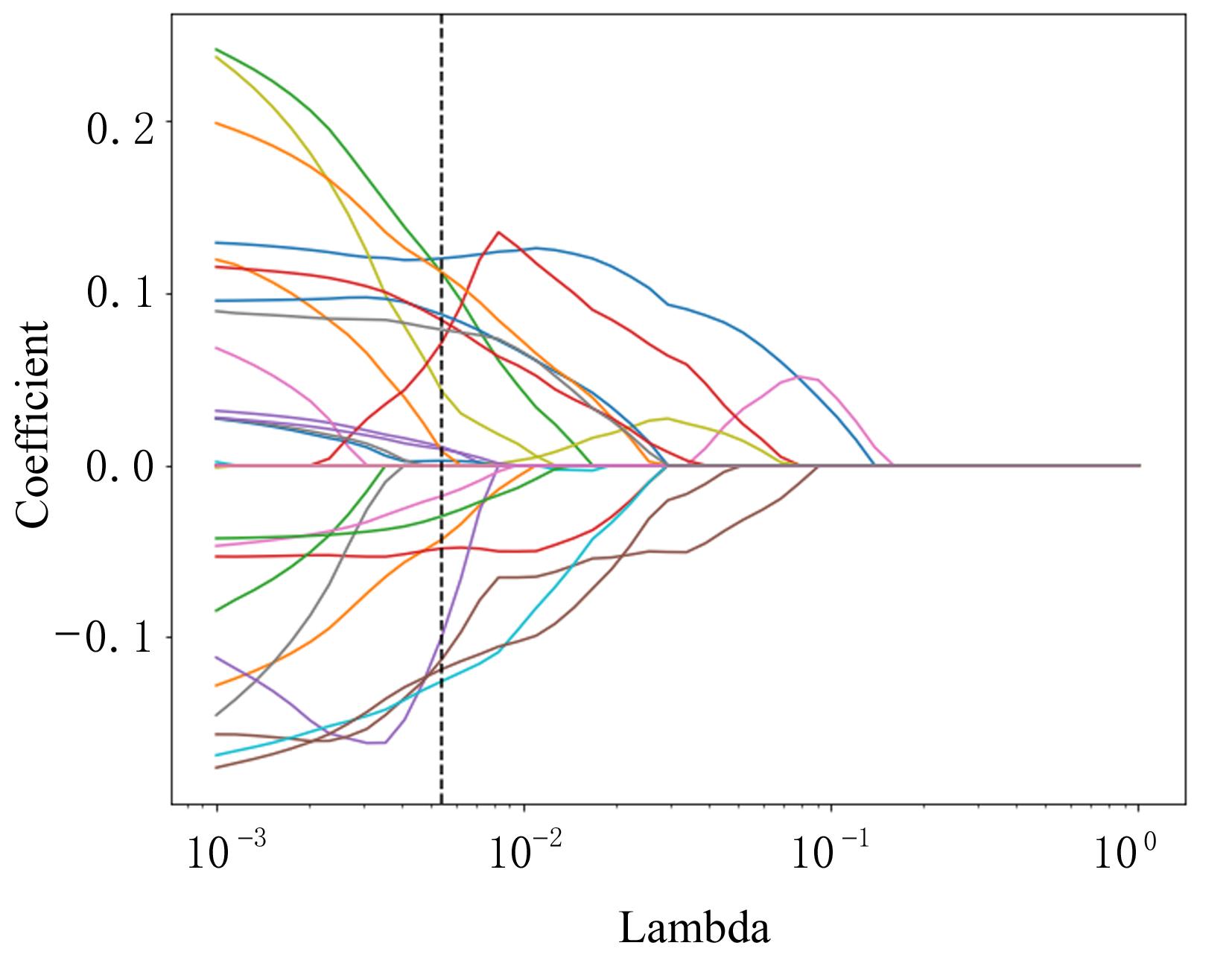
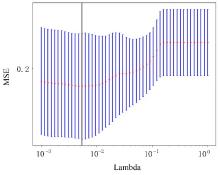
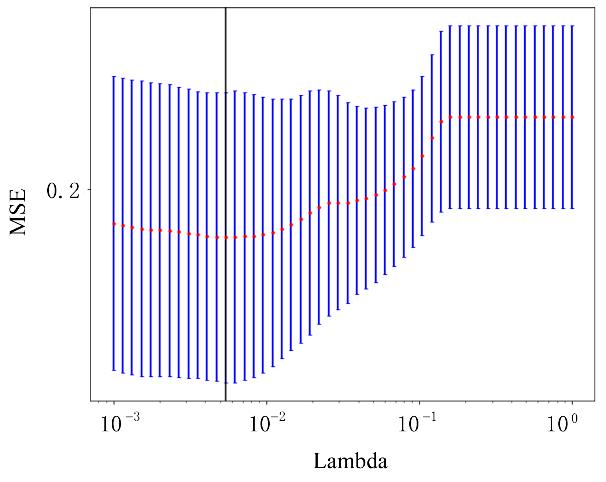
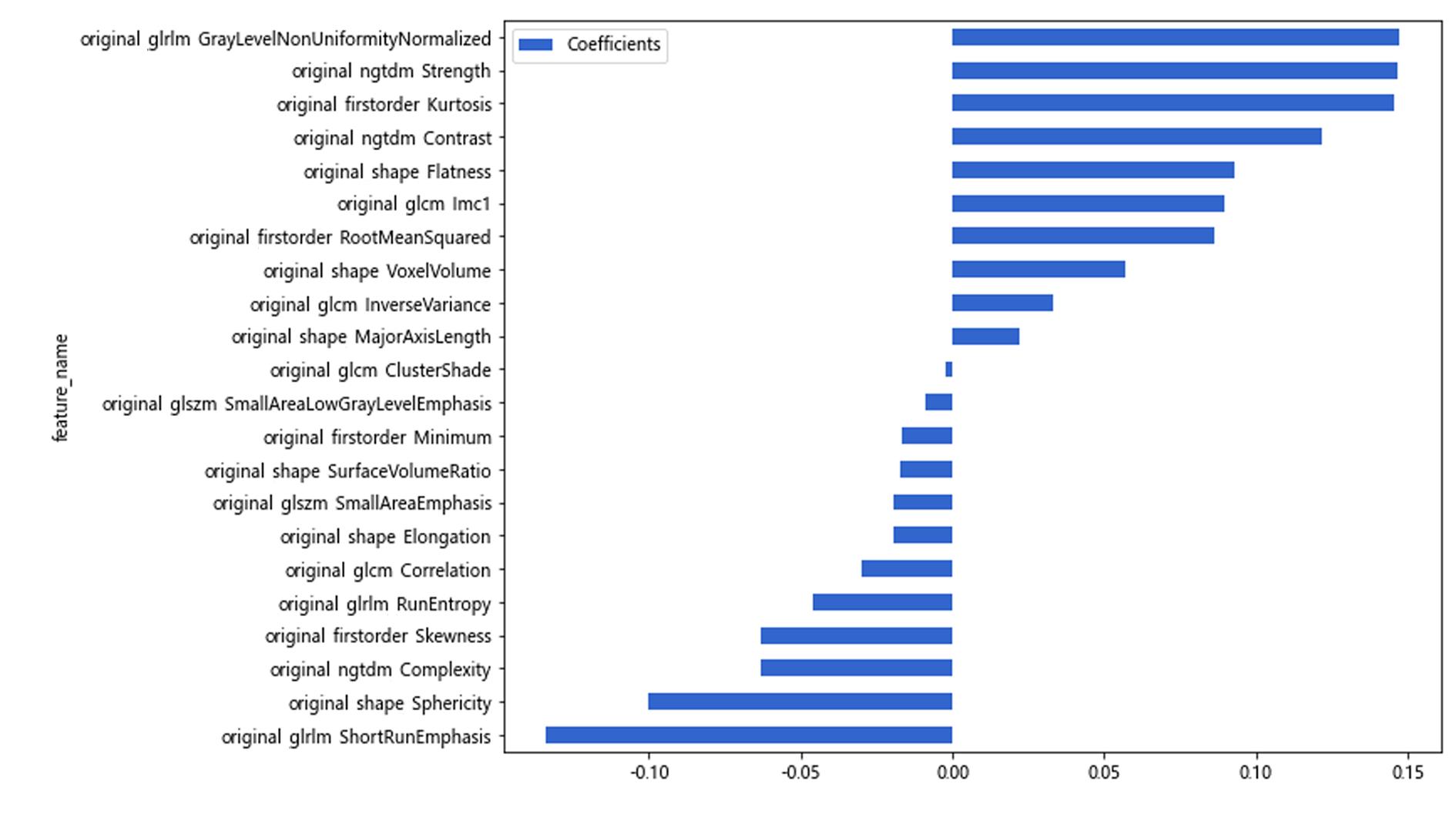
| 1 |
中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-682.
|
| 2 |
CHENG N T, KIM A S. Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke within 3 hours versus between 3 and 4.5 hours of symptom onset[J]. Neurohospitalist, 2015, 5(3): 101-109.
|
| 3 |
JAUCH E C, SAVER J L, ADAMS H P J R, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J]. Stroke, 2013, 44(3): 870-947.
|
| 4 |
霍晓川, 高 峰. 急性缺血性卒中血管内治疗中国指南2018[J]. 中国卒中杂志, 2018, 13(7): 706-729.
|
| 5 |
CAMPBELL B C V, MA H, RINGLEB P A, et al. Extending thrombolysis to 4·5-9 h and wake-up stroke using perfusion imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10193): 139-147.
|
| 6 |
THOMALLA G, BOUTITIE F, FIEBACH J B,et al. Stroke with unknown time of symptom onset: baseline clinical and magnetic resonance imaging data of the first thousand patients in WAKE-UP (efficacy and safety of MRI-based thrombolysis in wake-up stroke:a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial)[J]. Stroke, 2017, 48(3): 770-773.
|
| 7 |
李昊朋. 基于机器学习方法的智能机器人探究[J]. 通讯世界, 2019, 26(4): 241-242.
|
| 8 |
韩小伟, 李 茗, 张 冰. 人工智能在脑卒中神经影像中的应用[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2021, 12(5): 749-754.
