吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 133-142.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250116
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
漆酚底涂剂对脱矿牙本质的再矿化及粘接性能的影响
- 吉林大学口腔医院修复科,吉林 长春 130021
Effect of urushiol primer on remineralization and adhesion properties of demineralized dentin
Tingting BAI,Fei WEI,Guangdi SUN,Xue CHEN,Song ZHU( )
)
- Department of Prosthodontics,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
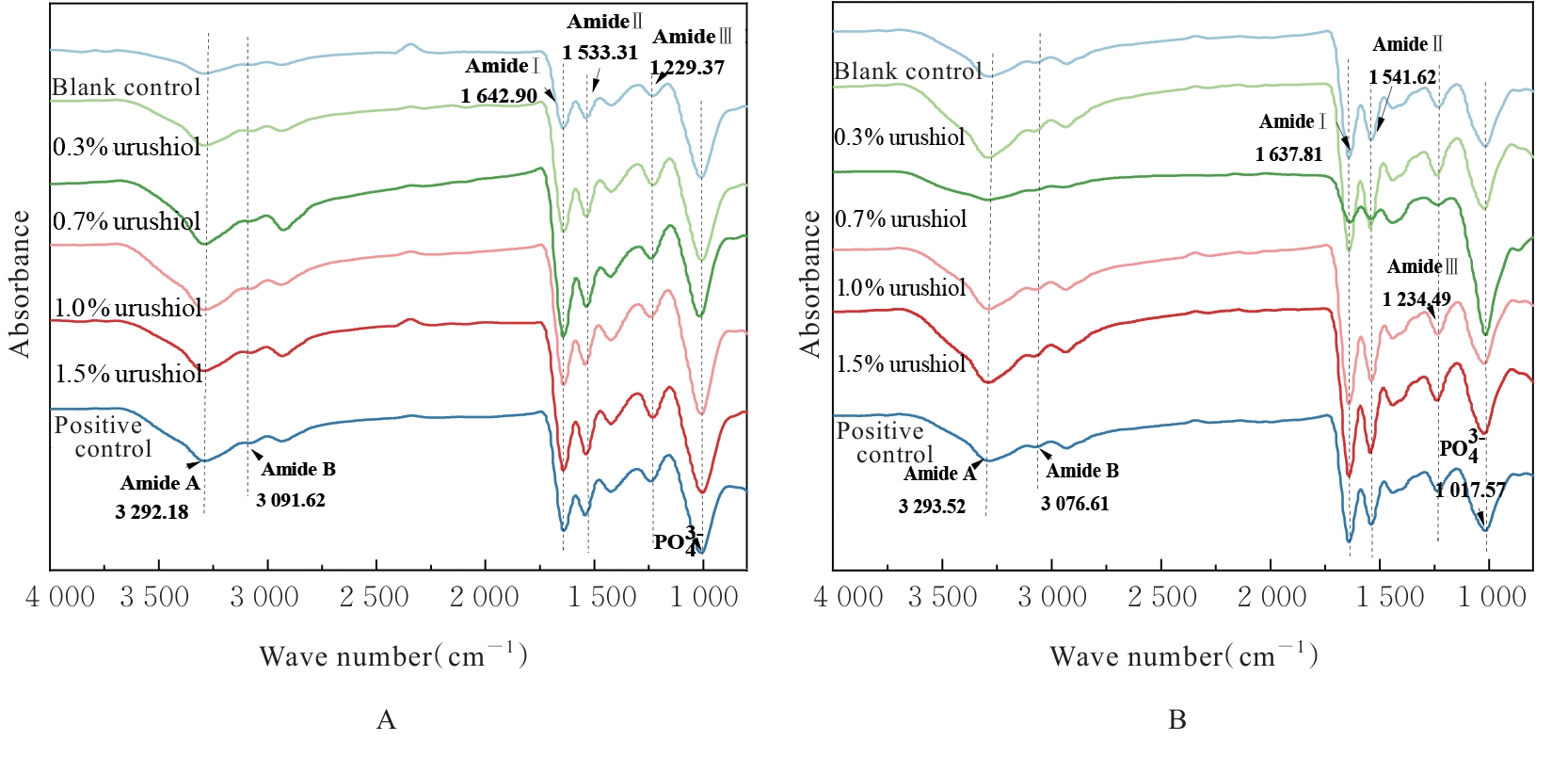
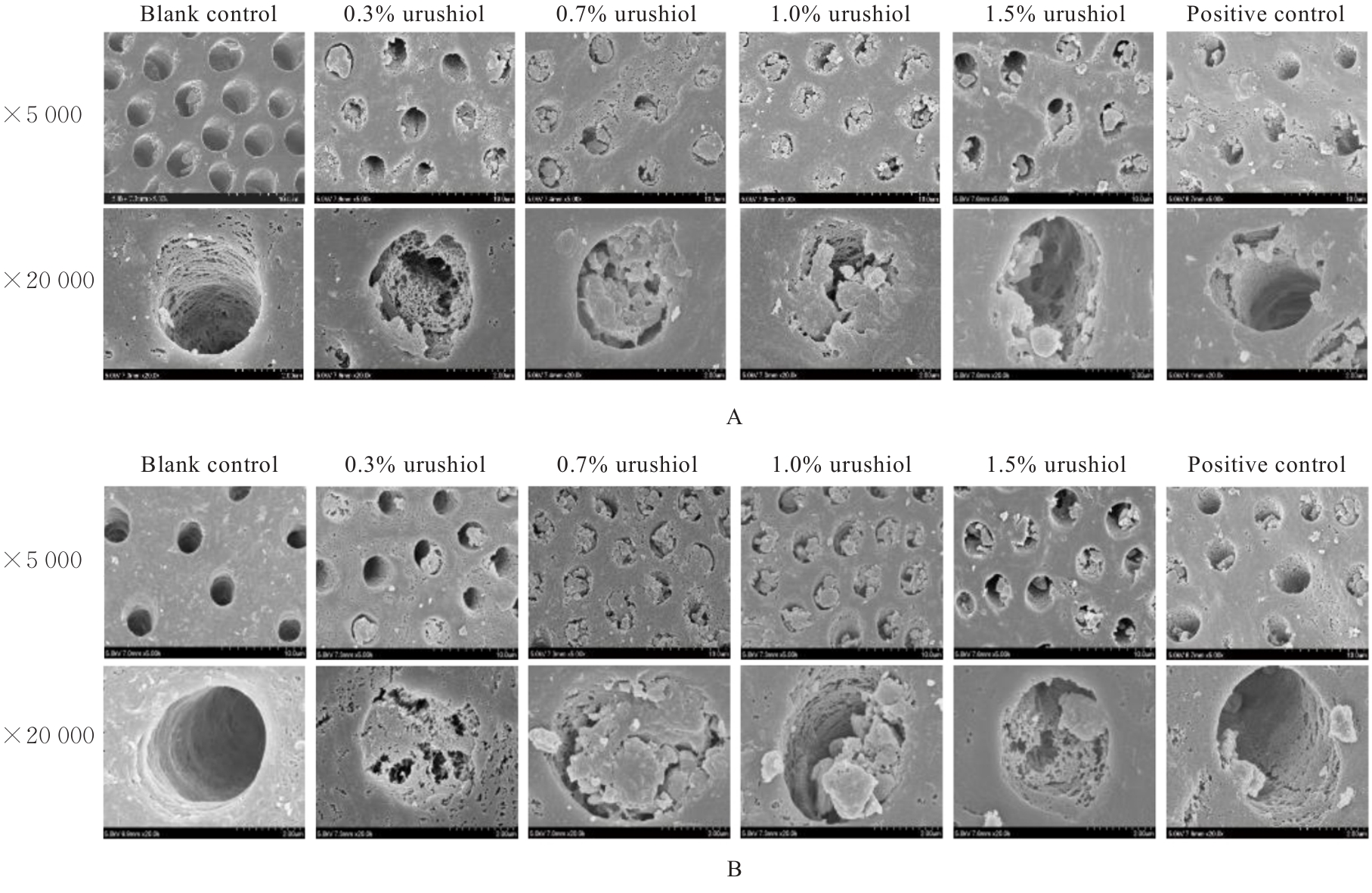
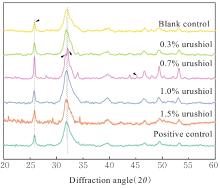
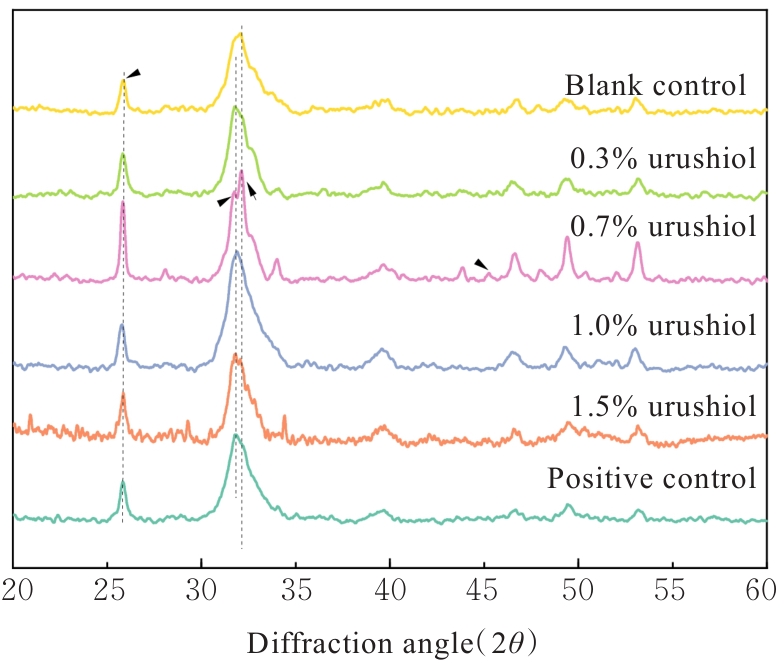
