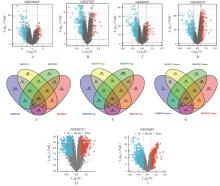
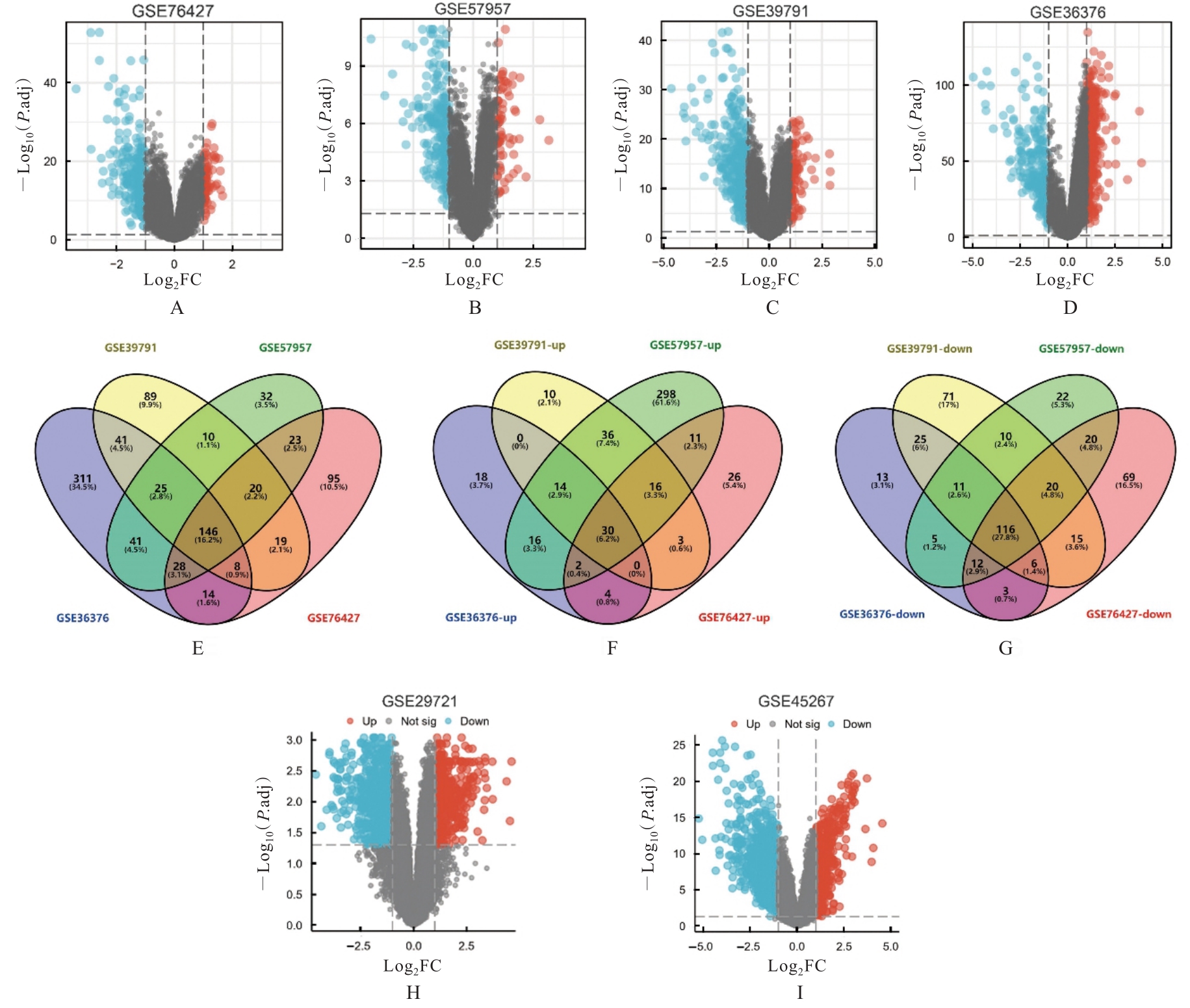
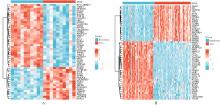
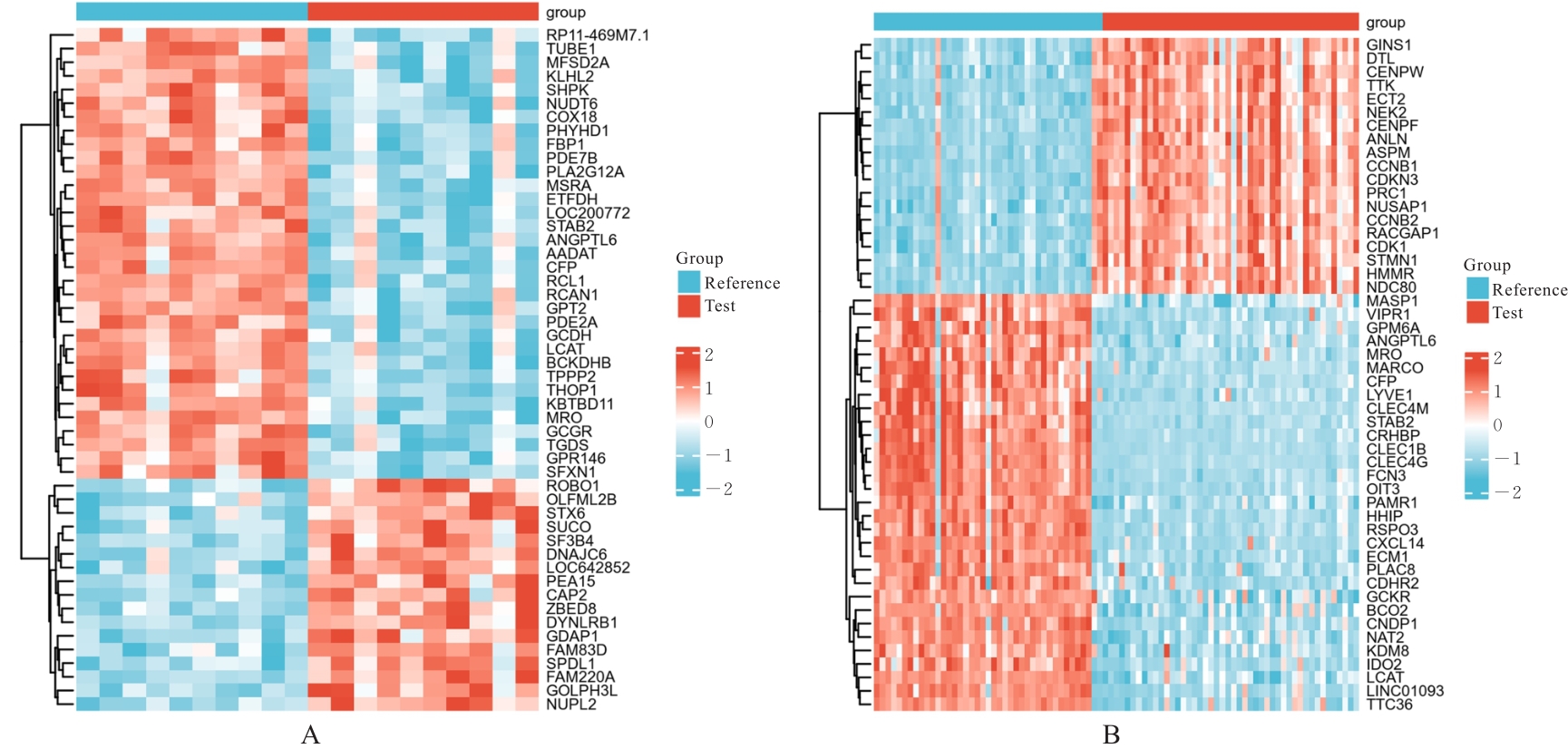
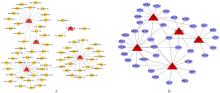
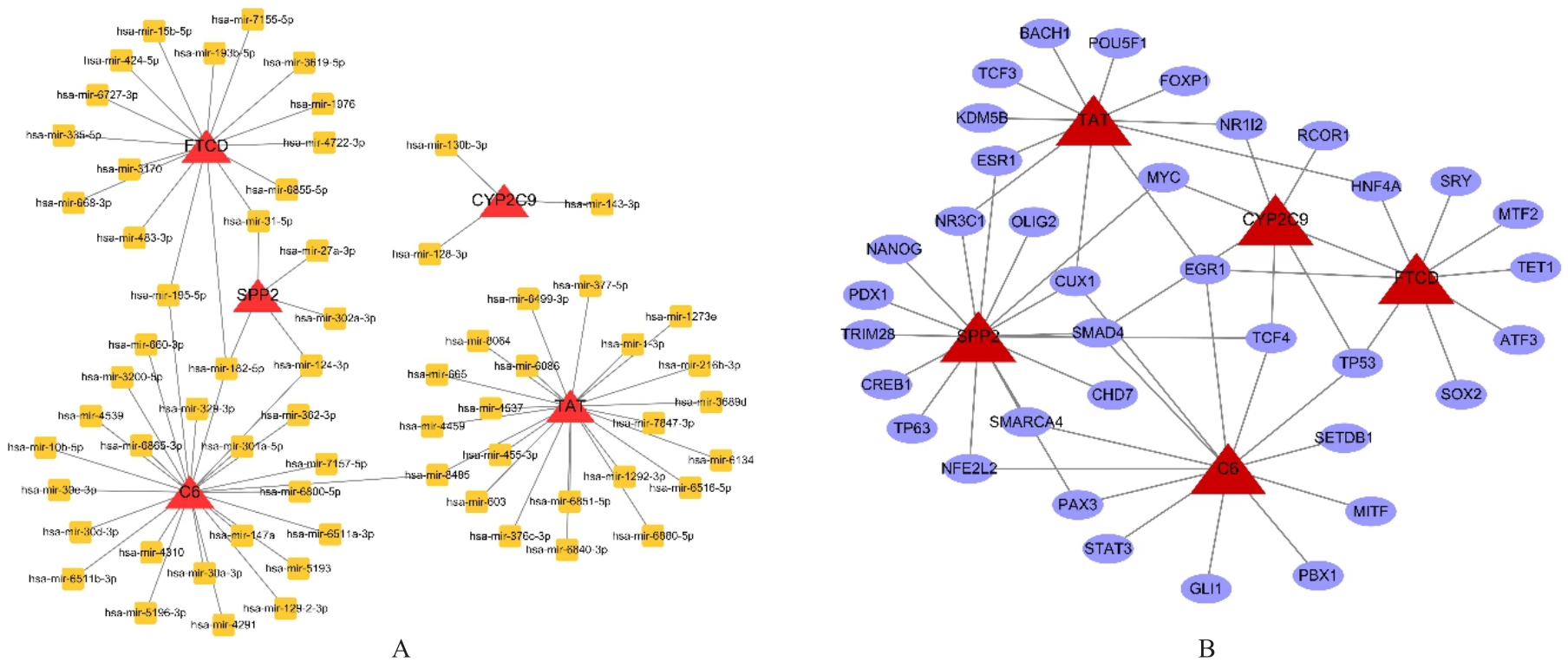
| 1 |
BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.
|
| 2 |
LLOVET J M, KELLEY R K, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 6.
|
| 3 |
MALUCCIO M, COVEY A. Recent progress in understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2012, 62(6): 394-399.
|
| 4 |
BURKHART R A, RONNEKLEIV-KELLY S M, PAWLIK T M. Personalized therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular markers of prognosis and therapeutic response[J]. Surg Oncol, 2017, 26(2): 138-145.
