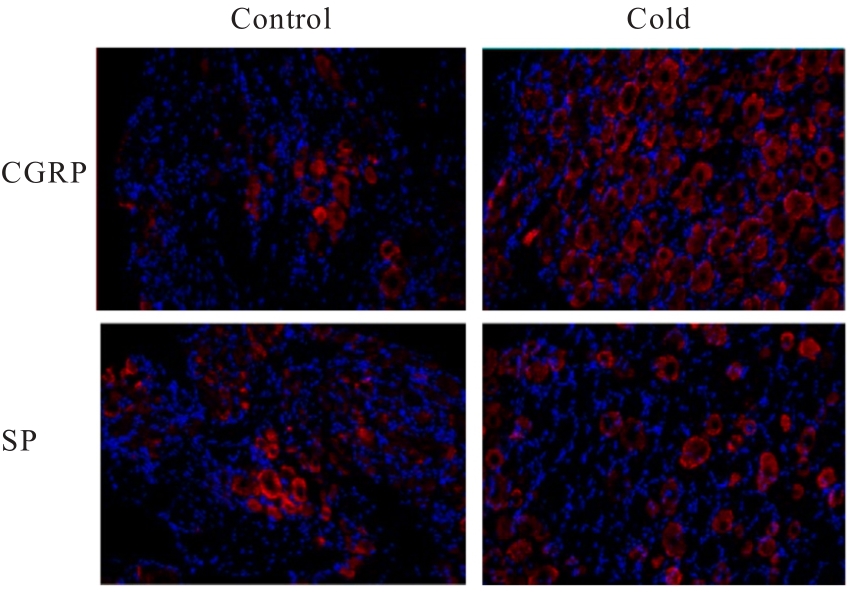
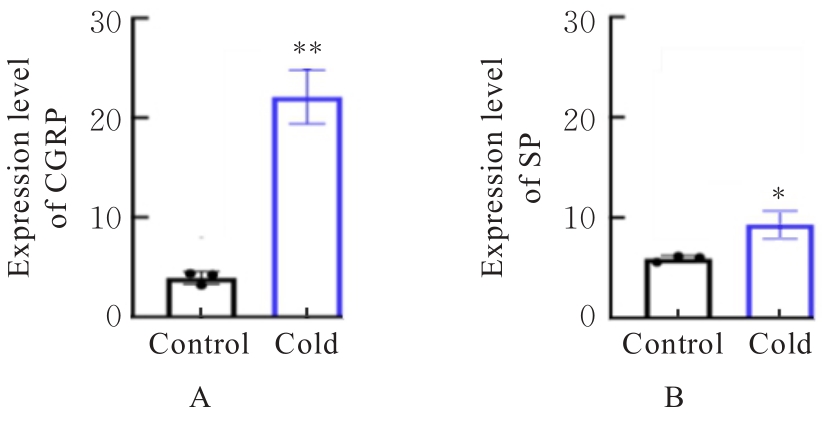
| 1 |
金 璐, 董维雲, 边祥雨, 等. 药食同源物质组方对急性寒冷暴露雌性大鼠HPO轴及HPA轴功能的影响[J]. 军事医学, 2023, 47(7): 521-526.
|
| 2 |
XUE Y, CHEN Y, JIANG D, et al. Self-reported weather sensitivity is associated with clinical symptoms and structural abnormalities in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study[J]. Rheumatol Ther, 2021, 8(3): 1405-1417.
|
| 3 |
ZIADÉ N, BOUZAMEL M, MRAD-NAKHLÉ M, et al. Prospective correlational time-series analysis of the influence of weather and air pollution on joint pain in chronic rheumatic diseases[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2021, 40(10): 3929-3940.
|
| 4 |
李丽梅, 郑宝森, 张志利, 等. 背根神经节解剖及其参与神经病理性疼痛机制的研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2022, 28(7): 531-540.
