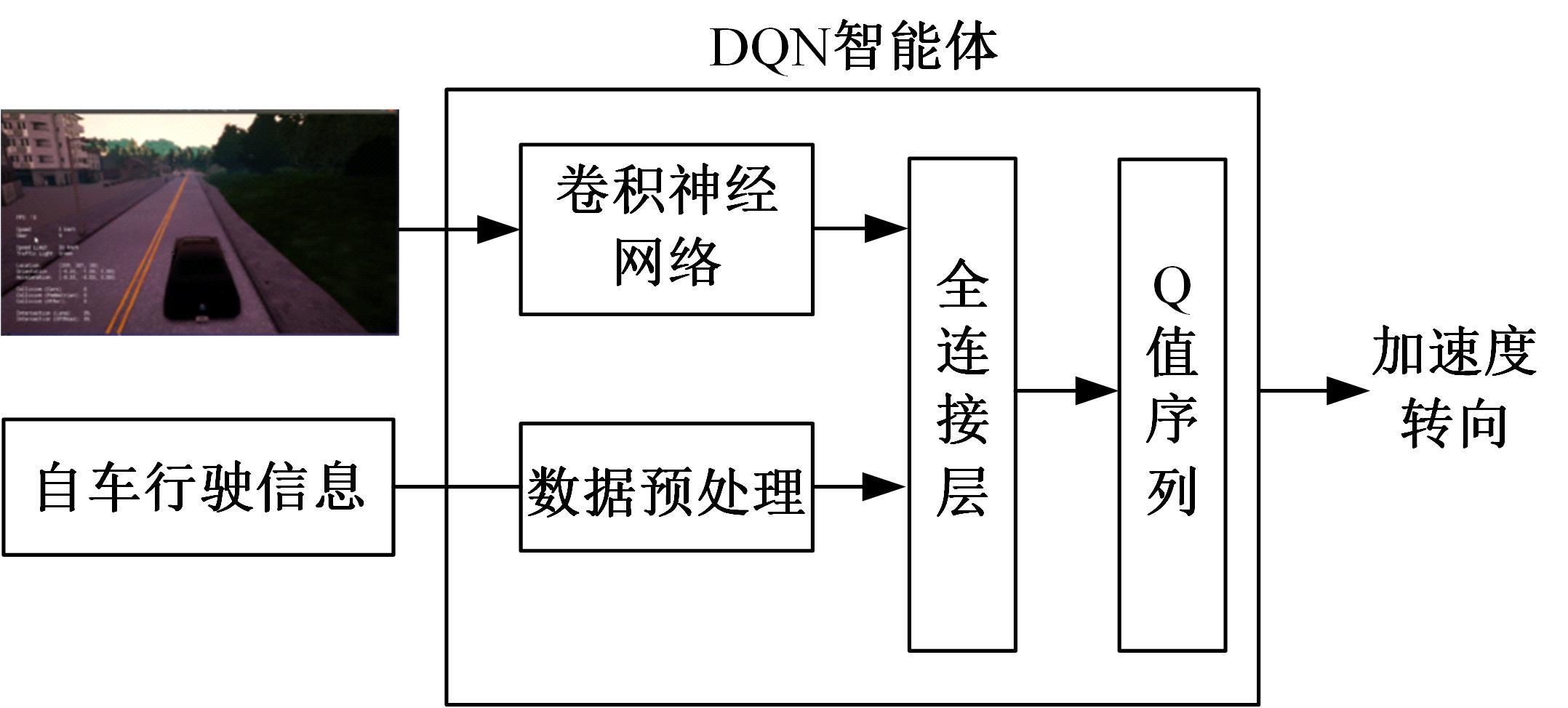
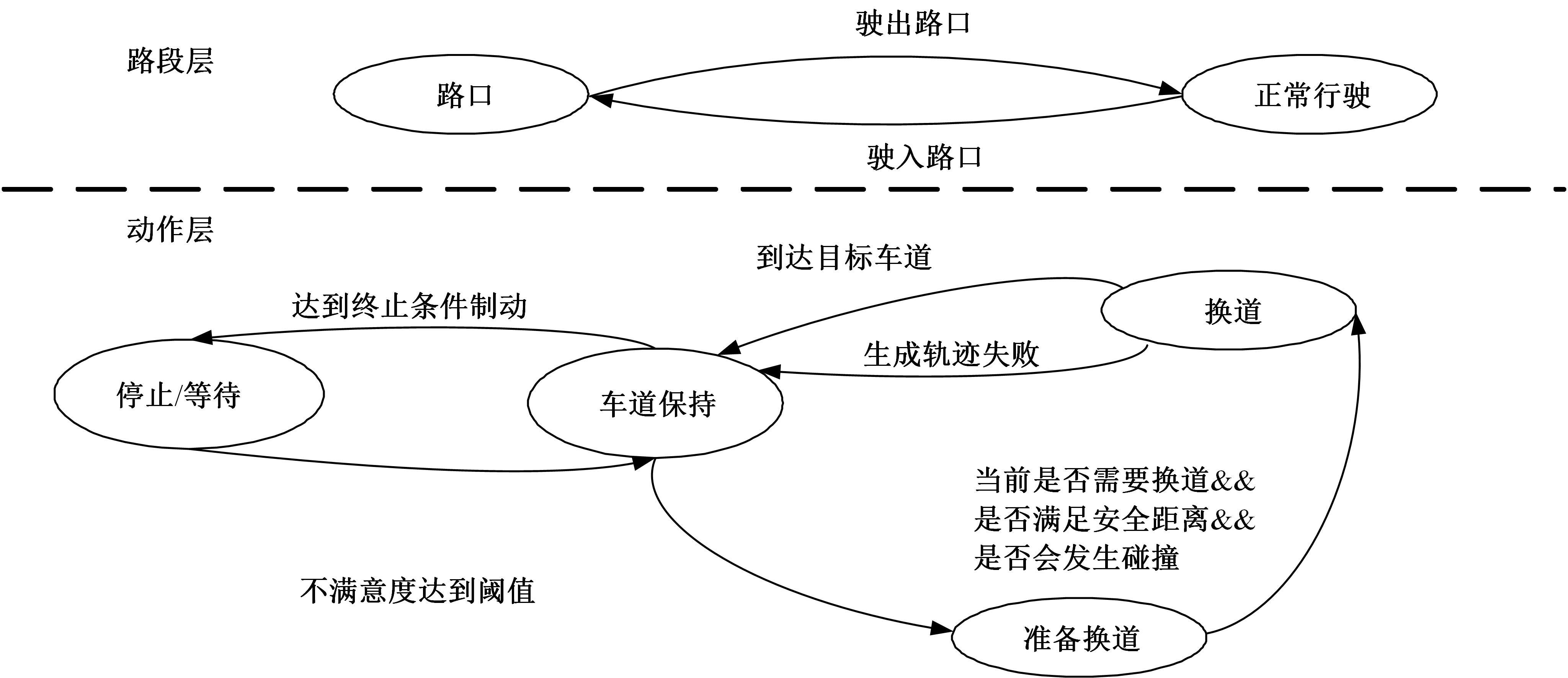
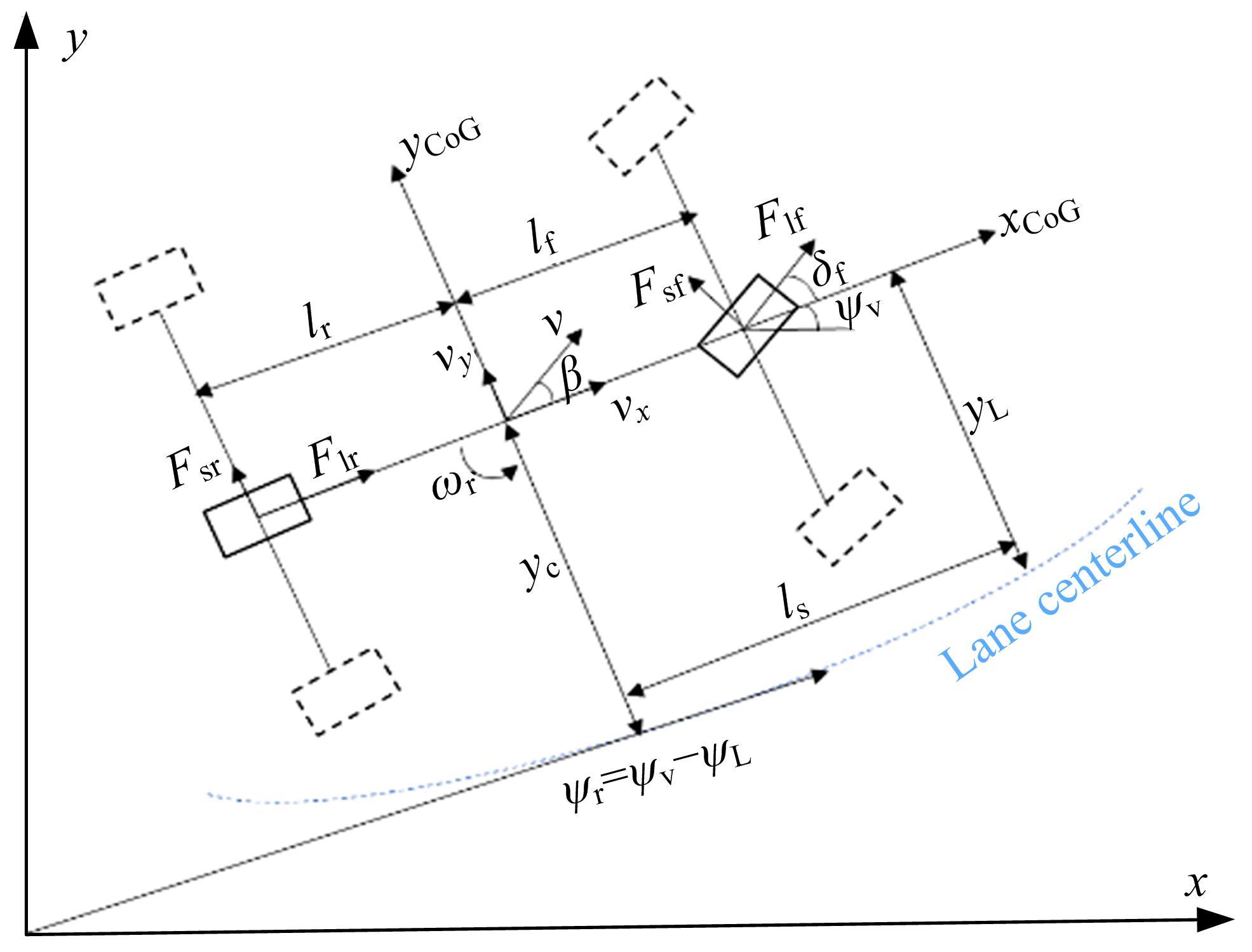
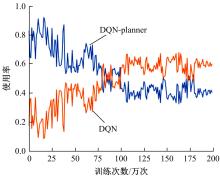
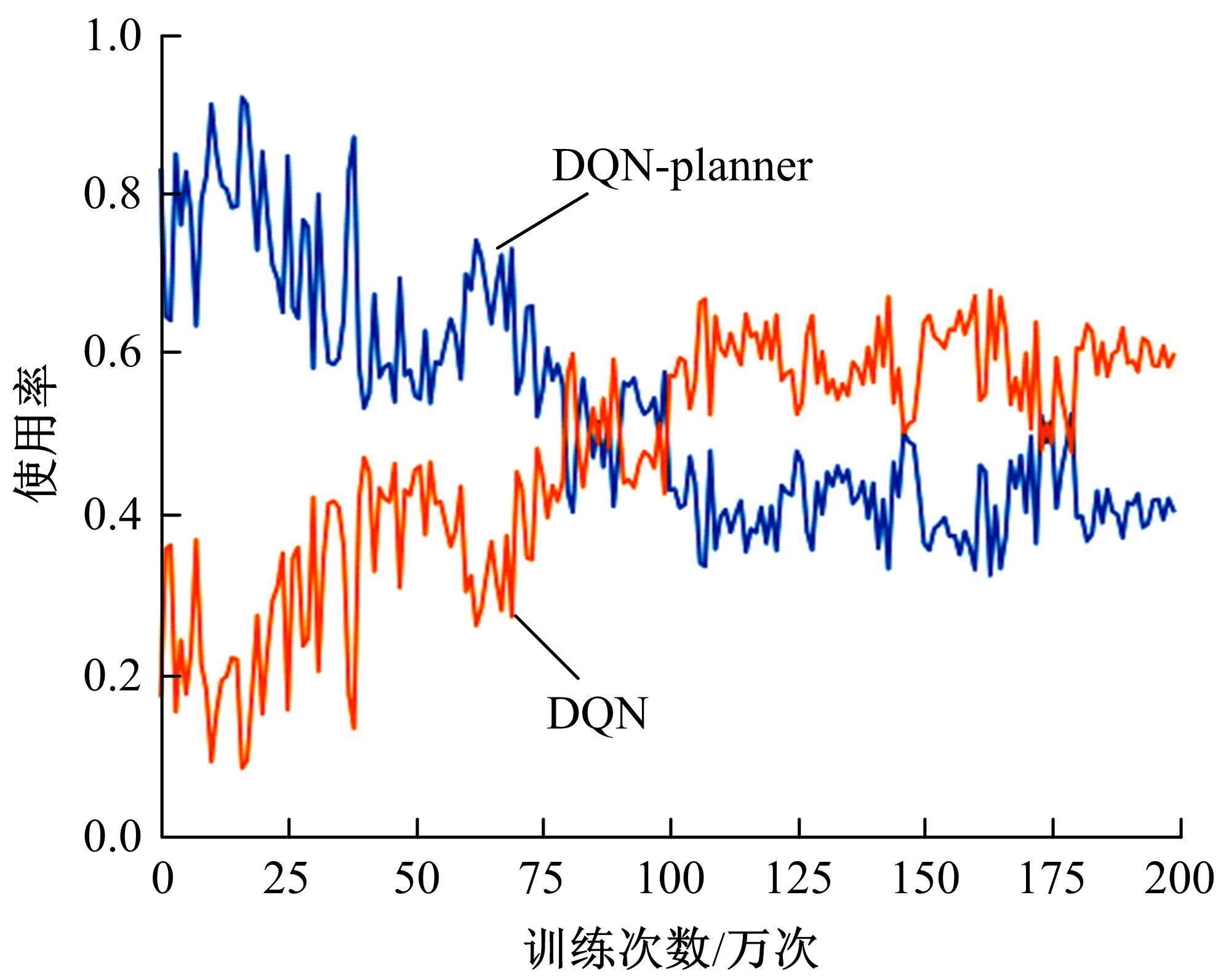
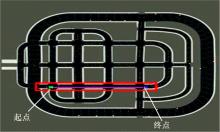
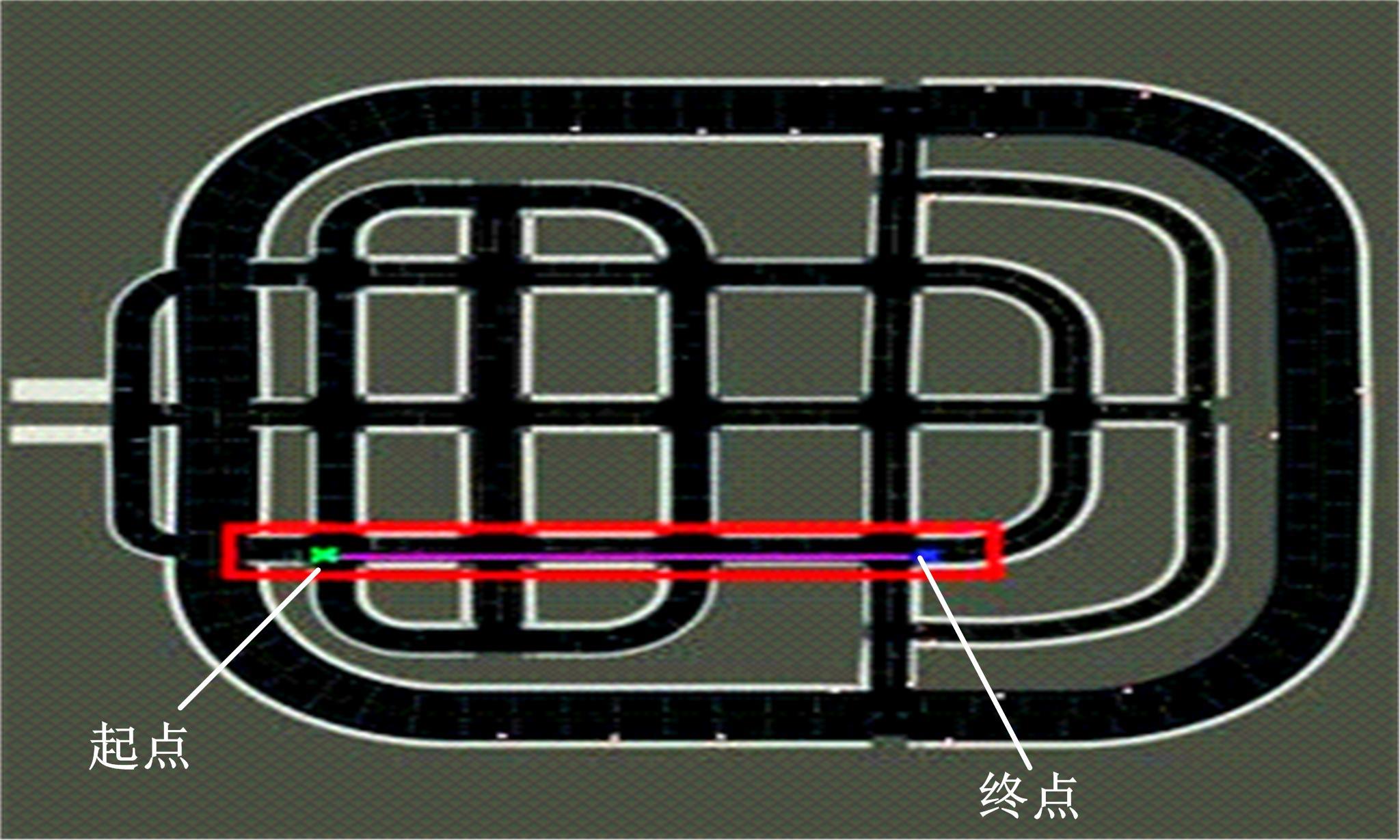
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 682-692.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221441
Deep reinforcement learning augmented decision⁃making model for intelligent driving vehicles
Yan-tao TIAN( ),Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE
),Yan-shi JI,Huan CHANG,Bo XIE
- College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- U495
| 1 | 王喆, 杨柏婷, 刘昕, 等. 基于模糊聚类的驾驶决策判别[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2015,45(5): 1414-1419. |
| Wang Zhe, Yang Bai-ting, Liu Xin, et al. Discriminant analysis of driving decisions based on fuzzy clustering[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. | |
| 2 | Montemerlo M, Becker J, Bhat S, et al. Junior: the stanford entry in the urban challenge[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2008, 25(9): 569-597. |
| 3 | Urmson C, Baker C, Dolan J, et al. Autonomous driving in traffic: boss and the urban challenge[J]. The AI Magazine, 2009, 30(2): 17-28. |
