吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1310-1317.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230526
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅰ类错 成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质特征分析及其临床意义
成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质特征分析及其临床意义
张惠超,刘佳,曹宇,叶素荣,余岭,许竞予,叶子桐,杨陆一( )
)
- 吉林大学口腔医院正畸科,吉林 长春 130021
Analysis on bone characteristic in infrazygomatic crest region in adult patients with different vertical skeletal patterns of skeletal classⅠmalocclusion and its clinical significance
Huichao ZHANG,Jia LIU,Yu CAO,Surong YE,Ling YU,Jingyu XU,Zitong YE,Luyi YANG( )
)
- Department of Orthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
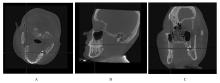
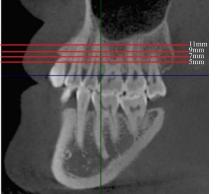
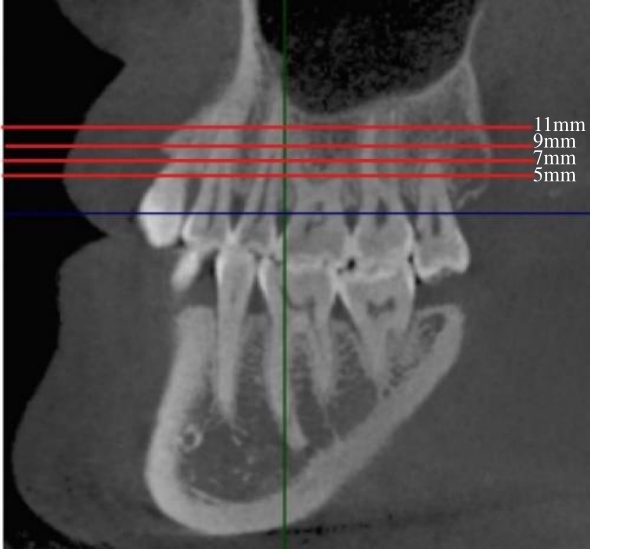
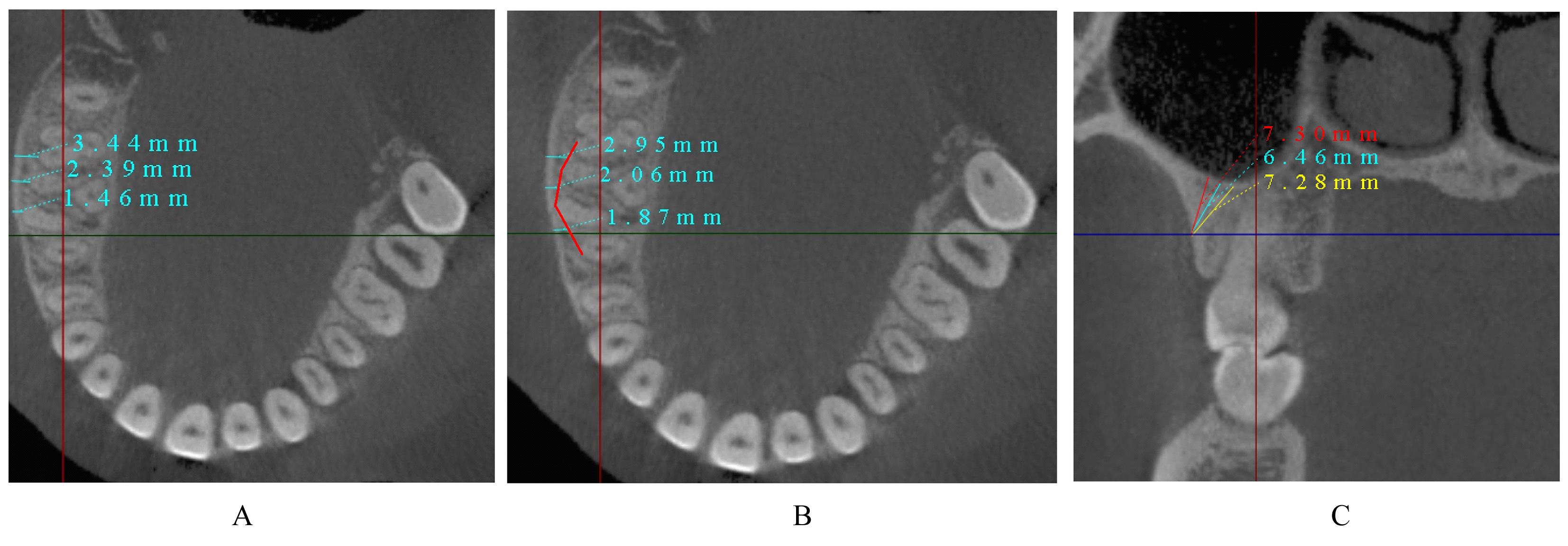
目的 采用锥形束计算机断层扫描(CBCT)评估不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅰ类错 成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质厚度差异,为正畸科医生临床治疗方案的选择提供依据。 方法 选取骨性Ⅰ类成人患者共90例,分为低角组、均角组和高角组,每组30例。采用CBCT测量不同垂直截面及近远中层面各组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度,且在颊侧牙槽骨厚度≥3 mm处以50°、60°和70°植入并测量有效骨量。 结果 在不同垂直截面上,除上颌第一磨牙近中颊根(U6mb)层面,其余层面患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度由牙槽嵴顶向根方逐渐增大(P<0.05)。在不同近远中层面上,除U6mb层面,其余层面患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度由近中向远中方向逐渐增大(P<0.05)。颊侧牙槽骨最大厚度位于上颌第二磨牙近中颊根(U7mb)距牙槽嵴顶11 mm处;最小厚度位于U6mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm处。不同垂直骨面型患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),低角组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度大于均角组和高角组(P<0.05), 均角组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度大于高角组(P<0.05)。在低角组患者中,上颌第一磨牙远中颊根与上颌第二磨牙近中颊根间(U6db-U7mb)距牙槽嵴顶7 mm、U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm和9 mm、U6mb-U6db距牙槽嵴顶11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),于U6db-U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm和U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm以3种角度植入、在U7mb距牙槽嵴顶9 mm处以70°植入时骨质厚度≥6 mm。在均角组患者中,U6db-U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm、U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm和11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),在U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶7 mm以3种角度植入、在U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm以70°植入时骨质厚度≥6 mm。