目的 探讨漆酚底涂剂应用于酸蚀-冲洗类粘接剂对脱矿牙本质再矿化作用的促进作用,阐明漆酚底涂剂对牙本质粘接耐久性的影响。 方法 选用96颗新鲜无龋第三磨牙制备成牙本质样本,采用37%磷酸凝胶酸蚀后进行预处理,随机分为空白对照组,0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组及阳性对照(丙酮溶液)组,处理后的样本置于改良模拟体液中再矿化14和28 d。采用衰减全反射傅里叶变换红外光谱(ATR-FTIR)检测各组牙本质小管内矿物的相对质量,X射线衍射仪(XRD)和X射线能谱仪(EDS)分析各组牙本质表面物质成分,扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察各组样本表面形态,维氏硬度仪测量各组样本表面的显微硬度,微拉伸强度(μTBS)测试检测各组样本粘接强度。 结果 粘接剂双键转化率(DC),与空白对照组比较,阳性对照组底涂剂对粘接剂DC降低,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组底涂剂对粘接剂DC均明显升高(P<0.05)。XRD和EDS检测,0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组牙本质小管内新形成的矿物质为羟基磷灰石(HA)晶体。SEM检测,再矿化14和28 d后,与空白对照组比较,阳性对照组牙本质小管内见少量膜状物;0.3%漆酚组牙本质小管矿化物较少;0.7%漆酚组牙本质小管内可见大量松散矿物颗粒沉积堵塞管口;1.0%漆酚组牙本质小管内可见小块矿物沉淀;1.5%漆酚组中牙本质小管较空。显微硬度测试,再矿化14 d后,与空白对照组比较,阳性对照组牙本质显微硬度未见明显提升(P>0.05),而与0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5% 漆酚组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);再矿化14 d后,与阳性对照组比较,0.7%和1.0%漆酚组牙本质显微硬度提升明显(P<0.05);再矿化28 d后,与空白对照组和阳性对照组比较,各漆酚组牙本质显微硬度明显升高(P<0.05),其中0.7%和1.5%漆酚组牙本质显微硬度明显增强(P<0.05)。μTBS测试,再矿化14 d后,与阳性对照组比较,0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组的μTBS明显增强(P<0.05);再矿化28 d后,空白对照组μTBS最低,且与空白对照组比较,阳性对照组μTBS差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);与阳性对照组比较,0.3%、0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组μTBS升高(P<0.05),0.7%、1.0%和1.5%漆酚组μTBS升高更为明显(P<0.05)。 结论 天然来源的漆酚作为一种新型底涂剂对脱矿的牙本质基质进行预处理,可以促进牙本质胶原的交联,裸露的胶原可通过漆酚吸引钙离子和磷离子,包裹牙本质胶原纤维促进再矿化,因而提高树脂-牙本质粘接界面的强度。
中图分类号:
- R783.1