| 4 | Li Hong-hui, Xi Yi-kun, Lu Hai-liang, et al. Improved C4.5 algorithm based on k-means[J]. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering, 2020, 20(1): 177-189. |
| 5 | 杜明博. 基于人类驾驶行为的无人驾驶车辆行为决策与运动规划方法研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学信息科学技术学院, 2016. |
| Du Ming-bo. Research on behavioral decision making and motion planning methods of autonomous vehicle based on human driving behavior[D]. Hefei: College of Information Science and Technology, University of Science and Technology of China, 2016. | |
| 6 | 曹轩豪. 自动驾驶汽车跟驰换道运动控制与决策规划研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学通信工程学院, 2022. |
| Cao Xuan-hao. Motion control and decision planning for car following and lane changing of autonomous vehicle[D]. Changchun: College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, 2022. | |
| 7 | Isele D, Rahimi R, Cosgun A, et al. Navigating occluded intersections with autonomous vehicles using deep reinforcement learning[C]∥2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 2034-2039. |
| 8 | Li L Z, Ota K, Dong M X, et al. Humanlike driving: empirical decision-making system for autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 6814-6823. |
| 9 | 高振海, 孙天骏, 何磊, 等. 汽车纵向自动驾驶的因果推理型决策[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. |
| Gao Zhen-hai, Sun Tian-jun, He Lei, et al. Causal reasoning decision-making for vehicle longitudinal automatic driving[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1392-1404. | |
| 10 | Barto A G, Mahadevan S. Recent advances in hierarchical reinforcement learning[J]. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems, 2003, 13(1/2): 41-77. |
| 11 | Russell S J, Norvig P. Artificial Intelligence: a Modern Approach[M]. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1995. |
| 12 | Toledo T, Koutsopoulos H N, Ben-akiva M. Integrated driving behavior modeling[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2007, 15(2): 96-112. |
| 13 | Kurzer K, Engelhorn F, Zoellner J M, et al. Decentralized cooperative planning for automated vehicles with hierarchical monte carlo tree search[C]∥2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Hawaii, USA, 2018:452-459. |
| 14 | Sefati M, Chandiramani J, Kreiskoether K, et al. Towards tactical behaviour planning under uncertainties for automated vehicles in urban scenarios[C]∥2017 IEEE 20th International Conference On Intelligent Transportation Systems(ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 2018: 1-7. |
