吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 943-950.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210417
薯蓣皂苷对滑膜炎大鼠症状的改善作用和对TLR2-NF-κB信号通路的调节作用及其机制
- 河南大学淮河医院骨科,河南 开封 475001
Improvement effect of diosgenin on symptoms of synovitis rats and its reglatory effect on TLR2-NF-κB signaling pathway and mechanism
Haojie WU,Minghui ZHANG( ),Chengzhi HONG
),Chengzhi HONG
- Department of Orthopedics,Huaihe Hospital,Henan University,Kaifeng 475001,China
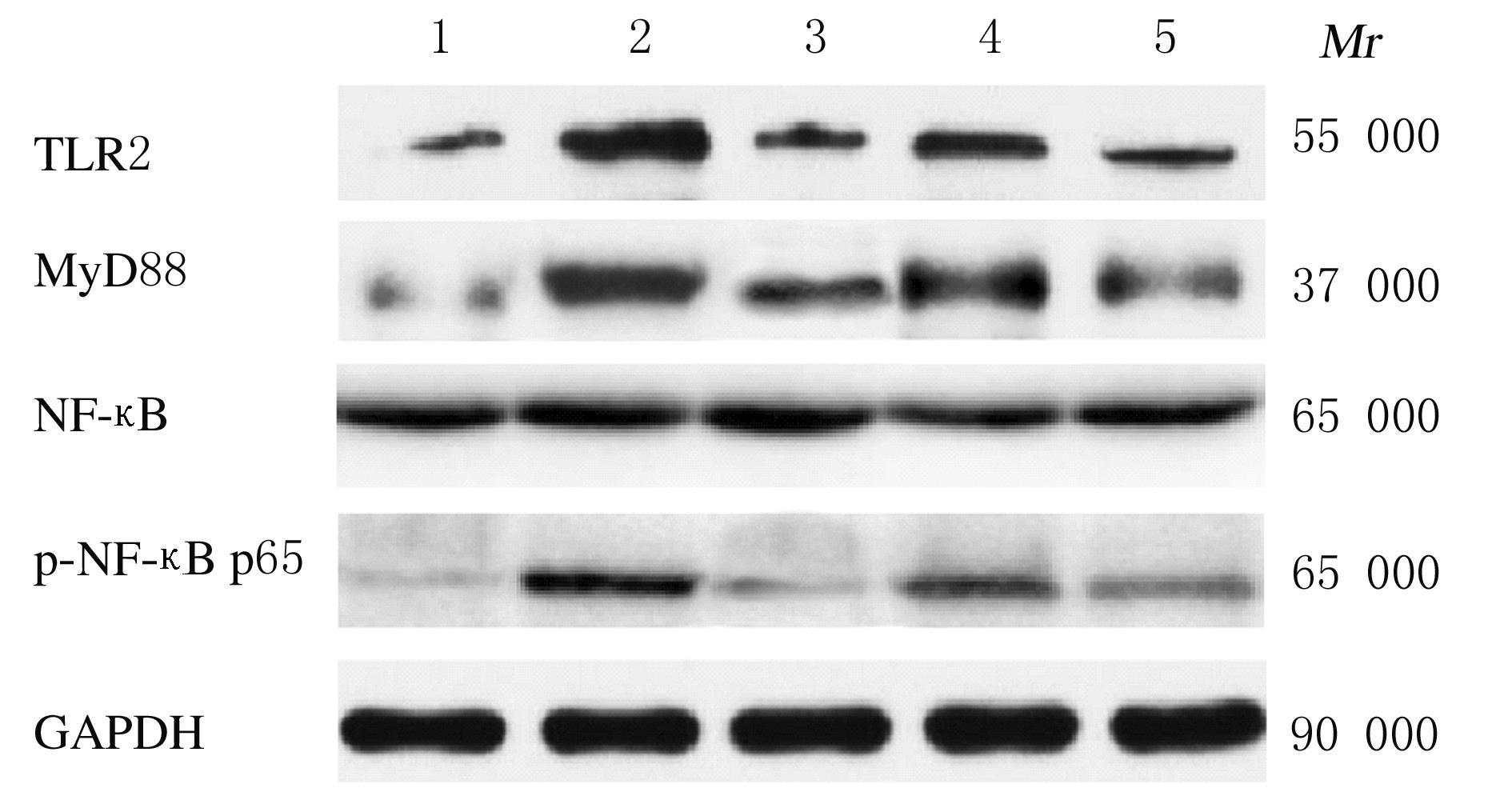
摘要: 探讨薯蓣皂苷对滑膜炎大鼠症状的改善作用及对Toll样受体2(TLR2)-核转录因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路的影响,阐明薯蓣皂苷治疗滑膜炎的可能机制。 通过皮内注射弗氏完全佐剂的方法建立滑膜炎大鼠模型,随机分为模型组10只、阳性药组(吲哚美辛10 mg·kg-1)11只、低剂量薯蓣皂苷(60 mg·kg-1)组12只和高剂量薯蓣皂苷(120 mg·kg-1)组12只,另取10只健康SD大鼠设为对照组。采用屈关节疼痛实验评分法和水容积法评价干预后第3、7、14和21天各组大鼠关节疼痛和肿胀情况,酶联免疫吸附测定法检测大鼠滑膜组织中肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)水平,HE染色观察各组大鼠滑膜组织病理形态表现,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠滑膜组织中TLR2、髓样分化因子88(MyD88)、NF-κB和磷酸化NF-κB(p-NF-κB )p65蛋白表达水平。 与对照组比较,各时间点模型组、阳性药组、低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠疼痛评分明显升高(P<0.05),足趾肿胀程度明显增加(P<0.05),关节滑膜组织中TNF-α和IL-1β水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,各时间点阳性药组、低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组疼痛评分明显降低(P<0.05),足趾肿胀程度明显降低(P<0.05),关节滑膜组织中TNF-α和IL-1β水平明显降低(P<0.05);与阳性药组比较,各时间点低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量大鼠薯蓣皂苷组疼痛评分明显升高(P<0.05),足趾肿胀程度明显增加(P<0.05),关节滑膜组织中TNF-α和IL-1β水平明显升高(P<0.05);与低剂量薯蓣皂苷组比较,各时间点高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠疼痛评分明显降低(P<0.05),足趾肿胀程度明显降低(P<0.05),关节滑膜组织中TNF-α和IL-1β水平明显降低(P<0.05)。HE染色,对照组大鼠滑膜组织形态正常,细胞排列整齐,无水肿、充血和增生,未见炎症细胞浸润;模型组大鼠滑膜组织水肿、充血严重,滑膜细胞排列紊乱并大量增生,大量炎症细胞浸润;低剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织充血、水肿减轻,细胞增生略有减少;阳性药组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织轻度水肿、充血,细胞排列相对整齐,少量炎症细胞浸润,少见增生。与对照组比较,模型组、阳性药组、低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织中TLR2、MyD88和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,阳性药组、低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织中TLR2、MyD88和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05);与阳性药组比较,低剂量薯蓣皂苷组和高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织中TLR2、MyD88和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05);与低剂量薯蓣皂苷组比较,高剂量薯蓣皂苷组大鼠滑膜组织中TLR2、MyD88和p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。 薯蓣皂苷可能通过抑制TLR2-NF-κB信号通路改善滑膜炎大鼠症状。
中图分类号:
- R285.5