Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 947-953.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230614
Previous Articles Next Articles
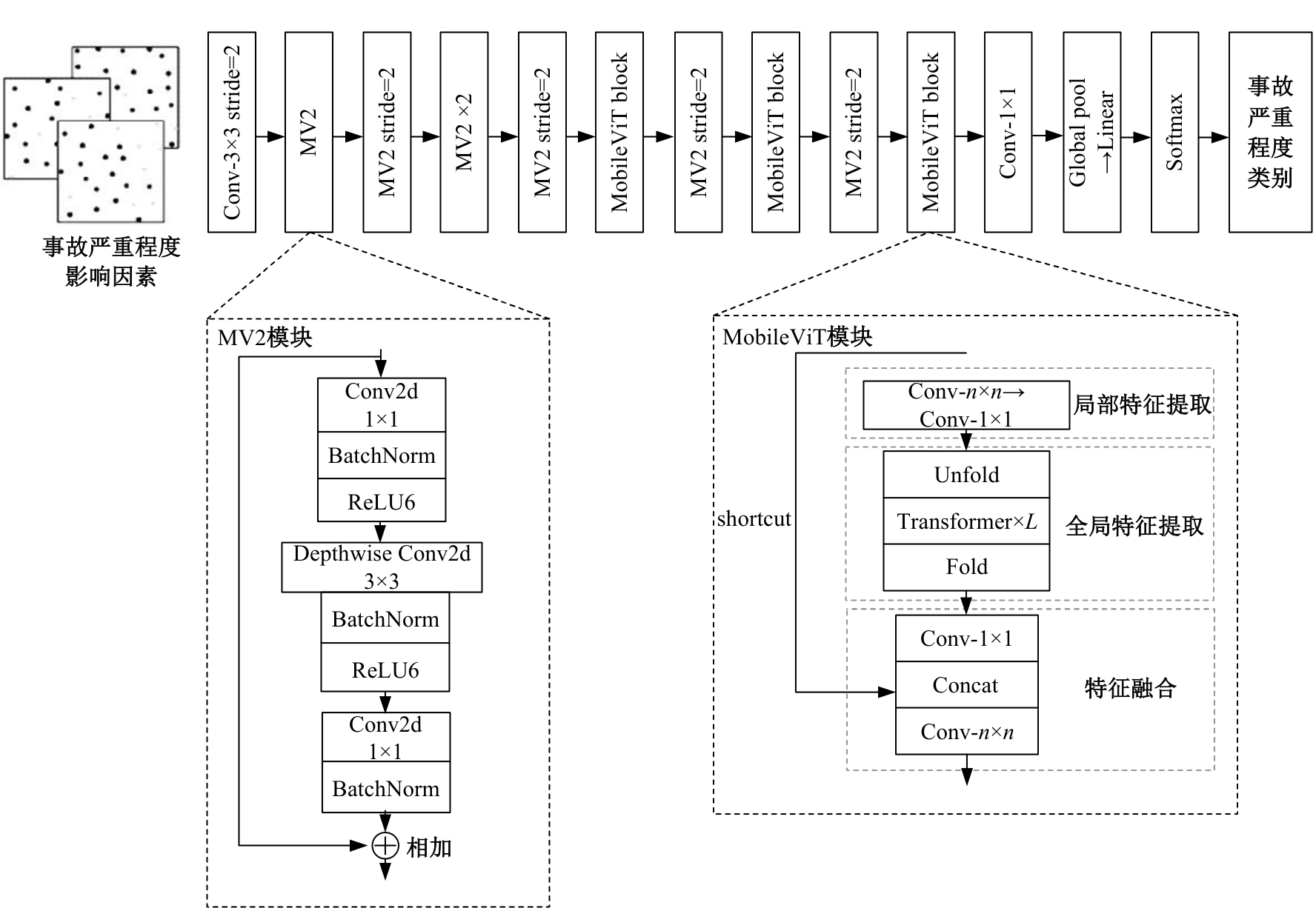
Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data
- College of Automobile and Traffic Engineering,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
CLC Number:
- U491.31
| 1 | 潘义勇, 吴静婷, 缪炫烨. 老年驾驶员事故严重程度影响因素时间不稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. |
| Pan Yi-yong, Wu Jing-ting, Miao Xuan-ye. Temporal instability analysis of factors affecting accident severity of elderly drivers[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. | |
| 2 | 戢晓峰, 乔新. 建成环境对行人交通事故严重程度的非线性影响[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2023, 23(1): 314-323. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Qiao Xin. Nonlinear influence of built environment on pedestrian traffic accident severity[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2023, 23(1): 314-323. | |
| 3 | Zheng M, Li T, Zhu R, et al. Traffic accident´s severity prediction: a deep-learning approach-based CNN network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39897-39910. |
| 4 | 吕璞, 柏强, 陈琳. 融合深度反残差与注意力机制的山区高速公路事故严重程度预测模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(6): 205-213. |
| Lv Pu, Bai Qiang, Chen Lin. A model for predicting the severity of accidents on mountainous expressways based on deep inverted residuals and attention mechanisms[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(6): 205-213. | |
| 5 | Wang S, Zhang J, Li J, et al. Traffic accident risk prediction via multi-view multi-task spatio-temporal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(12): 12323-12336. |
| 6 | Tian Z, Zhang S. Deep learning method for traffic accident prediction security[J]. Soft Computing, 2022, 26(11): 5363-5375. |
| 7 | Mehta S, Rastegari M. Mobilevit: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[J/OL].[2023-06-07]. |
| 8 | Rahim M A, Hassan H M. A deep learning based traffic crash severity prediction framework[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021,154: No. 106090. |
| 9 | Khan M N, Ahmed M M. A novel deep learning approach to predict crash severity in adverse weather on rural mountainous freeway[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2023, 15(8): 795-825. |
| 10 | 刘文文. 基于深度学习的摩托车事故严重程度预测研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2022. |
| Liu Wen-wen. Research on motorcycle accident severity prediction based on deep learning[D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic & Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University 2022. | |
| 11 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 12 | Sharma A, Vans E, Shigemizu D, et al. DeepInsight: a methodology to transform a non-image data to an image for convolution neural network architecture[J]. Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1): No. 11399. |
| 13 | 马永杰, 程时升, 马芸婷, 等. 卷积神经网络及其在智能交通系统中的应用综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(4): 48-71. |
| Ma Yong-jie, Cheng Shi-sheng, Ma Yun-ting, et al. Review of convolutional neural network and its application in intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 48-71. | |
| 14 | Yan H, Ma X, Pu Z. Learning dynamic and hierarchical traffic spatiotemporal features with transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(11): 22386-22399. |
| 15 | Li Y, Yang Z, Xing L, et al. Crash injury severity prediction considering data imbalance: a wasserstein generative adversarial network with gradient penalty approach[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 192: No.107271. |
| 16 | Niyogisubizo J, Liao L, Zou F, et al. Predicting traffic crash severity using hybrid of balanced bagging classification and light gradient boosting machine[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2023, 27(1): 79-101. |
