吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (6): 1655-1660.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250621
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
泛免疫炎症指数对老年冠心病患者PCI术后1年内主要心血管不良事件的预测价值
- 江苏大学附属医院心内科,江苏 镇江 212001
Predictive value of pan-immune-inflammation index for major adverse cardiovascular events within 1 year after PCI in elderly patients with coronary heart disease
Tao SUN,Zhiyin DAI( ),Xuan LI,Chaopu ZHANG,Shu DING,Jianwei ZHAO
),Xuan LI,Chaopu ZHANG,Shu DING,Jianwei ZHAO
- Department of Cardiology,Affiliated Hospital,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212001,China
摘要:
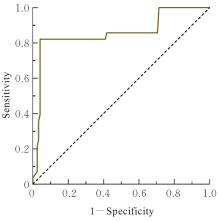
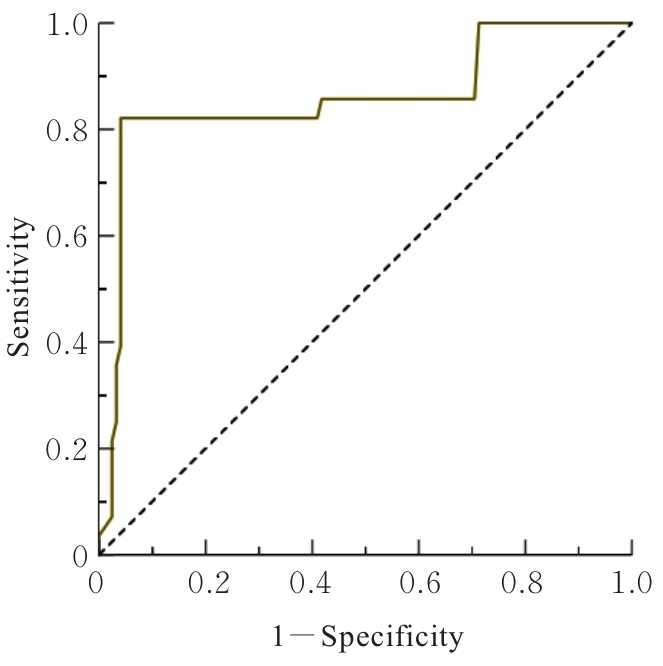
目的 探讨泛免疫炎症指数(PIV)在老年冠心病患者接受经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)后1年内预测主要心血管不良事件(MACE)的临床价值,阐明炎症反应在冠心病患者术后恢复和预后中的作用。 方法 选取2020年7月—2023年8月接受PCI术治疗的150例老年冠心病患者作为研究对象,依据术后1年是否出现MACE分为MACE组(n=28)和未发生MACE组(n=122),采集患者基线资料和生化指标,并计算PIV,多因素Logistic回归分析老年冠心病患者PCI术后1年内发生MACE的影响因素,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析PIV对老年冠心病患者PCI术后1年内发生MACE的预测价值。 结果 与未发生MACE组比较,MACE组患者总胆固醇(TC)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)水平及中性粒细胞(NEUT)、血小板(PLT)计数和PIV均明显升高(P<0.05),2组患者其他资料比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析,TC(OR=1.571,95%CI:1.088~2.270)及LDL-C(OR=32.506,95%CI:8.880~118.994)水平和PIV(OR=1.014,95%CI:1.010~1.019)均为老年冠心病患者PCI术后1年发生MACE的影响因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析,PIV预测MACE的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)值为0.857(95%CI:0.762~0.951),灵敏度为0.821,特异度为0.959,最大约登指数为0.780,最佳阈值为778.805(P<0.01)。 结论 PIV对老年冠心病患者PCI术后1年内发生MACE具有重要的预测价值。
中图分类号:
- R541.4