吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 600-605.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220307
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
黄芩素对大鼠神经病理痛的镇痛作用及其机制
- 1.陕西中医药大学生理学教研室, 陕西 咸阳 712046
2.陕西省针药结合重点实验室, 陕西 咸阳 712046
Analgesic effect of baicalein on neuropathic pain of rats and its mechanism
Xiaohua LIU1( ),Bingying FANG1,Man HAN1,Haifa QIAO2,Yuanwang YU1
),Bingying FANG1,Man HAN1,Haifa QIAO2,Yuanwang YU1
- 1.Department of Physiology, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712046, China
2.Key Laboratory of Acupuncture and Drug Combination, Shaanxi Province, Xianyang 712046, China
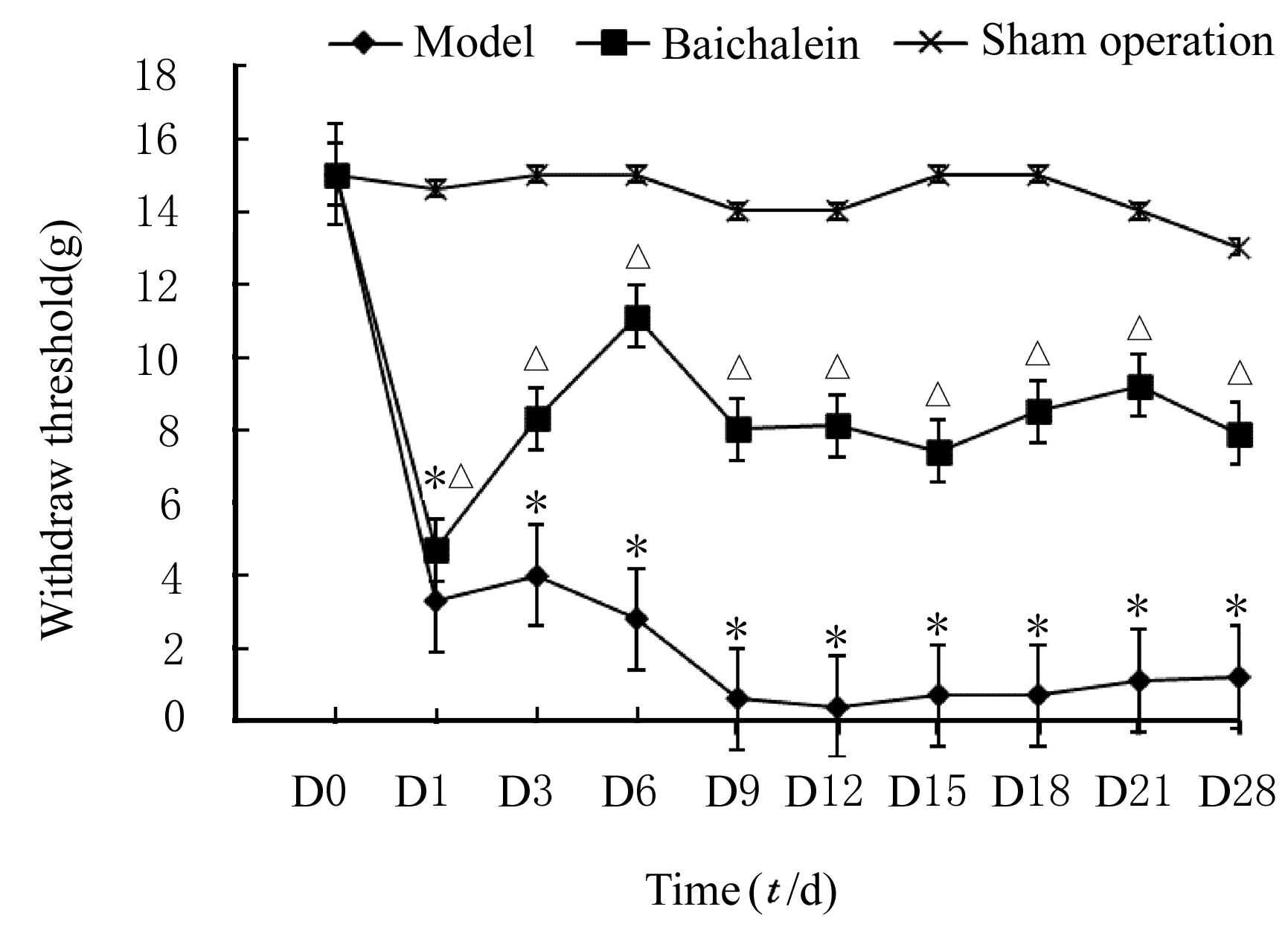
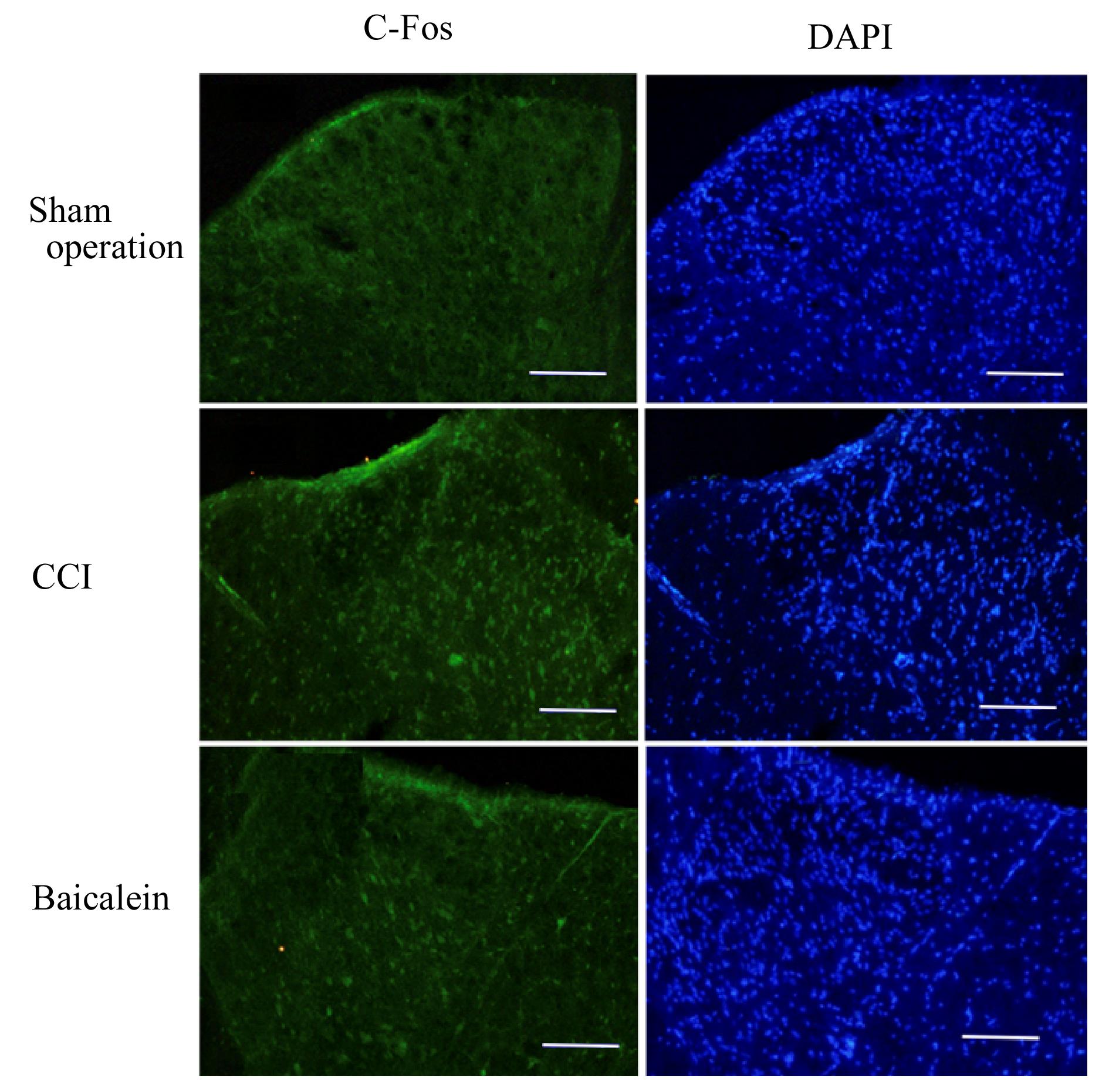
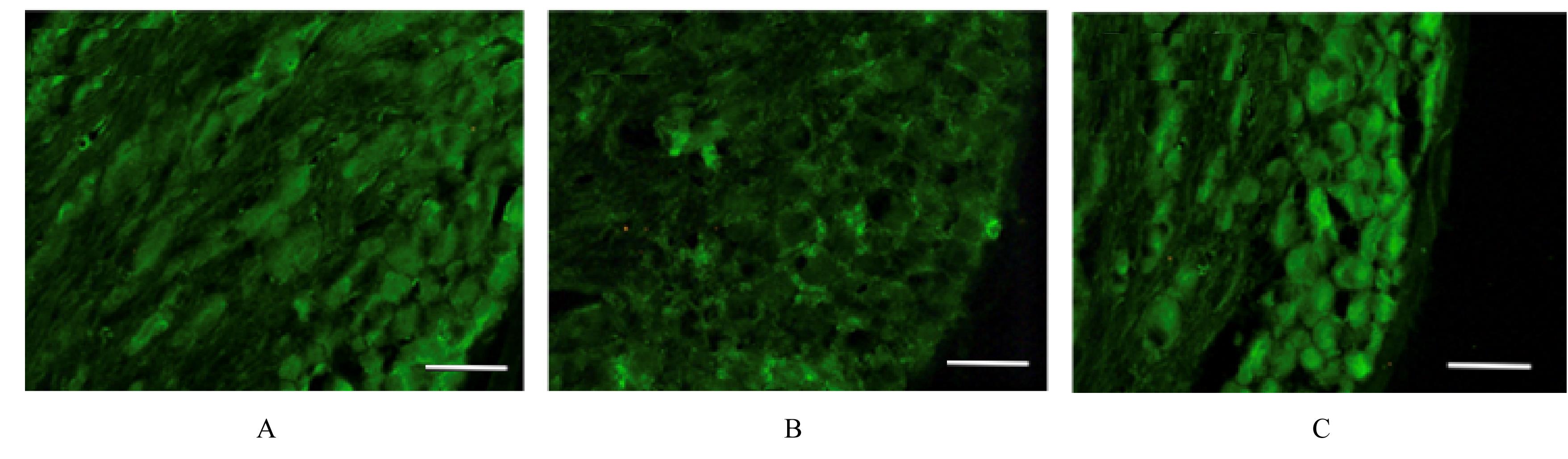
摘要: 观察黄芩素对大鼠坐骨神经慢性压迫引起痛行为的抑制作用及初级感觉神经元中胶质细胞源性神经营养因子(GDNF)表达的调控作用,阐明黄芩素对神经病理痛的镇痛机制。 48只健康雄性SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和黄芩素组,每组16只。各组大鼠麻醉后,假手术组大鼠仅暴露坐骨神经,模型组和黄芩素组大鼠行坐骨神经慢性缩窄手术建立大鼠慢性缩窄性神经损伤(CCI)模型。造模成功后黄芩素组大鼠腹腔连续注射黄芩素7 d。手术前后不同时间点分别检测各组大鼠患侧机械缩足反射阈值(MWT)和热缩足反射潜伏期(TWL)以评价神经损伤引起的痛行为。第11天,每组选取6只大鼠,免疫荧光染色检测各组大鼠脊髓背角组织中c-Fos阳性细胞数;第28天检测各组其余大鼠背根神经节(DRG)中GDNF荧光强度。 手术前各组大鼠MWT和TWL比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与假手术组比较,术后1 d模型组和黄芩素组大鼠MWT 和TWL 明显降低(P<0.05),给药后3 d黄芩素组大鼠MWT和TWL升高(P>0.05);与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脊髓背角组织中c-Fos阳性细胞数升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,黄芩素组大鼠脊髓背角组织中c-Fos阳性细胞数降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠DRG中GDNF荧光强度降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,黄芩素组大鼠DRG中GDNF荧光强度升高(P<0.05)。 黄芩素对大鼠神经病理痛具有镇痛作用。初级感觉神经元中GDNF参与坐骨神经损伤引起的神经病理痛,黄芩素对神经病理痛的镇痛作用可能与其调控GDNF的表达有关。
中图分类号:
- R741.02