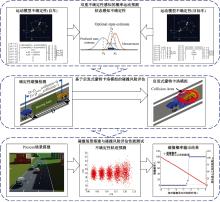
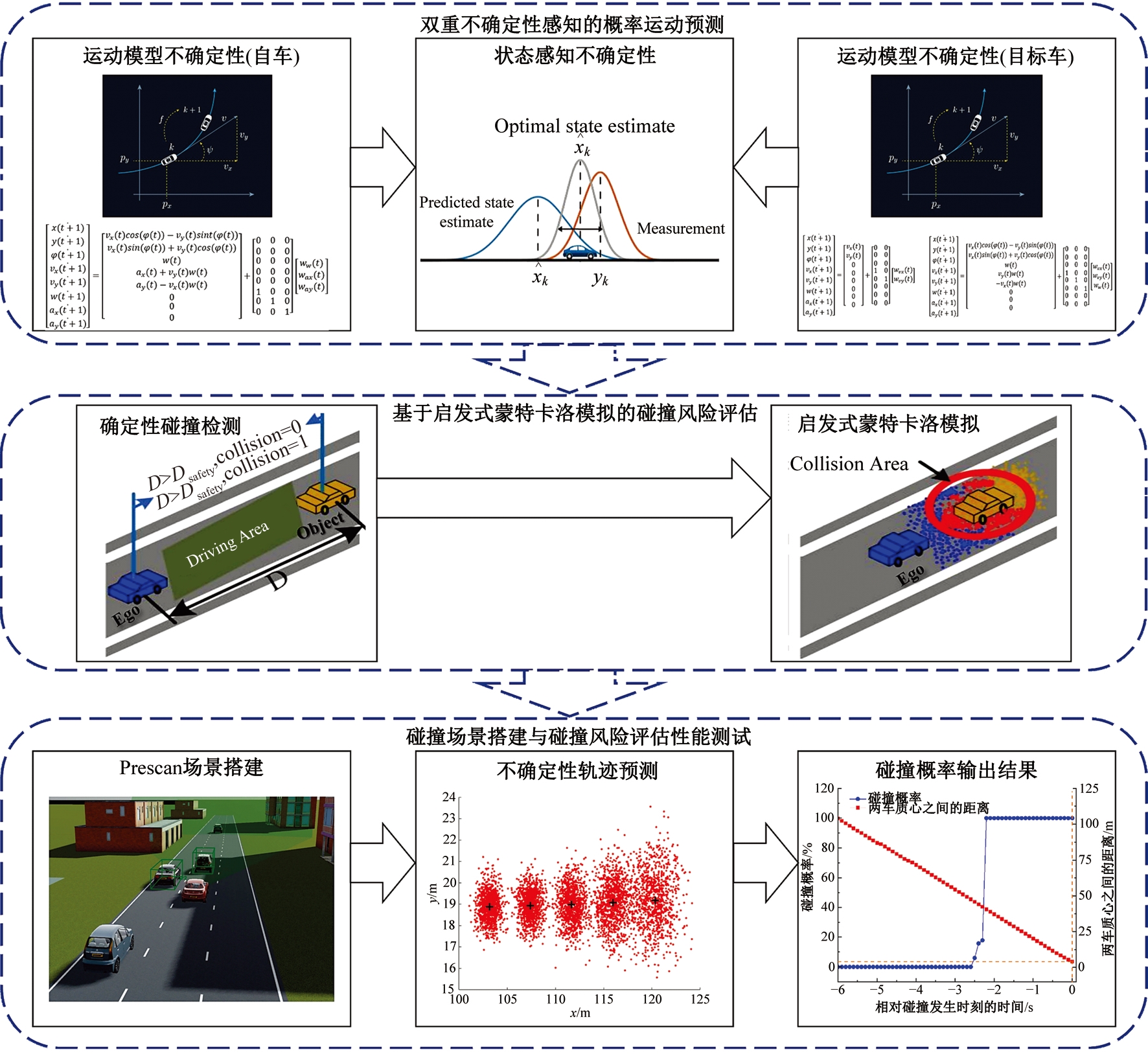
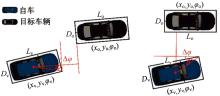
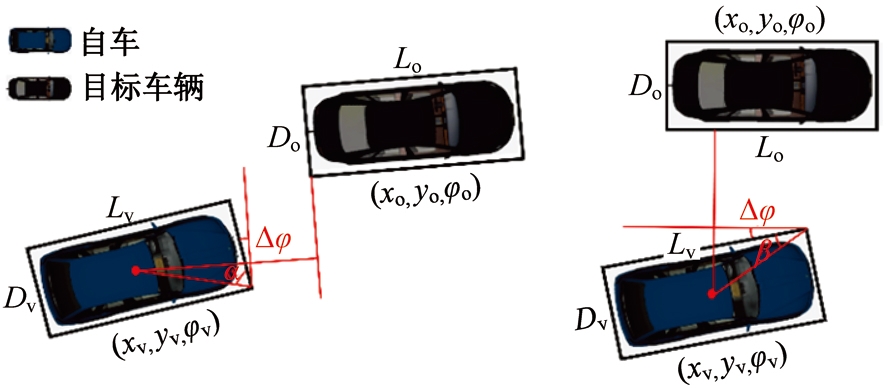
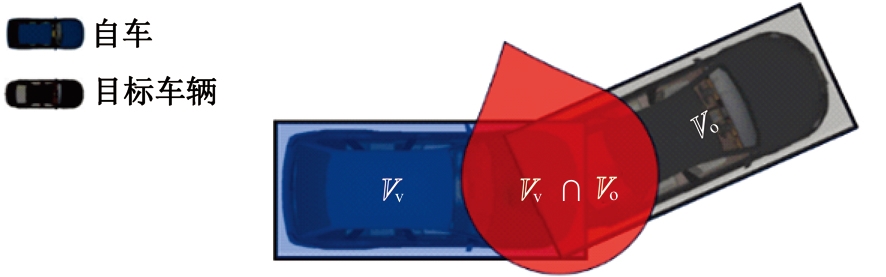
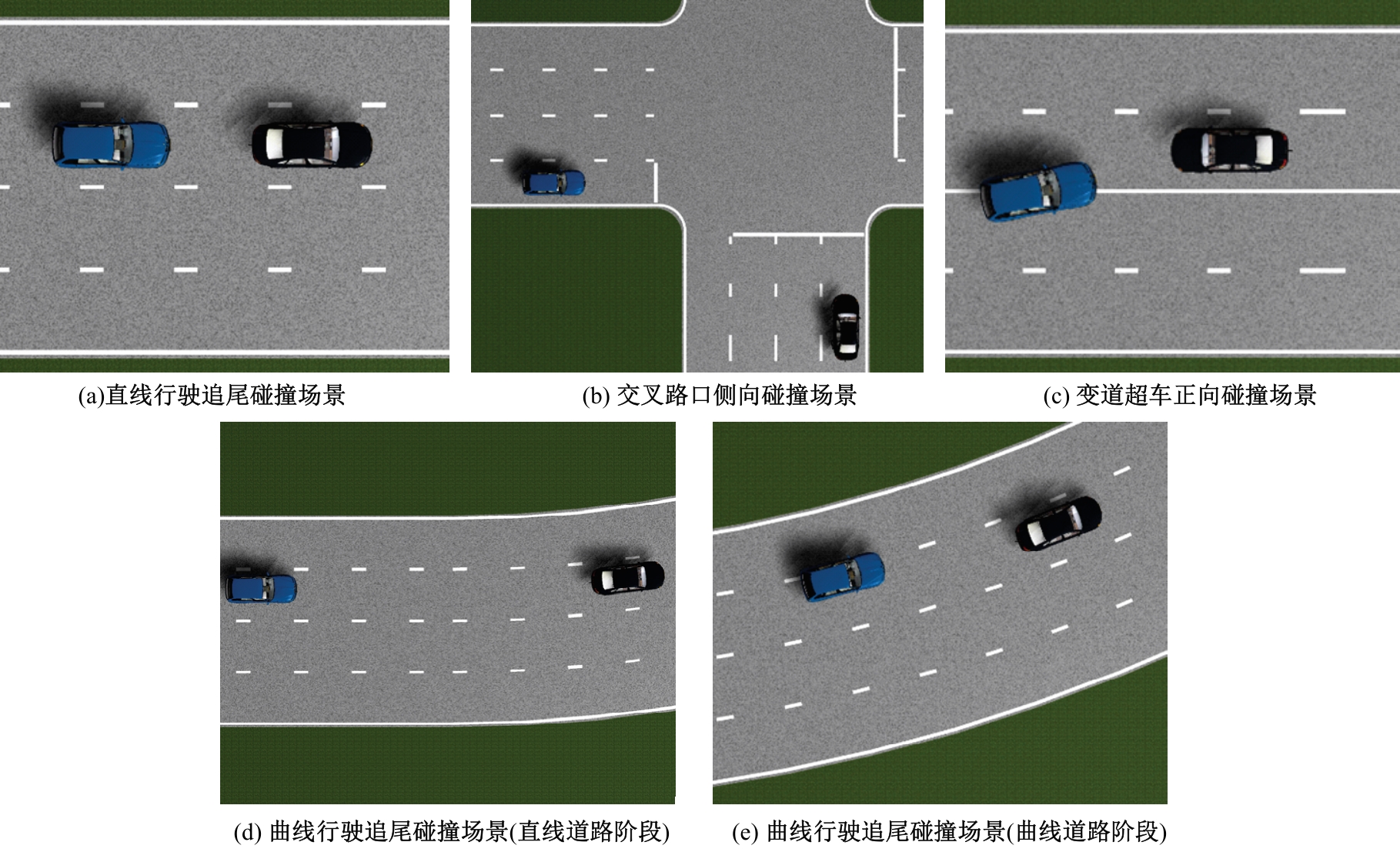
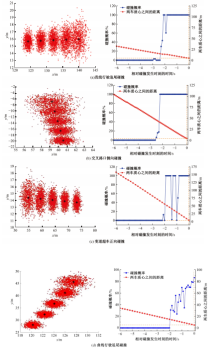
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2597-2610.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231290
Intelligent vehicle collision risk assessment considering dual uncertainties
Rui ZHAO1( ),Qi-rui YUAN1,Jia-jun LIAN1,Fei GAO2(
),Qi-rui YUAN1,Jia-jun LIAN1,Fei GAO2( ),Hong-yu HU2,Zhen-hai GAO2
),Hong-yu HU2,Zhen-hai GAO2
- 1.College of Automotive Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| [1] | Huang C, Hang P, Hu Z, et al. Collision-probability-aware human-machine cooperative planning for safe automated driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 9752-9763. |
| [2] | Katrakazas C, Quddus M, Chen W H. A new integrated collision risk assessment methodology for autonomous vehicles[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 127: 61-79. |
| [3] | Tan H S, Huang J. DGPS-based vehicle-to-vehicle cooperative collision warning: Engineering feasibility viewpoints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2006, 7(4): 415-428. |
| [4] | Hillenbrand J, Spieker A M, Kroschel K. A multilevel collision mitigation approach—Its situation assessment, decision making, and performance tradeoffs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2006, 7(4): 528-540. |
| [5] | Noh S, An K. Decision-making framework for automated driving in highway environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(1): 58-71. |
| [6] | Chu K, Lee M, Sunwoo M. Local path planning for off-road autonomous driving with avoidance of static obstacles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1599-1616. |
| [7] | Kaempchen N, Schiele B, Dietmayer K. Situation assessment of an autonomous emergency brake for arbitrary vehicle-to-vehicle collision scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(4): 678-687. |
| [8] | Ferguson D, Darms M, Urmson C, et al. Detection, prediction, and avoidance of dynamic obstacles in urban environments[C]∥Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Eindhoven: IEEE, 2008: 1149-1154. |
| [9] | Yang Z, Shi C, Zheng Y, et al. A study on a vehicle semi-active suspension control system based on road elevation identification[J]. Plos One, 2022, 17(6):No. e0269406. |
