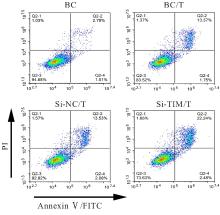
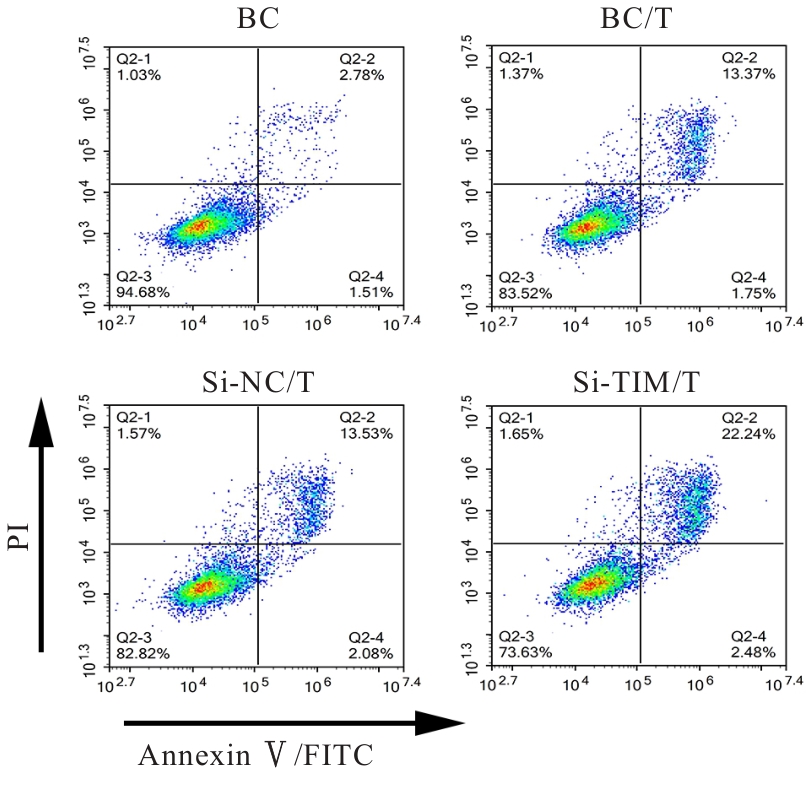
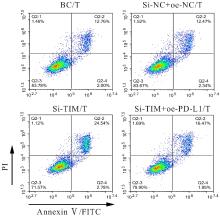
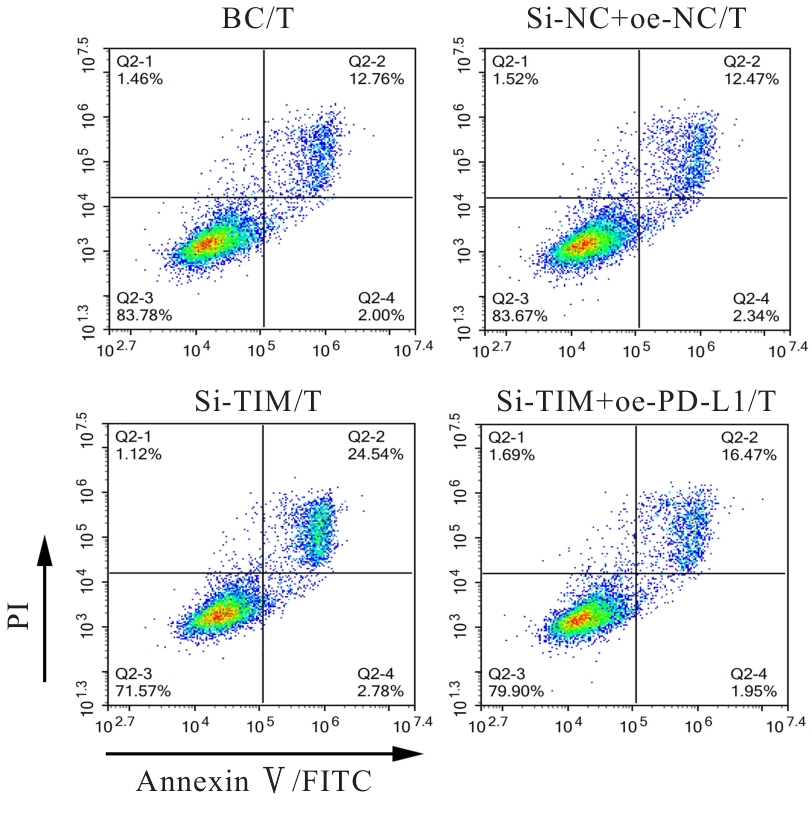
| [1] |
SONG J, SOKOLL L J, ZHANG Z, et al. VCAM-1 complements CA-125 in detecting recurrent ovarian cancer[J]. Clin Proteomics, 2023, 20(1): 25.
|
| [2] |
LAMPROPOULOU D I, PAPADIMITRIOU M, PAPADIMITRIOU C, et al. The role of EMT-related lncRNAs in ovarian cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(12): 10079.
|
| [3] |
PREETAM S, MONDAL S, PRIYA S, et al. Targeting tumour markers in ovarian cancer treatment[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2024, 559: 119687.
