吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 330-337.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210211
肌肽对脂多糖诱导星形胶质细胞炎症因子释放的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.锦州医科大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,辽宁 锦州 121001
2.锦州卫生学校外科教研室,辽宁 锦州 121001
Inhibitory effect of carnosine on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release in astrocytes and its mechanism
Xue BAI1,Lu YU1,Wenqiang YANG1,Xin HE1,Xinsheng YANG2,Jing YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,College of Basic Medical Sciences,Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121001,China
2.Department of Surgery,Jinzhou Health School,Jinzhou 121001,China
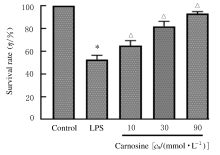
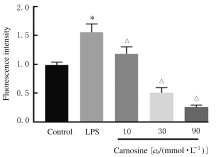
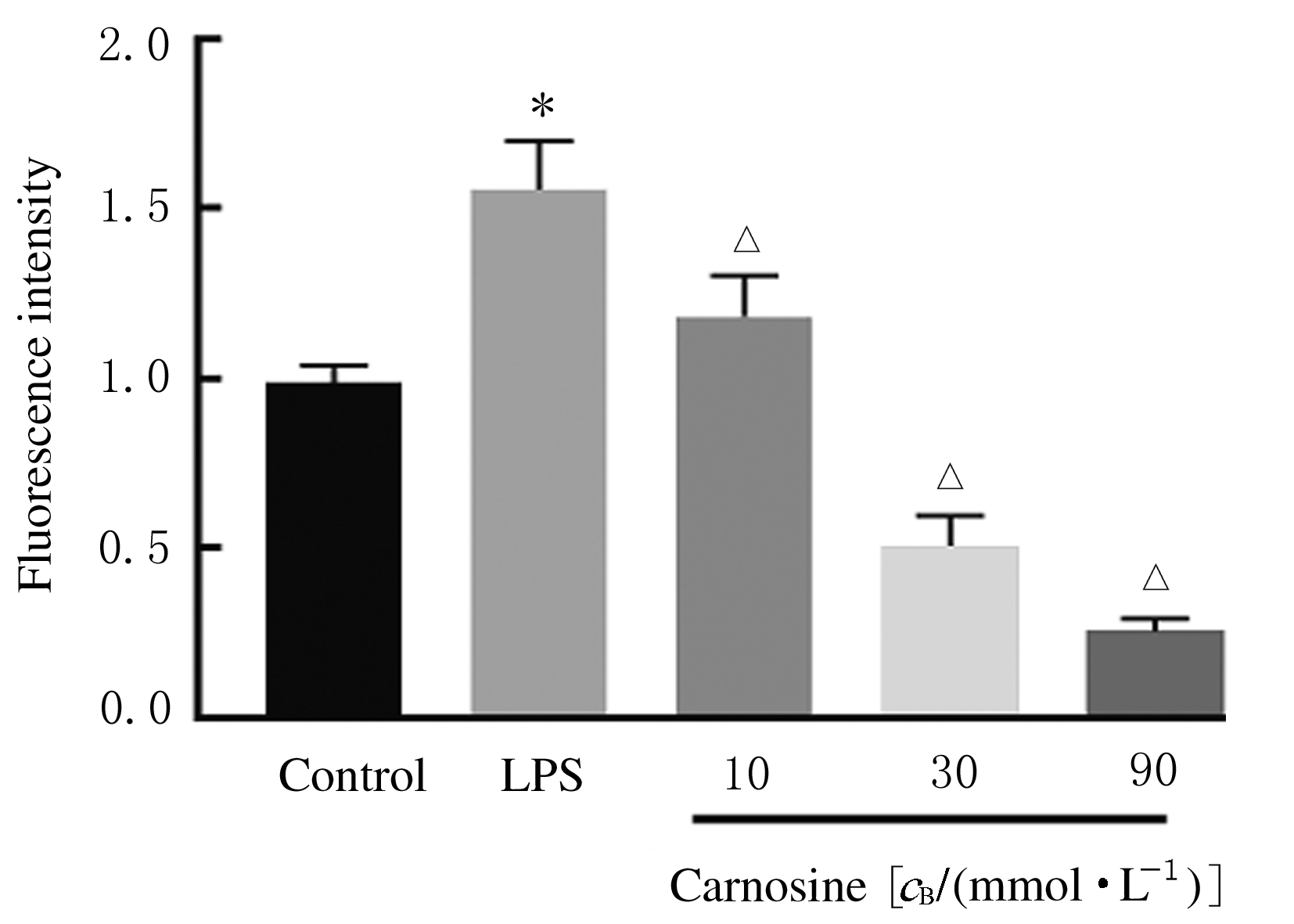
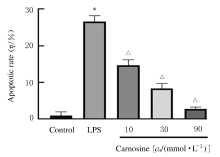
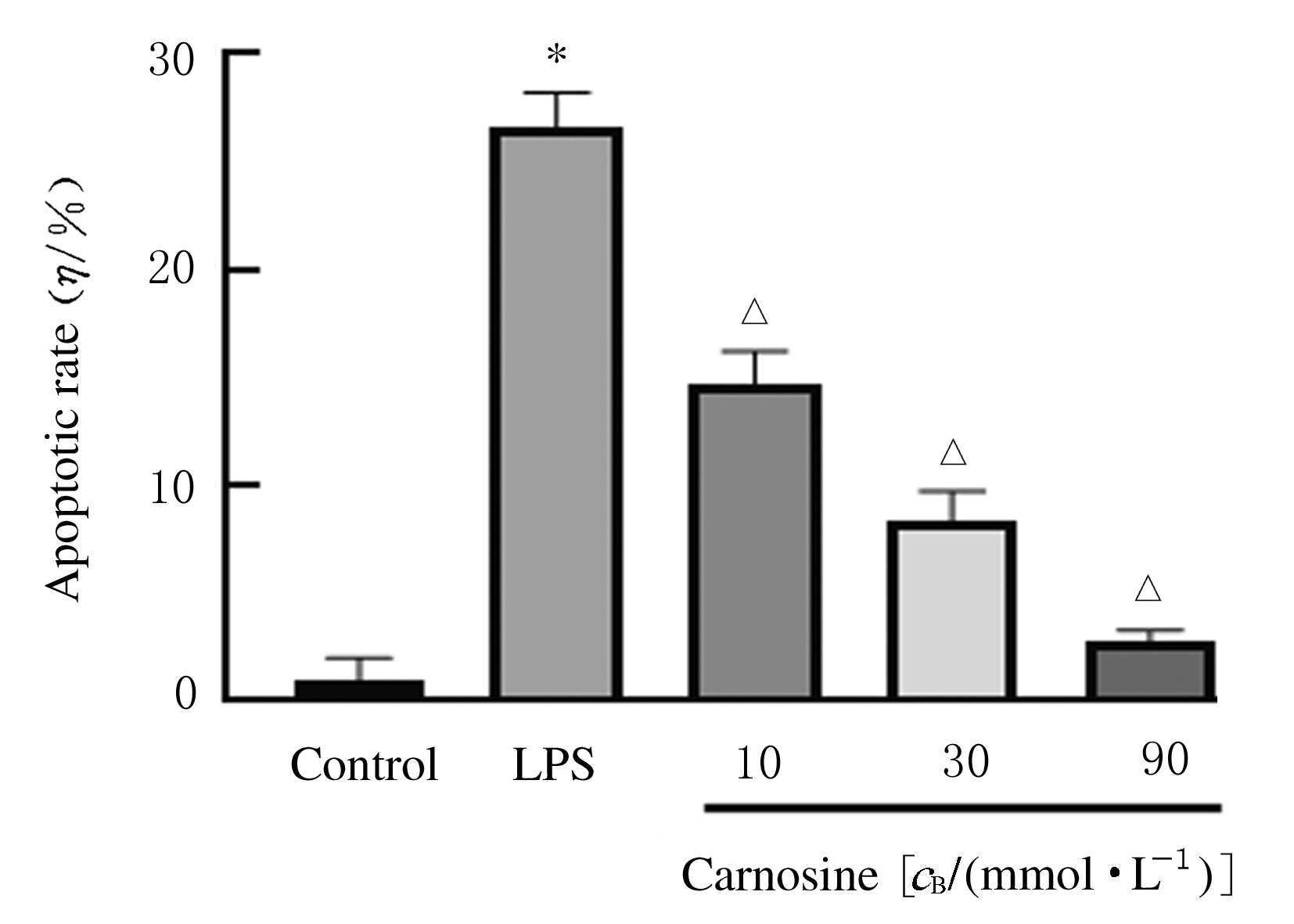
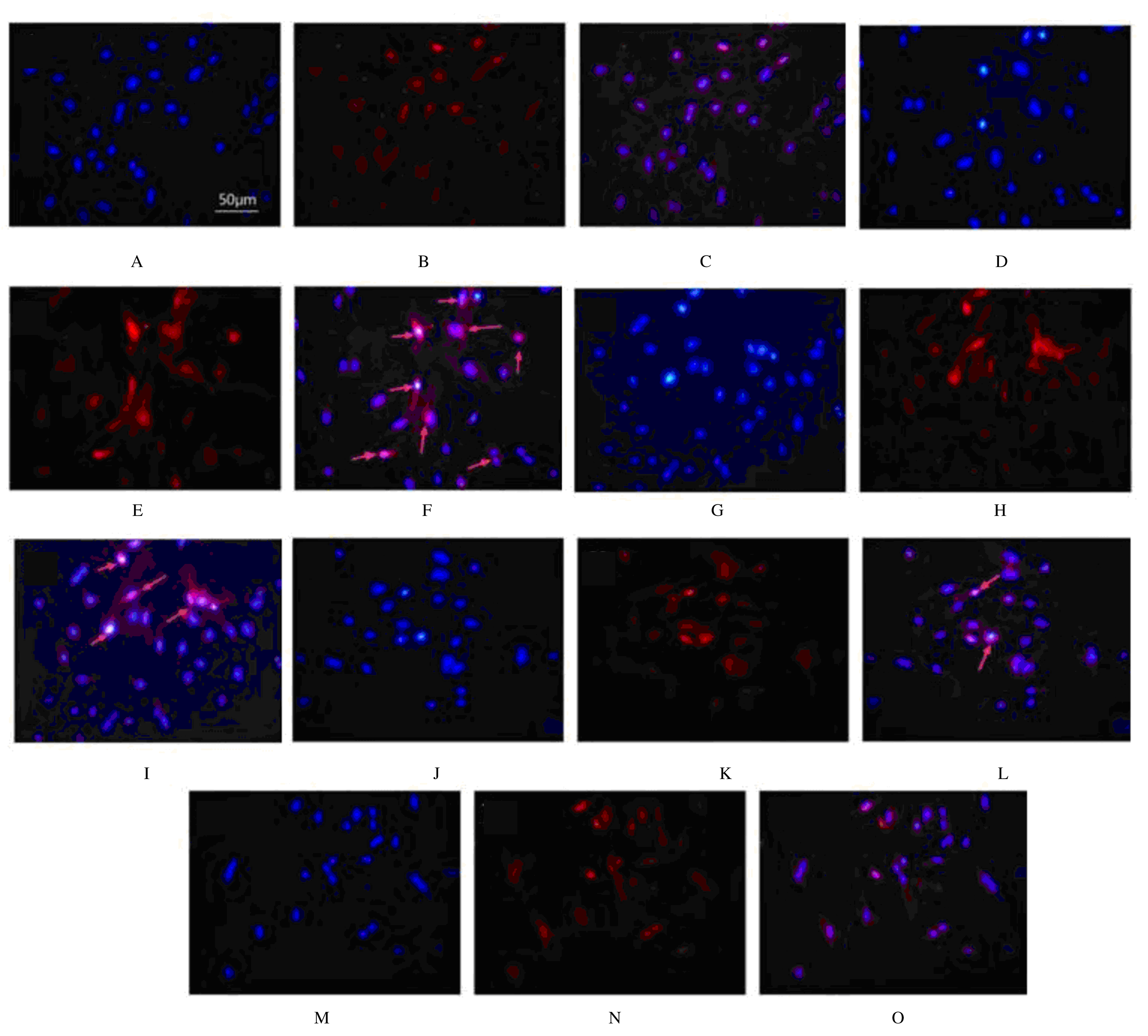
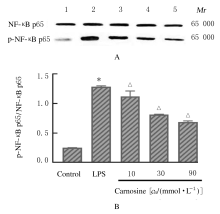
摘要: 探讨肌肽对脂多糖(LPS)诱导的星形胶质细胞(AS)炎症因子释放的影响,初步阐明其作用机制。 体外培养新生大鼠大脑皮质AS并纯化,随机分为对照组、LPS组和LPS+肌肽组(10、30和90 mmol·L-1肌肽)。对照组只加入完全培养基,LPS组培养基中加入终浓度为1 mg·L-1 LPS,体外刺激细胞 24 h构建炎症损伤模型,LPS+肌肽组培养基中预先分别加入10、30和90 mmol·L-1肌肽,培养1 h后再加入终浓度为1 mg·L-1 的LPS。MTT法检测各组AS存活率,ELISA法检测各组AS培养液中白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,DCFH-DA探针法检测各组AS中活性氧(ROS)水平,Hoechst 33258荧光染色法检测各组AS凋亡率,免疫荧光染色法测定各组AS中磷酸化核转录因子κB p65(p-NF-κB p65)蛋白表达情况和p-NF-κB p65阳性细胞数,采用Western blotting 法检测各组AS中p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,LPS组AS存活率明显降低(P<0.05),AS培养液中IL-1β和TNF-α水平升高(P<0.05),AS中ROS水平、AS凋亡率和p-NF-κB p65阳性细胞数均明显升高(P<0.05),AS中p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。与LPS组比较,LPS+肌肽组AS存活率明显升高(P<0.05),AS培养液中IL-1β和TNF-α水平降低(P<0.05),AS中ROS水平、AS凋亡率和p-NF-κB p65阳性细胞数均明显降低(P<0.05),AS中p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 肌肽可抑制LPS引起的AS中炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α释放,其机制可能与肌肽抑制LPS诱导AS中ROS生成、进而抑制NF-κB p65激活有关。
中图分类号:
- Q78