吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 642-652.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250309
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
M2巨噬细胞通过调控NF-κB信号通路对非小细胞肺癌A549细胞上皮-间质转化和顺铂耐药的促进作用
- 1.北华大学基础医学院免疫学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.吉林大学第一医院肿瘤妇科,吉林 长春 130021
Promotive effect of M2 macrophages on epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway
Xingxiang WANG1,Ying ZHAO1,Qiaotong REN1,Hefei WANG2,Gang PU1,Chun LI1( )
)
- 1.Department of Immunology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Oncological Gynecology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
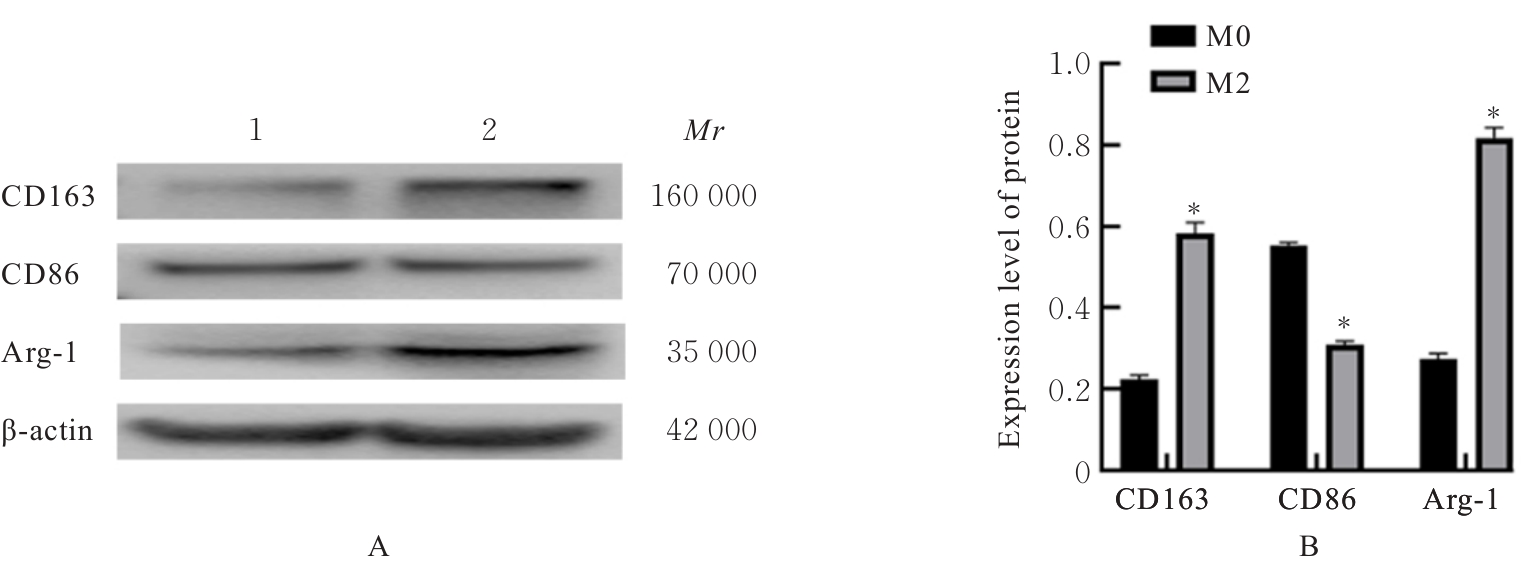
