吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 567-575.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250302
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
活化T淋巴细胞核因子5在高盐诱导小鼠平滑肌细胞衰老中的作用及其机制
- 1.江苏大学附属医院心血管内科,江苏 镇江 212001
2.江苏省常州市妇幼保健院心血管内科,江苏 常州 213003
Effect of nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes 5 on senescence of smooth muscle cells of mice induced by high-salt and its mechanism
Wei ZHONG1,Zhiyin DAI1,Xinggang CUI1,Bo LI1,Yu JIANG1,2( )
)
- 1.Department of Cardiology,Affiliated Hospital,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212001,China
2.Department of Cardiology,Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital,Changzhou City,Jiangsu Province,Changzhou 213003,China
摘要:
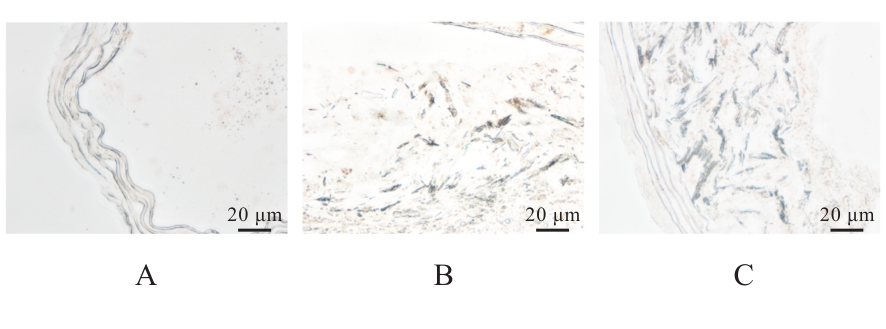
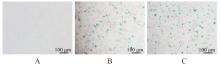