| 15 | Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature(London), 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. |
| 16 | Mnih V, Badia A P, Mirza M, et al. Asynchronous methods for deep reinforcement learning[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, San Diego, USA, 2016:1-10 |
| 17 | Li C J, Czarnecki K. Urban driving with multi-objective deep reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems,Montreal,Canada,2019: 359-367. |
| 18 | Chen J, Yuan B, Tomizuka M. Model-free deep reinforcement learning for urban autonomous driving[C]∥2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), New York, USA, 2019: 2765-2771. |
| [1] | Yan-tao TIAN,Fu-qiang XU,Kai-ge WANG,Zi-xu HAO. Expected trajectory prediction of vehicle considering surrounding vehicle information [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [2] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Xuan-qi LAI,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Wheel odometry error prediction model based on transformer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [3] | Ke HE,Hai-tao DING,Nan XU,Kong-hui GUO. Enhanced localization system based on camera and lane markings [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 663-673. |
| [4] | Deng-feng WANG,Hong-li CHEN,Jing-xin NA,Xin CHEN. Failure comparison of single and double lap joints after high temperature aging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 346-354. |
| [5] | Pei ZHANG,Zhi-wei WANG,Chang-qing DU,Fu-wu YAN,Chi-hua LU. Oxygen excess ratio control method of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air system for vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [6] | Ke-yong WANG,Da-tong BAO,Su ZHOU. Data-driven online adaptive diagnosis algorithm towards vehicle fuel cell fault diagnosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [7] | Qi-ming CAO,Hai-tao MIN,Wei-yi SUN,Yuan-bin YU,Jun-yu JIANG. Hydrothermal characteristics of proton exchange membrane fuel cell start⁃up at low temperature [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [8] | Hai-lin KUI,Ze-zhao WANG,Jia-zhen ZHANG,Yang LIU. Transmission ratio and energy management strategy of fuel cell vehicle based on AVL⁃Cruise [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [9] | Yan LIU,Tian-wei DING,Yu-peng WANG,Jing DU,Hong-hui ZHAO. Thermal management strategy of fuel cell engine based on adaptive control strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [10] | Cheng LI,Hao JING,Guang-di HU,Xiao-dong LIU,Biao FENG. High⁃order sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2203-2212. |
| [11] | Feng-xiang CHEN,Qi WU,Yuan-song LI,Tian-de MO,Yu LI,Li-ping HUANG,Jian-hong SU,Wei-dong ZHANG. Matching,simulation and optimization for 2.5 ton fuel cell/battery hybrid forklift [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [12] | Xiao-hua WU,Zhong-wei YU,Zhang-ling ZHU,Xin-mei GAO. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell buses [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [13] | Xun-cheng CHI,Zhong-jun HOU,Wei WEI,Zeng-gang XIA,Lin-lin ZHUANG,Rong GUO. Review of model⁃based anode gas concentration estimation techniques of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [14] | Yao-wang PEI,Feng-xiang CHEN,Zhe HU,Shuang ZHAI,Feng-lai PEI,Wei-dong ZHANG,Jie-ran JIAO. Temperature control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell thermal management system based on adaptive LQR control [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [15] | Guang-di HU,Hao JING,Cheng LI,Biao FENG,Xiao-dong LIU. Multi⁃objective sliding mode control based on high⁃order fuel cell model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
|
||