吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 145-151.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.20210120
姜黄素对结直肠癌小鼠肿瘤生长的抑制作用及其PTEN/PI3K/Akt信号通路机制
- 河北医科大学第一医院普外三科,河北 石家庄 050031
Inhibitory effect of curcumin on tumor growth in colorectal cancer mice and its mechanism of PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathwayPEI Yongbin, WANG Guiqi, LI Wei, JIANG Xia, JIANG Haibo, ZHAO Zengren (Department of General Surgery,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031,China)
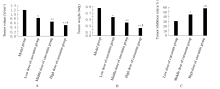
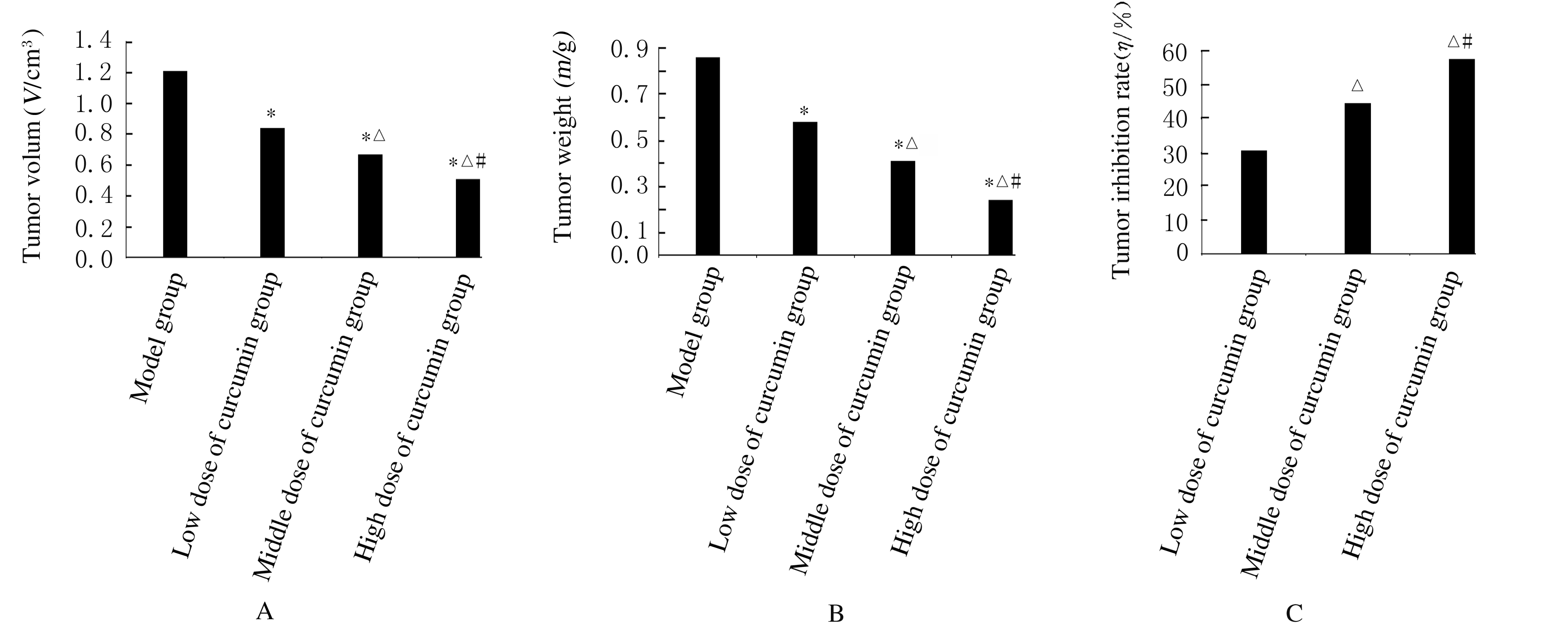
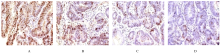
