吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 939-946.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240407
PTMC/PVP温控收缩性纳米纤维膜与小鼠成纤维细胞的生物相容性及其对大鼠皮肤全层缺损的修复作用
刘丽萍1,李驰宇2,杨韬1,王少如1,刘昀1,刘国民2,程志强3,罗云纲4( ),刘志辉1(
),刘志辉1( )
)
- 1.吉林大学口腔医院修复科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第二医院骨科,吉林 长春 130041
3.吉林农业大学资源与环境学院,吉林 长春 130118
4.吉林大学第一医院 净月分院口腔医学中心,吉林 长春 130118
Biocompatibility of PTMC/PVP temperature-controlled shrinkage nanofiber membrane with mouse fibroblasts and its repairment effect on full-thickness skin defects in rats
Liping LIU1,Chiyu LI2,Tao YANG1,Shaoru WANG1,Yun LIU1,Guomin LIU2,Zhiqiang CHENG3,Yungang LUO4( ),Zhihui LIU1(
),Zhihui LIU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
2.Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130041, China
3.School of Resources and Environment, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun 130118, China
4.Stomatology Center, Jingyue Campus, First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130118, China
摘要:
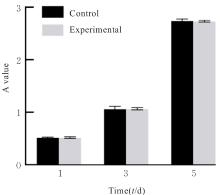
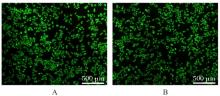
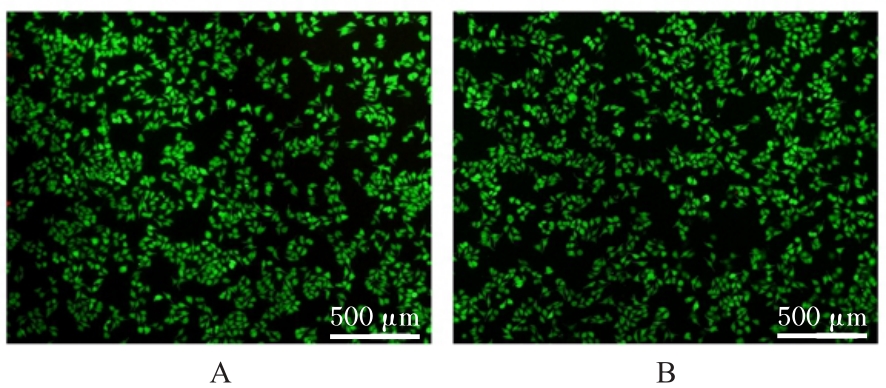
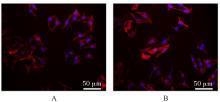
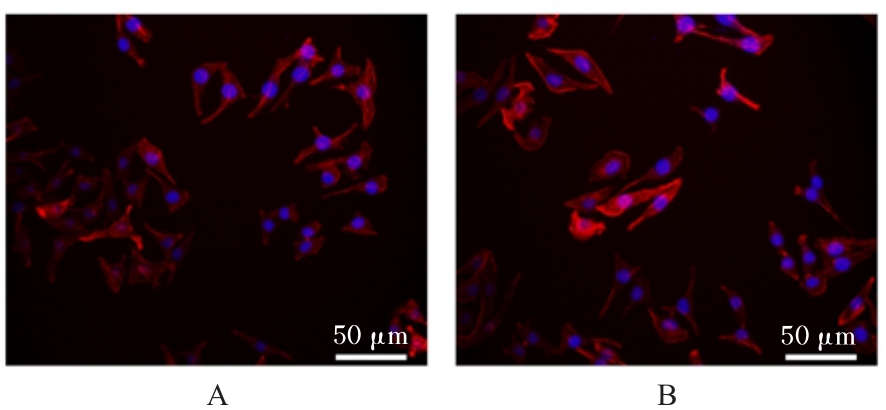
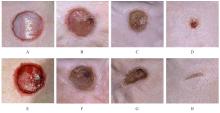
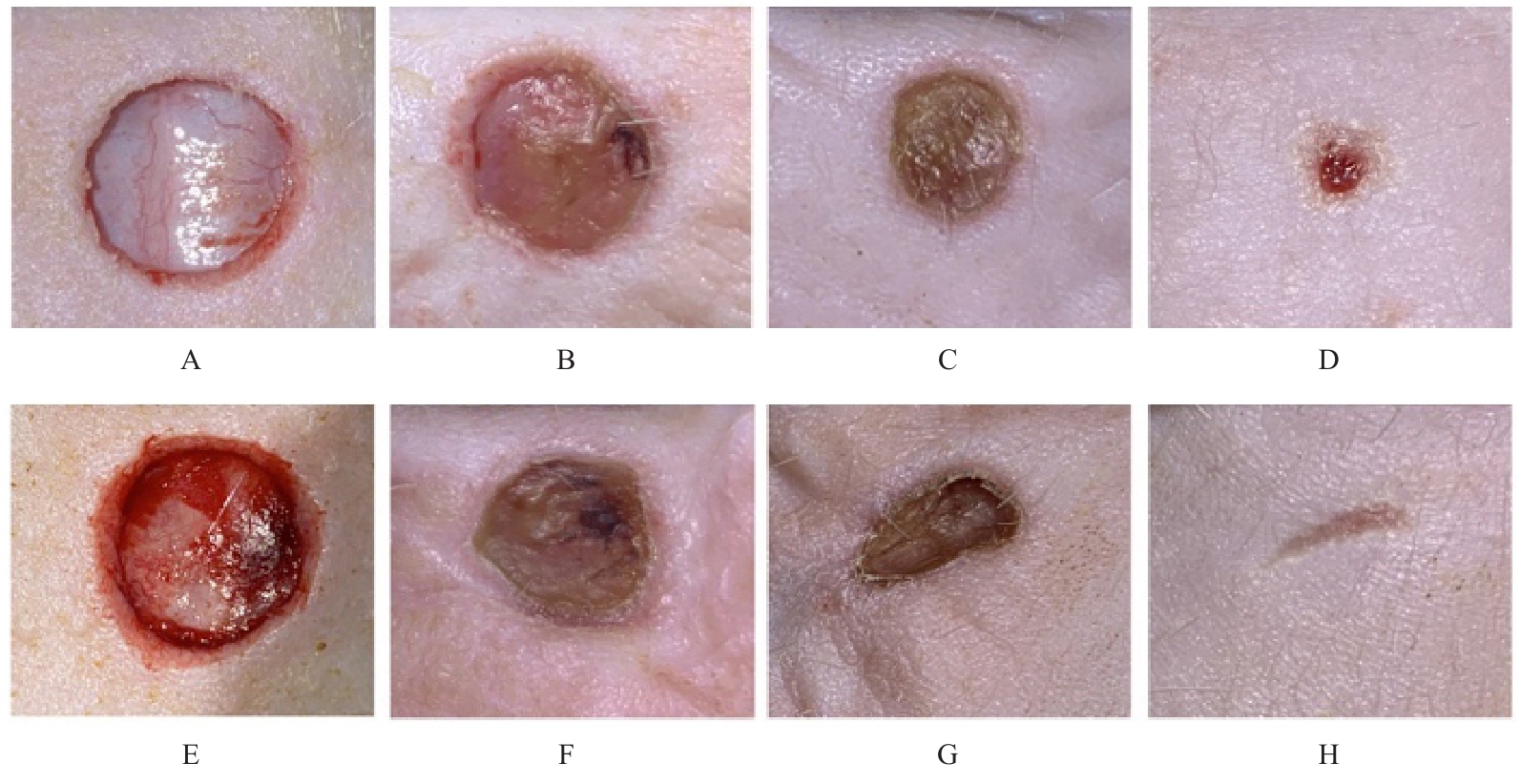
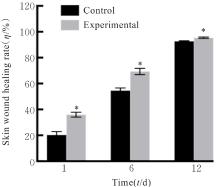
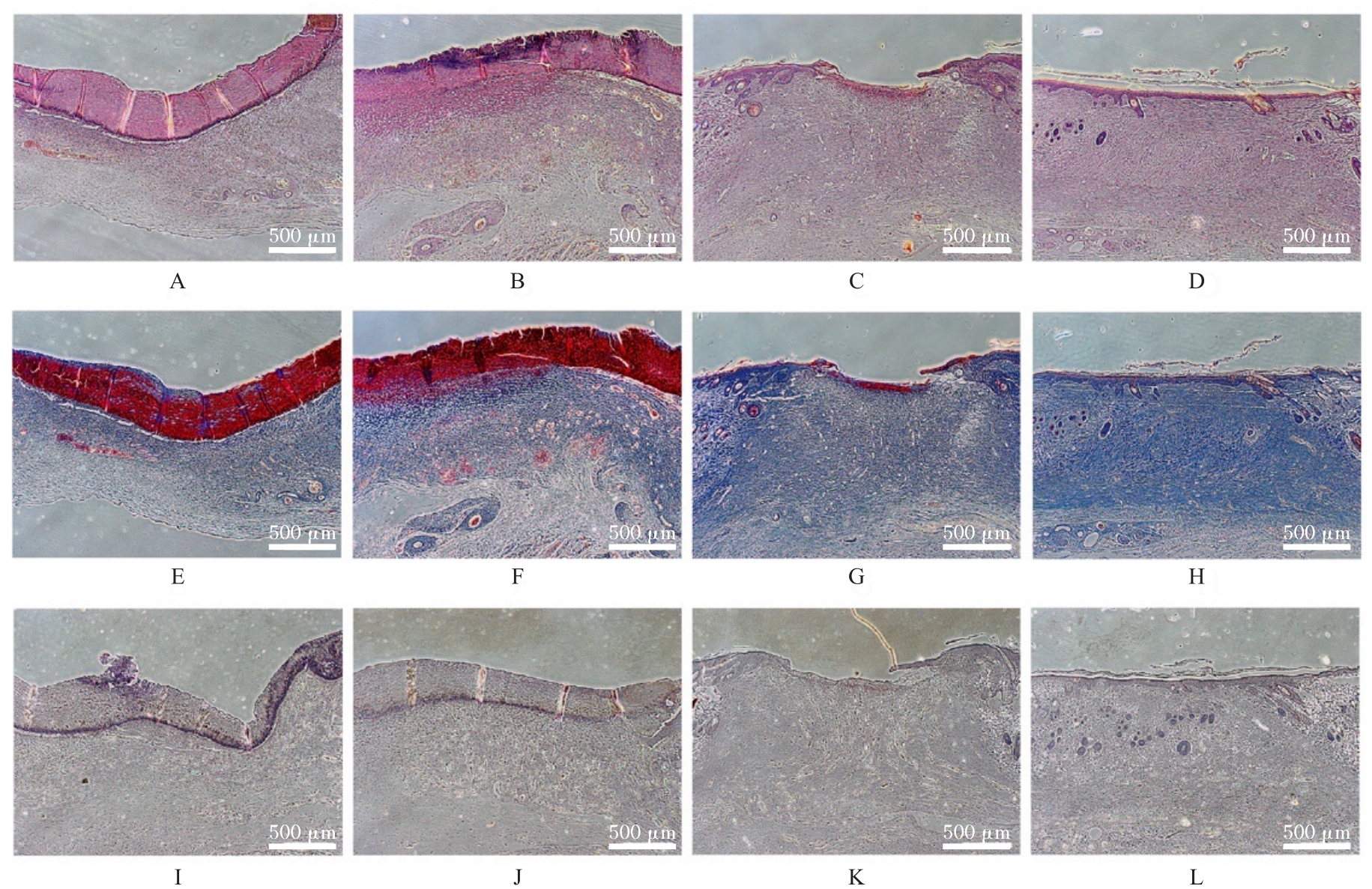
目的 探讨温控收缩性聚三亚甲基碳酸酯(PTMC)/聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)纳米纤维膜对小鼠成纤维细胞生物学行为的影响及对大鼠全层皮肤缺损的修复作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 体外实验选用小鼠成纤维L929细胞,分为对照组和实验组(采用PTMC/PVP纳米纤维膜处理),CCK-8法检测2组细胞增殖活性,活/死细胞染色实验观察2组细胞中活/死细胞数量,细胞骨架染色实验观察2组细胞形态表现。