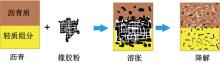
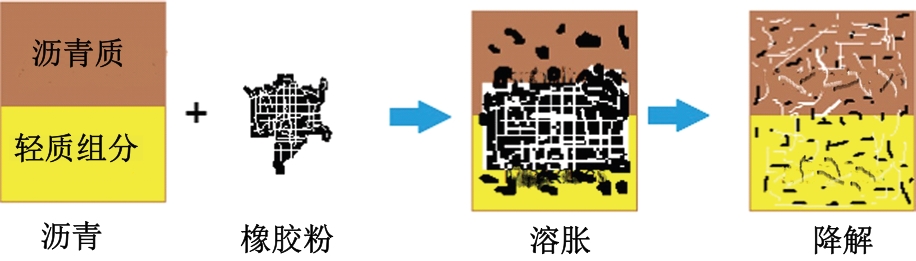
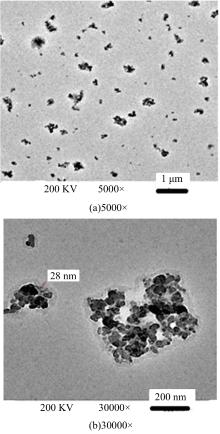
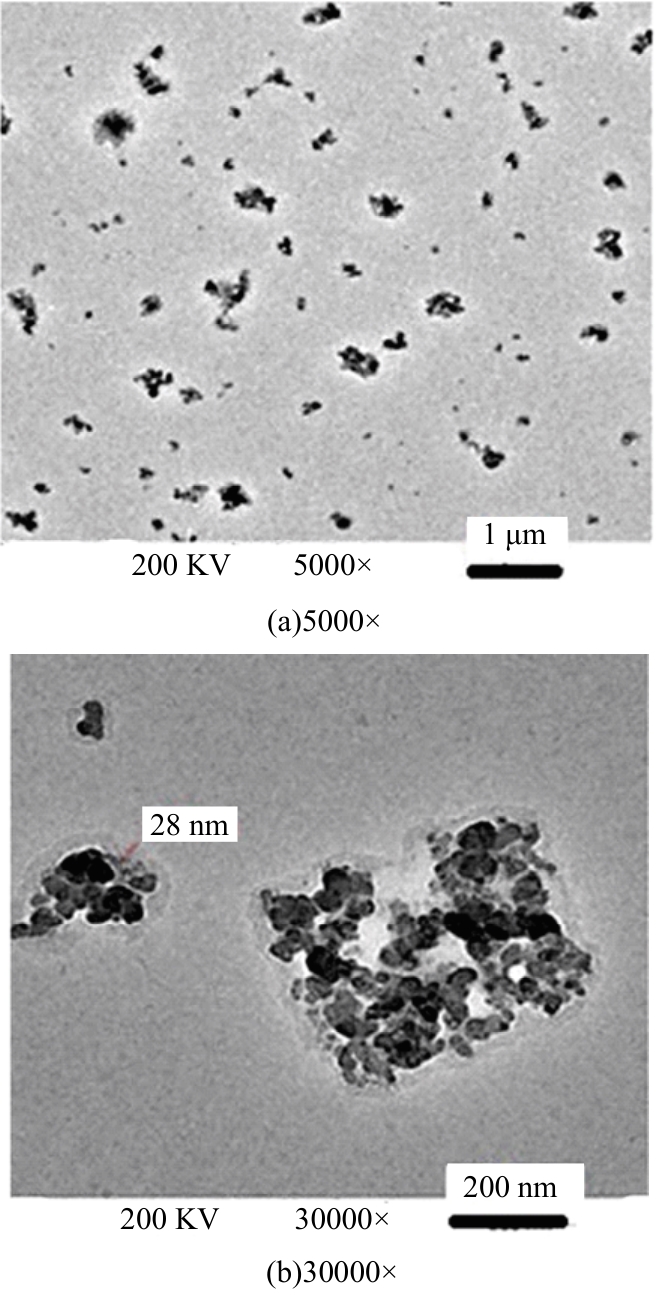
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (6): 1834-1853.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240796
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress on modification mechanism, preparation and performance of waste rubber powder modified asphalt
Wan-feng WEI1,2,3( ),Hong-gang ZHANG2,3,Yang-peng ZHANG2,3,Fan YANG4,Bo-ming TANG5,Ling-yun KONG5(
),Hong-gang ZHANG2,3,Yang-peng ZHANG2,3,Fan YANG4,Bo-ming TANG5,Ling-yun KONG5( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Guangxi Key Laboratory of Road Structure and Materials,Guangxi Academy of Transportation Sciences,Nanning 530007,China
3.Research and Development Center on Technologies,Materials and Equipment of High Grade Highway Construction and Maintenance,Ministry of Transport,Nanning 530007,China
4.Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
5.National and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Transportation Civil Engineering Materials,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
CLC Number:
- U414
| [1] | Presti D L. Recycled tyre rubber modified bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: a literature review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 863-881. |
| [2] | Chen S T, Chen S Q, Jin J H, et al. Analyzing moisture diffusion in the interface between rubber-modified asphalt and aggregate: a 3D study considering multiple influencing factors[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 425: No.136033. |
| [3] | Zhu J W, Li L H, Yin C E, et al. Study on viscosity reduction mechanism of warm-mixed rubber modified asphalt: a green sustainable perspective[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 21: No.e03494. |
| [4] | Wang S F, Cheng D X, Xiao F P. Recent developments in the application of chemical approaches to rubberized asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 131: 101-113. |
| [5] | 徐光霁, 范剑伟, 马涛, 等. 高掺量废胎胶粉改性沥青性能研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(16): 5-12. |
| Xu Guang-ji, Fan Jian-wei, Ma Tao, et al. Study on performances of asphalt modified by high content waste tire rubber powder[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(16): 5-12. | |
| [6] | 姚震, 张凌波, 梁鹏飞, 等. 多种湿法橡胶改性沥青的综合性能评价与改性机理研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(16): 97-103. |
| Yao Zhen, Zhang Ling-bo, Liang Peng-fei, et al. Comprehensive performance evaluation and modification mechanism of various wet rubber modified asphalt[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(16): 97-103. | |
| [7] | Zhou H, Holikatti S, Vacura P. Caltrans use of scrap tires in asphalt rubber products: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2014, 1(1): 39-48. |
| [8] | 朱月风, 姜鹏. 掺加国产TOR的橡胶沥青黏温特性及路用性能研究[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(12): 134-139. |
| Zhu Yue-feng, Jiang Peng. Viscosity-temperature characteristics and pavement performance rubber-modified asphalt added with domestic TOR[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(12): 134-139. | |
| [9] | Li H B, Hu Y H, Shi X, et al. Influence of rubber powder movement on properties of asphalt rubber from the mesoscopic view[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Materials Science Edition), 2023, 38(2): 312-324. |
| [10] | Zhou Y X, Xu G, Wang H Z, et al. Investigation of the rheological properties of devulcanized rubber-modified asphalt with different rubber devulcanization degrees and rubber contents[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2024,25(9):1950-1963. |
