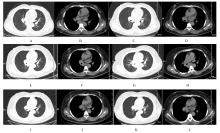
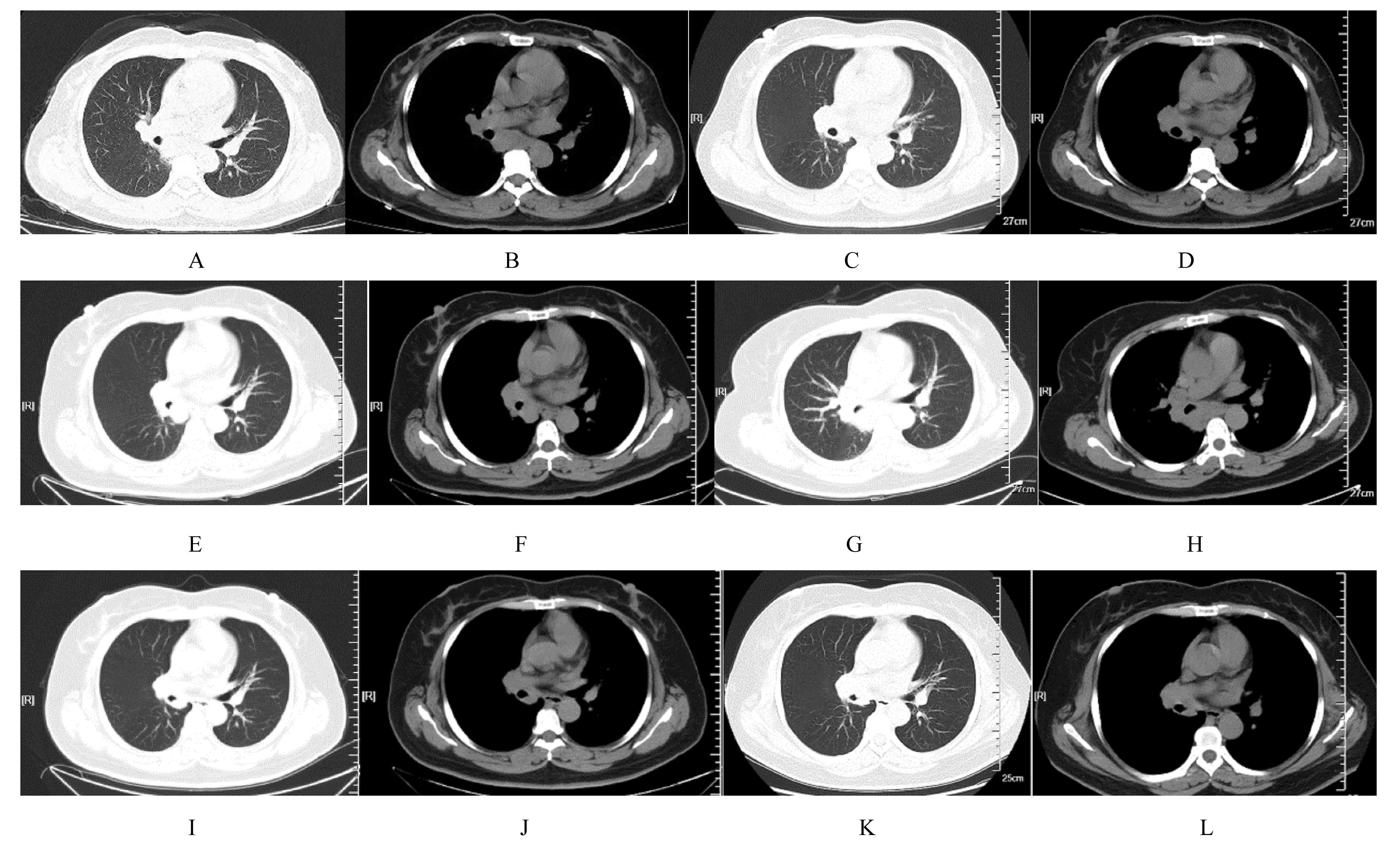
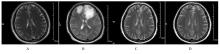
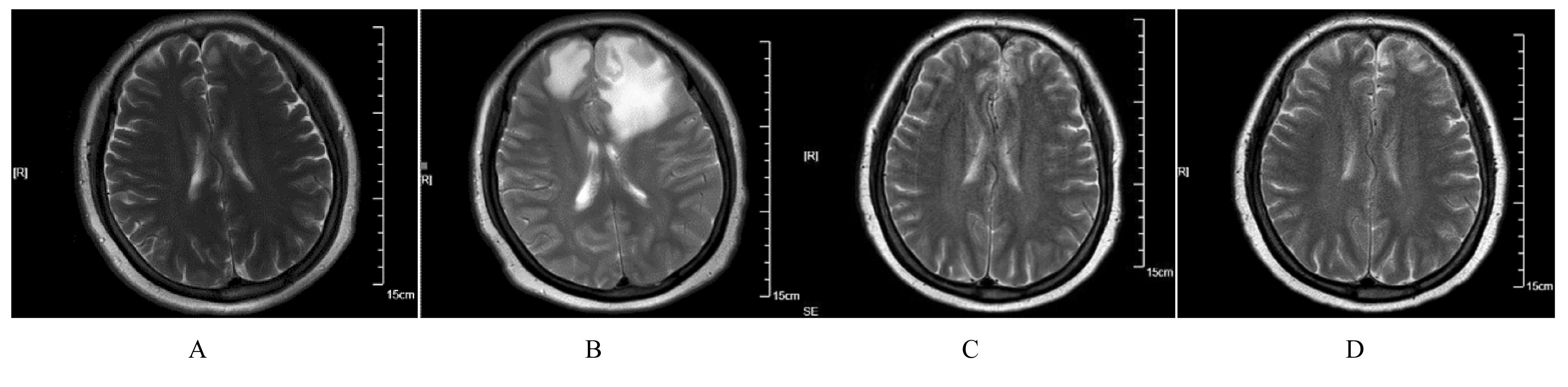
| 1 |
WU S G, SHIH J Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 38.
