吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 265-274.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210203
毛樱桃总黄酮对小鼠皮肤增生性瘢痕的抑制作用及其机制
邹天琪1,柏林1,张铮旭1,李贺1,王春梅1,孙靖辉1,陈建光1,陈曦2( ),张成义1(
),张成义1( )
)
- 1.北华大学药学院药理教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.北华大学医学院病原学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
Inhibitory effect of prunus tomentosa thunb total flavonoids on skin hypertrophic scar in mice and its mechanism
Tianqi ZOU1,Lin BAI1,Zhengxu ZHANG1,He LI1,Chunmei WANG1,Jinghui SUN1,Jianguang CHEN1,Xi CHEN2( ),Chengyi ZHANG1(
),Chengyi ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Pharmacology,College of Pharmacy,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Etiology,College of Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
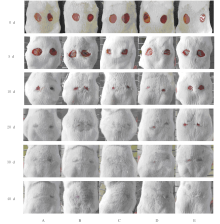
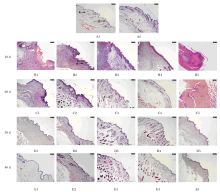
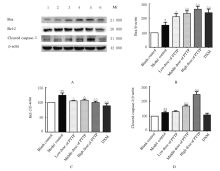
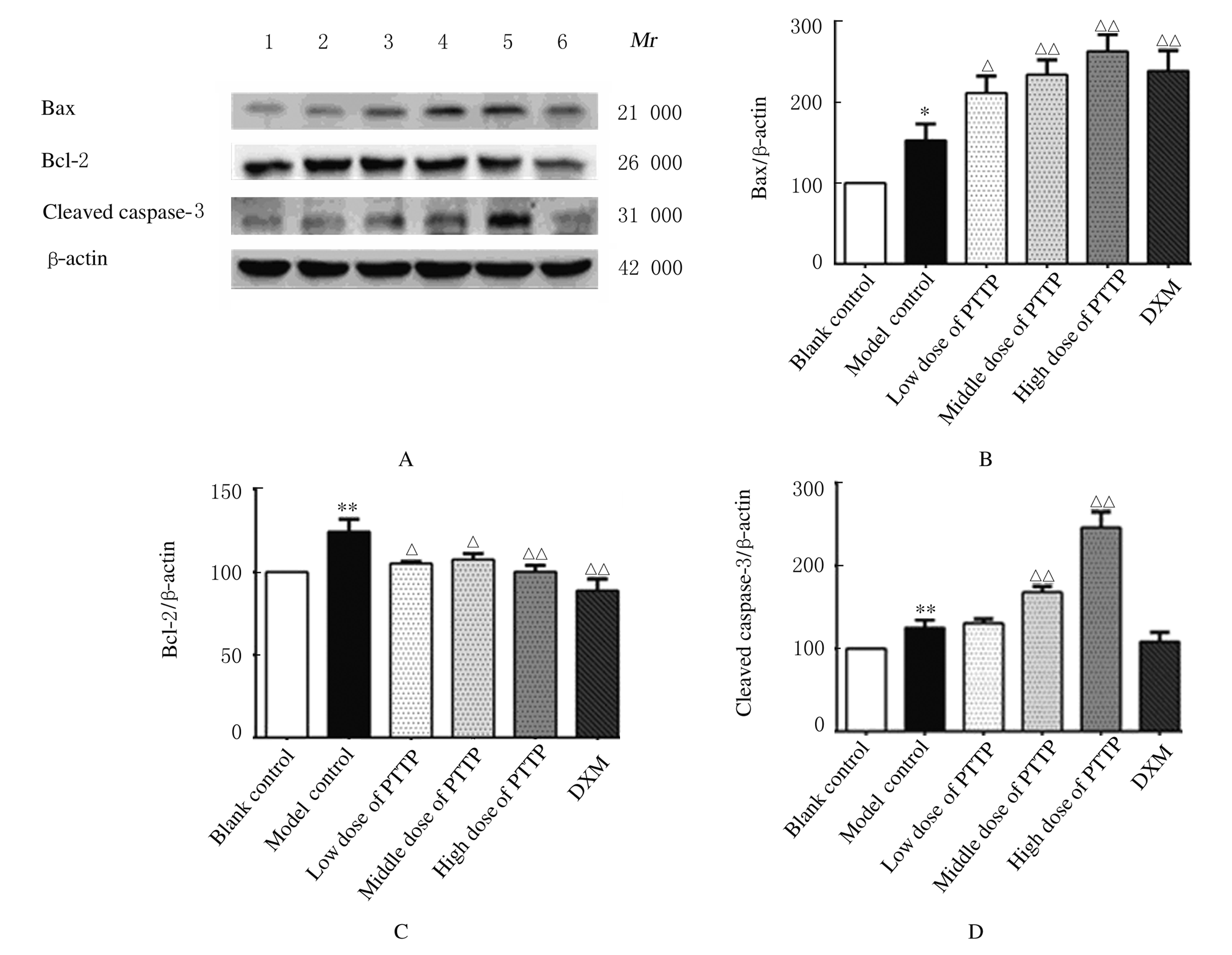
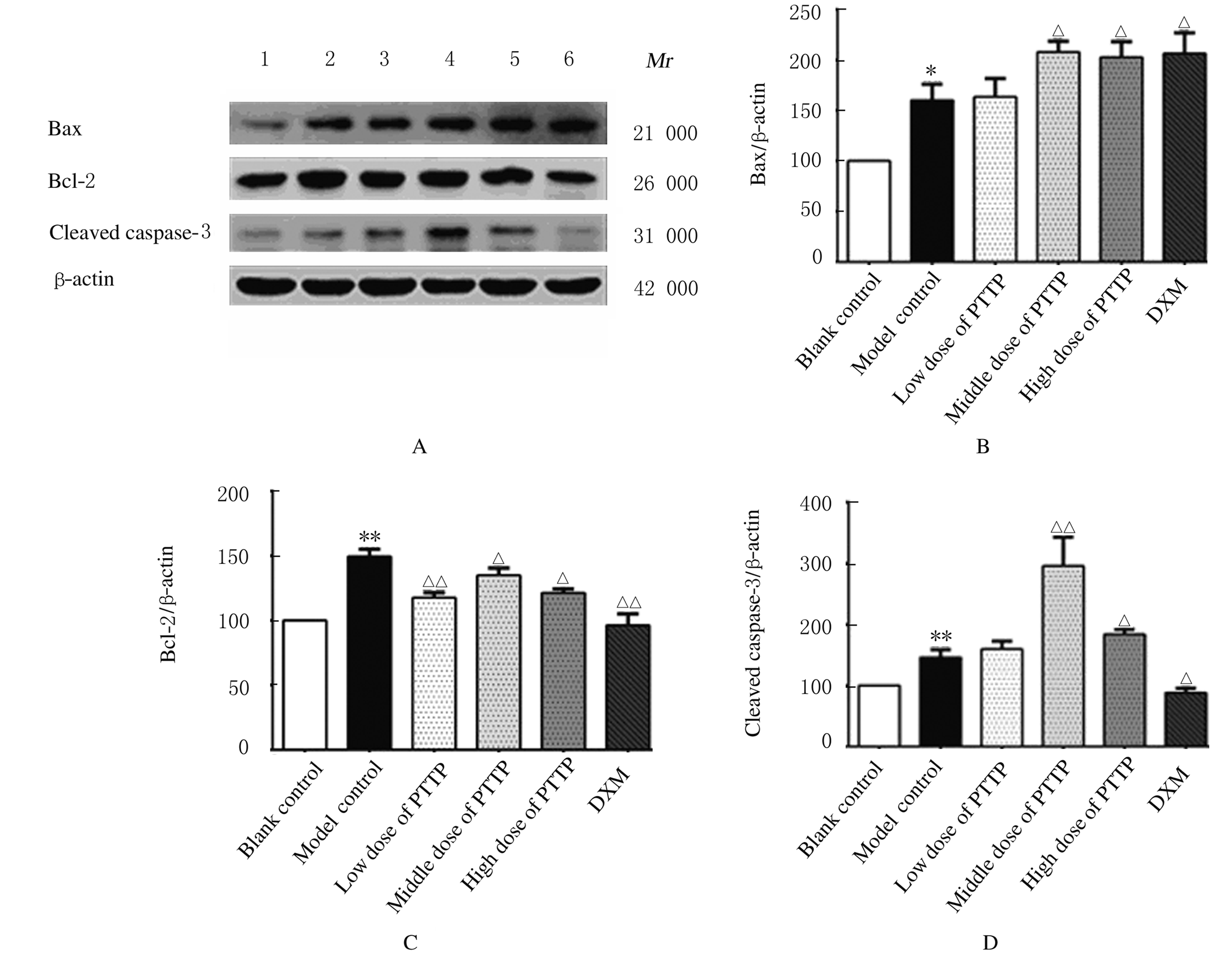
