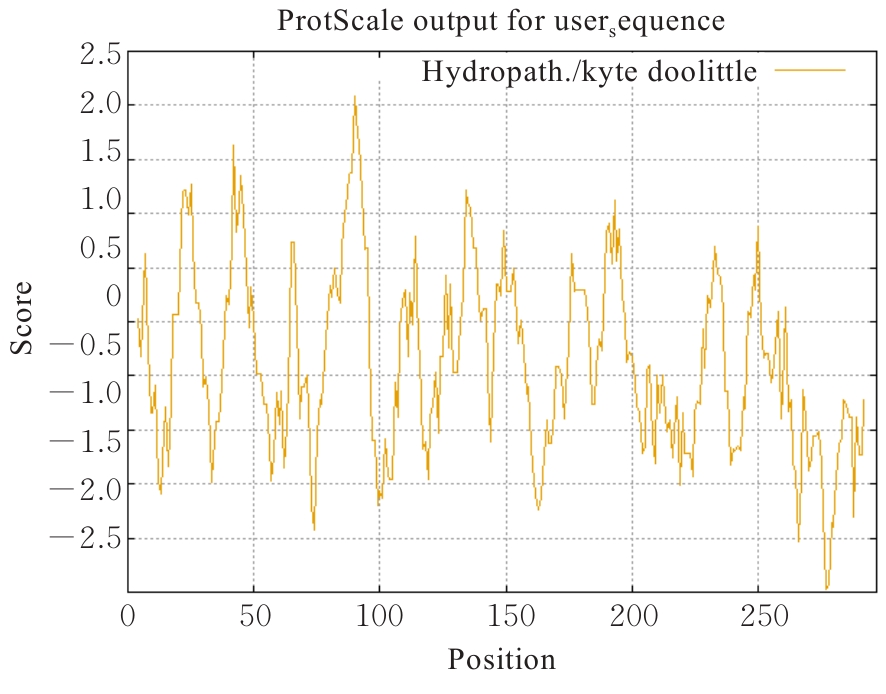
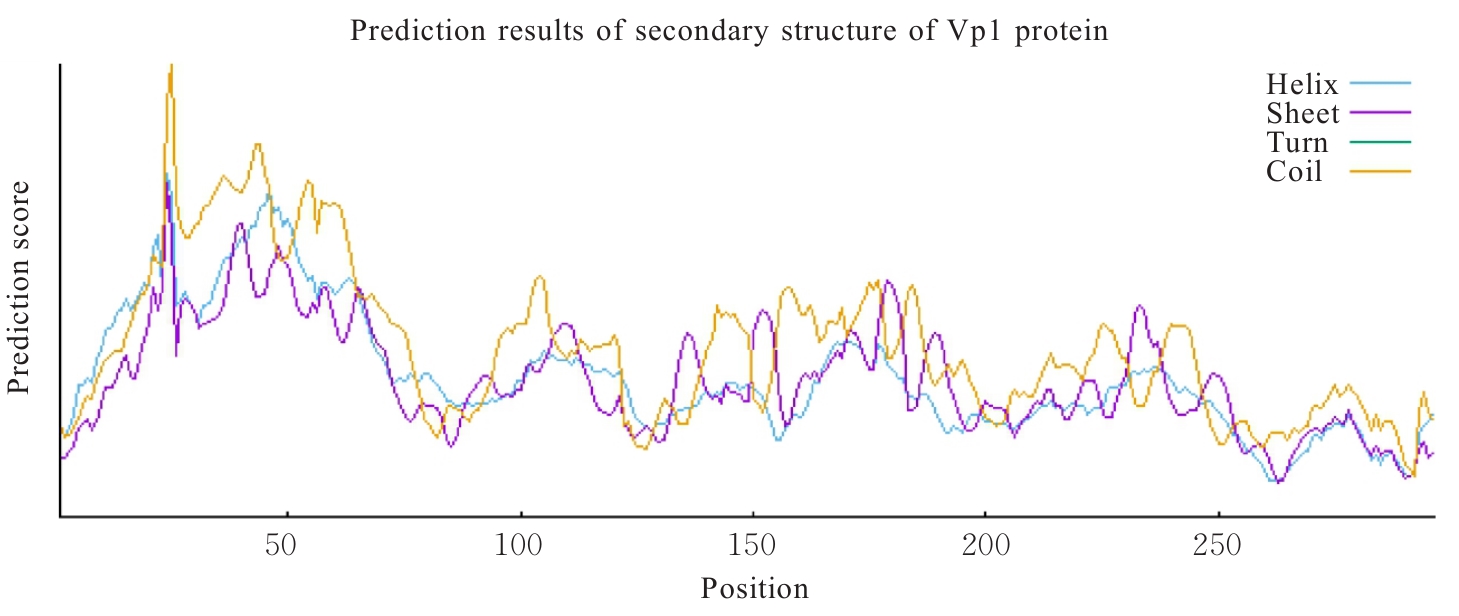
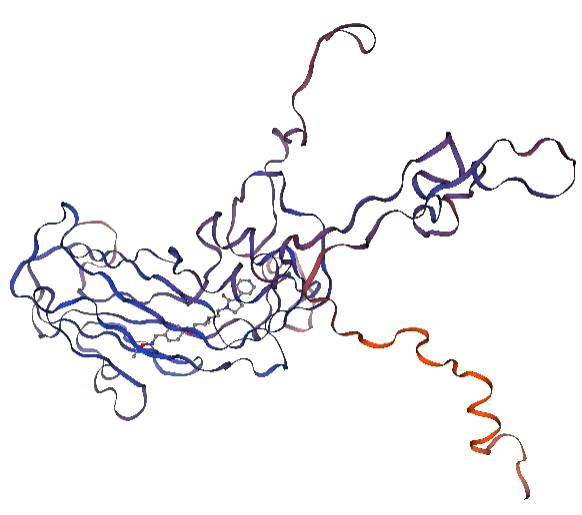
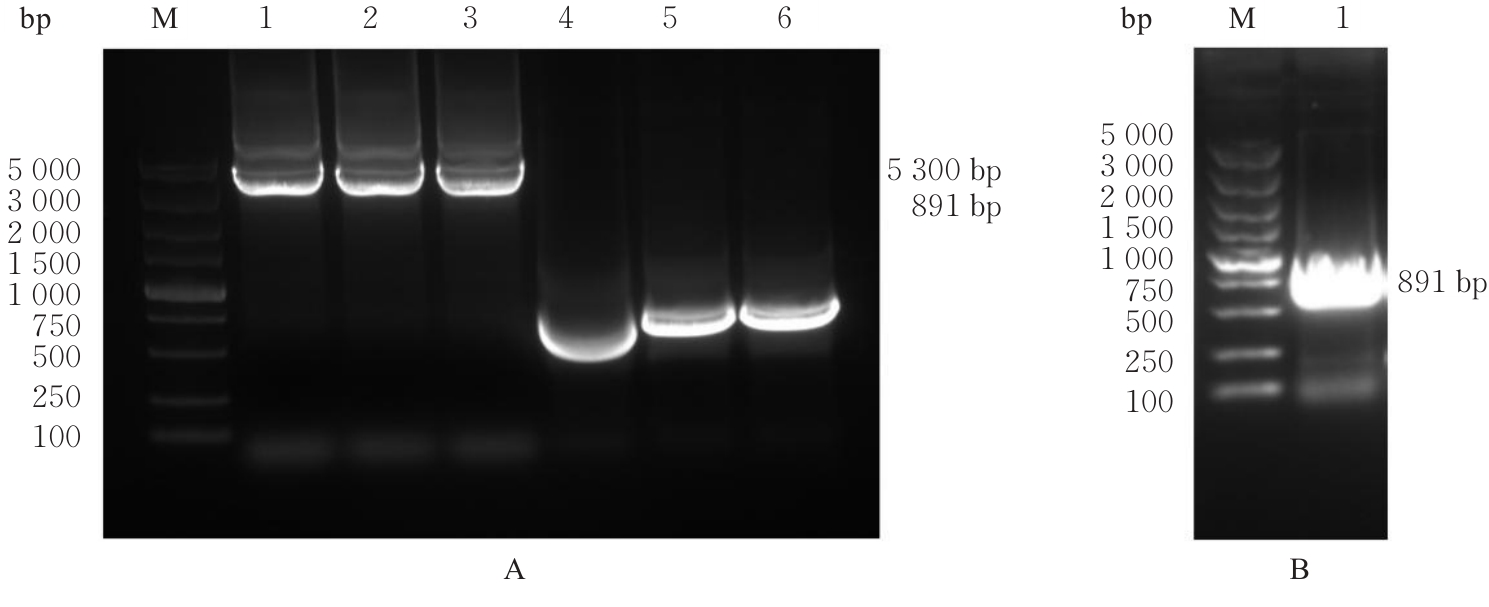
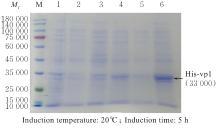
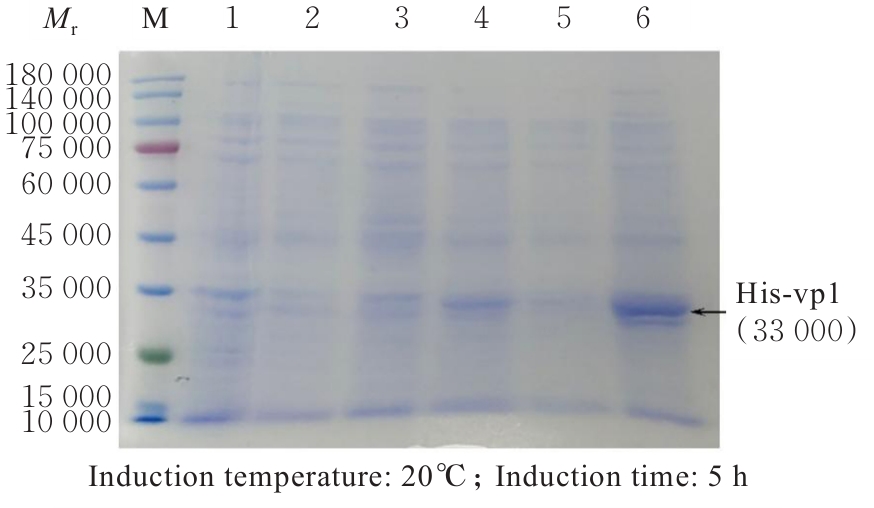
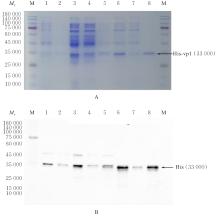
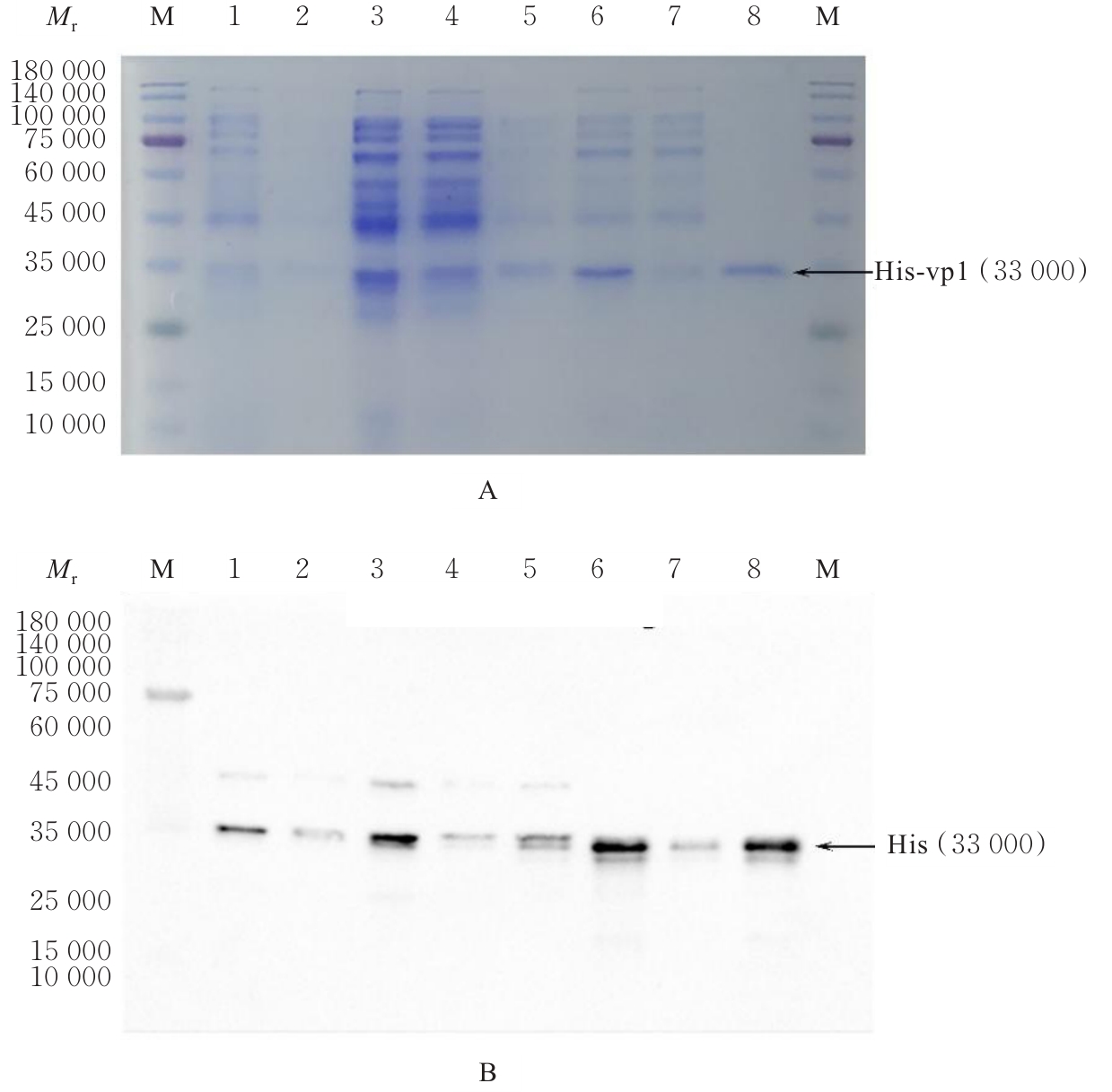