|
| 2 |
郭宗儒. 我国自行研制的抗癌药物赛沃替尼[J]. 药学学报, 2022, 57(3): 839-844.
|
| 3 |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2021,71(3):209-249.
|
| 4 |
ZENG Q, VOGTMANN E, JIA M M, et al. Tobacco smoking and trends in histological subtypes of female lung cancer at the Cancer Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences over 13 years [J]. Thorac Cancer, 2019, 10(8): 1717-1724.
|
| 5 |
MAEMONDO M, INOUE A, KOBAYASHI K, et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR [J]. N Engl J Med,2010,362(25): 2380-2388.
|
| 6 |
SHI Y K, ZHANG L, LIU X Q, et al. Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ICOGEN): a randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial [J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013, 14(10): 953-961.
|
| 7 |
杨 洪, 刘怡文, 孔金玉. 有氧运动对非小细胞肺癌吉非替尼耐药的延缓作用[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(5): 670-676.
|
| 8 |
SHI Y K, WANG L, HAN B H, et al. First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): a phase 3, open-label, randomized study [J]. Ann Oncol, 2017, 28(10): 2443-2450.
|
| 9 |
QU J, WANG Y N, XU P, et al. Clinical efficacy of icotinib in lung cancer patients with different EGFR mutation status: a meta-analysis [J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(20): 33961-33971.
|
| 10 |
DONG R F, ZHU M L, LIU M M, et al. EGFR mutation mediates resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC: from molecular mechanisms to clinical research [J]. Pharmacol Res,2021,167: 105583.
|
| 11 |
YU H A, ARCILA M E, REKHTMAN N, et al. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2013, 19(8): 2240-2247.
|
| 12 |
MATSUO N, AZUMA K, SAKAI K, et al. Association of EGFR exon 19 deletion and EGFR-TKI treatment duration with frequency of T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung cancer patients [J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 36458.
|
| 13 |
YUN C H, MENGWASSER K E, TOMS A V, et al. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2008, 105(6): 2070-2075.
|
| 14 |
JÄNNE P A, YANG J C, KIM D W, et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. N Engl J Med, 2015, 372(18): 1689-1699.
|
| 15 |
GOSS G, TSAI C M, SHEPHERD F A, et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study [J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(12): 1643-1652.
|
| 16 |
SORIA J C, OHE Y, VANSTEENKISTE J, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. N Engl J Med,2018, 378(2): 113-125.
|
| 17 |
OXNARD G R, YANG J C, YU H, et al. TATTON: a multi-arm, phase Ib trial of osimertinib combined with selumetinib, savolitinib, or durvalumab in EGFR-mutant lung cancer[J].Ann Oncol,2020,31(4):507-516.
|
| 18 |
ENGELMAN J A, ZEJNULLAHU K, MITSUDOMI T,et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling [J]. Science, 2007, 316(5827): 1039-1043.
|
| 19 |
OXNARD G R, HU Y B, MILEHAM K F, et al. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib [J]. JAMA Oncol, 2018, 4(11): 1527-1534.
|
| 20 |
IN G, MASON J, LIN S, et al. Development of metastatic brain disease involves progression through lung metastases in EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancer [J].Converg Sci Phys Oncol,2017,3(3):034001.
|
| 21 |
CHEN Y, DENG J, LIU Y, et al. Analysis of metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation [J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(3): 206.
|
| 22 |
KRAWCZYK P, DUCHNOWSKA R, NICOŚ M, et al. Preventing central nervous system metastases in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2018, 18(11): 1077-1083.
|
| 23 |
LE X N, PURI S, NEGRAO M V, et al. Landscape of EGFR-dependent and -independent resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and continuation therapy beyond progression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC [J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(24): 6195-6203.
|
| 24 |
SHI P Y, OH Y T, ZHANG G J, et al. Met gene amplification and protein hyperactivation is a mechanism of resistance to both first and third generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer treatment [J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 380(2): 494-504.
|
| 25 |
ZHOU B, GONG Q, LI B, et al. Clinical outcomes and safety of osimertinib plus anlotinib for patients with previously treated EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC: a retrospective study [J].J Clin Pharm Ther,2022,47(5): 643-651.
|
| 26 |
REUNGWETWATTANA T, NAKAGAWA K, CHO B C, et al. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018: JCO2018783118.
|
| 27 |
SHAIKH M, SHINDE Y, PAWARA R, et al. Emerging approaches to overcome acquired drug resistance obstacles to osimertinib in non-small-cell lung cancer [J]. J Med Chem, 2022, 65(2): 1008-1046.
|
| 28 |
SEQUIST L V, HAN J Y, AHN M J, et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study [J]. Lancet Oncol, 2020, 21(3): 373-386.
|
| 29 |
LEONETTI A, FACCHINETTI F, TISEO M. Upfront osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: is brain still a sanctuary? [J]. Ann Transl Med, 2018, 6(): S110.
|
| 30 |
WU Y L, AHN M J, GARASSINO M C, et al. CNS efficacy of osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: data from a randomized phase Ⅲ trial (AURA3) [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(26): 2702-2709.
|
 )
)