吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 958-967.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250412
肺癌A549细胞源性外泌体中lncRNA DUXAP8对肺癌细胞生长和肿瘤免疫逃逸的作用及其机制
何小双1,徐丽娜1,崔梅2,赵宇3,王蓓1,黄征1,王玉超1,辛雯艳1,邬超1( )
)
- 1.石河子大学第一附属医院呼吸与危重症医学科,新疆 石河子 832099
2.新疆维吾尔自治区人民 医院病理科,新疆 石河子 830001
3.石河子大学第一附属医院胃肠外科,新疆 石河子 832099
Effects of lncRNA DUXAP8 in lung cancer A549 cells-derived exosomes on lung cancer cell growth and its mechnism
Xiaoshuang HE1,Lina XU1,Mei CUI2,Yu ZHAO3,Bei WANG1,Zheng HUANG1,Yuchao WANG1,Wenyan XIN1,Chao WU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832099,China
2.Department of Pathology,People’s Hospital,Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Shihezi 830001,China
3.Department of Gastroenterology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832099,China
摘要:
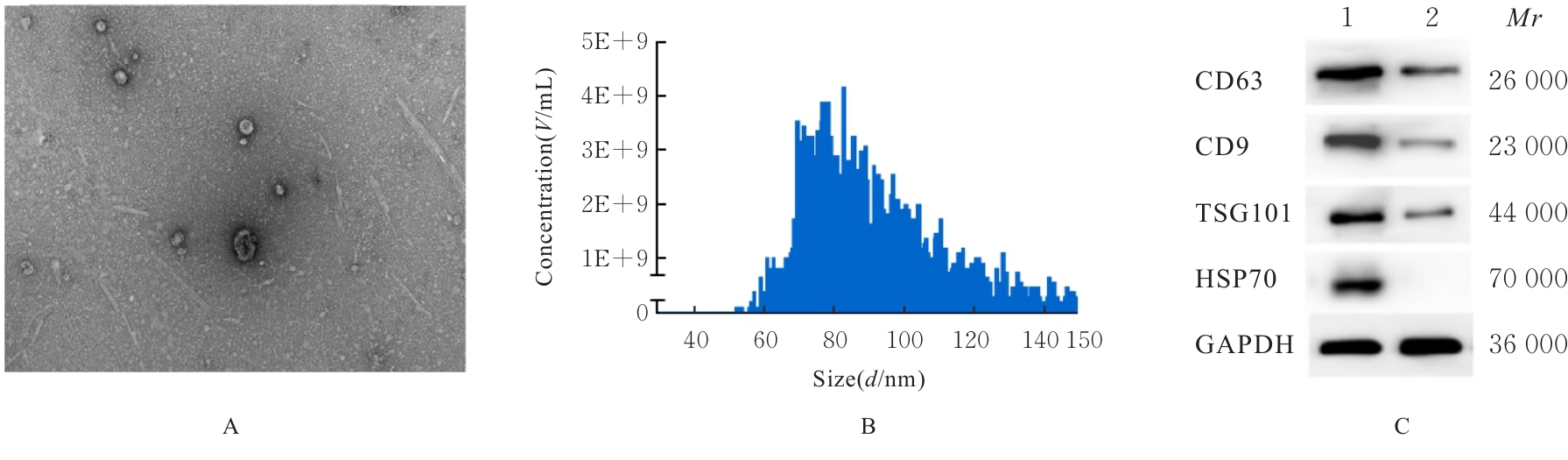
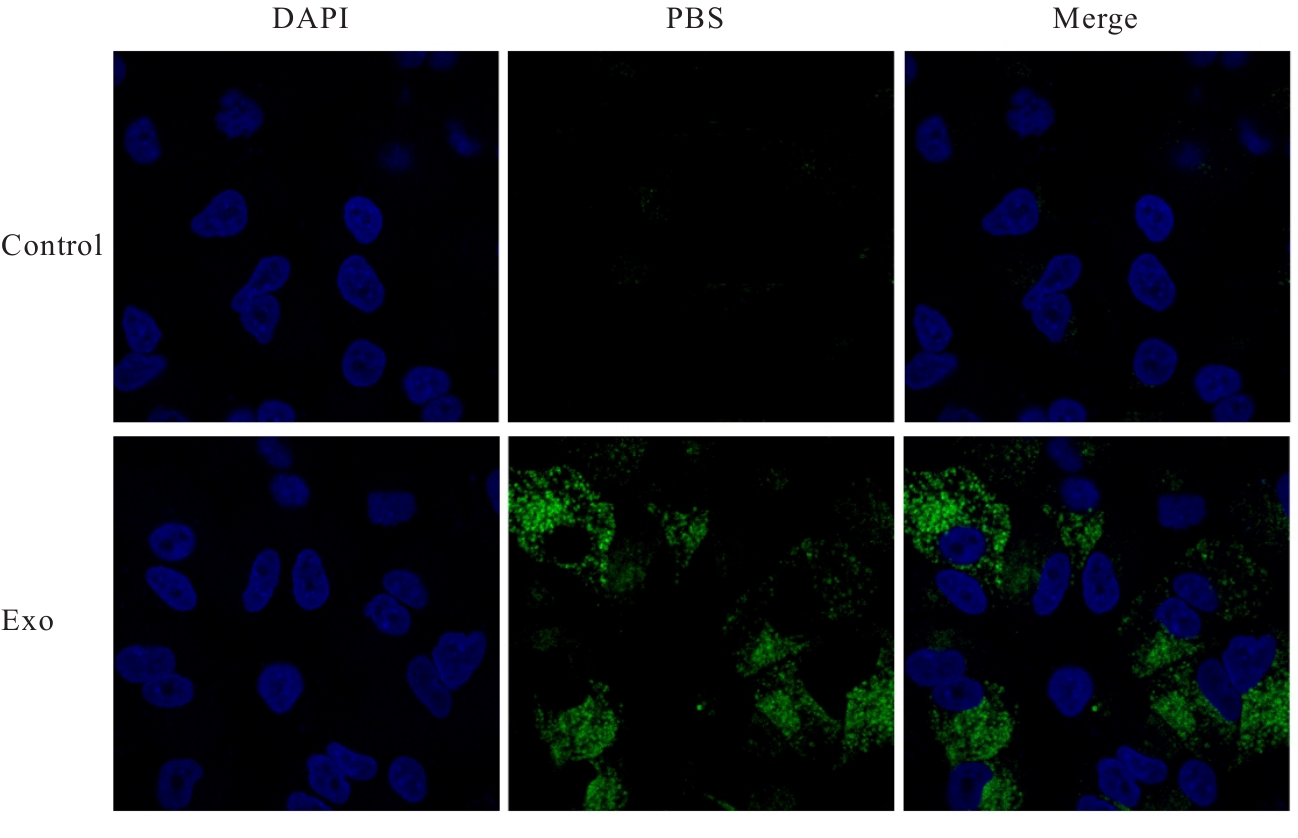
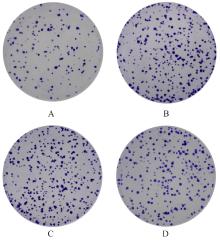
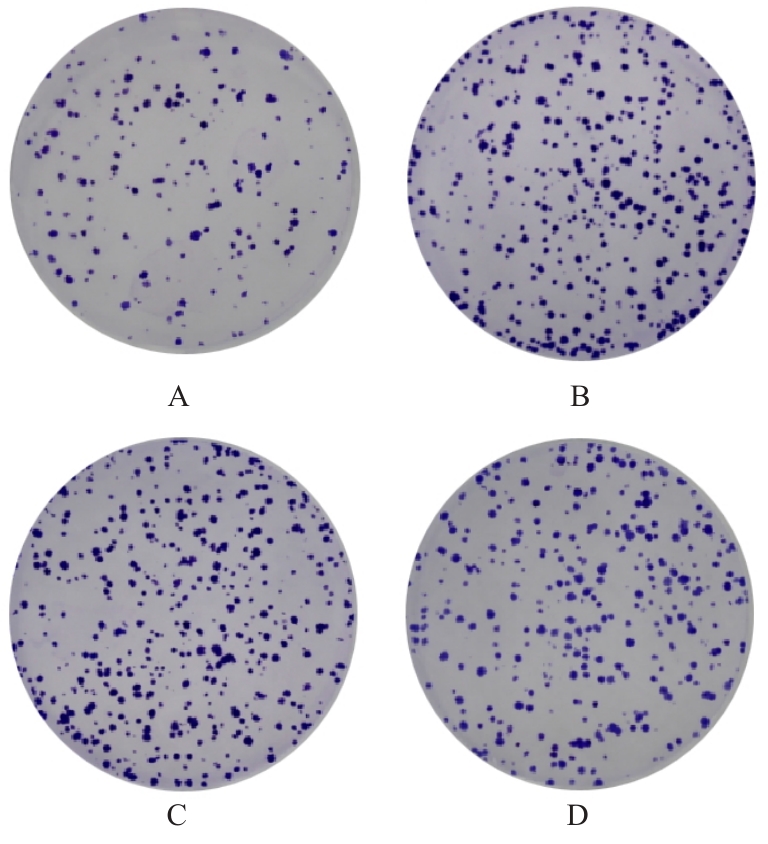
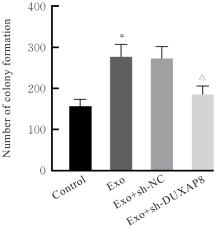
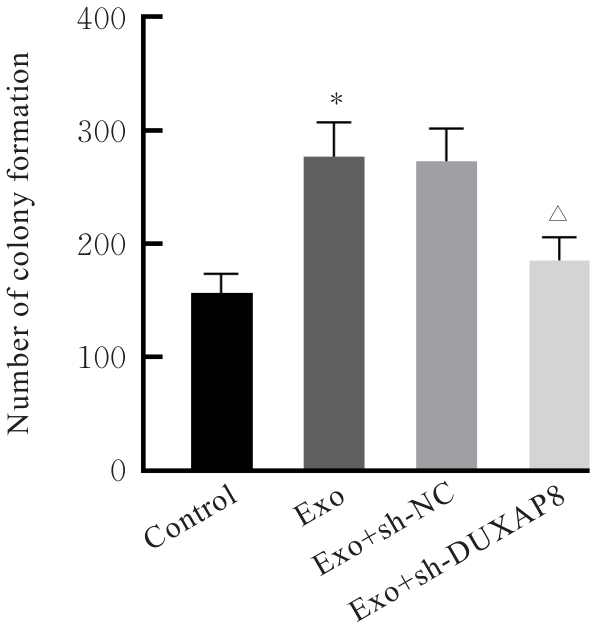
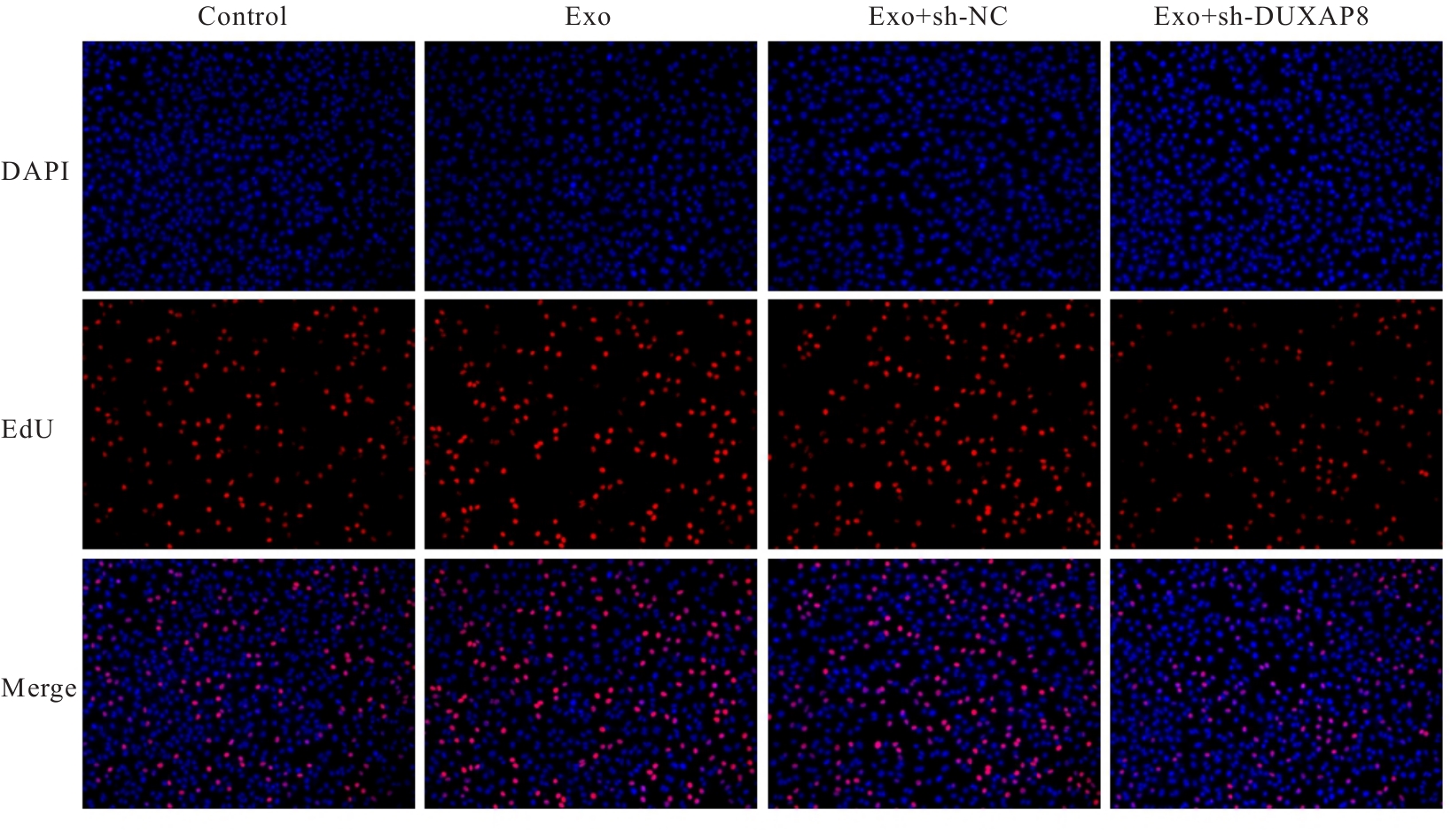
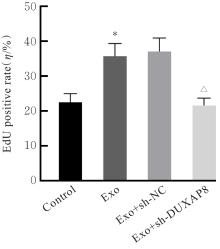
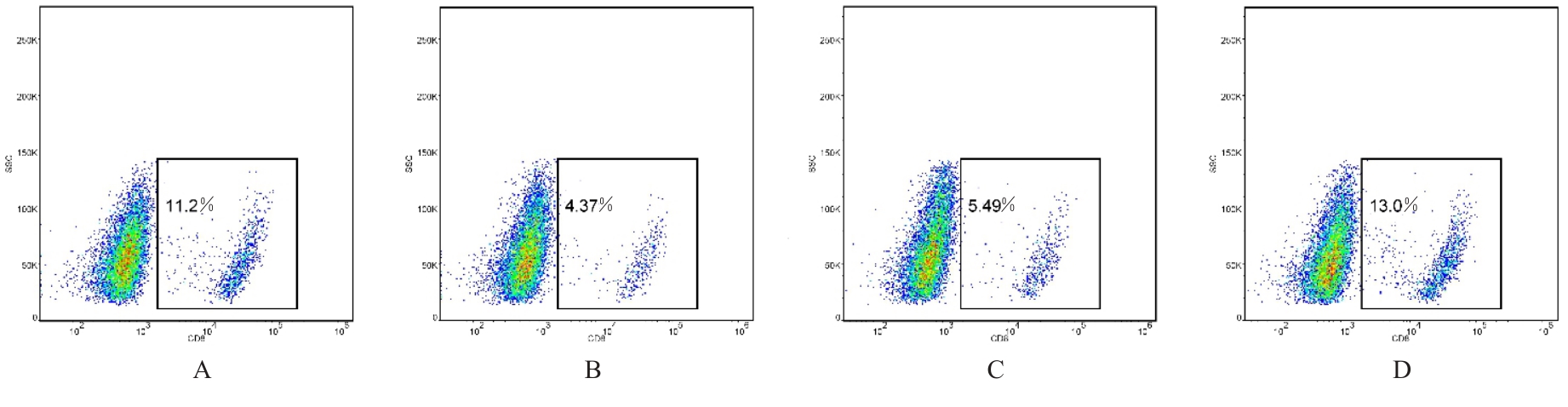
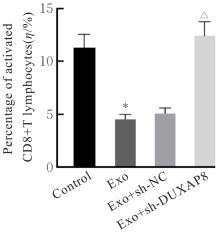
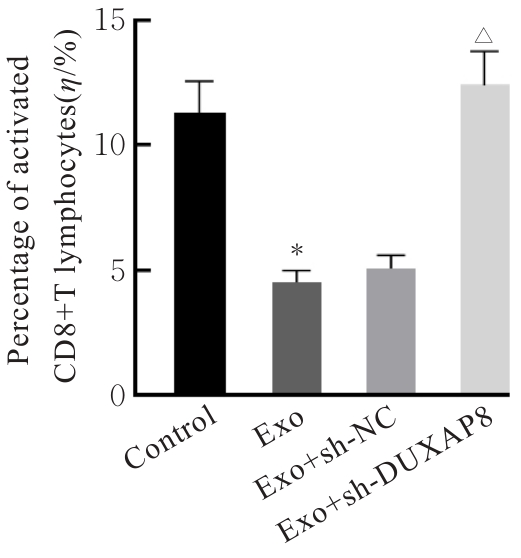