|
| 5 |
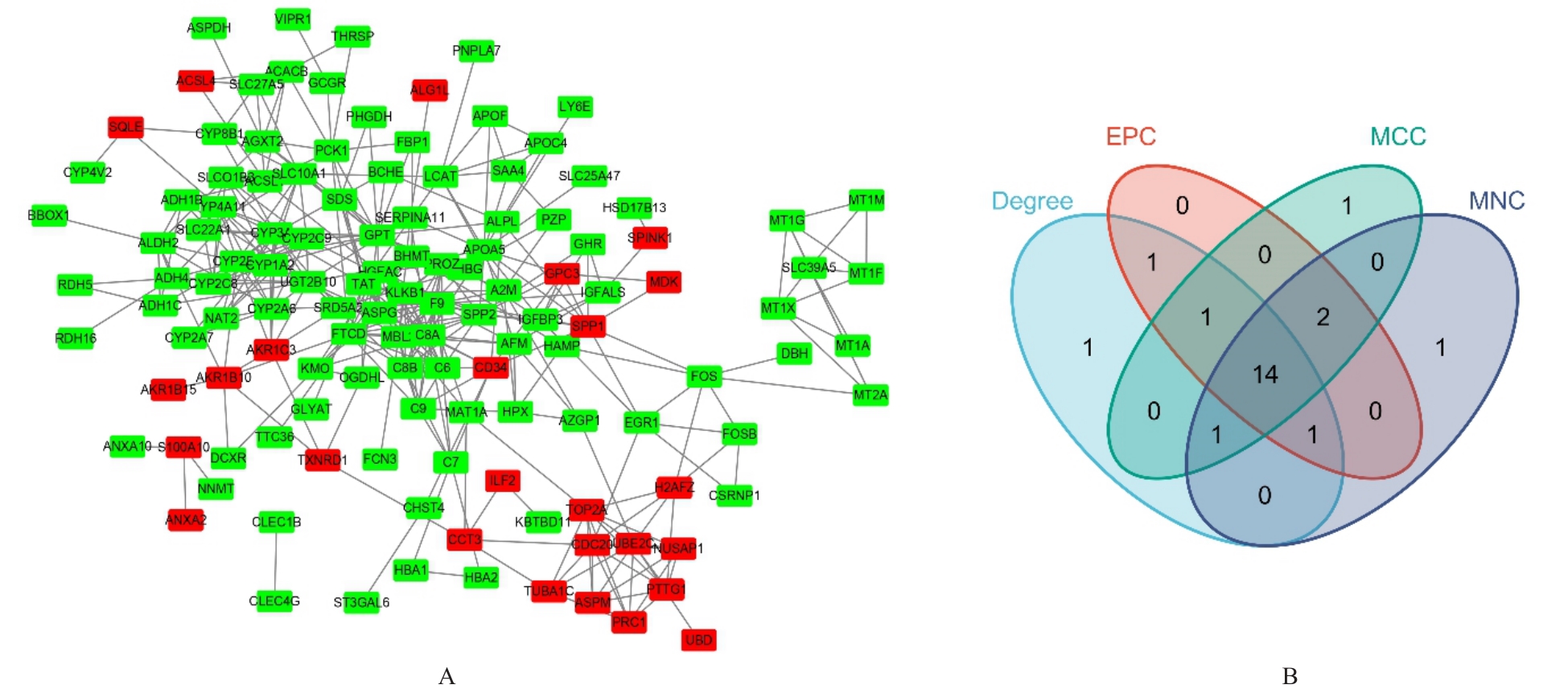
LI B H, XU T C, LIU C H, et al. Liver-enriched genes are associated with the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 11197.
|
| 6 |
NAULT J C, REYNIÈS A D, VILLANUEVA A, et al. A hepatocellular carcinoma 5-gene score associated with survival of patients after liver resection[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145(1): 176-187.