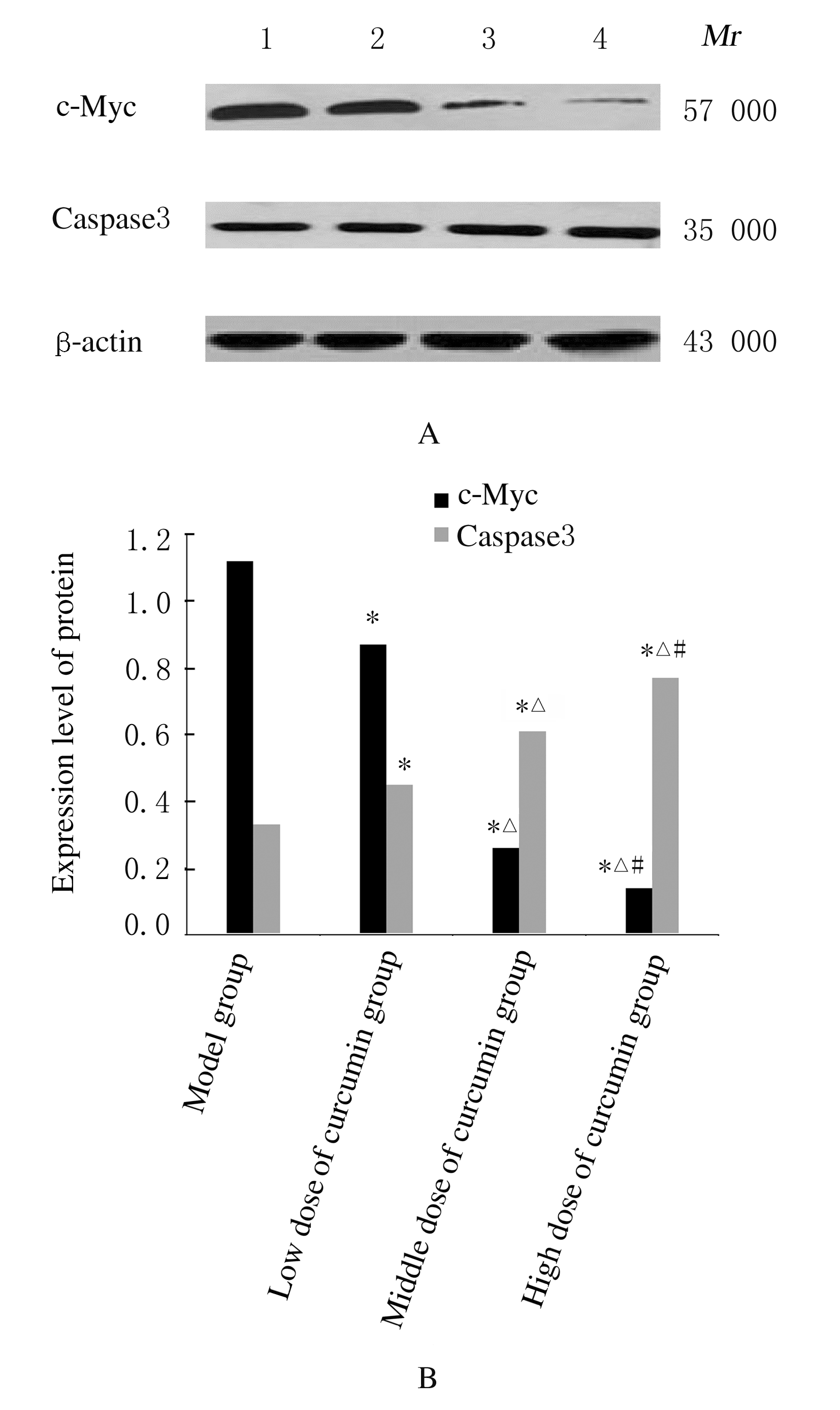
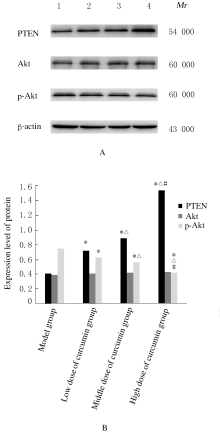
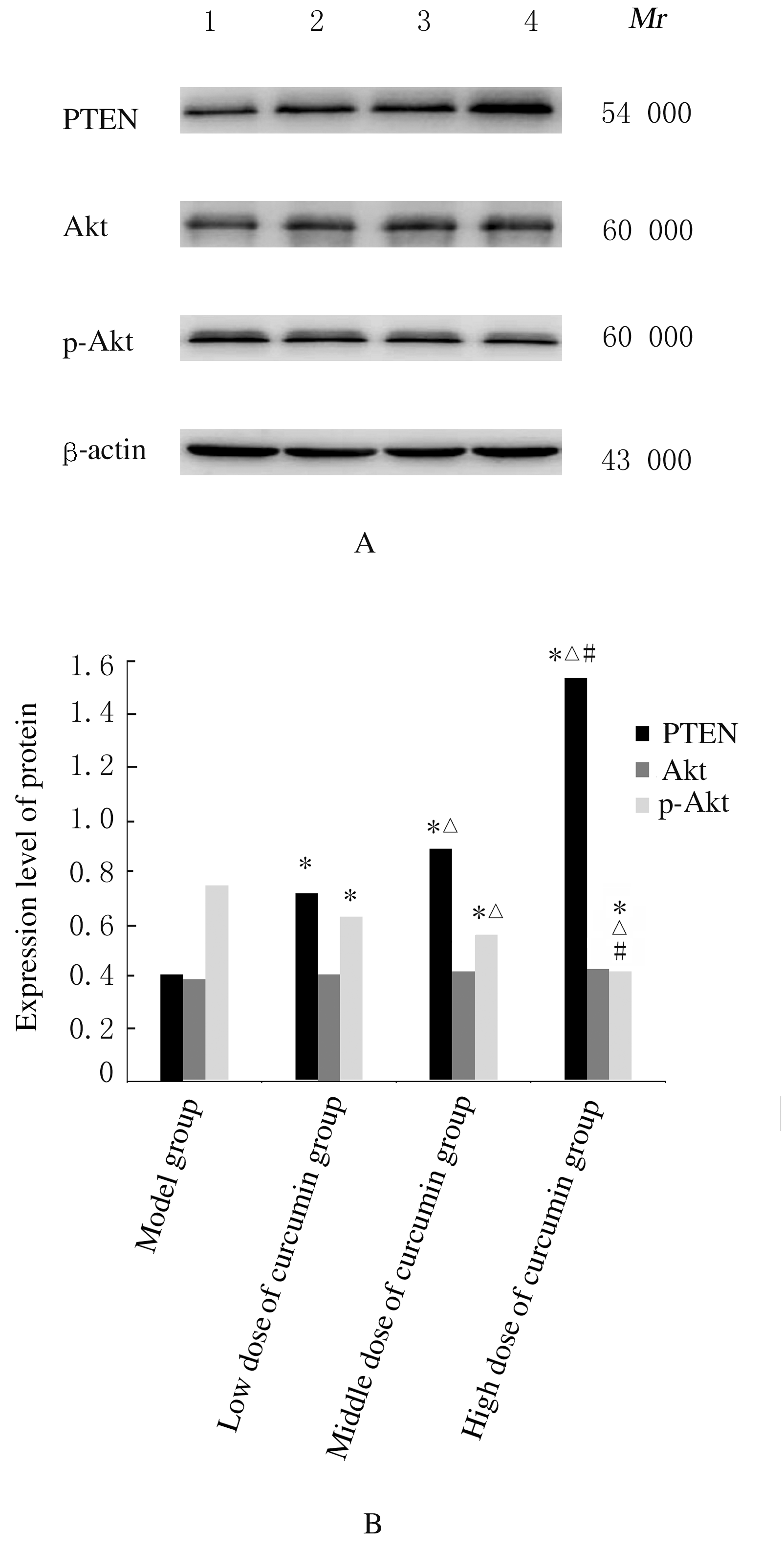
摘要: 探讨姜黄素对结直肠癌小鼠肿瘤生长及第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶和张力蛋白的同源基因/磷酯酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PTEN/PI3K/Akt)信号通路的影响,阐明姜黄素对结直肠癌的可能作用机制。 60只小鼠随机分为模型组、低剂量姜黄素组、中剂量姜黄素组和高剂量姜黄素组,每组15只。接种结直肠癌LOVO细胞建立小鼠结直肠癌模型,低、中和高剂量姜黄素组分别给予25、50和100 mg·kg-1姜黄素灌胃,共4周。末次灌胃后24 h,检测各组小鼠肿瘤体积、肿瘤质量和抑瘤率,免疫组织化学染色检测各组小鼠肿瘤组织中增殖细胞核抗原(PCNA)蛋白表达,并计算细胞增殖指数(PI),HE染色观察各组小鼠肿瘤组织病理形态表现,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肿瘤组织中人髓细胞增生原癌基因c-Myc、半胱氨酸蛋白酶3(caspase3)、PTEN、Akt和磷酸化Akt(p-Akt)蛋白表达水平。 