吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 925-938.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240406
基于消斑通脉方抗动脉粥样硬化作用机制的网络药理学分析和体外实验验证
- 1.河南中医药大学中医学院方剂教研室,河南 郑州 450046
2.河南中医药大学教务处,河南 郑州 450046
3.河南中医药大学研究生院,河南 郑州 450046
4.河南中医药大学医学院 病理生理学教研室,河南 郑州 450046
5.河南中医药大学基础实验中心,河南 郑州 450046
Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula
Shan CAO1( ),Yijia ZHANG2,Yang BAI3,Fang CHEN4,Sha XIE4,Qianqian HAN5
),Yijia ZHANG2,Yang BAI3,Fang CHEN4,Sha XIE4,Qianqian HAN5
- 1.Department of Formula,School of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
2.Department of Academic Affairs,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
3.Graduate School,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
4.Department of Pathophysiology,School of Medical Sciences,Henan University of Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
5.Basic Experimental Center,Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Zhengzhou 450046,China
摘要:
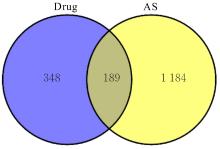
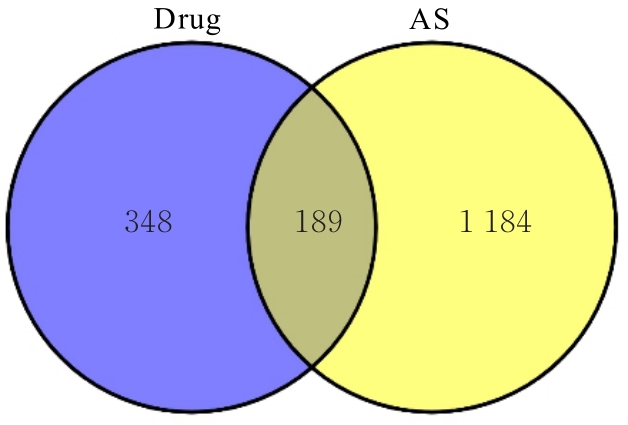
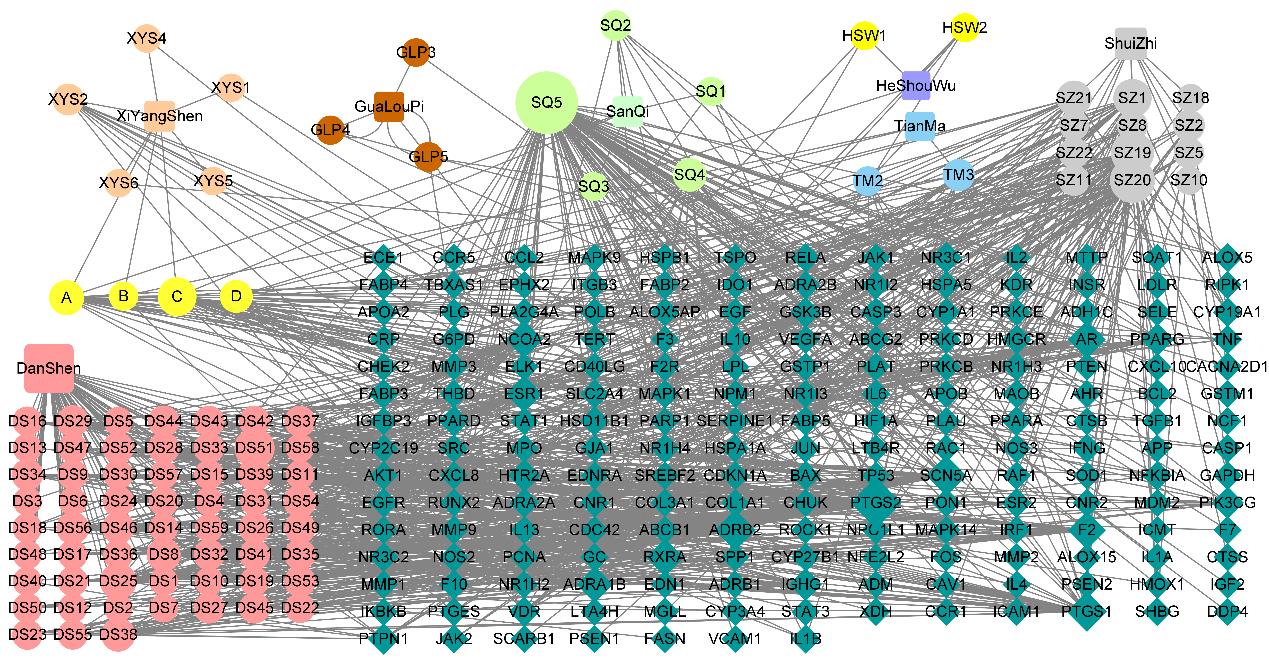
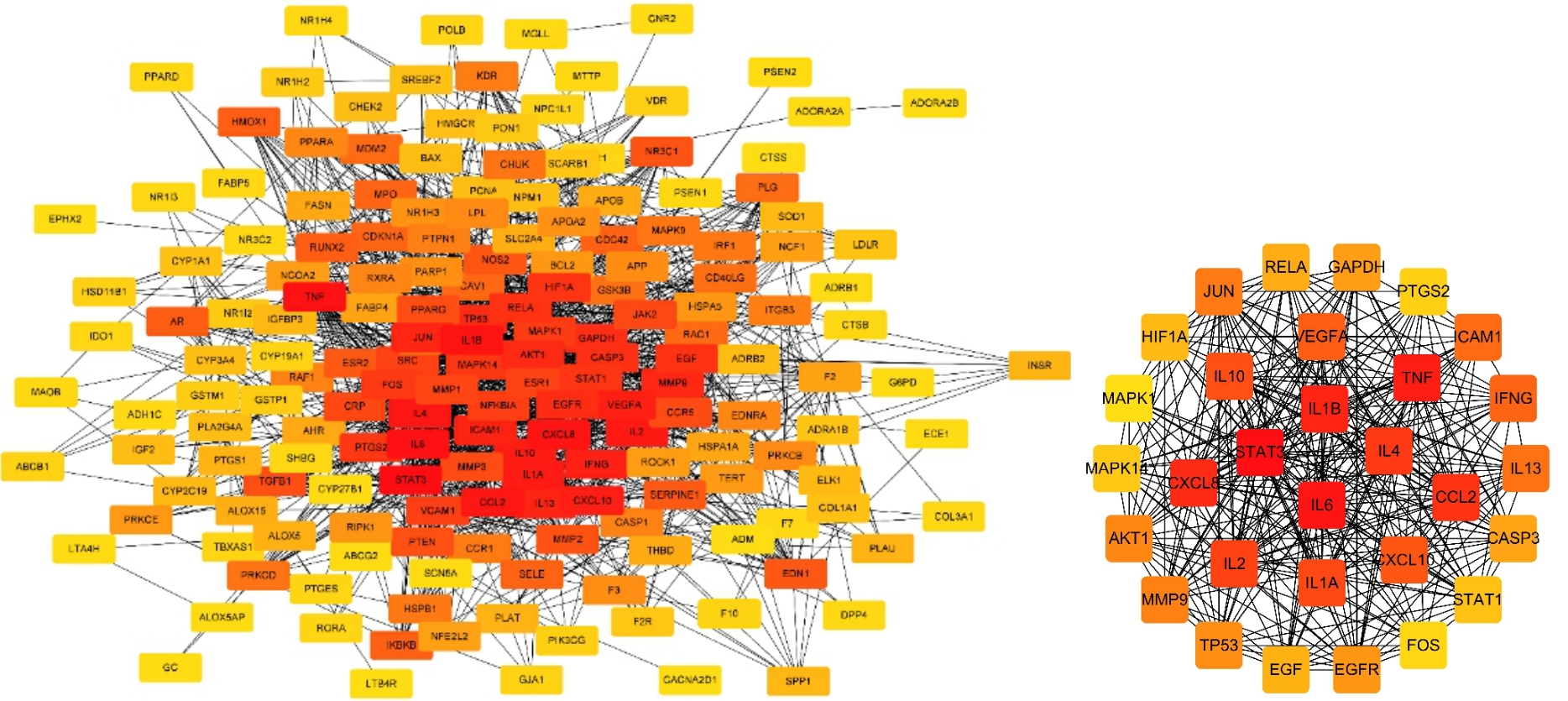
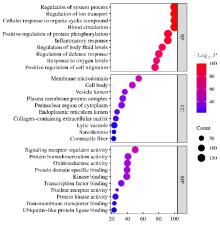
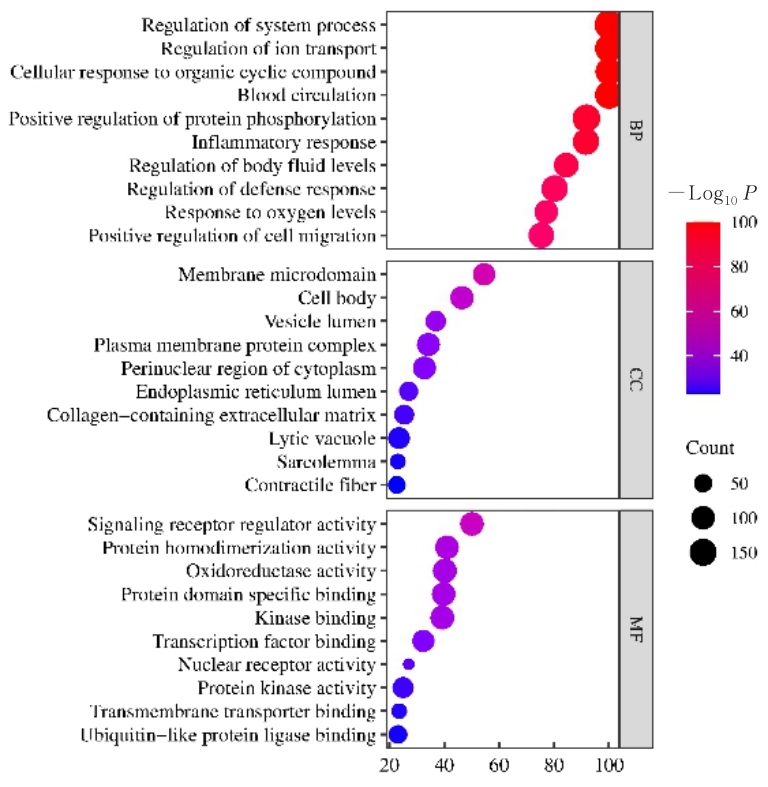
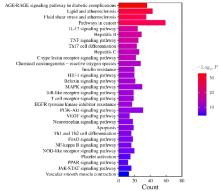
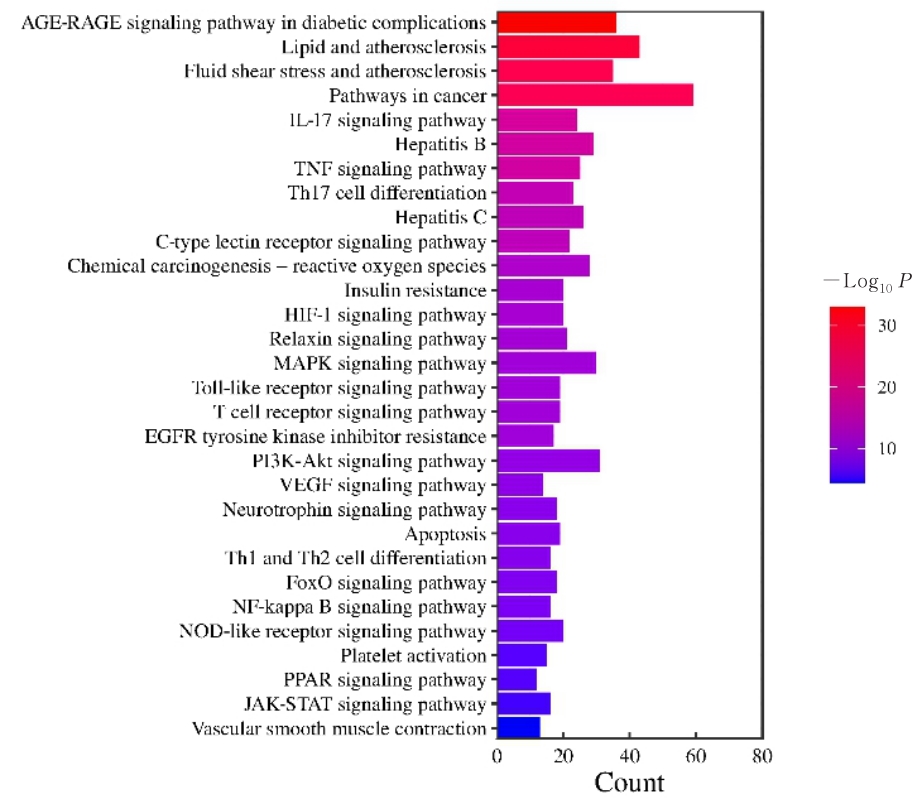
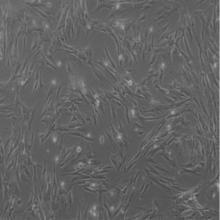
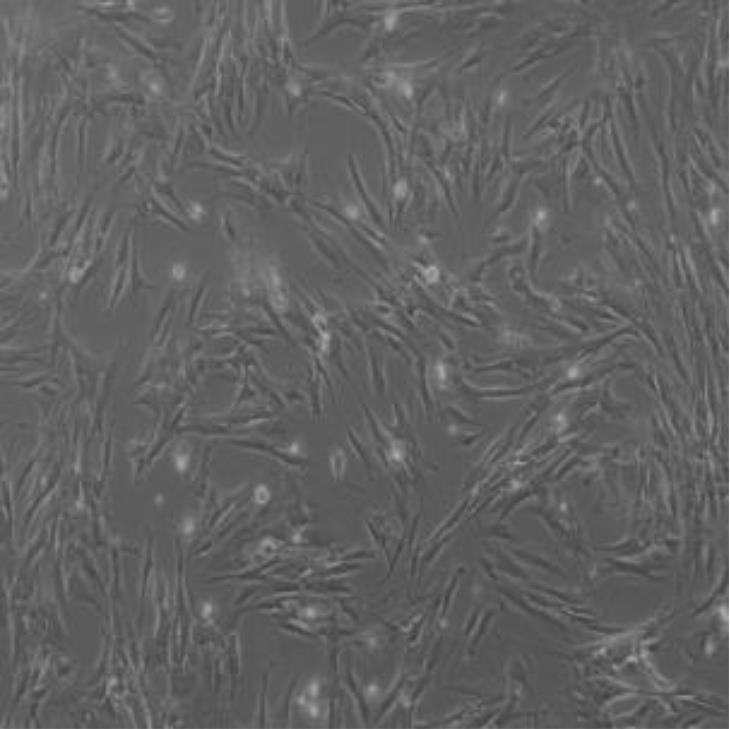
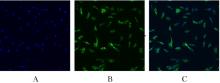
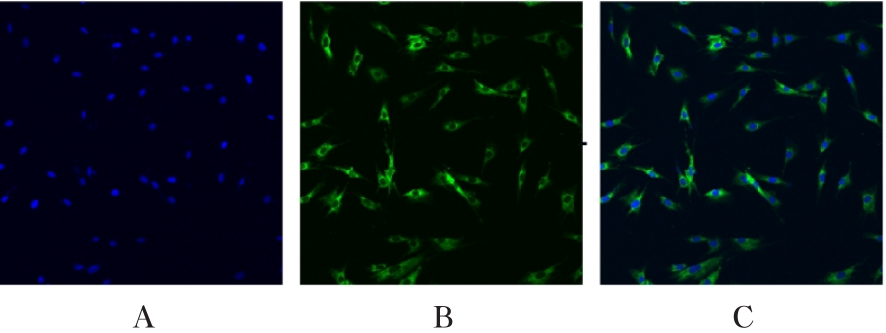
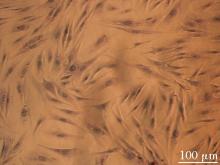
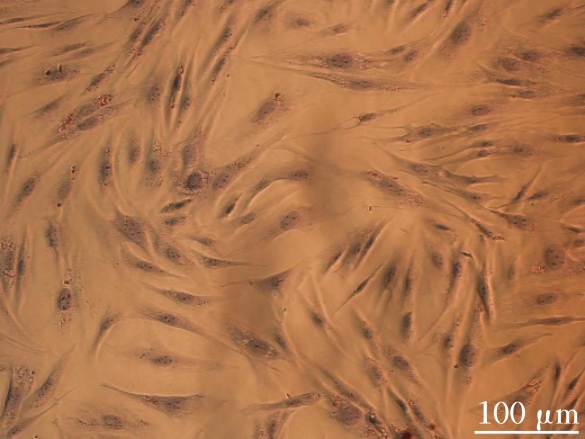
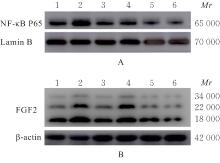
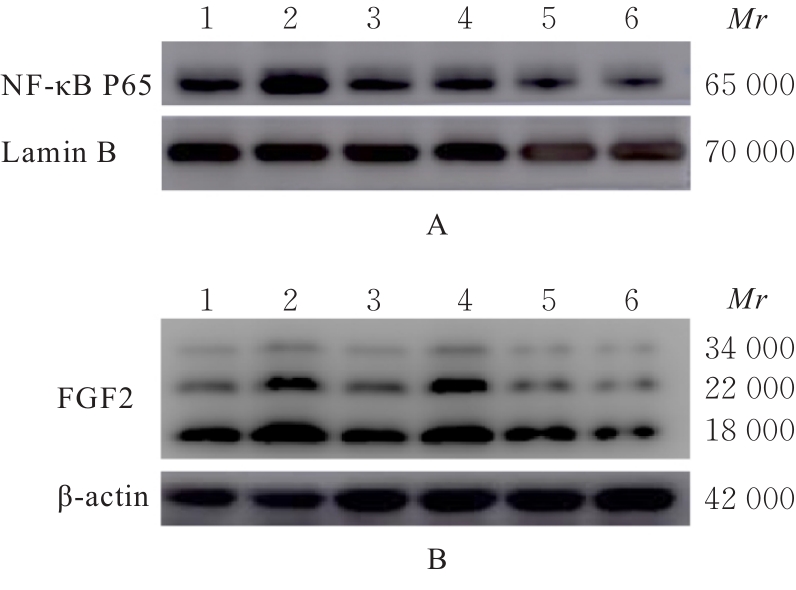