| [11] | Li D N, Leng Z, Zhang S W, et al. Blending efficiency of reclaimed asphalt rubber pavement mixture and its correlation with cracking resistance[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2022, 185: No. 106506. |
| [12] | Lv Y, Wu S P, Li N, et al. Performance and VOCs emission inhibition of environmentally friendly rubber modified asphalt with UiO-66 MOFs[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 385: No.135633. |
| [13] | Mohajerani A, Burnett L, Smith J V, et al. Recycling waste rubber tyres in construction materials and associated environmental considerations: a review[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 155: No.104679. |
| [14] | Wang Q Z, Wang N N, Tseng M L, et al. Waste tire recycling assessment: Road application potential and carbon emissions reduction analysis of crumb rubber modified asphalt in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 249: No.119411. |
| [15] | Liu L L, Cai G J, Zhang J, et al. Evaluation of engineering properties and environmental effect of recycled waste tire-sand/soil in geotechnical engineering: a compressive review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 126: No.109831. |
| [16] | 朱洪洲, 苏春力, 唐乃膨, 等. 胶粉改性沥青排放物采样及定量分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(10): 2922-2929. |
| Zhu Hong-zhou, Su Chun-li, Tang Nai-peng, et al. Sampling and quantitative analysis method of emissions from crumb rubber modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2922-2929. | |
| [17] | Cong P L, Xun P J, Xing M L, et al. Investigation of asphalt binder containing various crumb rubbers and asphalts[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 40: 632-641. |
| [18] | Yu B, Jiao L Y, Ni F J, et al. Evaluation of plastic–rubber asphalt: Engineering property and environmental concern[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 71: 416-424. |
| [19] | 郑睢宁, 何锐, 路天宇, 等. RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| Zheng Sui-ning, He Rui, Lu Tian-yu, et al. Preparation and evaluation of RET/rubber composite modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. | |
| [20] | 马涛, 陈葱琳, 张阳, 等. 胶粉应用于沥青改性技术的发展综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 1-16. |
| Ma Tao, Chen Cong-lin, Zhang Yang, et al. Development of using crumb rubber in asphalt modification: a review[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(10): 1-16. | |
| [21] | Bocci E, Prosperi E. Recyclability of reclaimed asphalt rubber pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 403: No.133040. |
| [22] | Baqersad M, Ali H. Rheological and chemical characteristics of asphalt binders recycled using different recycling agents[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 228: No.116738. |
| [23] | Qiu Y K, Gao Y, Zhang X, et al. Conventional properties, rheological properties, and storage stability of crumb rubber modified asphalt with WCO and ABS[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 392: No.131987. |
| [24] | Zhao X, Li F, Zhang X, et al. Rheological properties and viscosity reduction mechanism of aromatic/naphthenic oil pre-swelling crumb rubber modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 398: No.132545. |
| [25] | Yan Y, Huan H Y, Guo R X, et al. Effect of vulcanisation on the properties of natural rubber-modified asphalt[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024, 214: No.118588. |
| [26] | Gao Z W, Fu H, Chen Q, et al. Rheological properties and viscosity reduction mechanism of SBS warm-mix modified asphalt[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2020, 38(6): 556-564. |
