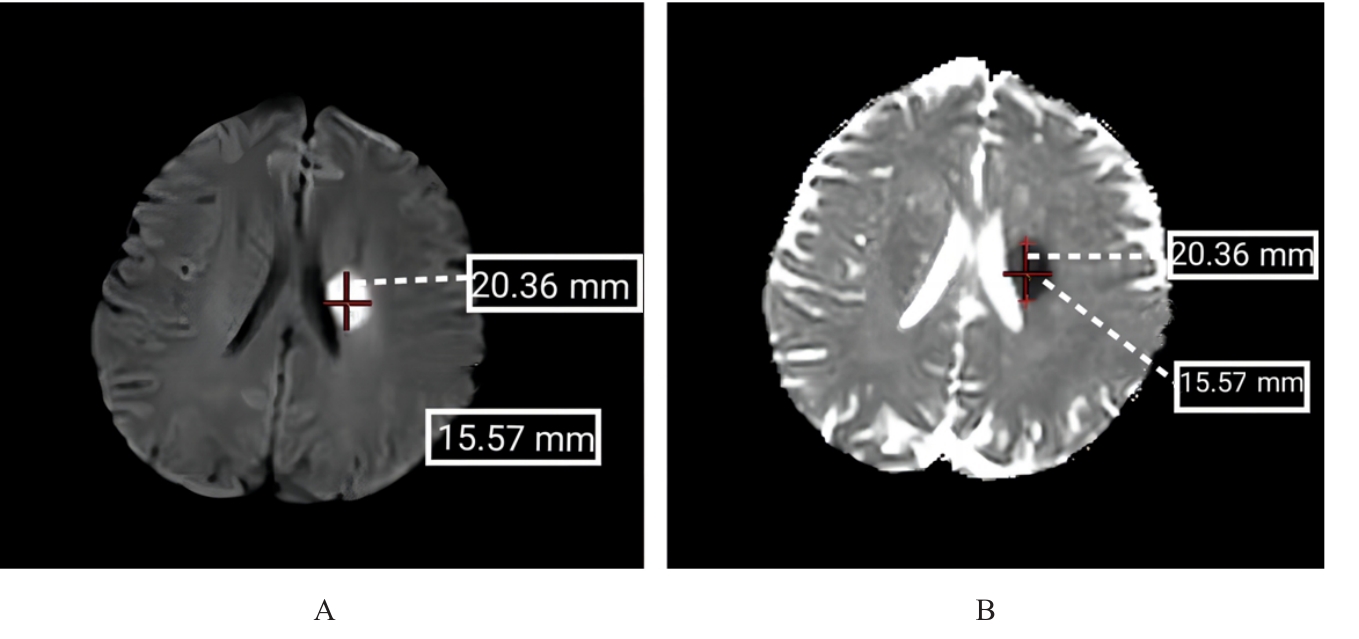
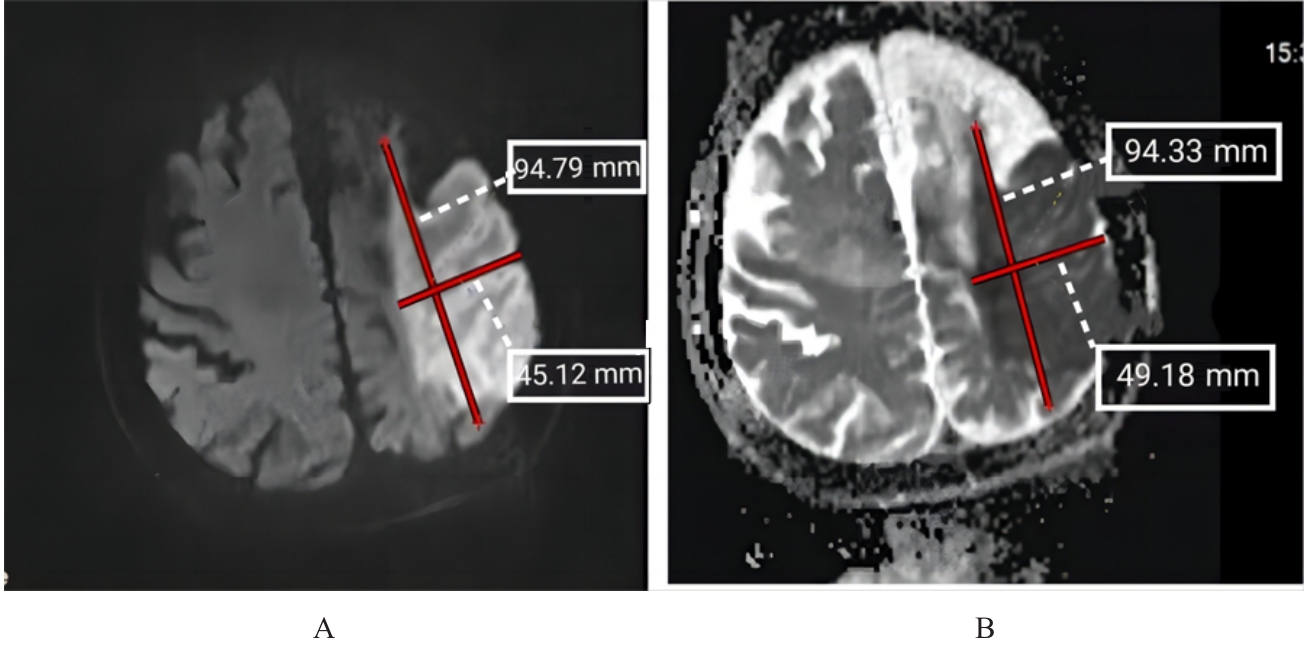
| 1 |
PAN J R, Li X P, PENG Y. Remote ischemic conditioning for acute ischemic stroke: dawn in the darkness[J]. Rev Neurosci, 2016, 27(5): 501-510.
|
| 2 |
NOBRE M C, MONTEIRO M, DE ALBUQUERQUE A C, et al. [Decompressive craniectomy for treatment of intracranial hypertension secondary to large ischemic cerebral infarction: analysis of 34 cases][J]. Arq Neuropsiquiatr, 2007, 65(1): 107-113.
|
| 3 |
VELTKAMP R, GILL D. Clinical trials of immunomodulation in ischemic stroke [J]. Neurotherapeutics, 2016, 13(4): 791-800.
|
| 4 |
彭斐斐, 陈梅玲. 自身免疫性疾病引起脑梗死的发病机制的研究进展[J]. 中国当代医药, 2018, 25(4): 25-28.
|
| 5 |
YANG K L, ZENG L T, GE A Q, et al. A systematic review of the research progress of non-coding RNA in neuroinflammation and immune regulation in cerebral infarction/ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 930171.
|
| 6 |
WANG S W, ZHANG H, XU Y. Crosstalk between microglia and T cells contributes to brain damage and recovery after ischemic stroke[J]. Neurol Res, 2016, 38(6): 495-503.
|
| 7 |
BONDOC E N, MARINESCU D, MARINESCU I, et al. Current understanding of psycho-neurobiology in depressive disorders with suicidal thoughts - translational models[J]. Rom J Morphol Embryol, 2019, 60(2): 389-402.
|
| 8 |
HENEIN M Y, VANCHERI S, LONGO G, et al. The role of inflammation in cardiovascular disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21): 12906.
|
| 9 |
CHEN P J, PAN Y Y, WANG J K, et al. The value of computed tomography perfusion deficit volumes in acute isolated brainstem infarction[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 14: 1233784.
|
| 10 |
YUAN M, HAN B, XIA Y P, et al. Augmentation of peripheral lymphocyte-derived cholinergic activity in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. BMC Neurol, 2019, 19(1): 236.