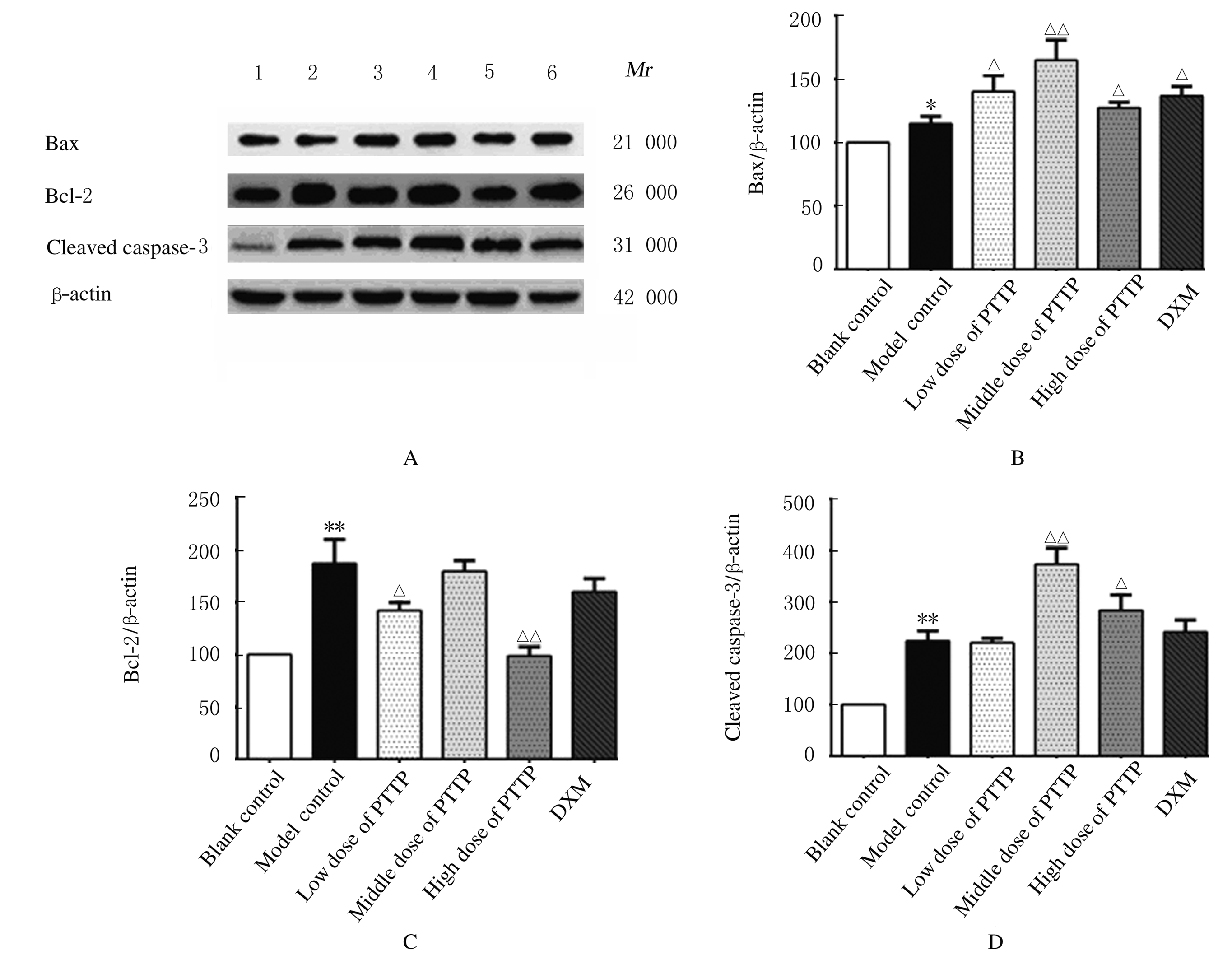
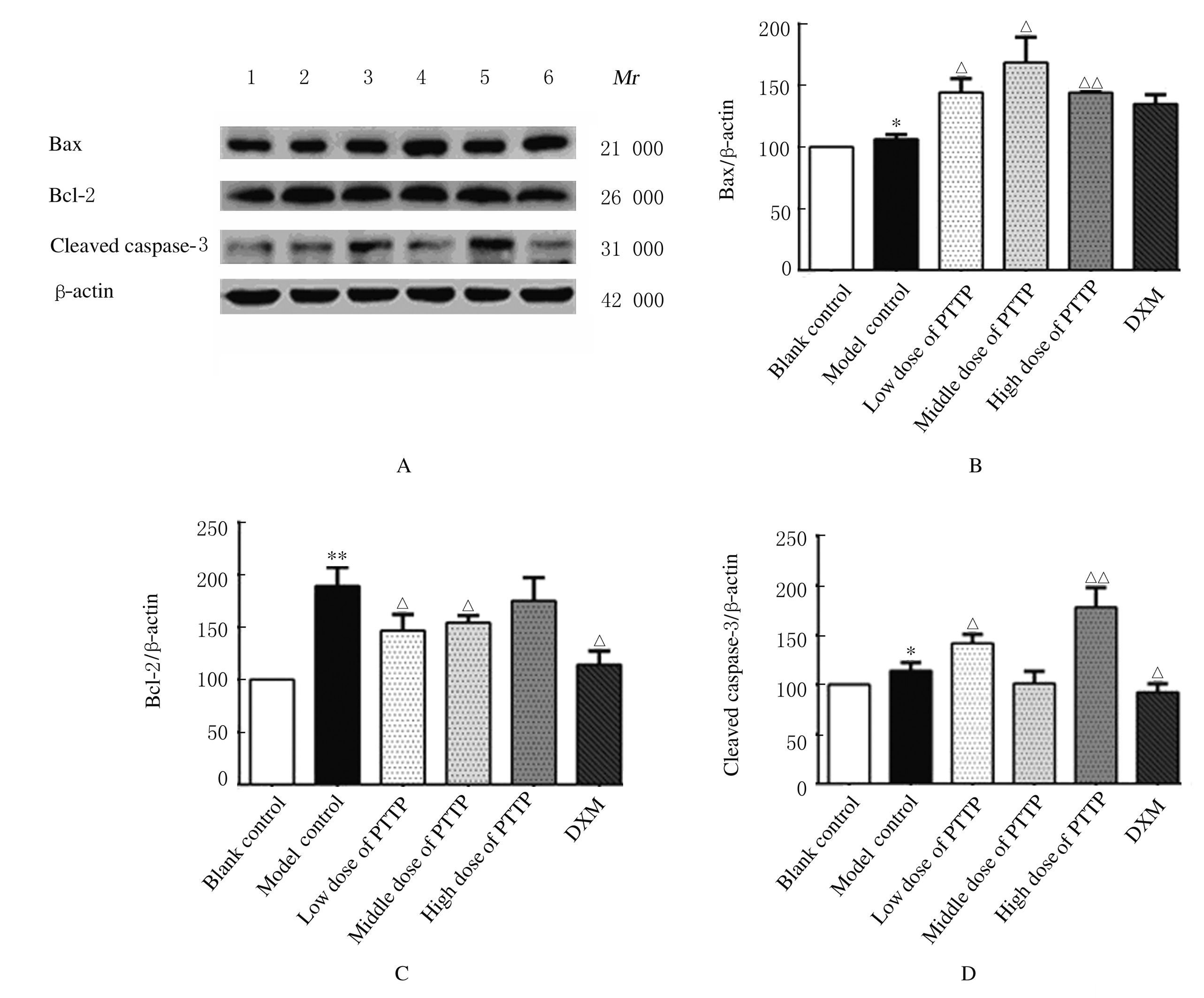
摘要: 探讨毛樱桃总黄酮(PTTTF)对小鼠皮肤增生性瘢痕(HS)形成的作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 将96只ICR雄性小鼠随机分为空白对照组,模型对照组(给予相同剂量的涂膜剂空白基质),低、中和高剂量毛樱桃涂膜剂(PTTP)组(分别给予0.4、0.8 和1.6 mg·L-1 PTTP),阳性对照复方醋酸地塞米松乳膏(DXM)组,每组16只。除空白对照组外,其余各组小鼠均采用皮肤打孔器,以脊柱为中线在背部两侧制造2个直径为10 mm的全层皮肤缺损模型,每天给药1次,每次给药0.1 mL涂抹。每天观察各组小鼠创面愈合情况,计算伤口愈合率。分别于造模第10、20、30和40天处死每组小鼠4只,取创面全层皮肤组织。采用HE染色观察HS皮肤组织病理形态表现,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠皮肤瘢痕组织中活化的含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白酶3(Cleaved caspase-3)、B细胞淋巴瘤2(Bcl-2)和Bcl-2相关X蛋白(Bax)蛋白表达水平。 与模型对照组比较,造模第40天时,低、中和高剂量PTTP组小鼠创面愈合率分别为98.94%、99.14%和99.04%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。HE染色,与模型对照组比较,各剂量PTTP组小鼠伤口愈合较快,逐渐恢复到正常皮肤结构,有皮脂腺、毛囊和汗腺等皮肤附属器生成。Western blotting法检测,与模型对照组比较,各剂量PTTP组小鼠皮肤瘢痕组织中Cleaved caspase-3和Bax蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 PTTTF可促进伤口愈合,对小鼠HS的形成具有一定的抑制作用,其作用机制可能与诱导细胞凋亡有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5