| 17 | Cicek E, Akin M, Uysal F, et al. Comparison of traffic accident injury severity prediction models with explainable machine learning[J]. Transportation Letters, 2023, 15(9): 1043-1054. |
| 18 | Zhang Y, Li H, Ren G. Analyzing the injury severity in single-bicycle crashes: an application of the ordered forest with some practical guidance[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 189: No. 107126. |
| 19 | Mohammadpour S I, Khedmati M, Zada M J H. Classification of truck-involved crash severity: dealing with missing, imbalanced, and high dimensional safety data[J]. PLoS one, 2023, 18(3): No.e0281901. |
| 20 | Silagyi II D V, Liu D. Prediction of severity of aviation landing accidents using support vector machine models[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 187: No. 107043. |
| [1] | Xi-zhen ZHOU,He GONG,Dun-dun LI,Yan-jie JI,Jie YAN. Nonlinear model for impact of built environment on curb parking spaces occupancy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [2] | Ya-qin QIN,Zheng-fu QIAN,Ji-ming XIE. Vehicle cooperative obstacle avoidance strategy driven by CLAM model and trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [3] | Hong-tao LI,Lin-hong WANG,Jun-da LI. Influence of lighting and speed limit on visual search ability at highway intersections [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [4] | Wei-tiao WU,Kun ZENG,Wei ZHOU,Peng LI,Wen-zhou JIN. Deep learning method for bus passenger flow prediction based on multi-source data and surrogate-based optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [5] | Zhen-liang LIU,Cun-bao ZHAO,Yun-peng WU,Mi-na MA,Long-shuang MA. Life⁃cycle seismic resilience assessment of highway bridge networks using data⁃driven method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [6] | Hong-fei JIA,Ying-jun XU,Li-li YANG,Nan WANG. League member selection and benefit distribution of commercial vehicles multi⁃modal transportation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [7] | Chao SUN,Hao-wei YIN,Wen-yun TANG,Zhao-ming CHU. Sensor deployment strategy and expansion inference of mobile phone data for traffic demand estimation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [8] | Zhi-wei LIU,Zheng-yun SONG,Jian-rong LIU. Impact of shared autonomous vehicles on choice of subway station connection methods [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3424-3431. |
| [9] | Jin XU,Yan-peng WANG,Hai-yuan CHEN,Xiao-bo ZHANG,Cun-shu PAN. Longitudinal driving characteristics and operating speed prediction model of cars on hairpin curves of mountainous roads [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(12): 3432-3445. |
| [10] | Wen-jing WU,Kang-bei XIONG,Li-li YANG,Si-xu PU. Optimization of bus transfer preferential strategy in passenger corridor based on mental account theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(11): 3113-3121. |
| [11] | Xiu-feng CHEN,Yu-tong GUO,Yue-chen WU,Da-yi QU,Meng-yuan GAO. Multi-objective optimization of traffic signal timings based on dandelion algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(11): 3122-3129. |
| [12] | Lang SONG,Jian WANG,Bin-yu YANG,Yong ZHU. Signal timing optimization model for left-turn intersection using double-exit lanes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(10): 2826-2838. |
| [13] | Hui-qiu LU,Feng ZHAO,Bo XIE,Yan-tao TIAN. Driver's lane change intention recognition in snow and ice environment based on neural network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 273-284. |
| [14] | Wen-bo HUANG,Yan-yan CHEN,Shu-shan CHAI. Decision⁃making behavior of pedestrians in cold competition area under the intervention of mobile information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 132-140. |
| [15] | Xian-min SONG,Shu-tian YANG,Ming-xin LIU,Zhi-hui LI. Fluctuation characteristics and prediction method of bus travel time between stations [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
|
||