| 1 |
LEVINE M. Treatment of thrombotic disorders in cancer patients[J]. Haemostasis, 1997, 27(): 38-43.
|
| 2 |
MOIK F, CHAN W E, WIEDEMANN S, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of venous and arterial thromboembolism in immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy[J]. Blood, 2021, 137(12): 1669-1678.
|
| 3 |
KHORANA A A, KUDERER N M, MCCRAE K, et al. Cancer associated thrombosis and mortality in patients with cancer stratified by khorana score risk levels[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(21): 8062-8073.
|
| 4 |
ABDULLA A, DAVIS W M, RATNAWEERA N, et al. A meta-analysis of case fatality rates of recurrent venous thromboembolism and major bleeding in patients with cancer[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2020, 120(4): 702-713.
|
| 5 |
LYMAN G H, CULAKOVA E, PONIEWIERSKI M S, et al. Morbidity, mortality and costs associated with venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with cancer[J]. Thromb Res, 2018, 164(): S112-S118.
|
| 6 |
HUSSEINZADEH H, CARRIER M. Occult cancer detection in patients with hemostatic disorder and venous thromboembolism[J]. Thromb Res, 2018, 163: 242-245.
|
| 7 |
GRILZ E, POSCH F, NOPP S, et al. Relative risk of arterial and venous thromboembolism in persons with cancer vs. persons without cancer-a nationwide analysis[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(23): 2299-2307.
|
| 8 |
DEBBIE JIANG M D, ALFRED IAN LEE M D. Thrombotic risk from chemotherapy and other cancer therapies[J]. Cancer Treat Res, 2019, 179: 87-101.
|
| 9 |
MOIK F, AY C, PABINGER I. Risk prediction for cancer-associated thrombosis in ambulatory patients with cancer: past, present and future[J]. Thromb Res, 2020, 191(): S3-S11.
|
| 10 |
LI M, GUO Q, HU W M. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of venous thromboembolism after oncologic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Thromb Res, 2019, 173: 48-56.
|
| 11 |
PASTORI D, CORMACI V M, MARUCCI S, et al. A comprehensive review of risk factors for venous thromboembolism: from epidemiology to pathophysiology[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(4): 3169.
|
| 12 |
TAXBRO K, HAMMARSKJÖLD F, THELIN B, et al. Clinical impact of peripherally inserted central catheters vs implanted port catheters in patients with cancer: an open-label, randomised, two-centre trial[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2019, 122(6): 734-741.
|
| 13 |
CHEW H K, WUN T, HARVEY D, et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers[J]. Arch Intern Med, 2006, 166(4): 458-464.
|
| 14 |
KAKKAR A K, WILLIAMSON R C. Thromboprophylaxis in malignant disease[J]. Br J Surg, 1995, 82(6): 724-725.
|
| 15 |
SPYROPOULOS A C, ELDREDGE J B, ANAND L N, et al. External validation of a venous thromboembolic risk score for cancer outpatients with solid tumors: the COMPASS-CAT venous thromboembolism risk assessment model[J]. 2020, 25(7): e1083-e1090.
|
| 16 |
FALANGA A, AY C, DI NISIO M, et al. Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline[J]. Ann Oncol, 2023, 34(5): 452-467.
|
| 17 |
ABDEL-RAZEQ H, SHARAF B, AL-JAGHBEER M J, et al. COMPASS-CAT versus Khorana risk assessment model for predicting venous thromboembolic events in patients with non-small cell lung cancer on active treatment with chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy, the CK-RAM study[J]. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2023, 56(3): 447-453.
|
| 18 |
GEROTZIAFAS G T, TAHER A, ABDEL-RAZEQ H, et al. A predictive score for thrombosis associated with breast, colorectal, lung, or ovarian cancer: the prospective COMPASS-cancer-associated thrombosis study[J]. Oncologist, 2017, 22(10): 1222-1231.
|
| 19 |
WANG Y F, MA F, LIU B L, et al. Risk prediction of venous thromboembolism in non-small cell lung cancer patients based on COMPASS-CAT risk assessment model[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2020, 42(4): 340-345.
|
| 20 |
DETTERBECK F C, CHANSKY K, GROOME P, et al. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: methodology and validation used in the development of proposals for revision of the stage classification of NSCLC in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification of lung cancer[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2016, 11(9): 1433-1446.
|
| 21 |
YANG L, CHEONG N, WANG D Y, et al. Generation of monoclonal antibodies against Blo t 3 using DNA immunization with in vivo electroporation[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2003, 33(5): 663-668.
|
| 22 |
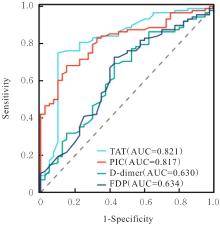
MEI H, JIANG Y, LUO L L, et al. Evaluation the combined diagnostic value of TAT, PIC, tPAIC, and sTM in disseminated intravascular coagulation: a multi-center prospective observational study[J]. Thromb Res, 2019, 173: 20-26.
|
| 23 |
KINASEWITZ G T, ZEIN J G, LEE G L, et al. Prognostic value of a simple evolving disseminated intravascular coagulation score in patients with severe sepsis[J]. Crit Care Med, 2005, 33(10): 2214-2221.
|
| 24 |
DHAINAUT J F, SHORR A F, MACIAS W L, et al. Dynamic evolution of coagulopathy in the first day of severe sepsis: relationship with mortality and organ failure[J]. Crit Care Med, 2005, 33(2): 341-348.
|
| 25 |
ZHOU K, ZHANG J, ZHENG Z R, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of TAT, PIC, TM, and t-PAIC in malignant tumor patients with venous thrombosis[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2020, 26: 1076029620971041.
|
| 26 |
ZHAO X X, YANG S Y, LEI R N, et al. Clinical study on the feasibility of new thrombus markers in predicting massive cerebral infarction[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 13: 942887.
|
| 27 |
LUNDBECH M, KRAG A E, CHRISTENSEN T D, et al. Thrombin generation, thrombin-antithrombin complex, and prothrombin fragment F1+2 as biomarkers for hypercoagulability in cancer patients[J]. Thromb Res, 2020, 186: 80-85.
|
| 28 |
LING L Q, HUANG X B, LIU C N, et al. Monitoring coagulation-fibrinolysis activation prompted timely diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-related disseminated intravascular coagulation[J]. Thromb J, 2021, 19(1): 82.
|
| 29 |
YAMADA S, ASAKURA H. Management of disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with aortic aneurysm and vascular malformations[J]. Int J Hematol, 2021, 113(1): 15-23.
|
| 30 |
SONG P P, XIE J Q, LI W, et al. Effect of plasma thrombin-antithrombin complex on ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Syst Rev, 2023, 12(1): 17.
|
| 31 |
CUI C J, GAO J, LI J, et al. Value of TAT and PIC with D-dimer for cancer patients with metastasis[J]. Int J Lab Hematol, 2020, 42(4): 387-393.
|
| 32 |
LIU Y E, MA J T, SHI Q Y, et al. Quantitatively monitoring acute ischemic stroke patients post recombinant tissue plasminogen activator treatment[J]. Health Sci Rep, 2021, 4(1): e218.
|
| 33 |
KEY N S, KHORANA A A, KUDERER N M, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and treatment in patients with cancer: ASCO clinical practice guideline update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(5): 496-520.
|
| 34 |
GALMICHE A, RAK J, ROUMENINA L T, et al. Coagulome and the tumor microenvironment: an actionable interplay[J]. Trends Cancer, 2022, 8(5): 369-383.
|
 )
)
 )
)