在高角组患者中,U6db-U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶11 mm和U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。各层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度排序为70°>50°>60°。 结论 不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅰ类错
成人患者颧牙槽嵴区骨质厚度差异,为正畸科医生临床治疗方案的选择提供依据。 方法 选取骨性Ⅰ类成人患者共90例,分为低角组、均角组和高角组,每组30例。采用CBCT测量不同垂直截面及近远中层面各组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度,且在颊侧牙槽骨厚度≥3 mm处以50°、60°和70°植入并测量有效骨量。 结果 在不同垂直截面上,除上颌第一磨牙近中颊根(U6mb)层面,其余层面患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度由牙槽嵴顶向根方逐渐增大(P<0.05)。在不同近远中层面上,除U6mb层面,其余层面患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度由近中向远中方向逐渐增大(P<0.05)。颊侧牙槽骨最大厚度位于上颌第二磨牙近中颊根(U7mb)距牙槽嵴顶11 mm处;最小厚度位于U6mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm处。不同垂直骨面型患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),低角组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度大于均角组和高角组(P<0.05), 均角组患者颊侧牙槽骨厚度大于高角组(P<0.05)。在低角组患者中,上颌第一磨牙远中颊根与上颌第二磨牙近中颊根间(U6db-U7mb)距牙槽嵴顶7 mm、U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm和9 mm、U6mb-U6db距牙槽嵴顶11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),于U6db-U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm和U7mb距牙槽嵴顶7 mm以3种角度植入、在U7mb距牙槽嵴顶9 mm处以70°植入时骨质厚度≥6 mm。在均角组患者中,U6db-U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm、U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm和11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),在U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶7 mm以3种角度植入、在U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶9 mm以70°植入时骨质厚度≥6 mm。在高角组患者中,U6db-U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶11 mm和U7mb 距牙槽嵴顶11 mm层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。各层面以3种角度植入的骨质厚度排序为70°>50°>60°。 结论 不同垂直骨面型骨性Ⅰ类错 成人患者颧牙槽嵴区颊侧牙槽骨厚度有差异,低角组患者可选择的植入位点更多,高角组患者易出现上颌窦穿孔的情况,临床上在此处植入种植钉和设计正畸方案时应将垂直骨面型纳入考虑范围。
成人患者颧牙槽嵴区颊侧牙槽骨厚度有差异,低角组患者可选择的植入位点更多,高角组患者易出现上颌窦穿孔的情况,临床上在此处植入种植钉和设计正畸方案时应将垂直骨面型纳入考虑范围。
中图分类号:
- R783.5
 )患者上颌尖牙冠根角及周围骨结构的锥形束CT测量[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2023,58(4):568-572.
)患者上颌尖牙冠根角及周围骨结构的锥形束CT测量[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2023,58(4):568-572.