|
| 7 |
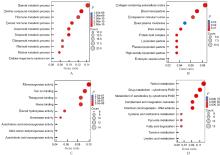
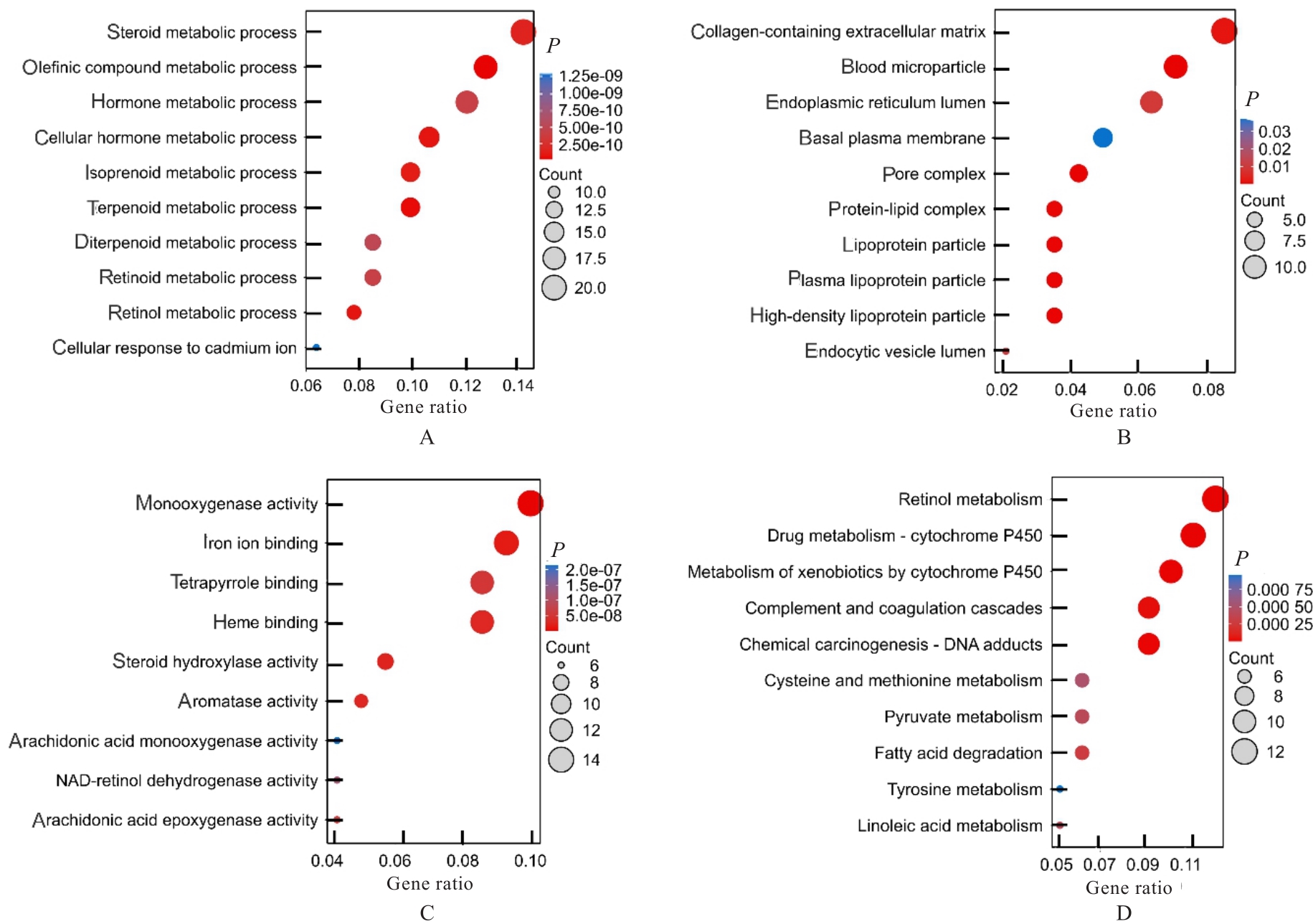
TU J X, CHEN J J, HE M M, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of molecular genetic targets and key pathways for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 5153-5162.
|
| 8 |
刘 迁, 祁国萍, 于华裔, 等. 结肠癌核心基因和独立预后因子筛选的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(3): 755-765.
|
| 9 |
李 楠, 陈 蕾, 许天敏, 等. 子宫内膜异位症患者细胞外基质相关基因筛选的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(1): 188-194.
|
| 10 |
RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47.
|
| 11 |
MANDREKAR J N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2010, 5(9): 1315-1316.
|
| 12 |
LI M H, XIN S Y, GU R Y, et al. Novel diagnostic biomarkers related to oxidative stress and macrophage ferroptosis in atherosclerosis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 8917947.