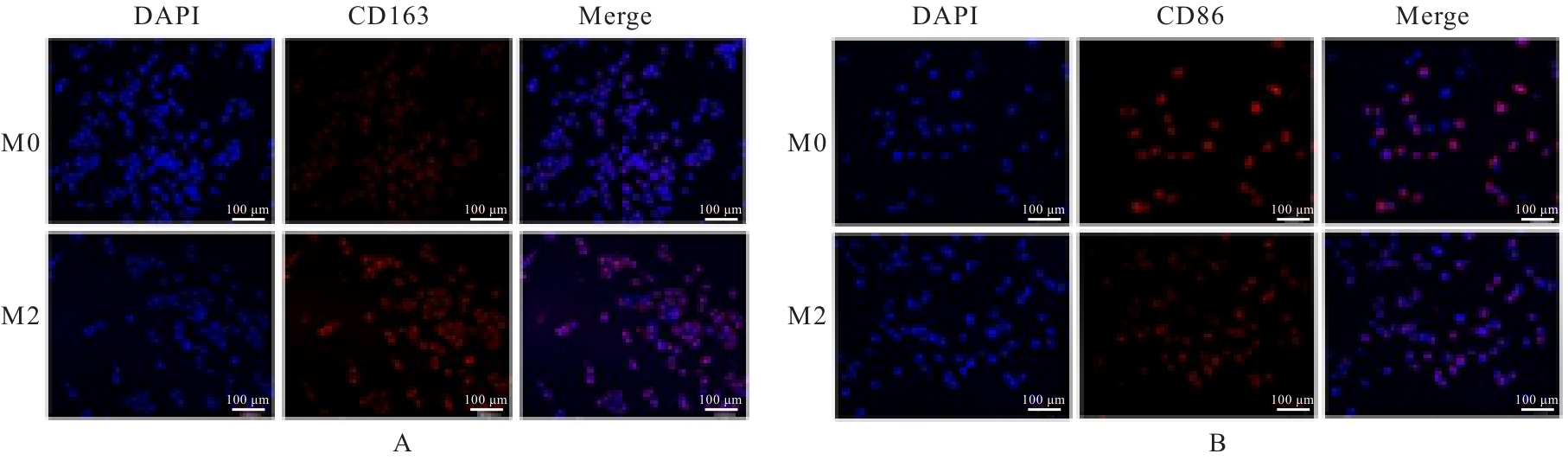
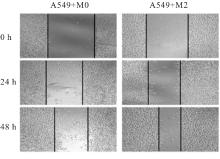
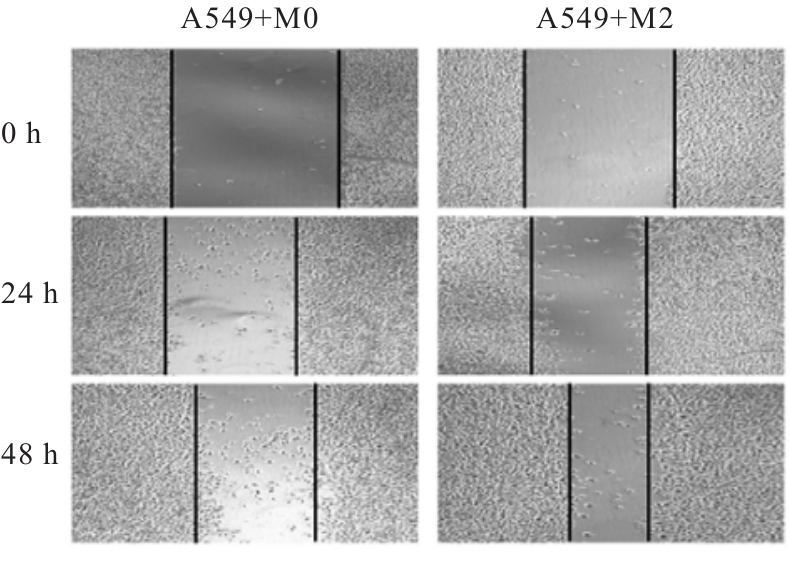
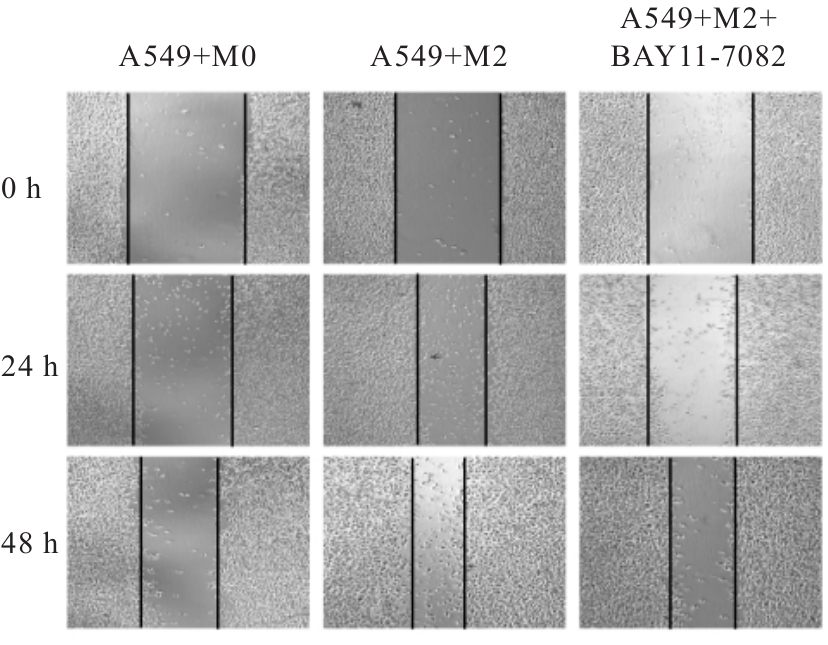
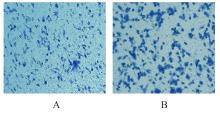
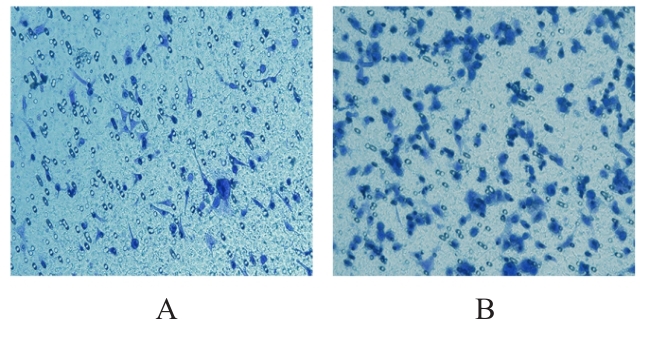
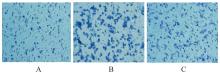
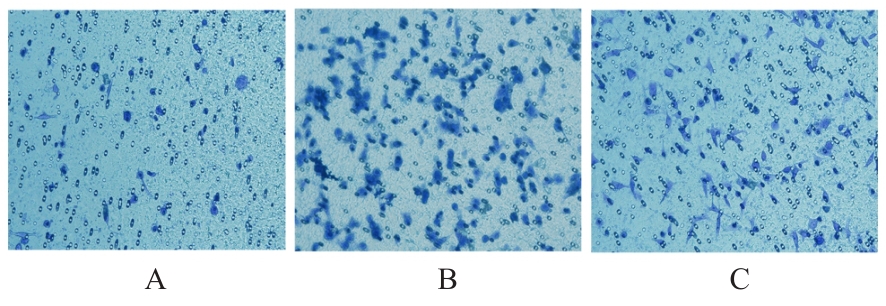
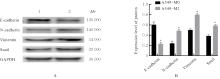
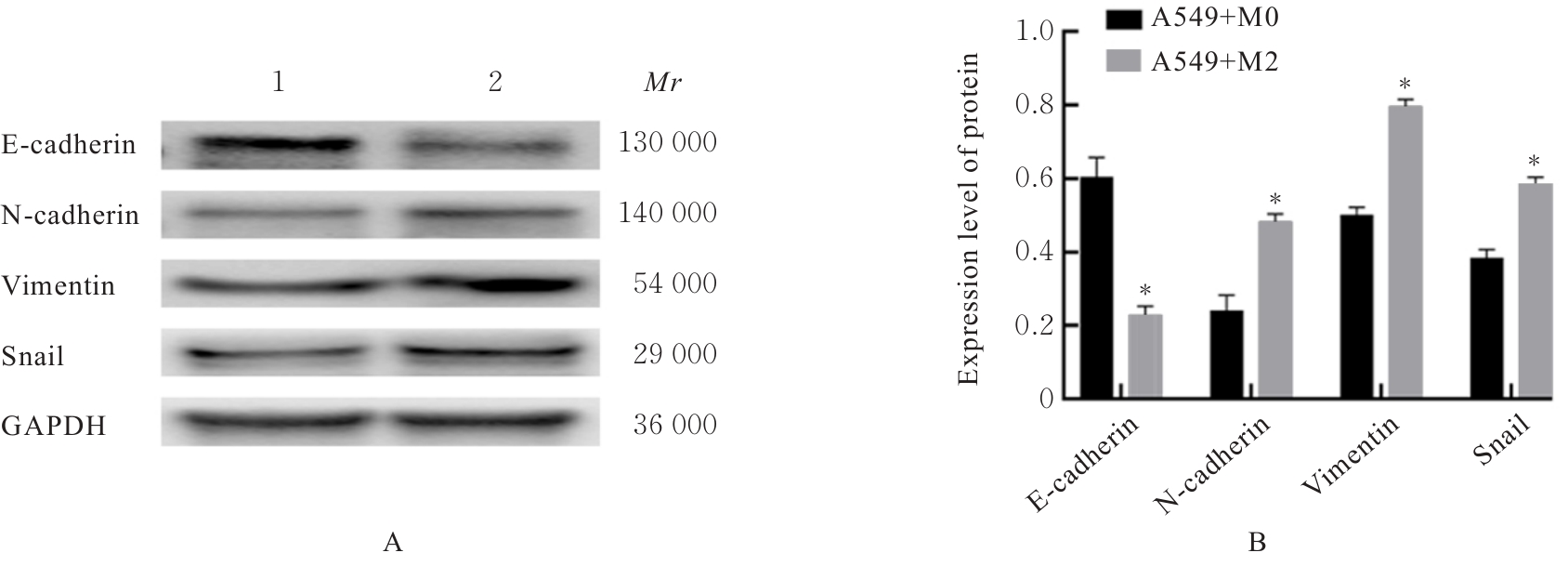
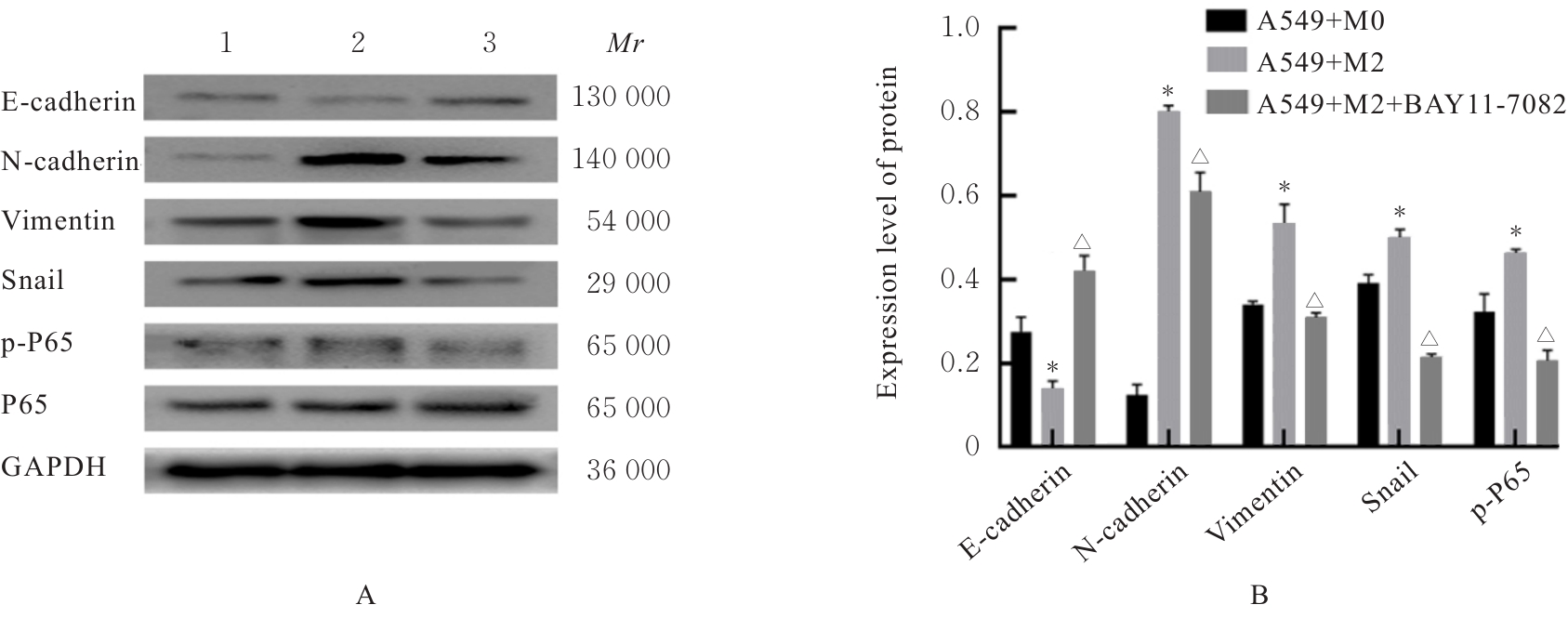
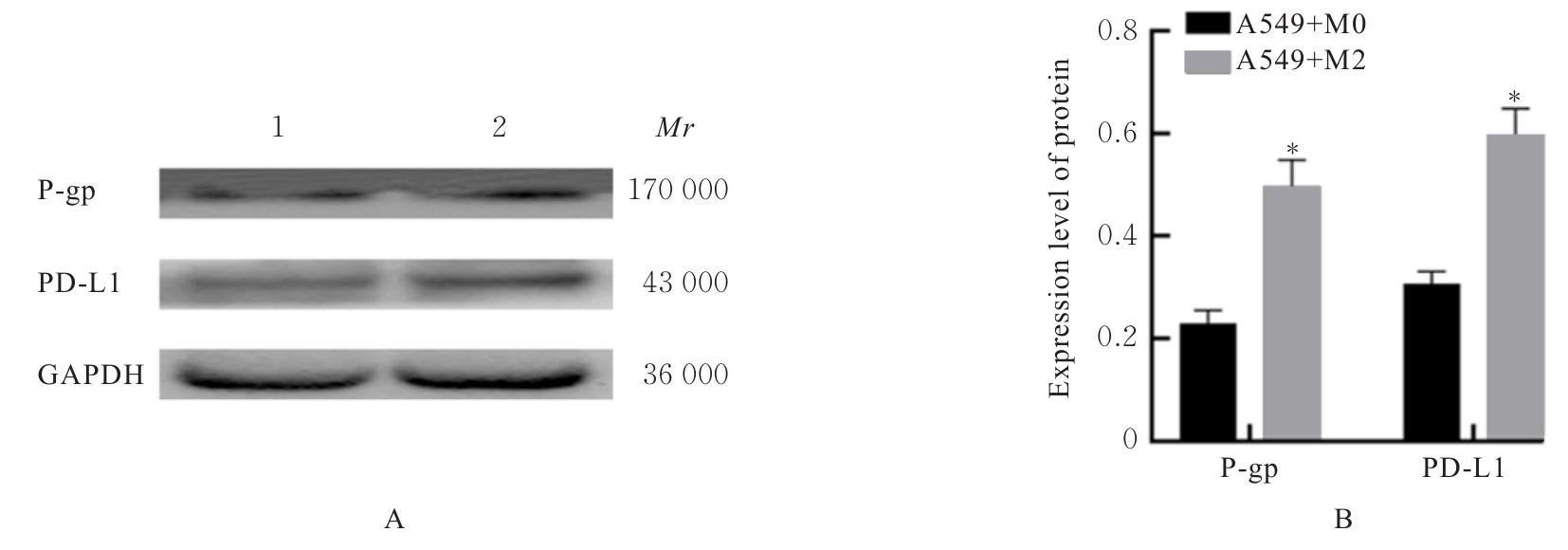
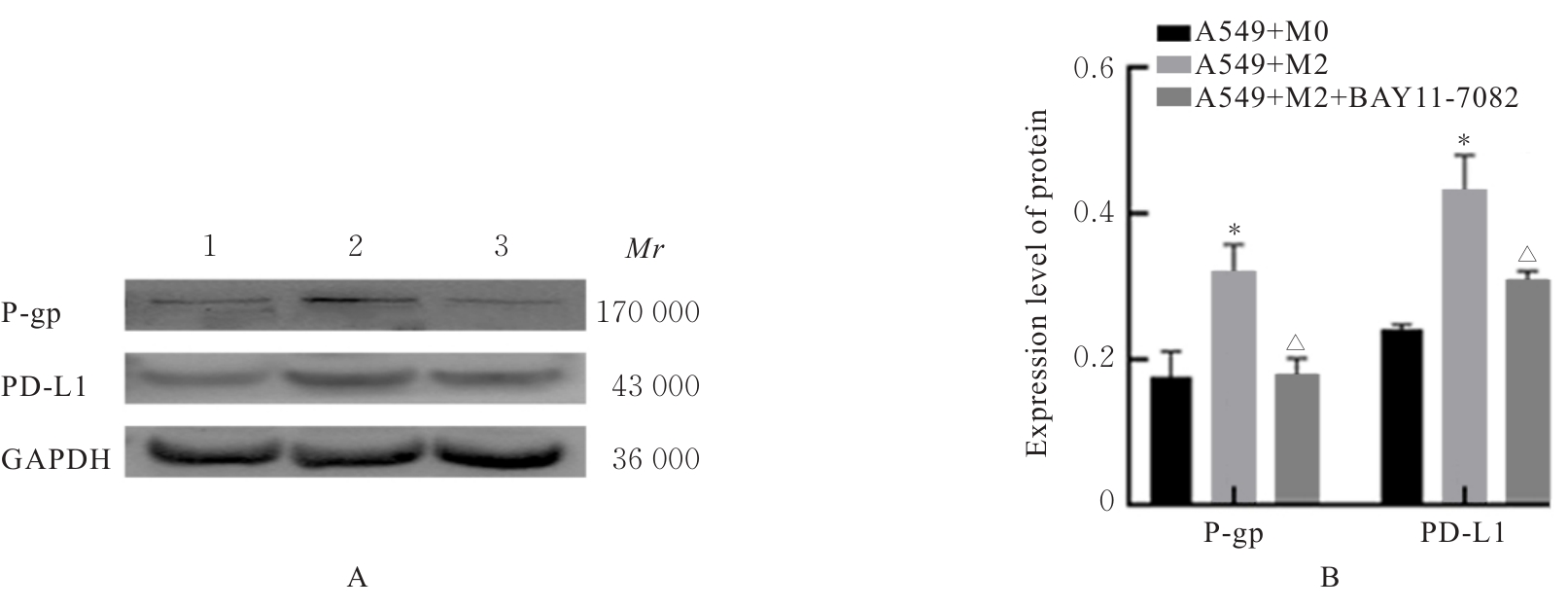
目的 探讨M2巨噬细胞在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)上皮-间质转化(EMT)和顺铂(DDP)耐药中的作用,阐明核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路的调控机制。 