|
| 9 |
傅 璠, 卢 洁. 人工智能在缺血性脑卒中影像的研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2020, 22(10): 1110-1112.
|
| 10 |
HO K C, SPEIER W, ZHANG H Y, et al. A machine learning approach for classifying ischemic stroke onset time from imaging[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2019, 38(7): 1666-1676.
|
| 11 |
LEE H, LEE E J, HAM S, et al. Machine learning approach to identify stroke within 4.5 hours[J]. Stroke, 2020, 51(3): 860-866.
|
| 12 |
董建民, 刘建新. 基于PyRadiomics的医疗影像纹理获取原型系统集成[J]. 软件导刊, 2020, 19(7): 223-226.
|
| 13 |
王俊秀. 基于影像组学和机器学习的脑部胶质瘤分级模型研究[J]. 软件工程, 2022, 25(2): 22-25.
|
| 14 |
史灵雪. 多参数MR影像组学特征对腮腺多形性腺瘤及腺淋巴瘤诊断价值的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.
|
| 15 |
杨晋芳. 基于支持向量回归的煤粉工业锅炉烟气氧含量预测[J]. 煤质技术, 2021, 36(4): 24-29.
|
| 16 |
宋德胜, 刘媛媛, 李长平, 等. 如何正确运用t检验: 相关系数与0比较t检验及SAS实现[J]. 四川精神卫生, 2020, 33(4): 312-316.
|
| 17 |
王 璐, 孙聚波. Lasso回归方法在特征变量选择中的应用[J]. 吉林工程技术师范学院学报, 2021, 37(12): 109-112.
|
| 18 |
孙诗明. 基于概率计算的SVM研究与实现[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2020.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Q, SHENG J H, ZHANG Q, et al. Enhanced Harris Hawks optimization-based fuzzy k-nearest neighbor algorithm for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 165: 107392.
|
| 20 |
BOTHA D, STEYN M. The use of decision tree analysis for improving age estimation standards from the acetabulum[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2022, 341: 111514.
|
| 21 |
徐凌霄, 刘 俊, 韩春霞, 等. 基于机器学习的重症股骨颈骨折患者死亡风险预测模型构建和验证[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版), 2022, 43(6): 812-818.
|
| 22 |
蒋文萍, 蒋珍存, 董正心. 基于XGBoost的心力衰竭死亡风险评价模型及其应用[J]. 现代电子技术, 2022, 45(8): 155-158.
|
| 23 |
唐 淇, 李 丹, 李原吉. 基于LightGBM算法的癫痫状态识别[J]. 电子测试, 2021(22): 62-64.
|
| 24 |
许昕茼. 多模式MRI指导急性缺血性卒中患者静脉溶栓治疗的临床预后分析[D]. 长春: 长春中医药大学, 2021.
|
| 25 |
毛旖川. 颅颈动脉血栓形成时间的定量MRI研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2019.
|
| 26 |
THOMALLA G, SIMONSEN C Z, BOUTITIE F,et al.MRI-guided thrombolysis for stroke with unknown time of onset[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 379(7): 611-622.
|
| 27 |
吴迎春, 王俊梅. DWI/Flair不匹配在醒后卒中和不明发病时间卒中患者再灌注治疗中应用研究[J]. 医学综述, 2018, 24(19): 3824-3828.
|
| 28 |
EMERIAU S, SERRE I, TOUBAS O, et al. Can diffusion-weighted imaging-fluid-attenuated inversion recovery mismatch (positive diffusion-weighted imaging/negative fluid-attenuated inversion recovery) at 3 Tesla identify patients with stroke at <4.5 hours?[J]. Stroke, 2013, 44(6): 1647-1651.
|
| 29 |
郭静丽, 彭明洋, 王同兴, 等. 基于DWI和FLAIR的机器学习预测急性脑卒中发病时间的研究[J]. 磁共振成像, 2022, 13(3): 22-25.
|
| 30 |
QIU W, KUANG H L, TELEG E, et al. Machine learning for detecting early infarction in acute stroke with non-contrast-enhanced CT[J].Radiology,2020,294(3): 638-644.
|
| 31 |
KUANG H, NAJM M, CHAKRABORTY D, et al. Automated ASPECTS on noncontrast CT scans in patients with acute ischemic stroke using machine learning[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2019, 40(1): 33-38.
|
| 32 |
GARG R, OH E, NAIDECH A, et al. Automating ischemic stroke subtype classification using machine learning and natural language processing[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2019, 28(7): 2045-2051.
|
| 33 |
KUANG H L, QIU W, BOERS A M, et al. Computed tomography perfusion-based machine learning model better predicts follow-up infarction in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 2021, 52(1): 223-231.
|
| 34 |
CHOI J M, SEO S Y, KIM P J, et al. Prediction of hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke using machine learning[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11(9): 863.
|
| 35 |
GOYAL M, OSPEL J M. Letter by goyal and ospel regarding article, multimodal predictive modeling of endovascular treatment outcome for acute ischemic stroke using machine-learning[J]. Stroke, 2021, 52(2): e83-e84.
|
 )
)