| [27] | 邓国香. 胶粉/SBS复合改性沥青储存稳定性研究[D]. 武汉:武汉工程大学化工与制药学院, 2016. |
| Deng Guo-xiang. Research on storage stability of crumb rubber/SBS composite modified asphalt binder[D]. Wuhan: School of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Wuhan Institute of Technology, 2016. | |
| [28] | Nanjegowda V H, Biligiri K P. Recyclability of rubber in asphalt roadway systems: a review of applied research and advancement in technology[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 155: No.104655. |
| [29] | Mark J E. The science and Technology of Rubber[M]. Waltham, Massachusetts, USA: Academic Press, 2013. |
| [30] | 陈瑞璞. 橡胶改性沥青热氧老化机理与性能评价[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2023. |
| Chen Rui-pu. Crumb rubber modified asphalt binder thermal-oxygen aging mechanism and performance evaluation[D]. Chongqing: School of Transportation, Chongqing Tiaotong University, 2023. | |
| [31] | 于晓晓, 李彦伟, 蔡斌, 等. 胶粉改性沥青研究进展: 从分子到工程[J]. 合成橡胶工业, 2022, 45(1): 2-12. |
| Yu Xiao-xiao, Li Yan-wei, Cai Bin, et al. Advance in crumb rubber modified asphalt: From molecule to engineering[J]. China Synthetic Rubber Industry, 2022, 45(1): 2-12. | |
| [32] | Milad A, Ahmeda A, Taib A M, et al. A review of the feasibility of using crumb rubber derived from end-of-life tire as asphalt binder modifier[J]. Journal of Rubber Research, 2020, 23(3): 203-216. |
| [33] | Zhang L, Zhang C P, Zhang Z, et al. Characterization, properties and mixing mechanism of rubber asphalt colloid for sustainable infrastructure[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(20): No.4429. |
| [34] | Xiang Y, Xie Y, Long G, et al. Ultraviolet irradiation of crumb rubber on mechanical performance and mechanism of rubberised asphalt[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2019, 20(7): 1624-1637. |
| [35] | Liu S J, Zhou S B, Peng A H, et al. Analysis of the performance and mechanism of desulfurized rubber and low-density polyethylene compound-modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019, 136(45): No.48194. |
| [36] | 黄明, 汪翔, 黄卫东. 橡胶沥青混合料疲劳性能的自愈合影响因素分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2013, 26(4): 16-22. |
| Huang Ming, Wang Xiang, Huang Wei-dong. Analysis of influencing factors for self healing of fatigue performance of asphalt rubber mixture[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2013, 26(4): 16-22. | |
| [37] | Wang T, Xiao F P, Amirkhanian S, et al. A review on low temperature performances of rubberized asphalt materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 145: 483-505. |
| [38] | 唐乃膨, 薛晨阳, 刘少鹏, 等. 胶粉改性沥青老化机理及表征评价研究综述[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024,54(1):22-43. |
| Tang Nai-peng, Xue Chen-yang, Liu Shao-peng, et al. Review on aging mechanism, characterization and evaluation of crumb rubber modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1):22-43. | |
| [39] | 邱延峻, 丁海波. 基于热分析与低温光谱的沥青热可逆老化机理[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(6): 221-229. |
| Qiu Yan-jun, Ding Hai-bo. Mechanisms of thermoreversible aging of asphalt binders based on thermal analysis and low-temperature fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(6): 221-229. | |
| [40] | Wang H P, Liu X Y, Apostolidis P, et al. Numerical investigation of rubber swelling in bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 214: 506-515. |
| [41] | Li S, Wan C Y, Wu X Y, et al. Core-shell structured carbon nanoparticles derived from light pyrolysis of waste tires[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2016, 129: 192-198. |
