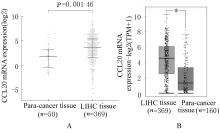
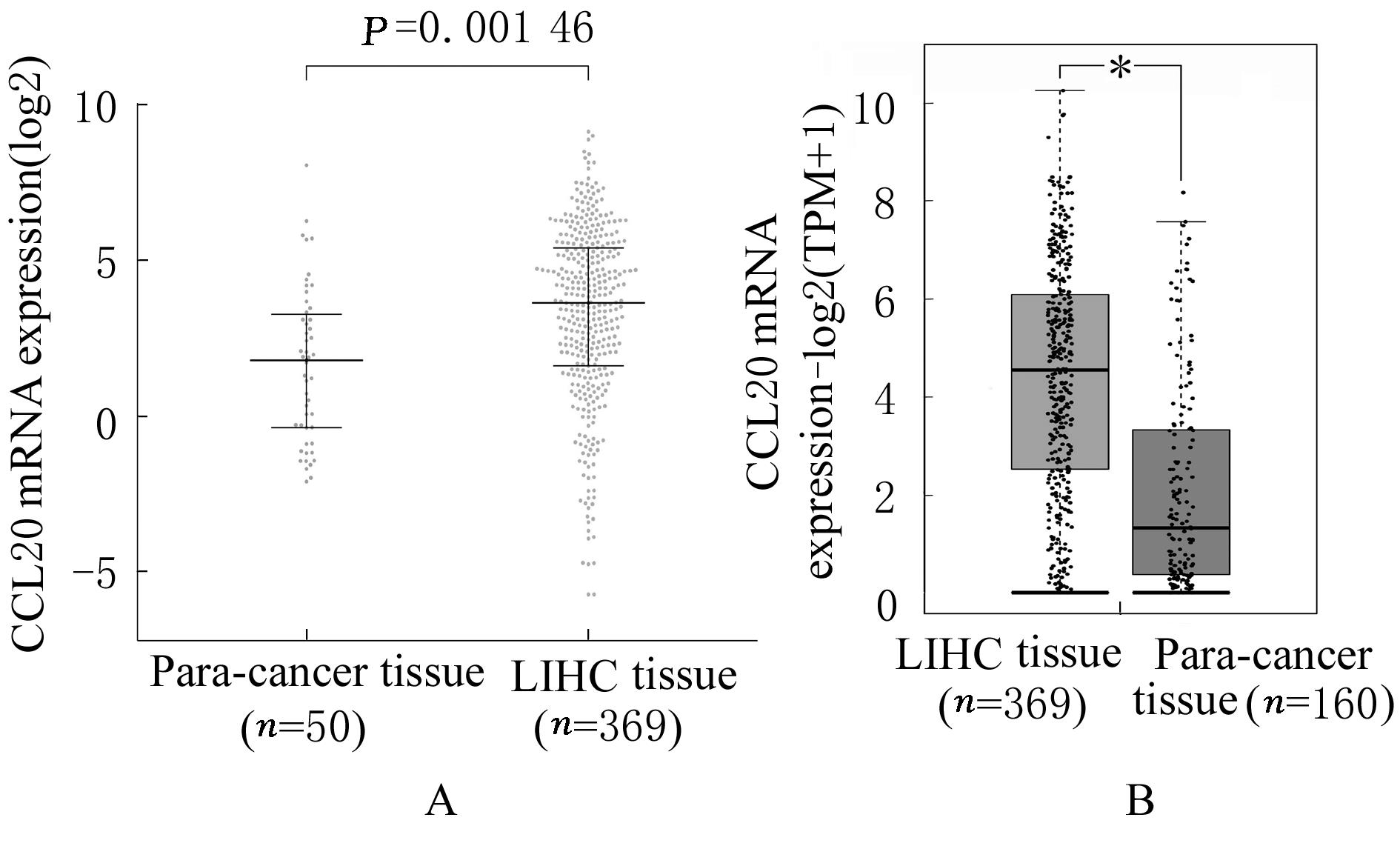
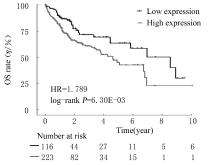
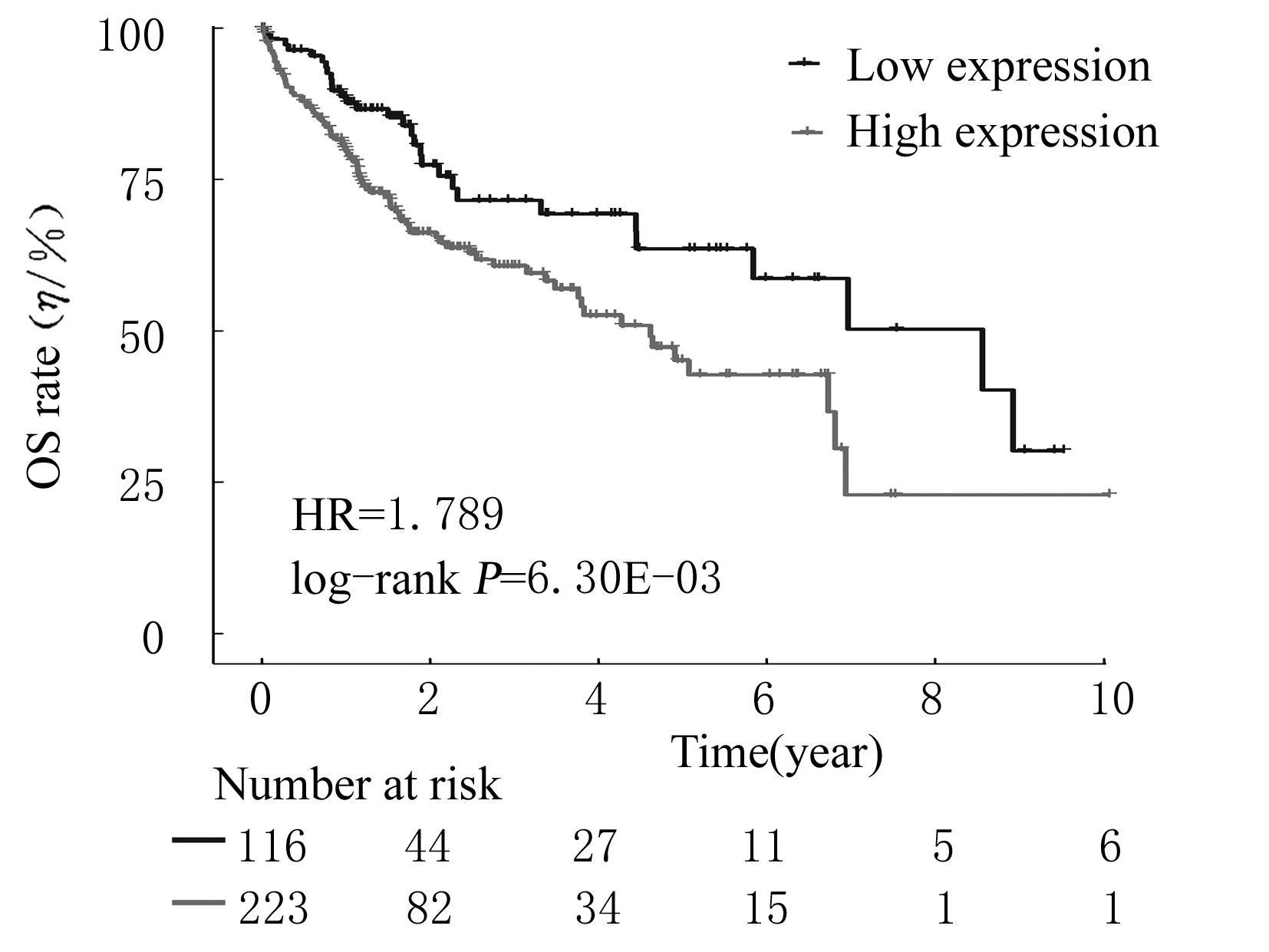
| 1 |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.
|
| 2 |
BARBARIC J, SEKERIJA M, AGIUS D, et al. Disparities in melanoma incidence and mortality in South-Eastern Europe: increasing incidence and divergent mortality patterns. Is progress around the corner? [J]. Eur J Cancer, 2016, 55: 47-55.
|
| 3 |
HUANG F, GENG X P. Chemokines and hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16(15): 1832-1836.
|
| 4 |
DING X J, WANG K X, WANG H, et al. High expression of CCL20 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2012,16(4): 828-836.
|
| 5 |
LEE A Y, PHAN T K, HULETT M D, et al. The relationship between CCR6 and its binding partners: does the CCR6-CCL20 axis have to be extended? [J]. Cytokine, 2015, 72(1): 97-101.
|
| 6 |
WILLIAMS I R. CCR6 and CCL20: partners in intestinal immunity and lymphorganogenesis[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2006, 1072: 52-61.
|
| 7 |
ACOSTA-RODRIGUEZ E V, RIVINO L, GEGINAT J, et al. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells[J]. Nat Immunol, 2007, 8(6): 639-646.
|
| 8 |
GUO W B, LI H, LIU H, et al. DEPDC1 drives hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis by regulating the CCL20/CCR6 signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 42(3): 1075-1089.