| [10] | Greene D, Liu J, Reich J, et al. An efficient computational architecture for a collision early-warning system for vehicles, pedestrians, and bicyclists[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 12(4): 942-953. |
| [11] | Kim J H, Kum D S. Threat prediction algorithm based on local path candidates and surrounding vehicle trajectory predictions for automated driving vehicles[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Seoul: IEEE, 2015: 1220-1225. |
| [12] | Kim J, Kum D. Collision risk assessment algorithm via lane-based probabilistic motion prediction of surrounding vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(9): 2965-2976. |
| [13] | Toledo M R, Zamora I M A. IMM-based lane-change prediction in highways with low-cost GPS/INS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(1): 180-185. |
| [14] | Kasper D, Weidl G, Dang T, et al. Object-oriented bayesian networks for detection of lane change maneuvers[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2012, 4(3): 19-31. |
| [15] | Schreier M, Willert V, Adamy J. An integrated approach to maneuver-based trajectory prediction and criticality assessment in arbitrary road environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(10): 2751-2766. |
| [16] | Kim I H, Bong J H, Park J, et al. Prediction of driver's intention of lane change by augmenting sensor information using machine learning techniques[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(6): No.17061350. |
| [17] | Bahram M, Hubmann C, Lawitzky A, et al. A combined model-and learning-based framework for interaction-aware maneuver prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(6): 1538-1550. |
| [18] | Bahram M, Lawitzky A, Friedrichs J, et al. A game-theoretic approach to replanning-aware interactive scene prediction and planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2015, 65(6): 3981-3992. |
| [19] | Li Y, Yu R, Shahabi C, et al. Diffusion convolutional recurrent neural network: Data-driven traffic forecasting[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2017, 7: No.170701926. |
| [20] | Gao H, Su H, Cai Y, et al. Trajectory prediction of cyclist based on dynamic Bayesian network and long short-term memory model at unsignalized intersections[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(7): No.172207. |
| [21] | Wang H, Lu B, Li J, et al. Risk assessment and mitigation in local path planning for autonomous vehicles with LSTM based predictive model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2021, 19(4): 2738-2749. |