| [42] | Yao H R, Zhou S, Wang S F. Structural evolution of recycled tire rubber in asphalt[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2016, 133(6): No.42954. |
| [43] | 叶奋, 杨思远, 吴晓羽, 等. 深度降解橡胶改性沥青的流变性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2016, 19(5): 945-949. |
| Ye Fen, Yang Si-yuan, Wu Xiao-yu, et al. Rheological property of highly degraded rubber modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2016, 19(5): 945-949. | |
| [44] | Li D N, Leng Z, Wang H P, et al. Structural and mechanical evolution of the multiphase asphalt rubber during aging based on micromechanical back-calculation and experimental methods[J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 215: No.110421. |
| [45] | Yu X X, Li D N, Leng Z, et al. Weathering characteristics of asphalt modified by hybrid of micro-nano tire rubber and SBS[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 389: No.131785. |
| [46] | Lv Q, Huang W D, Zheng M, et al. Understanding the particle effects and interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt regarding bonding properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 348: No.128716. |
| [47] | 张晓亮, 陈华鑫, 张奔, 等. 不同来源橡胶粉对橡胶沥青性能影响[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 38(5): 1-8. |
| Zhang Xiao-liang, Chen Hua-xin, Zhang Ben, et al. Performance of asphalt binders modified by different crumb rubbers[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 38(5): 1-8. | |
| [48] | Ma T, Wang H, He L, et al. Property characterization of asphalt binders and mixtures modified by different crumb rubbers[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(7): No.04017036. |
| [49] | 李丹阳, 刘志华, 李鑫, 等. 硫醇化合物/月桂酸对废胶粉精准脱硫的影响及机理[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2022, 38(10): 103-109. |
| Li Dan-yang, Liu Zhi-hua, Li Xin, et al. Role and mechanism of thiol compound A/laurie acid for accurate desulphurisation of waste rubber powder[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2022, 38(10): 103-109. | |
| [50] | 刘斌清, 胡松山, 谭华, 等. 沥青四组分与橡胶沥青性能指标的相关性分析[J]. 中外公路, 2015, 35(6): 321-326. |
| Liu Bin-qing, Hu Song-shan, Tan Hua, et al. Asphalt and rubber asphalt four components performance index of correlation analysis[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2015, 35(6): 321-326. | |
| [51] | 胡松山, 谭华, 覃润浦, 等. 基于流变学的橡胶粉与基质沥青配伍性试验[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(12): 3487-3499. |
| Hu Song-shan, Tan Hua, Qin Run-pu, et al. Compatibility test of rubber powder and matrix asphalt based on rheology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(12): 3487-3499. | |
| [52] | Pettinari M, Simone A. Effect of crumb rubber gradation on a rubberized cold recycled mixture for road pavements[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 85: 598-606. |
| [53] | Venudharan V, Biligiri K P. Effect of crumb rubber gradation on asphalt binder modification: rheological evaluation, optimization and selection[J]. Materials and Structures, 2017, 50: 1-14. |
| [54] | 徐安花, 王小雯, 熊锐, 等. 橡胶粉改性沥青制备及性能试验研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(4): 1326-1332. |
| Xu An-hua, Wang Xiao-wen, Xiong Rui, et al. Experimental investigation on preparation technology and performance of rubber powder modified asphalt[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 36(4): 1326-1332. | |
| [55] | Zhang H G, Zhang Y P, Chen J, et al. Effect of activation modes on the property characterization of crumb rubber powder from waste tires and performance analysis of activated rubber-modified asphalt binder[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(12): No.2490. |
