. Investigating the high-temperature and low-temperature performance of warm crumb rubber–modified bituminous binders using rheological tests[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 2021, 147(4): No.04021067. |
| 15 | Vignali V, Mazzotta F, Sangiorgi C, et al. Rheological and 3D DEM characterization of potential rutting of cold bituminous mastics[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 73: 339-349. |
| 16 | Li Q, Li G, Ma X, et al. Linear viscoelastic properties of warm-mix recycled asphalt binder, mastic, and fine aggregate matrix under different aging levels[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 192: 99-109. |
| 17 | 王志臣, 孙雅珍, 桑海军, 等. 沥青与矿粉的交互作用评价及影响机理分析[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 39(2): 339-347. |
| Wang Zhi-chen, Sun Ya-zhen, Sang Hai-jun, et al. Evaluation of the interaction between asphalt and mineral powder and analysis of the influence mechanism[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Architecture (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 39(2): 339-347. | |
| 18 | Domingos M D I, Faxina A L. Susceptibility of asphalt binders to rutting: literature review[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2016, 28(2): No.04015134. |
| 19 | Do N D, Liao M C, Mamuye Y, et al. Characteristics of alkali-activated slag filler and its effects on rheology of asphalt mastic[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2023, 35(4): No.04023003. |
| 20 | Li S, Ni F, Dong Q, et al. Effect of filler in asphalt mastic on rheological behaviour and susceptibility to rutting[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2021, 22(1): 87-96. |
| 21 | Tan Y, Li Z, Zhang X, et al. Research on high- and low-temperature properties of asphalt-mineral filler mastic[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2010, 22(8): 811-819. |
| 22 | Tabatabaee N, Tabatabaee H A. Multiple stress creep and recovery and time sweep fatigue tests: crumb rubber modified binder and mixture performance[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2010, 2180(1): 67-74. |
| 23 | 郭咏梅, 许丽, 吴亮, 等. 基于MSCR试验的改性沥青高温性能评价[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(1): 154-158. |
| Guo Yong-mei, Xu Li, Wu Liang, et al. High temperature performance evaluation of modified asphalt based on multipe stress creep recover test[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(1): 154-158. | |
| 24 | 罗蓉, 许苑, 刘涵奇, 等. DCLR改性沥青的流变力学性质[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(6): 165-171. |
| Luo Rong, Xu Yuan, Liu Han-qi, et al. Rheological mechanical properties of DCLR-modified asphalt binders[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(6): 165-171. | |
| 25 | Angelo J A. The relationship of the MSCR test to rutting[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2011, 10(s1): 61-80. |
| 26 | Domingos M, Faxina A L. Literature review of the multiple stress creep and recovery, performance-related test[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 2021, 147(1): No.03121001. |
| 27 | Liao M C, Airey G, Chen J S. Mechanical properties of filler-asphalt mastics[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2013, 6(5): 576-581. |
| 28 | 郑传峰, 冯玉鹏, 郭学东, 等. 粉胶比对沥青胶浆低温黏结强度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(2): 426-431. |
| Zheng Chuan-feng, Feng Yu-peng, Guo Xue-dong, et al. Effect of filler-to-bitumen ratio on low-temperature cohesive strength of asphalt mortar[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(2): 426-431. | |
| 29 | 张亚刚, 林梅, 薛瑛, 等. 基于灰熵关联的沥青胶浆高低温性能研究[J]. 公路, 2023, 68(1): 345-348. |
| Zhang Ya-gang, Lin Mei, Xue Ying, et al. Research on high and low temperature performance of asphalt mastic based on ash-entropy correlation[J]. Highways, 2023, 68(1): 345-348. | |
| 30 | Chen M, Javilla B, Hong W, et al. Rheological and interaction analysis of asphalt binder, mastic and mortar[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(1): 128-150. |
| 31 | Cardone F, Frigio F, Ferrotti G, et al. Influence of mineral fillers on the rheological response of polymer-modified bitumens and mastics[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2015, 2(6): 373-381. |
| 32 | 王志臣, 郭乃胜, 赵颖华, 等. 基于细观力学的沥青胶浆动态剪切模量预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(2): 459-467. |
| Wang Zhi-chen, Guo Nai-sheng, Zhao Ying-hua, et al. Dynamic shear modulus prediction of asphalt mastic based on micromechanics[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(2): 459-467. | |
| 33 | Anderson D, Bahia H, Dongre R. Rheological Properties of Mineral Filler-asphalt Mastics and its Importance to Pavement Performance[M]. West Conhawken: ASTM International, 1992. |
| 34 | Qiu H, Tan X, Shi S, et al. Influence of filler-bitumen ratio on performance of modified asphalt mortar by additive[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2013, 21(1): 40-46. |
| 35 | Underwood B S, Kim Y R. Experimental investigation into the multiscale behaviour of asphalt concrete[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2011, 12(4): 357-370. |
| 36 | Wang H, Alqadi I, Faheem A, et al. Effect of mineral filler characteristics on asphalt mastic and mixture rutting potential[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2011, 2: 33-39. |
| 37 | Hajikarimi P, Fakhari T F, Moghadas N F, et al. Mechanical behavior of polymer-modified bituminous mastics: experimental approach[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 31(1): No.04018337. |
| 38 | 交通部公路科学研究院. 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2011. |
| 39 | Zeng M, Wu C. Effects of type and content of mineral filler on viscosity of asphalt mastic and mixing and compaction temperatures of asphalt mixture[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2008, 2051(1): 31-40. |
| 40 | 刘安刚, 周庆福, 胡义成, 等. 基于MSCR与测力延度试验的阻燃改性沥青高低温性能评价[J]. 武汉理工大学学报: 交通科学与工程版, 2022, 46(4): 713-717. |
| Liu An-gang, Zhou Qing-fu, Hu Yi-cheng, et al. Evaluation of high and low temperature performance of flame-retardant modified asphalt based on MSCR and force ductility test[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Transportation Science and Engineering Edition), 2022, 46(4): 713-717. |
| [1] | Ya-zhen SUN,Bo-xin XUE,Yan SUN,Zhi-chen WANG,Jia-wei PAN. Mesoscale simulation of cracking behavior of asphalt mixture considering heterogeneity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1708-1718. |
| [2] | WANG Zhi-chen, GUO Nai-sheng, ZHAO Ying-hua, CHEN Zhong-da. Dynamic shear modulus prediction of asphalt mastic based on micromechanics [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 459-467. |
|
||