吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 778-784.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250323
• 临床研究 • 上一篇
卵巢癌患者血清中ST2、CA125和HE4水平检测及其临床意义
- 吉林省肿瘤医院检验科,吉林 长春 130012
Detection of ST2, CA125, and HE4 levels in serum of ovarian cancer patients and their clinical significances
Chunying TIAN,Ting LI,Yuanyuan CHEN,Wenyan LIU,Ruiyao LI,Xiuyan YU( )
)
- Department of Clinical Laboratory,Tumor Hospital,Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
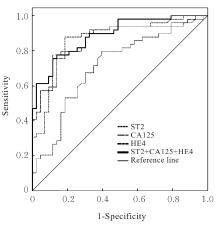
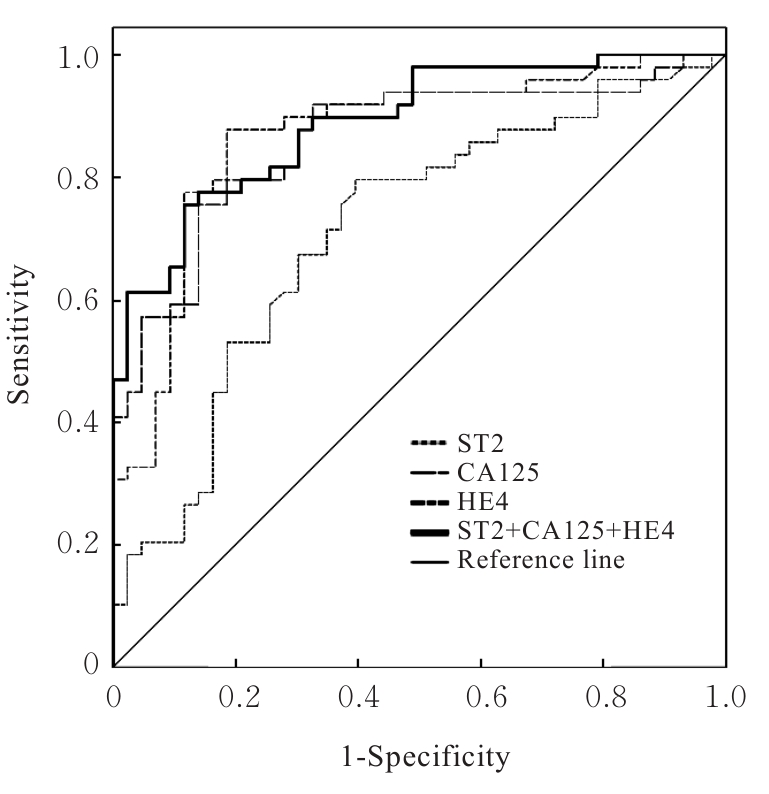
目的 探讨卵巢癌患者血清中生长刺激表达基因2蛋白(ST2)、糖类抗原125(CA125)和人附睾蛋白4(HE4)水平在卵巢癌诊断中的价值,阐明其与卵巢癌患者临床病理参数的关系。 方法 随机选取于本院就诊并经术后组织病理检查证实的卵巢良性病变和卵巢恶性肿瘤首诊患者136例作为研究对象,其中卵巢良性病变组53例,卵巢癌组83例,另取同期体检的55名健康女性志愿者作为健康对照组。所有研究对象入院第1天抽取空腹肘静脉血并留取血清,采用循环增强荧光免疫发光法检测各组研究对象ST2水平,化学发光法检测各组研究对象血清中CA125和HE4水平。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评估各指标诊断卵巢癌的性能,计算截断值(Cut-off值)和ROC曲线下面积(AUC)值,以AUC值代表各指标的诊断性能。采用Kendall法分析血清中ST2表达水平与卵巢癌患者TNM分期、肿瘤最大直径、远端转移、淋巴结转移、腹膜转移、癌胚抗原(CEA)、CA125、糖类抗原199(CA199)、HE4、P53和Ki67的相关性。 结果 与健康对照组比较,卵巢良性病变组患者血清中CA125水平明显升高(P<0.05);与健康对照组和卵巢良性病变组比较,卵巢癌组患者血清中ST2、CA125和HE4水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。ST2的AUC值为0.719(95%CI:0.616~0.822),CA125的AUC值为0.868(95%CI:0.794~0.942),HE4的AUC值为0.867(95%CI:0.793~0.942),ST2+CA125+HE4联合检测的AUC值为0.894(95%CI:0.832~0.955)。不同TNM分期及有无淋巴结转移、远端转移和腹膜转移的卵巢癌患者血清中ST2、CA125及HE4水平比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),不同年龄和肿瘤最大直径卵巢癌患者血清中ST2、CA125及HE4水平比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。卵巢癌患者血清中ST2水平与TNM分期、远端转移、淋巴结转移、腹膜转移、CA125水平、HE4水平和Ki67水平呈正相关关系(P<0.05),ST2水平与肿瘤最大直径、CEA、CA199水平和P53水平无相关性(P>0.05)。 结论 ST2、CA125和HE4在卵巢癌患者血清中高表达,血清ST2、CA125和HE4联合检测筛查卵巢癌具有较好的灵敏度及特异度,可提高卵巢癌患者的诊断效能。ST2与卵巢癌高TNM分期和癌转移有关,可能参与了卵巢癌的发生发展过程。
中图分类号:
- R737.9