|
| 9 |
WANG Z N, JENSEN M A, ZENKLUSEN J C. A practical guide to the cancer genome atlas(TCGA)[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2016, 1418: 111-141.
|
| 10 |
TANG Z F, LI C W, KANG B X, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(W1): W98-W102.
|
| 11 |
SHEN Y, PENG X W, SHEN C L. Identification and validation of immune-related lncRNA prognostic signature for breast cancer[J]. Genomics,2020,112(3): 2640-2646.
|
| 12 |
WU M W, LI X B, ZHANG T P, et al. Identification of a nine-gene signature and establishment of a prognostic nomogram predicting overall survival of pancreatic cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2019, 9: 996.
|
| 13 |
ZHANG D L, ZHOU H G, LIU J, et al. Long noncoding RNA ASB16-AS1 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioma cells[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2019, 2019: 5437531.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG Y, HONG Y K, ZHUANG D W, et al. Bladder cancer survival nomogram: development and validation of a prediction tool, using the SEER and TCGA databases[J].Medicine (Baltimore),2019,98(44): e17725.
|
| 15 |
BI K W, WEI X G, QIN X X, et al. BTK has potential to be a prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma and an indicator for tumor microenvironment remodeling: a study based on TCGA data mining[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 424.
|
| 16 |
LEE H J, LEE H Y, LEE J H, et al. Prognostic significance of biallelic loss of PTEN in clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Urol, 2014, 192(3): 940-946.
|
| 17 |
SCHOBER P, BOER C, SCHWARTE L A. Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation[J]. Anesth Analg, 2018, 126(5): 1763-1768.
|
| 18 |
BENKHEIL M, PAESHUYSE J, NEYTS J, et al. HCV-induced EGFR-ERK signaling promotes a pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic signature contributing to liver cancer pathogenesis[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2018, 155: 305-315.
|
| 19 |
BENKHEIL M, MVAN HAELE, ROSKAMS T,et al. CCL20, a direct-acting pro-angiogenic chemokine induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV): potential role in HCV-related liver cancer[J].Exp Cell Res,2018,372(2):168-177.
|
| 20 |
ANNUNZIATO F, COSMI L, SANTARLASCI V, et al. Phenotypic and functional features of human Th17 cells[J]. J Exp Med, 2007, 204(8): 1849-1861.
|
| 21 |
PICKUP M W, MOUW J K, WEAVER V M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer[J]. EMBO Rep, 2014, 15(12): 1243-1253.
|
| 22 |
张海利, 李娟芳, 李晓晴, 等. CCR6通过上皮间质转化促进结直肠癌肝转移的机制研究[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志, 2020, 47(1): 29-34.
|
| 23 |
CREMEL M, BERLIER W, HAMZEH H, et al. Characterization of CCL20 secretion by human epithelial vaginal cells: involvement in Langerhans cell precursor attraction[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2005, 78(1): 158-166.
|
| 24 |
OZAKYOL A. Global epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC epidemiology)[J]. J Gastrointest Cancer, 2017, 48(3): 238-240.
|
| 25 |
NEDOSZYTKO B, LANGE M, SOKOŁOWSKA-WOJDYŁO M, et al. The role of regulatory T cells and genes involved in their differentiation in pathogenesis of selected inflammatory and neoplastic skin diseases. Part Ⅰ:Treg properties and functions[J].Postepy Dermatol Alergol, 2017, 34(4): 285-294.
|
| 26 |
MUSCELLA A, VETRUGNO C, MARSIGLIANTE S.CCL20 promotes migration and invasiveness of human cancerous breast epithelial cells in primary culture[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2017, 56(11): 2461-2473.
|
| 27 |
KAPUR N, MIR H, CLARK III C E, et al. CCR6 expression in colon cancer is associated with advanced disease and supports epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Br J Cancer, 2016, 114(12): 1343-1351.
|
| 28 |
CAMPBELL D J, KOCH M A. Phenotypical and functional specialization of FOXP3+regulatory T cells[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 11(2): 119-130.
|
| 29 |
赵 阳, 周 林, 贺 强. CD8+调节性T细胞诱导移植免疫耐受的研究进展[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2020, 41(7): 743-745, 751.
|
| 30 |
FUJII H, ITOH Y, YAMAGUCHI K, et al. Chemokine CCL20 enhances the growth of HuH7 cells via phosphorylation of p44/42 MAPK in vitro [J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2004, 322(3):1052-1058.
|
 ),王伟群1,2(
),王伟群1,2( )
)
 ),Weiqun WANG1,2(
),Weiqun WANG1,2( )
)