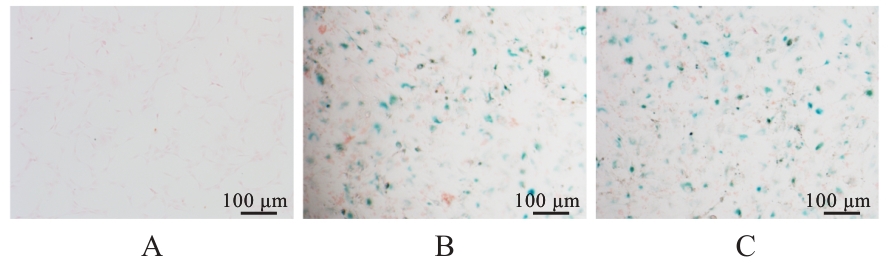
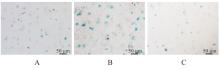
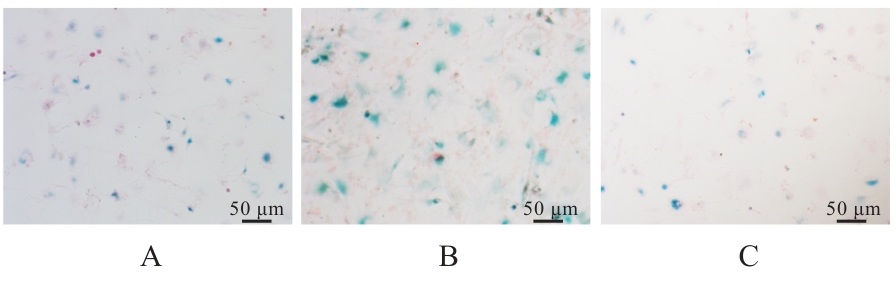
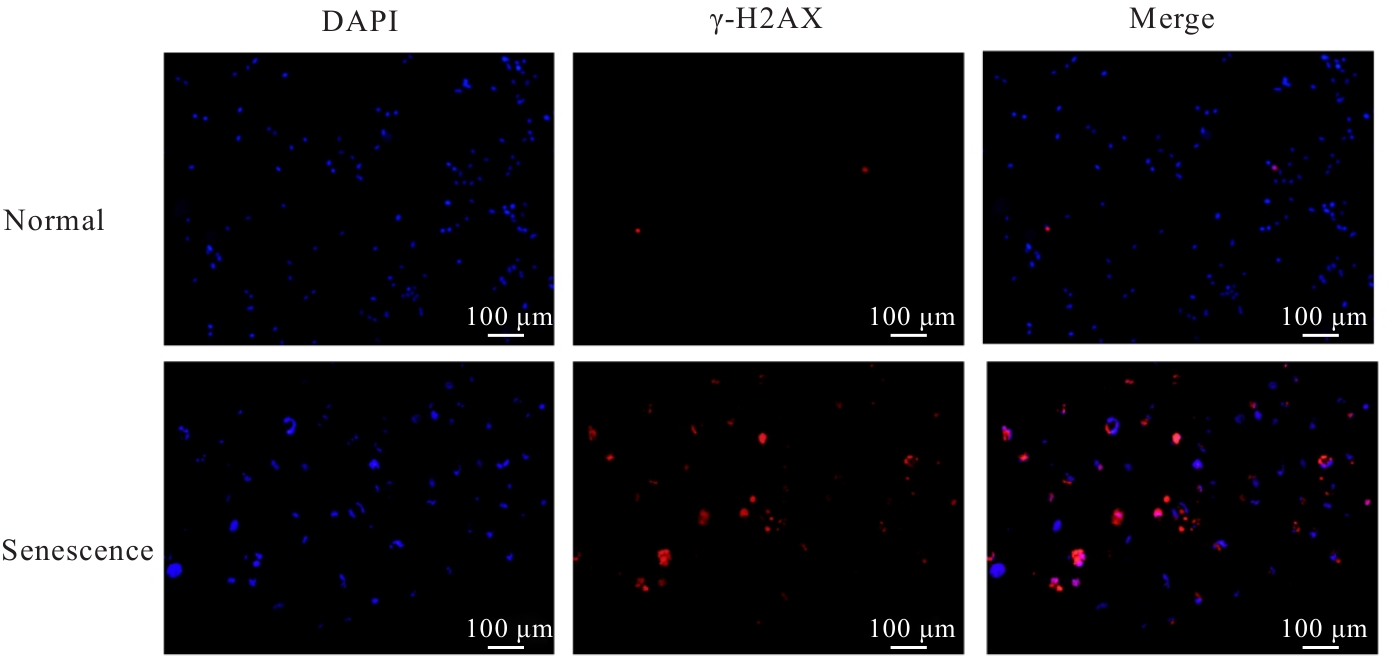
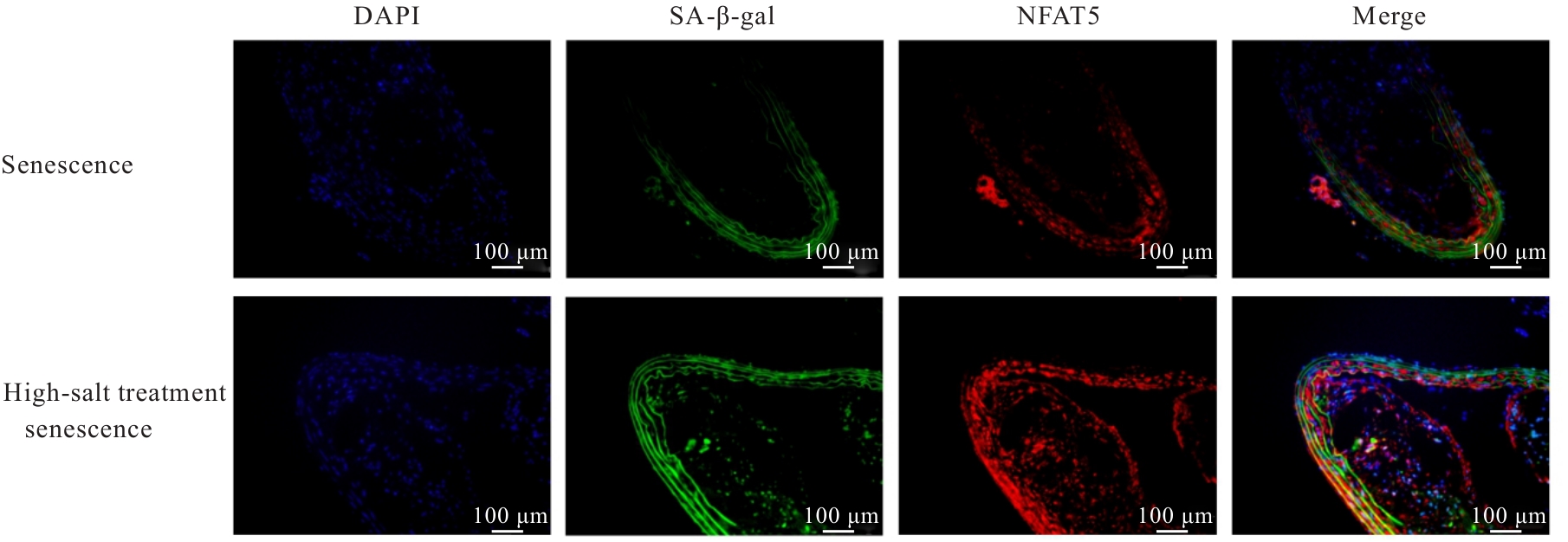
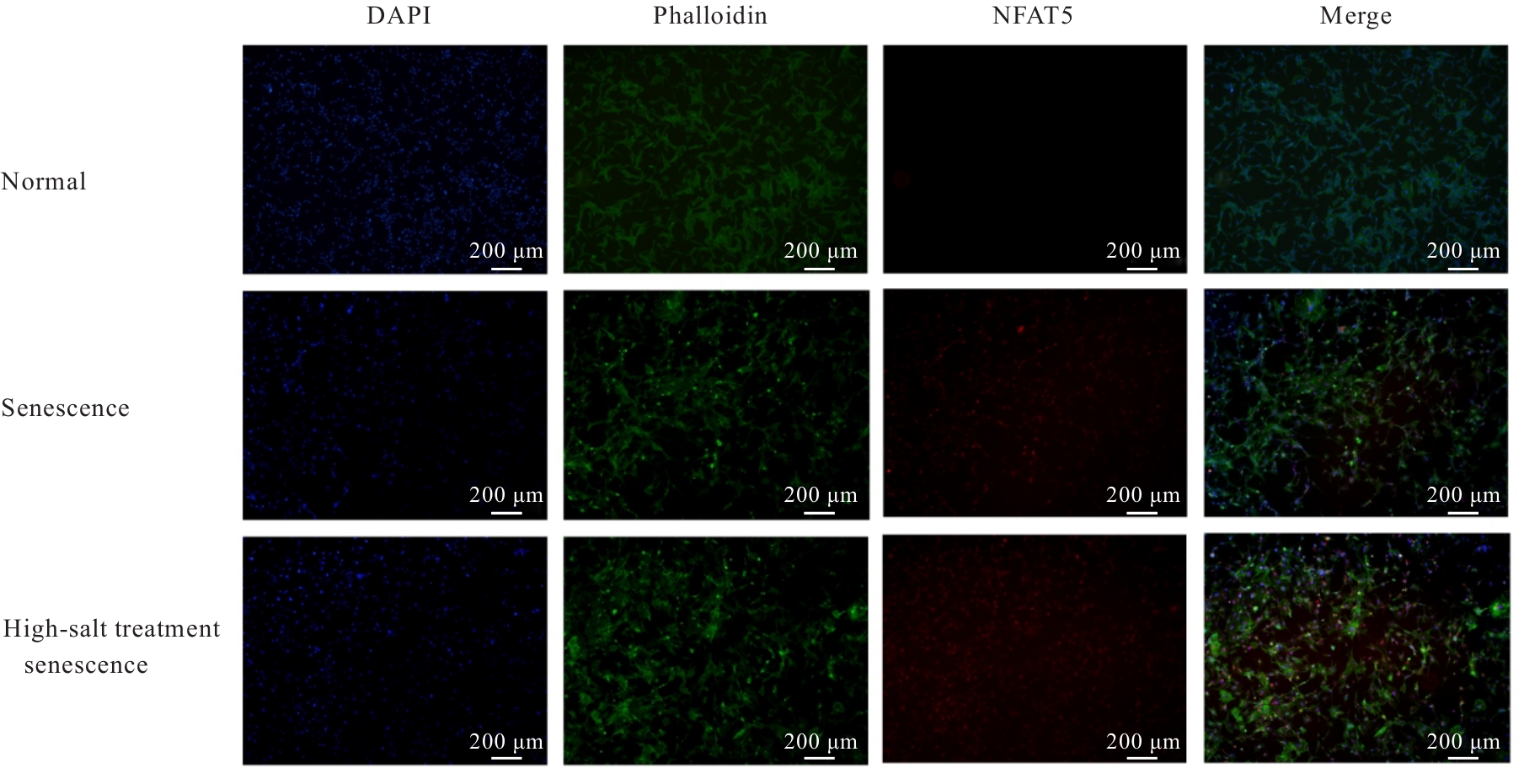
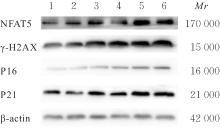
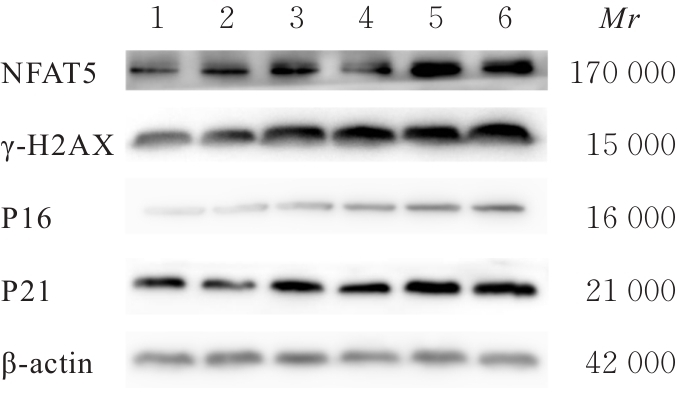
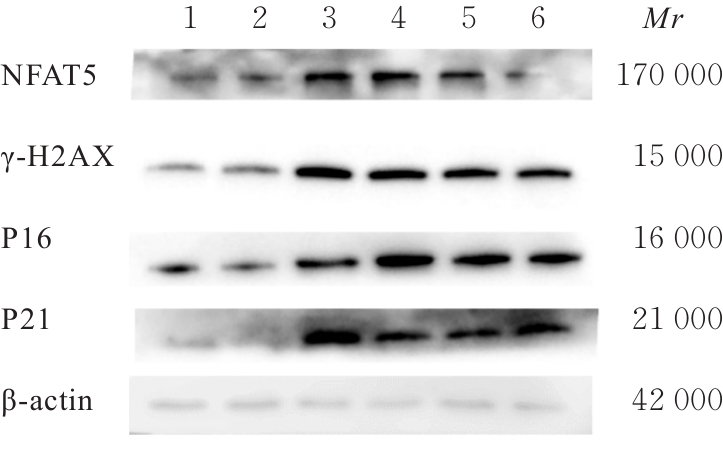
目的 探讨活化T淋巴细胞核因子5(NFAT5)抑制剂KRN5在高盐诱导小鼠血管平滑肌细胞(VSMCs)衰老中的作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 30只8周龄雄性ApoE-/-小鼠分为正常组、衰老组和高盐处理衰老组,每组10只,衰老组和高盐处理衰老组构建小鼠自然衰老模型;分离培养小鼠VSMCs,将VSMCs分为正常组、衰老组、高盐处理衰老组和高盐处理衰老+KRN5组。采用β-半乳糖苷酶(Sa-β-gal)染色法检测各组小鼠主动脉组织和VSMCs衰老情况,免疫荧光法检测各组小鼠主动脉组织和VSMCs中NFAT5和磷酸化的组蛋白H2A变异体X(γ-H2AX)蛋白表达情况,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组细胞中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、细胞周期依赖性激酶抑制剂2A(P16)和细胞周期依赖性激酶抑制剂1A(P21)mRNA表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16和P21蛋白表达水平。 