| [56] | Zhang H G, Zhang Y P, Chen J, et al. Effect of desulfurization process variables on the properties of crumb rubber modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(7): No.1365. |
| [57] | 张洪刚, 谭华, 王彬, 等. 橡胶沥青的性能评价、改性机理与应用研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(): 299-303. |
| Zhang Hong-gang, Tan Hua, Wang Bin, et al. Performance evaluation, modification mechanism and application research progress of rubber asphalt[J].Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(Sup.2): 299-303. | |
| [58] | Yao H R, Zhou S, Wang S F. Structural evolution of recycled tire rubber in asphalt[J]. Journal Of Applied Polymer Science, 2016, 133(6): No.42954. |
| [59] | Ghavibazoo A, Abdelrahman M, Ragab M. Mechanism of crumb rubber modifier dissolution into asphalt matrix and its effect on final physical properties of crumb rubber-modified binder[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2013(2370): 92-101. |
| [60] | 栗培龙, 王霄, 孙胜飞, 等. 不同制备方法的橡胶沥青黏度特性对比分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(9): 3159-3167. |
| Li Pei-long, Wang Xiao, Sun Sheng-fei, et al. Comparative analysis of viscosity characteristic of rubber asphalt with different preparation methods[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2021, 40(9): 3159-3167. | |
| [61] | Ghavibazoo A, Abdelrahman M. Composition analysis of crumb rubber during interaction with asphalt and effect on properties of binder[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2013, 14(5): 517-530. |
| [62] | Lei Y, Wang H, Fini E H, et al. Evaluation of the effect of bio-oil on the high-temperature performance of rubber modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 191: 692-701. |
| [63] | Li Y M, Abdelmagid A A A, Qiu Y J, et al. Study on the aging mechanism and microstructure analysis of rice-husk-ash- and crumb-rubber-powder-modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(10): No.1969. |
| [64] | 谢艳玲. 轮胎橡胶的绿色再生及其路用特性研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学化学化工学院, 2020. |
| Xie Yan-ling. Study on the green reclamation of tire rubberand its application in road[D]. Shanghai: School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020. | |
| [65] | 侯德华. 微波活化胶粉及其改性沥青性能研究[D].西安: 长安大学材料学院, 2018. |
| Hou De-hua. Study on properties of microwave activated crumb rubber modified asphalt[D]. Xi'an: School of Materials Science, Chang'an University, 2018. | |
| [66] | Liu W H, Xu Y S, Wang H J. Enhanced storage stability and rheological properties of asphalt modified by activated waste rubber powder[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(10): No.2693. |
| [67] | Zhang R, Wang H X, Ji J, et al. Influences of different modification methods on surface activation of waste tire rubber powder applied in cement-based materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 314: No.125191. |
| [68] | Liang M, Xin X, Fan W Y, et al. Thermo-stability and aging performance of modified asphalt with crumb rubber activated by microwave and TOR[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 127: 84-96. |
| [69] | Xu M Z, Liu J, Li W Z, et al. Novel method to prepare activated crumb rubber used for synthesis of activated crumb rubber modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27(5): No.04014173. |
| [70] | Yin J M, Wang S Y, Lv F R. Improving the short-term aging resistance of asphalt by addition of crumb rubber radiated by microwave and impregnated in epoxidized soybean oil[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 712-719. |