体内实验选用12只6周龄雄性SD大鼠,随机分为对照组和实验组,每组6只,建立全层皮肤缺损模型,实验组大鼠采用PTMC/PVP纳米纤维膜治疗,术后拍照观察,第0、3、6和12天时计算2组大鼠创面愈合率,术后第6和12天切取2组大鼠皮肤创面和周围组织,采用HE染色观察皮肤创面和周围组织病理形态表现,Masson三色染色观察2组大鼠皮肤创面组织中胶原蛋白沉积情况,CD31免疫组织化学染色检测2组大鼠皮肤创面组织中血管形成数量。 结果 CCK-8实验,实验组细胞增殖活性在第1、3和5天均呈升高趋势,与对照组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。活/死细胞染色实验,与对照组比较,实验组细胞密度和数量无明显变化且以活细胞为主。细胞骨架染色实验,实验组和对照组细胞均呈梭形且细胞伸展。体内实验,第3、6和12 天时,与对照组比较,实验组大鼠创面愈合率升高(P<0.01),12 d时实验组大鼠创面愈合率为95.45%,创面基本愈合。HE染色,与对照组比较,第12天实验组大鼠创面皮肤结构更接近正常皮肤,有丰富的肉芽组织、规则的表皮结构和新血管生成。Masson三色染色,与对照组比较,实验组大鼠创面组织中胶原蛋白沉积量更多。免疫组织化学染色,与对照组比较,实验组大鼠创面组织中CD31表达增多,表明血管形成数量增加。 结论 PTMC/PVP温控收缩性纳米纤维膜具有良好的生物相容性,且能促进大鼠皮肤全层缺损的修复,其作用机制可能与增强基底细胞增殖活性有关。
中图分类号:
- R318.08