|
| [4] |
YIN S S, GAO F H. Molecular mechanism of tumor cell immune escape mediated by CD24/siglec-10[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1324.
|
| [5] |
JIANG X J, WANG J, DENG X Y, et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 10.
|
| [6] |
CAI Y D, CHIU J C. Timeless in animal circadian clocks and beyond[J]. FEBS J, 2022, 289(21): 6559-6575.
|
| [7] |
VIPAT S, MOISEEVA T N. The TIMELESS roles in genome stability and beyond[J]. J Mol Biol, 2024, 436(1): 168206.
|
| [8] |
COLANGELO T, CARBONE A, MAZZARELLI F, et al. Loss of circadian gene Timeless induces EMT and tumor progression in colorectal cancer via Zeb1-dependent mechanism[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2022, 29(8): 1552-1568.
|
| [9] |
XING X, GU F, HUA L Y, et al. TIMELESS promotes tumor progression by enhancing macrophages recruitment in ovarian cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 732058.
|
| [10] |
粟连秀, 陈静平, 杨达平, 等. 沉默生物钟基因Timeless对卵巢癌SKOV3细胞凋亡和侵袭能力的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1169-1175.
|
| [11] |
DONG X R, DAI H J, LIN Y P, et al. TIMELESS upregulates PD-L1 expression and exerts an immunosuppressive role in breast cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 400.
|
| [12] |
AKTAR N, CHEN Y T, ABBAS M, et al. Understanding of immune escape mechanisms and advances in cancer immunotherapy[J]. J Oncol, 2022, 2022: 8901326.
|
| [13] |
SAVID-FRONTERA C, VIANO M E, BAEZ N S, et al. Exploring the immunomodulatory role of virtual memory CD8+T cells: Role of IFN gamma in tumor growth control[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 971001.
|
| [14] |
GILES J R, GLOBIG A M, KAECH S M, et al. CD8+T cells in the cancer-immunity cycle[J]. Immunity, 2023, 56(10): 2231-2253.
|
| [15] |
QIN Y Y, BAO X Y, ZHENG M Z. CD8+T-cell immunity orchestrated by iNKT cells[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 13: 1109347.
|
| [16] |
WANG X M, ZHANG Y, ZHENG J, et al. LncRNA UCA1 attenuated the killing effect of cytotoxic CD8+T cells on anaplastic thyroid carcinoma via miR-148a/PD-L1 pathway[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2021, 70(8): 2235-2245.
|
| [17] |
杨 婷, 郑锦秀, 高书华, 等. 钙连蛋白(CNX)通过促进MHCⅠ表达增强CD8+T细胞对结直肠癌细胞的杀伤作用[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2022, 38(2): 97-102.
|
| [18] |
QIN R, ZHAO C, WANG C J, et al. Tryptophan potentiates CD8+T cells against cancer cells by TRIP12 tryptophanylation and surface PD-1 downregulation[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2021, 9(7): e002840.
|
| [19] |
CHANG W H, LAI A G. Timing gone awry: distinct tumour suppressive and oncogenic roles of the circadian clock and crosstalk with hypoxia signalling in diverse malignancies[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17(1): 132.
|
| [20] |
GAO Y Y, WU Y W, ZHANG N M, et al. IDH1 gene mutation activates Smad signaling molecules to regulate the expression levels of cell cycle and biological rhythm genes in human glioma U87-MG cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2021, 23(5): 354.
|
| [21] |
YANG Y C, TANG X Z, LIN Z J, et al. An integrative evaluation of circadian gene TIMELESS as a pan-cancer immunological and predictive biomarker[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28(1): 563.
|
| [22] |
ZHOU J H, ZHANG Y H, ZOU X W, et al. Aberrantly expressed timeless regulates cell proliferation and cisplatin efficacy in cervical cancer[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2020, 31(5/6): 385-395.
|
| [23] |
HOEKSTRA M E, VIJVER S V, SCHUMACHER T N. Modulation of the tumor micro-environment by CD8+ T cell-derived cytokines[J]. Curr Opin Immunol, 2021, 69: 65-71.
|
| [24] |
ZHU D, XU R D, HUANG X P, et al. Deubiquitinating enzyme OTUB1 promotes cancer cell immunosuppression via preventing ER-associated degradation of immune checkpoint protein PD-L1[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28(6): 1773-1789.
|
| [25] |
CHA J H, YANG W H, XIA W Y, et al. Metformin promotes antitumor immunity via endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation of PD-L1[J]. Mol Cell, 2018, 71(4): 606-620.e7.
|
| [26] |
DUMITRU A, DOBRICA E C, CROITORU A, et al. Focus on PD-1/PD-L1 as a therapeutic target in ovarian cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(20): 12067.
|
| [27] |
CHARDIN L, LEARY A. Immunotherapy in ovarian cancer: thinking beyond PD-1/PD-L1[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 795547.
|
| [28] |
KHATOON E, PARAMA D, KUMAR A, et al. Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 axis as new horizon for ovarian cancer therapy[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 306: 120827.
|
| [29] |
CHEN J X, YI X J, GAO S X, et al. The possible regulatory effect of the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway on Tregs in ovarian cancer[J]. Gen Physiol Biophys, 2020, 39(4): 319-330.
|
 )
)