| [71] | Li B, Zhou J N, Zhang Z H, et al. Effect of short-term aging on asphalt modified using microwave activation crumb rubber[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(7): No.1039. |
| [72] | Yin L, Yang X L, Shen A Q, et al. Mechanical properties and reaction mechanism of microwave-activated crumb rubber-modified asphalt before and after thermal aging[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 267: No.120773. |
| [73] | Liu H L, Wang X, Jia D M. Recycling of waste rubber powder by mechano-chemical modification[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 245: No.118716. |
| [74] | 易星宇. 废食用油脱硫胶粉沥青再生剂及性能初探[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学交通运输学院, 2019. |
| Yi Xing-yu. Properties investigation of a desulfurized rubber rejuvenator contained waste cooking oil[D]. Chongqing: School of Transportation, Chongqing University, 2019. | |
| [75] | Szerb E I, Nicotera I, Teltayev B, et al. Highly stable surfactant-crumb rubber-modified bitumen: NMR and rheological investigation[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2018, 19(5): 1192-1202. |
| [76] | 胡明翰. 废旧橡胶微生物脱硫再生利用[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学材料学院, 2014. |
| Hu Ming-han. Technology and application of recycling waste rubber by microorganisms[D]. Beijing: School of Materials Science, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2014. | |
| [77] | Chen S Y, Gong F Y, Ge D D, et al. Use of reacted and activated rubber in ultra-thin hot mixture asphalt overlay for wet-freeze climates[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 232: 369-378. |
| [78] | 李丽丽. 高掺量橡胶沥青技术研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学土木工程学院, 2011. |
| Li Li-li. Research on high dosage of crumb rubber modified asphalt[D]. Chongqing: College of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, 2011. | |
| [79] | 王歌. 基于活化技术的高掺量橡胶沥青性能[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学土木工程学院, 2013. |
| Wang Ge. The performance of high content asphalt rubber based on activation technique[D]. Chongqing: College of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, 2013. | |
| [80] | 倪彬. 大胶粉掺量橡胶沥青老化与再生机理研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通运输学院, 2022. |
| Ni Bin. The study on aging and regeneration mechanism of asphalt withhigh dosage of rubber[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2022. | |
| [81] | 郑凯军. 热解高掺量废胶粉改性沥青存储稳定性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学土木工程学院, 2017. |
| Zheng Kai-jun. Research on storage stability of pyrolytic high volume crumb rubber modified asphalt[D]. Chongqing: College of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, 2017. | |
| [82] | Liu B Q, Li J, Han M Z. Properties of polystyrene grafted activated waste rubber powder (PS-ARP) composite SBS modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 238: No.117737. |
| [83] | Ranieri M, Costa L M. Oliveira J R,et al. Asphalt surface mixtures with improved performance using waste polymers via dry and wet processes[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(10): No.04017169. |
| [84] | Meng Y J, Yan T Y, Muhammad Y, et al. Study on the performance and sustainability of modified waste crumb rubber and steel slag powder/SBS composite modified asphalt mastic[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 338: No.130563. |
| [85] | Kök B V, Yilmaz M, Geçkil A. Laboratory comparison of the crumb-rubber and SBS modified bitumen and hot mix asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(8): 3204-3212. |