方法 选取人单核细胞白血病THP-1细胞,通过佛波酯(PMA)诱导分化为M0巨噬细胞,白细胞介素(IL)-4和IL-13联合诱导M0巨噬细胞分化为M2巨噬细胞。采用Western blotting法和免疫荧光法检测M0和M2巨噬细胞中CD163、CD86及精氨酸酶1(Arg-1)蛋白表达情况。选取人NSCLC细胞A549,采用Transwell小室分别与M0和M2巨噬细胞非接触式共培养,细胞分为A549+M0组(A549细胞与M0巨噬细胞共培养)、A549+M2组(A549细胞与M2巨噬细胞共培养)和A549+M2+BAY11-7082组(A549细胞与M2巨噬细胞共培养后加入10 mmol·L-1 NF-κB抑制剂BAY11-7082)。细胞划痕实验检测各组A549细胞划痕愈合率,Transwell小室实验检测各组A549细胞中侵袭细胞数,细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测共培养体系中DDP处理的各组A549细胞生长抑制率和半数抑制浓度(IC50)值,Western blotting法检测各组A549细胞中波形蛋白(Vimentin)、E钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、N钙黏蛋白(N-cadherin)、转录因子Snail、磷酸化P65(p-P65)、P糖蛋白(P-gp)和细胞程序性死亡配体1(PD-L1)蛋白表达水平。 