结果 Sa-β-gal染色法,与正常组比较,衰老组和高盐处理衰老组小鼠主动脉组织衰老阳性面积比例均明显增加(P<0.05),小鼠VSMCs衰老细胞阳性比例均明显增加(P<0.05)。与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs衰老细胞阳性比例明显增加(P<0.05);与高盐处理衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老+KRN5组小鼠VSMCs衰老细胞阳性比例明显减少(P<0.01)。免疫荧光法,与正常组比较,衰老组小鼠VSMCs中γ-H2AX蛋白表达量明显增加(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组小鼠主动脉组织中SA-β-gal染色和NFAT5蛋白表达量均明显增加(P<0.05);与正常组比较,衰老组和高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5蛋白表达量明显增加(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5蛋白表达量明显增加(P<0.05)。RT-qPCR法,与正常组比较,衰老组和高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16及P21 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16和P21 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组和高盐处理衰老+KRN5组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16及P21 mRNA表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与高盐处理衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老+KRN5组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16和P21 mRNA表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与正常组比较,衰老组和高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16及P21蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16和P21蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老组和高盐处理衰老+KRN5组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16及P21蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与高盐处理衰老组比较,高盐处理衰老+KRN5组小鼠VSMCs中NFAT5、γ-H2AX、P16和P21蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 NFAT5对高盐诱导小鼠VSMCs衰老可能具有一定促进作用。
中图分类号:
- R339.38