| [86] | Zhao Z Z, Wang L L, Wang W S, et al. Experimental investigation of the high-temperature rheological and aging resistance properties of activated crumb rubber powder/SBS composite-modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(9): No.1905. |
| [1] | Zhen YANG,Rui-ping ZHENG,Zhe GONG. Highway infrastructure performance and traffic state prediction on road network [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1973-1983. |
| [2] | An-shun ZHANG,Wei FU,Jun-hui ZHANG,Feng GAO. Shear properties and stress-strain relationships characterization of Changsha compacted clay [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1604-1616. |
| [3] | Li-ming WANG,Zi-kun SONG,Hui ZHOU,Wen WEI,Hao YUAN. Rheological response and response mechanism of petroleum asphalt treated with ultrasound [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1346-1355. |
| [4] | Jing-yang YU,Dong-zhao LI,Zhi-qing ZHANG,Zhen WANG,Hai-lin SUN,Hai-ling BU,Ming-chun LI. Evolution of damage to performance of environment⁃friendly salt storage asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [5] | Jun-peng XU,Chuan-feng ZHENG,Yan-tao DU,Yu-hang WANG,Zheng LU,Wen-jun FAN. Damage effects of water⁃heat⁃force coupling in permeable asphalt mixture in cold region [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 877-887. |
| [6] | Yan-hai YANG,Bai-chuan LI,Ye YANG,Chong-hua WANG,Liang YUE. Aggregate ellipsoidal surface base reconstruction with virtual splitting tests [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 653-663. |
| [7] | Teng-fei NIAN,Zhao HAN,Zhi-qiang WEI,Guo-wei WANG,Jin-guo GE,Ping LI. Mesoscopic numerical modeling method of asphalt mix considering aggregate morphology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 639-652. |
| [8] | Wan-feng WEI,Ling-yun KONG,Wei-an XUAN,Fan YANG,Peng GUO. Review of characteristics of asphalt foaming and moisture sensitivity of warm mix mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 20-35. |
| [9] | Feng-chun GUO,Hai-peng BI,Hai-tao WANG,Shu-zheng WU,Hong-yu YANG. Viscoelastic behavior of carbon nano powder modified asphalt based on time-temperature equivalence [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 221-229. |
| [10] | Chao-lu TEMUR,Ya-ping ZHANG. Link anomaly detection algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on convolutional neural networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2295-2300. |
| [11] | Rong LUO,Yu LIANG,Long-chang NIU,Ting-ting HUANG,Qiang MIAO. Threshold value of water stability evaluation index of asphalt mixture under multi-temperature conditions [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1966-1977. |
| [12] | Ying-li GAO,Xiao-lei GU,Mei-jie LIAO,Xin-lang HU,Yu-tong XIE. Rheological properties and modification mechanism of SiO2 aerogel/reactive elastomer terpolymer/Polyphosphoric acid composite modified asphalt [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1978-1987. |
| [13] | Ya-ning CUI,Chun-di SI,Tao-tao FAN,Fei WANG. Analysis on crack propagation of asphalt bridge deck pavement under water-force coupling action [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1988-1996. |
| [14] | Yong-li XU,Xu-lan YANG,Ji-sen ZHOU,Song-han YANG,Ming-gang SUN. Asphalt fume composition of warm mix asphalt and smoke suppression performance of warm mix agent [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1701-1707. |
| [15] | Zu-zhong LI,Meng-yuan LI,Wei-dong LIU,Xiao-xiao PANG,Hao Tang,Xue-lei ZHANG,Chen-yang MA. Surface modification of bagasse fibers and road performances of asphalt mixture [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1738-1745. |
|