结果 Western blotting法,与M0组比较,M2组巨噬细胞中CD163和Arg-1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05),CD86蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。免疫荧光法,与M0组比较,M2组巨噬细胞中CD163蛋白表达增强,CD86蛋白表达减弱。细胞划痕实验,培养24和48 h时,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞划痕愈合率均明显升高(P<0.05);3组共培养体系中,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞划痕愈合率明显升高(P<0.05);与A549+M2组比较,A549+M2+BAY11-7082组A549细胞中划痕愈合率明显降低(P<0.05)。Transwell小室实验,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中侵袭细胞数明显增加(P<0.05);与A549+M2组比较,A549+M2+BAY11-7082组A549细胞中侵袭细胞数明显减少(P<0.05);3组共培养体系中,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中侵袭细胞数明显增加(P<0.05)。CCK-8法,2.50、5.00、10.00、20.00和40.00 mg·L-1 DDP处理后,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞生长抑制率均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),IC50值均明显升高(P<0.01);3组共培养体系中,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞生长抑制率均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01),IC50值均明显升高(P<0.01);与A549+M2组比较,A549+M2+BAY11-7082组A549细胞生长抑制率明显升高(P<0.05),IC50值均明显降低(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中E-cadherin蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),N-cadherin、Vimentin和Snail蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);3组共培养体系中,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中E-cadherin蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05),N-cadherin、Snail、Vimentin和p-P65蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与A549+M2组比较,A549+M2+BAY11-7082组A549细胞中,E-cadherin蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05),Vimentin、N-cadherin和p-P65蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中P-gp和PD-L1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);3组共培养体系中,与A549+M0组比较,A549+M2组A549细胞中P-gp和PD-L1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与A549+M2组比较,A549+M2+BAY11-7082组A549细胞中P-gp和PD-L1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 M2巨噬细胞可调控NSCLC细胞EMT促进肿瘤侵袭转移,调控P-gp和PD-L1蛋白表达促进DDP耐药,其作用机制可能与NF-κB信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R734.2