| [22] | Deo N, Trivedi M M. Multi-modal trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicles with maneuver based lstms[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Changshu: IEEE, 2018: 1179-1184. |
| [23] | Gao Z, Bao M, Gao F, et al. Probabilistic multi-modal expected trajectory prediction based on LSTM for autonomous driving[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2023, 238: No. 09544070 231167906. |
| [24] | Sheng Z, Xu Y, Xue S, et al. Graph-based spatial-temporal convolutional network for vehicle trajectory prediction in autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(10): 17654-17665. |
| [25] | Sui Z, Zhou Y, Zhao X, et al. Joint intention and trajectory prediction based on transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Prague:IEEE, 2021: 7082-7088. |
| [26] | Chen X, Zhang H, Zhao F, et al. Vehicle trajectory prediction based on intention-aware non-autoregressive transformer with multi-attention learning for Internet of Vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 1-12. |
| [27] | Huang Y, Du J, Yang Z, et al. A survey on trajectory-prediction methods for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2022, 7(3): 652-674. |
| [28] | Joerer S, Segata M, Bloessl B, et al. A vehicular networking perspective on estimating vehicle collision probability at intersections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2013, 63(4): 1802-1812. |
| [29] | Campos G R, Runarsson A H, Granum F, et al. Collision avoidance at intersections: A probabilistic threat-assessment and decision-making system for safety interventions[C]∥Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 17th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Qingdao:IEEE, 2014: 649-654. |
| 30] Tan H S, Huang J. DGPS-based vehicle-to-vehicle cooperative collision warning: Engineering feasibility viewpoints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2006, 7(4): 415-428. | |
| [31] | Tao L, Watanabe Y, Li Y, et al. Collision risk assessment service for connected vehicles: Leveraging vehicular state and motion uncertainties[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(14): 11548-11560. |
| [32] | Lambert A, Gruyer D, Saint Pierre G. A fast monte carlo algorithm for collision probability estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision. Hanoi: IEEE, 2008: 406-411. |