各组小鼠肿瘤体积、肿瘤质量、抑瘤率、肿瘤组织PI值及肿瘤组织中c-Myc、caspase3、PTEN和p-Akt蛋白表达水平比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,各剂量姜黄素组小鼠肿瘤体积和肿瘤质量均明显降低(P<0.05),抑瘤率增加(P<0.05),肿瘤组织PI值降低(P<0.05),肿瘤组织中c-Myc和p-Akt蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),caspase3和PTEN蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。免疫组织化学染色,与模型组比较,各剂量姜黄素组小鼠肿瘤组织中PCNA阳性细胞数明显减少。HE染色,模型组小鼠肿瘤组织中细胞排列紊乱,核质比例增加,核染色深;与模型组比较,各剂量姜黄素组小鼠肿瘤组织中细胞排列相对整齐,核质比例下降,核染色浅。姜黄素对结直肠癌肿瘤体积、肿瘤质量、抑瘤率、肿瘤组织PI值及肿瘤组织中c-Myc、caspase3、PTEN和p-Akt蛋白表达的影响呈剂量依赖性,不同剂量姜黄素组间上述各指标比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 姜黄素可抑制结直肠癌小鼠肿瘤生长,其机制可能与姜黄素抑制PTEN/PI3K/Akt信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R735.3