|
| 5 |
CAO S, LI Q M, HOU J F, et al. Intrathecal TRPM8 blocking attenuates cold hyperalgesia via PKC and NF-κB signaling in the dorsal root ganglion of rats with neuropathic pain[J]. J Pain Res, 2019, 12: 1287-1296.
|
| 6 |
MACDONALD D I, WOOD J N, EMERY E C. Molecular mechanisms of cold pain[J]. Neurobiol Pain, 2020, 7: 100044.
|
| 7 |
康欣欣, 唐志鹏, 王立娟, 等. 肉桂醛对0℃冷应激大鼠背根神经节神经细胞胞浆内Ca2+变化及TRPA1和TRPM8 mRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(1): 127-133.
|
| 8 |
CABAÑERO D, VILLALBA-RIQUELME E, FERNÁNDEZ-BALLESTER G, et al. ThermoTRP channels in pain sexual dimorphism: new insights for drug intervention[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 240: 108297.
|
| 9 |
MILENKOVIC N, ZHAO W J, WALCHER J, et al. A somatosensory circuit for cooling perception in mice[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2014, 17(11): 1560-1566.
|
| 10 |
KARASHIMA Y, TALAVERA K, EVERAERTS W, et al. TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2009, 106(4): 1273-1278.
|
| 11 |
CHRISTENSEN S L, HANSEN R B, STORM M A, et al. Von Frey testing revisited: Provision of an online algorithm for improved accuracy of 50% thresholds[J]. Eur J Pain, 2020, 24(4): 783-790.
|
| 12 |
SIMONE D A, KAJANDER K C. Excitation of rat cutaneous nociceptors by noxious cold[J]. Neurosci Lett, 1996, 213(1): 53-56.
|
| 13 |
ALLCHORNE A J, BROOM D C, WOOLF C J. Detection of cold pain, cold allodynia and cold hyperalgesia in freely behaving rats[J]. Mol Pain, 2005, 1: 36.
|
| 14 |
PRESCOTT S A, MA Q F, DE KONINCK Y. Normal and abnormal coding of somatosensory stimuli causing pain[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2014, 17(2): 183-191.
|
| 15 |
MUELLER-TRIBBENSEE S M, KARNA M, KHALIL M, et al. Differential contribution of TRPA1, TRPV4 and TRPM8 to colonic nociception in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(7): e0128242.
|
| 16 |
SHERKHELI M A, VOGT-EISELE A K, BURA D, et al. Characterization of selective TRPM8 ligands and their structure activity response (S.A.R) relationship[J]. J Pharm Pharm Sci, 2010, 13(2): 242.
|
| 17 |
STORY G M, PEIER A M, REEVE A J, et al. ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures[J]. Cell, 2003, 112(6): 819-829.
|
| 18 |
MICKLE A D, SHEPHERD A J, MOHAPATRA D P. Nociceptive TRP channels: sensory detectors and transducers in multiple pain pathologies[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2016, 9(4): 72.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG M, MA Y M, YE X L, et al. TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 261.
|
| 20 |
ASO K, IZUMI M, SUGIMURA N, et al. Nociceptive phenotype alterations of dorsal root Ganglia neurons innervating the subchondral bone in osteoarthritic rat knee joints[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2016, 24(9): 1596-1603.
|
| 21 |
SCHOU W S, ASHINA S, AMIN F M, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide and pain: a systematic review[J]. J Headache Pain, 2017, 18(1): 34.
|
| 22 |
MORAN M M, SZALLASI A. Targeting nociceptive transient receptor potential channels to treat chronic pain: current state of the field[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2018, 175(12): 2185-2203.
|
| 23 |
LOWIN T, BLECK J, SCHNEIDER M, et al. Selective killing of proinflammatory synovial fibroblasts via activation of transient receptor potential ankyrin (TRPA1)[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2018, 154: 293-302.
|
| 24 |
FERNANDES E S, RUSSELL F A, ALAWI K M, et al. Environmental cold exposure increases blood flow and affects pain sensitivity in the knee joints of CFA-induced arthritic mice in a TRPA1-dependent manner[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2016, 18(1): 7.
|
 )
)
 )
)