| [33] | Ammoun S, Nashashibi F. Real time trajectory prediction for collision risk estimation between vehicles[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE 5Th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing. Cluj-Napoca: IEEE, 2009: 417-422. |
| [34] | Houénou A, Bonnifait P, Cherfaoui V. Risk assessment for collision avoidance systems[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC). Qingdao: IEEE, 2014: 386-391. |
| [35] | Lee K, Peng H. Evaluation of automotive forward collision warning and collision avoidance algorithms[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2005, 43(10): 735-751. |
| [36] | Lambert A, Gruyer D, Saint P G. A fast monte carlo algorithm for collision probability estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision. Hanoi: IEEE, 2008: 406-411. |
| [1] | Jian WANG,Chen-wei JIA. Trajectory prediction model for intelligent connected vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1963-1972. |
| [2] | Hong-yu HU,Zheng-guang ZHANG,You QU,Mu-yu CAI,Fei GAO,Zhen-hai GAO. Driver behavior recognition method based on dual-branch and deformable convolutional neural networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 93-104. |
| [3] | Ling HUANG,Zuan CUI,Feng YOU,Pei-xin HONG,Hao-chuan ZHONG,Yi-xuan ZENG. Vehicle trajectory prediction model for multi-vehicle interaction scenario [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1188-1195. |
| [4] | Yan-tao TIAN,Xing HUANG,Hui-qiu LU,Kai-ge WANG,Fu-qiang XU. Multi⁃mode behavior trajectory prediction of surrounding vehicle based on attention and depth interaction [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [5] | Yan-ran LIU,Qing-yu MENG,Hong-yan GUO,Jia-lin LI. Vehicle trajectory prediction combined with high definition map in graph attention mode [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 792-801. |
| [6] | Yan-tao TIAN,Fu-qiang XU,Kai-ge WANG,Zi-xu HAO. Expected trajectory prediction of vehicle considering surrounding vehicle information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [7] | Yan-tao TIAN,Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE. Deep reinforcement learning augmented decision⁃making model for intelligent driving vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [8] | Yan-feng JIA,Da-yi QU,Lu LIN,Rong-han YAO,Xiao-long MA. Coordinated speed control of connected mixed traffic flow based on trajectory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
|
||