|
| 13 |
SHEN L, ZHOU K G, LIU H, et al. Prediction of mechanosensitive genes in vascular endothelial cells under high wall shear stress[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 796812.
|
| 14 |
WANG Y Y, KANG H E, XU T Y, et al. CeDR Atlas: a knowledgebase of cellular drug response[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D1164-D1171.
|
| 15 |
SNAEBJORNSSON M T, JANAKI-RAMAN S, SCHULZE A. Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31(1): 62-76.
|
| 16 |
CHAN A W, GILL R S, SCHILLER D, et al. Potential role of metabolomics in diagnosis and surveillance of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(36): 12874-12882.
|
| 17 |
CHENG X G, GU J, KLAASSEN C D. Adaptive hepatic and intestinal alterations in mice after deletion of NADPH-cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase (Cpr) in hepatocytes[J]. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014, 42(11): 1826-1833.
|
| 18 |
YAN T M, LU L L, XIE C, et al. Severely impaired and dysregulated cytochrome P450 expression and activities in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for personalized treatment in patients[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2015, 14(12): 2874-2886.
|
| 19 |
YU Z H, GE Y Y, XIE L, et al. Using a yeast two-hybrid system to identify FTCD as a new regulator for HIF-1α in HepG2 cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2014, 26(7): 1560-1566.
|
| 20 |
LU C Y, FANG S J, WENG Q Y, et al. Integrated analysis reveals critical glycolytic regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2020, 18(1): 97.
|
| 21 |
FU L, DONG S S, XIE Y W, et al. Down-regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase at a frequently deleted region 16q22 contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(5): 1624-1634.
|
| 22 |
WANG Q, TANG Q, ZHAO L J, et al. Time serial transcriptome reveals Cyp2c29 as a key gene in hepatocellular carcinoma development[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2020, 17(2): 401-417.
|
| 23 |
ROUMENINA L T, DAUGAN M V, PETITPREZ F, et al. Context-dependent roles of complement in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019, 19(12): 698-715.
|
| 24 |
HOBART M J, FERNIE B A, DISCIPIO R G, et al. A physical map of the C6 and C7 complement component gene region on chromosome 5p13[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 1993, 2(7): 1035-1036.
|
| 25 |
OKA R, SASAGAWA T, NINOMIYA I, et al. Reduction in the local expression of complement component 6 (C6) and 7 (C7) mRNAs in oesophageal carcinoma[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2001, 37(9): 1158-1165.
|
| 26 |
WANG Z, LIAO J, WU S, et al. Recipient C6 rs9200 genotype is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after orthotopic liver transplantation in a Han Chinese population[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2016, 23(6): 157-161.
|
| 27 |
GARNELO M, TAN A, HER Z, et al. Interaction between tumour-infiltrating B cells and T cells controls the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gut, 2017, 66(2): 342-351.
|
| 28 |
CHEN Q F, LI W, WU P H, et al. Significance of tumor-infiltrating immunocytes for predicting prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(35): 5266-5282.
|
| 29 |
KUANG D M, PENG C, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma promote expansion of memory T helper 17 cells[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 154-164.
|
| 30 |
SUN K, WANG L, ZHANG Y Y. Dendritic cell as therapeutic vaccines against tumors and its role in therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2006, 3(3): 197-203.
|
| 31 |
WEI L, WANG X W, LV L Y, et al. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 147.
|
| 32 |
VAN KEUREN-JENSEN K R, MALENICA I, COURTRIGHT A L, et al. MicroRNA changes in liver tissue associated with fibrosis progression in patients with hepatitis C[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36(3): 334-343.
|
| 33 |
CAO M Q, YOU A B, ZHU X D, et al. MiR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 11(1): 12.
|
| 34 |
LAMBERT S A, JOLMA A, CAMPITELLI L F, et al. The human transcription factors[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(2): 598-599.
|
| 35 |
WU Q, ZHANG B, SUN Y D, et al. Identification of novel biomarkers and candidate small molecule drugs in non-small-cell lung cancer by integrated microarray analysis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 3545-3563.
|
 )
)
 )
)