目的 利用网络药理学分析方法初步预测消斑通脉方抗动脉粥样硬化(AS)的潜在作用通路和靶点,联合体外细胞实验对其可能机制进行验证。 方法 采用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)、GeneCards、Swiss Target Prediction和Uniprot等数据库,收集消斑通脉方中活性化合物及对应靶点信息,构建“成分-靶点-疾病”网络,通过蛋白-蛋白互作(PPI)网络预测可能的作用靶点和通路,对交集靶点进行基因本体论(GO)功能富集分析和京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析。体外培养人主动脉血管平滑肌细胞(HA-VSMCs)并鉴定,采用氧化低密度脂蛋白(ox-LDL)诱导HA-VSMCs异常增殖并进行鉴定。MTT法检测不同浓度消斑通脉方作用后各组 HA-VSMCs 增殖活性,确定消斑通脉方安全性。HA-VSMCs分为空白组、模型组(诱导HA-VSMCs异常增殖)、瑞舒伐他汀组(诱导HA-VSMCs异常增殖后采用4 μmol·L-1瑞舒伐他汀干预)及低、中和高剂量消斑通脉方组(诱导HA-VSMCs异常增殖后分别采用0.025、0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方干预)。酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组HA-VSMCs培养上清中人单核细胞趋化蛋白1(MCP-1)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和白细胞介素8(IL-8)水平,实时荧光定量 PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组HA-VSMCs中核因子κB(NF- κB)p65 mRNA和成纤维细胞生长因子2(FGF2)mRNA表达水平,Western blotting 法检测各组HA-VSMCs中 NF- κB p65 和 FGF2 蛋白表达水平。 