|
| 11 |
YI X Y, ZHU L, SUI G, et al. Inflammation and endothelial function relevant genetic polymorphisms and carotid plaque in Chinese population[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2020, 27(9): 978-994.
|
| 12 |
IADECOLA C, BUCKWALTER M S, ANRATHER J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(6): 2777-2788.
|
| 13 |
QIU Y M, ZHANG C L, CHEN A Q, et al. Immune cells in the BBB disruption after acute ischemic stroke: targets for immune therapy? [J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 678744.
|
| 14 |
PAKZAD B, RAJAE E, SHAHRABI S, et al. T-Cell molecular modulation responses in atherosclerosis anergy[J]. Lab Med, 2020, 51(6): 557-565.
|
| 15 |
JIN W N, GONZALES R, FENG Y, et al. Brain ischemia induces diversified neuroantigen-specific T-Cell responses that exacerbate brain injury[J]. Stroke, 2018, 49(6): 1471-1478.
|
| 16 |
KORN T, KALLIES A. T cell responses in the central nervous system[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2017, 17(3):179-194.
|
| 17 |
SIMATS A, LIESZ A. Systemic inflammation after stroke: implications for post-stroke comorbidities [J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2022, 14(9): e16269.
|
| 18 |
WANG S W, ZHANG H, XU Y. Crosstalk between microglia and T cells contributes to brain damage and recovery after ischemic stroke[J]. Neurol Res, 2016,38(6): 495-503.
|
| 19 |
CRAMER J V, BENAKIS C, LIESZ A. T cells in the post-ischemic brain: Troopers or paramedics?[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2019, 326: 33-37.
|
| 20 |
REN H, LIU X, WANG L,et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio: a novel predictor of the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2017, 26(11): 2595-2602.
|
| 21 |
NAM K W, KIM T J, LEE J S, et al. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts stroke-associated pneumonia[J]. Stroke, 2018, 49(8): 1886-1892.
|
| 22 |
ADILIS M, KARLA D, FRAGOSO P, et al. Morita-baylis-hillman adduct 2-(3-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-oxoindolin-3-il) acrylonitrile (CISACN) ameliorates the pulmonary allergic inflammation in CARAS model by increasing IFN-γ/IL-4 ratio towards the Th1 immune response[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 130: 111737.
|
| 23 |
BUTOVSKY O, ZIV Y, SCHWARTZ A, et al. Microglia activated by IL-4 or IFN-gamma differentially induce neurogenesis and oligodendrogenesis from adult stem/progenitor cells[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2006, 31(1): 149-160.
|
| 24 |
WANG Y J, ZHANG J H, SHENG J F, et al. Immunoreactive cells after cerebral ischemia[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2781.
|
| 25 |
SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440.
|
| 26 |
YUAN M, HAN B, XIA Y P, et al. Augmentation of peripheral lymphocyte-derived cholinergic activity in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. BMC Neurol, 2019, 19(1): 236.
|
| 27 |
REN H, LIU X, WANG L, et al. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio: A novel predictor of the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2017, 26(11): 2595-2602.
|
| 28 |
BECKER K J, KALIL A J, TANZI P, et al. Autoimmune responses to the brain after stroke are associated with worse outcome[J]. Stroke, 2011, 42(10): 2763-2769.
|
| 29 |
JICKLING G C, LIU D Z, ANDER B P,et al. Targeting neutrophils in ischemic stroke: translational insights from experimental studies[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2015, 35(6): 888-901.
|
| 30 |
WESTENDORP W F, DAMES C, NEDERKOORN P J, et al. Immunodepression, infections, and functional outcome in ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 2022, 53(5):1438-1448.
|
| 31 |
JIAN Z H, LIU R, ZHU X Q, et al. The involvement and therapy target of immune cells after ischemic stroke[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2167.
|
 ),尤久琳,陈盈,冯良枢,王晶,冯加纯,王川(
),尤久琳,陈盈,冯良枢,王晶,冯加纯,王川( )
)
 ),Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG(
),Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG( )
)