目的 探讨肺癌A549细胞源性外泌体(Exo)中长链非编码 RNA(lncRNA)DUXAP8对肺癌细胞生长和免疫逃逸的影响,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 培养人肺癌细胞系A549细胞,提取其Exo并鉴定。采用PKH67标记的Exo处理A549细胞,观察A549细胞摄取Exo情况。实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测Exo处理前后A549细胞中lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平。将A549细胞分为对照组(不处理)、Exo组(Exo处理A549细胞)、Exo+sh-NC组(Exo处理A549细胞后,转染sh-NC至A549细胞)和Exo+sh-DUXAP8组(Exo处理A549细胞后,转染sh-DUXAP8至A549细胞)。RT-qPCR法检测各组A549细胞中lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平,平板集落形成实验检测各组A549细胞克隆形成能力,5-乙炔基-2'-脱氧尿苷(EdU)法检测各组A549细胞增殖能力。各组A549细胞与人外周血淋巴细胞共培养后,流式细胞术检测各组人外周血淋巴细胞中活化的CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率,3-(4,5-二甲基噻唑-2)-2,5-二苯基四氮唑溴盐(MTT)法检测各组人外周血淋巴细胞对A549细胞的杀伤率。 结果 Exo囊泡直径为50~150 nm,且分化簇63(CD63)、分化簇9(CD9)、肿瘤易感基因101(TSG101)和热休克蛋白70(HSP70)外泌体特异性标志物蛋白表达阳性,说明Exo提取成功。A549细胞能够很好地摄取PKH67标记的Exo。RT-qPCR法,与单独培养的A549细胞比较,Exo处理后,A549细胞中lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,Exo组A549细胞中lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平升高(P<0.05);与Exo组比较,Exo+sh-DUXAP8组A549细胞中lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平降低(P<0.05),Exo+sh-NC组lncRNA DUXAP8表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。平板集落形成实验,与对照组比较,Exo组A549细胞中集落形成数增加(P<0.05);与Exo组比较,Exo+sh-DUXAP8组A549细胞中集落形成数减少(P<0.05),Exo+sh-NC组A549细胞中集落形成数差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。EdU染色,与对照组比较,Exo组A549细胞中EdU阳性细胞率升高(P<0.05);与Exo组比较,Exo+sh-DUXAP8组A549细胞中EdU阳性细胞率降低(P<0.05),Exo+sh-NC组A549细胞中EdU阳性细胞率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。流式细胞术,与对照组比较,Exo组人外周血淋巴细胞中活化CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率降低(P<0.05);与Exo组比较,Exo+sh-DUXAP8组人外周血淋巴细胞中活化CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率升高(P<0.05),Exo+sh-NC组人外周血淋巴细胞中活化的CD8+T淋巴细胞百分率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。MTT法,与对照组比较,Exo组人外周血淋巴细胞对 A549细胞的杀伤率降低(P<0.05);与Exo组比较,Exo+sh-DUXAP8组人外周血淋巴细胞对 A549细胞的杀伤率升高(P<0.05),Exo+sh-NC组人外周血淋巴细胞对 A549细胞的杀伤率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 肺癌A549细胞源性Exo lncRNA DUXAP8促进肺癌细胞增殖和肿瘤免疫逃逸。
中图分类号:
- R734.2