结果 消斑通脉方中含有103种活性成分,可通过作用于189个靶基因发挥抗AS作用,潜在作用靶点包括IL-6、IL-8、血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)、核因子κB1(NF-κB1)和RELA(NF-κB p65)等。GO功能分析和KEGG信号通路富集分析,消斑通脉方通过调节脂质、缺氧诱导因子1(HIF-1)、表皮生长因子(EGF)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(PI3K/Akt)和NF-κB等信号通路发挥抗AS作用。细胞形态表现和免疫荧光染色结果证明细胞为HA-VSMCs。油红O染色,可观察到大量红色脂滴,表明造模成功。MTT法检测,在一定剂量范围内消斑通脉方对HA-VSMCs增殖率无明显影响,安全性良好。ELISA 法检测,与模型组比较,瑞舒伐他汀组和不同剂量消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs培养上清中MCP-1和IL-6水平降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMC培养上清中IL-8降低(P<0.01);与瑞舒伐他汀组比较,不同剂量消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs培养上清中MCP-1降低(P<0.01),0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs培养上清中IL-8降低(P<0.01)。与模型组比较,瑞舒伐他汀组和不同剂量消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中NF-κB p65 mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.01),瑞舒伐他汀组及0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中FGF2 mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.01);与瑞舒伐他汀组比较,0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中NF-κB p65和FGF2 mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与模型组比较,瑞舒伐他汀组和不同剂量消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中NF-κB p65和FGF2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01);与瑞舒伐他汀组比较,0.050和0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01),0.100 mg·L-1消斑通脉方组HA-VSMCs中FGF2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.01)。 结论 消斑通脉方具有抗炎、抑制HA-VSMCs增殖和抗AS作用,其作用机制可能与NF-κB/FGF2通路失活有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5