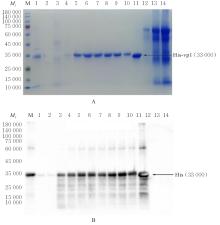
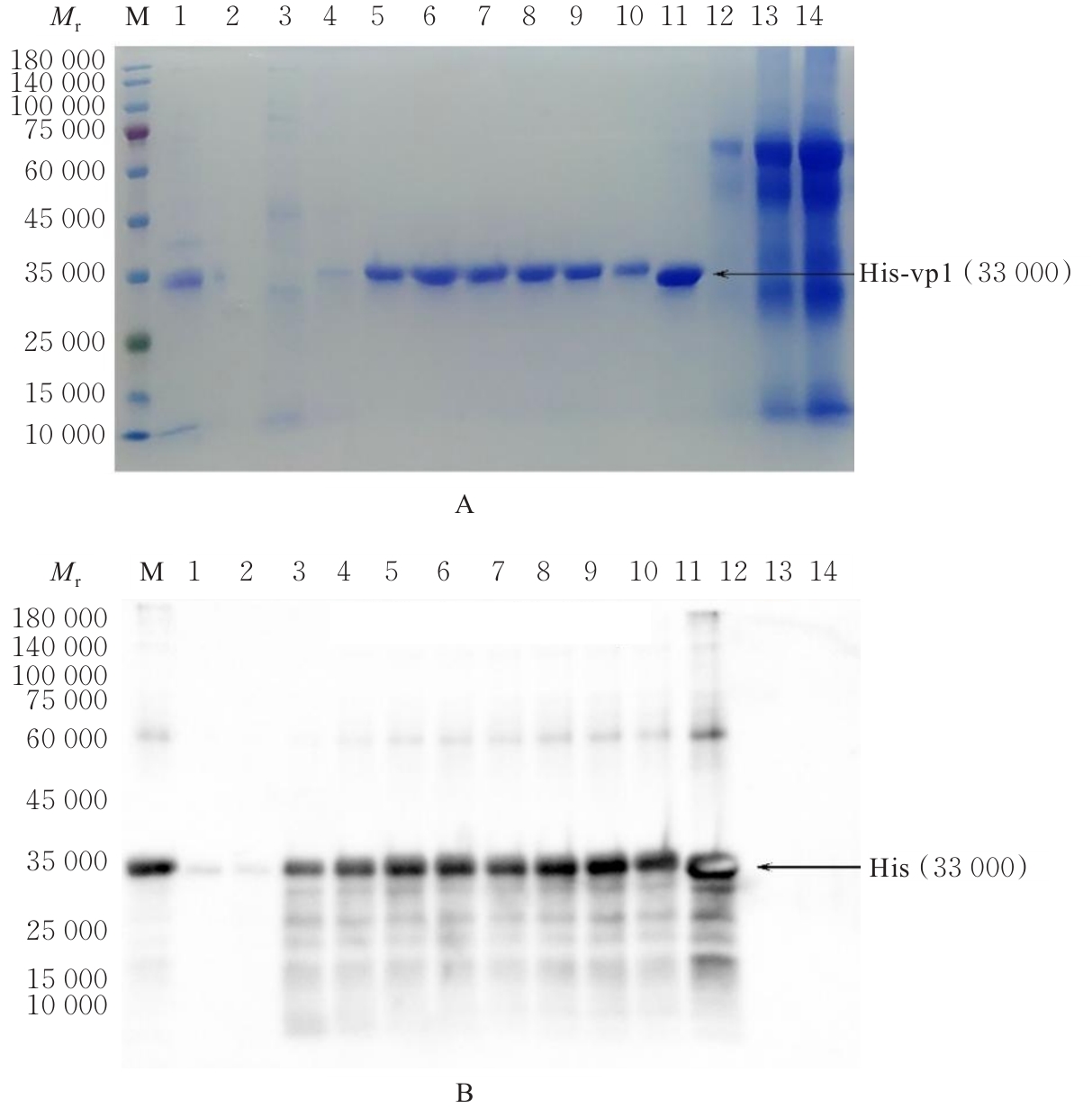
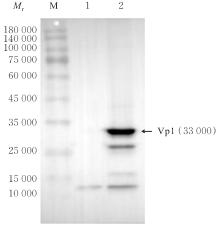
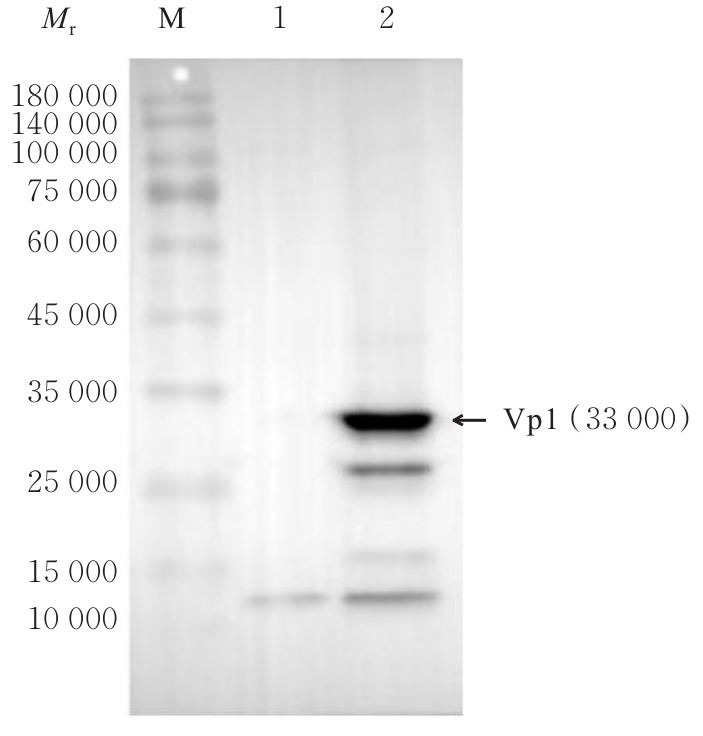
| [1] |
ZHANG C, LIU C X, SHI J P, et al. Molecular mechanism of antibody neutralization of coxsackievirus A16[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 7854.
|
| [2] |
REN J S, WANG X X, ZHU L, et al. Structures of coxsackievirus A16 capsids with native antigenicity: implications for particle expansion, receptor binding, and immunogenicity[J]. J Virol, 2015, 89(20): 10500-10511.
|
| [3] |
LEGAY F, LÉVÊQUE N, GACOUIN A, et al. Fatal coxsackievirus A-16 pneumonitis in adult[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2007, 13(7): 1084-1086.
|
| [4] |
GOTO K, SANEFUJI M, KUSUHARA K, et al. Rhombencephalitis and coxsackievirus A16[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2009, 15(10): 1689-1691.
|
| [5] |
ASTRUP B S, JOHNSEN I B G, ENGSBRO A L. The role of Coxsackievirus A16 in a case of sudden unexplained death in an infant-A SUDI case[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2016, 259: e9-13.
|
| [6] |
LIANG Z C, LIN C Y, HUO D, et al. First detection of multiple cases related to CV-A16 strain of B1c clade in Beijing in 2022[J]. J Med Virol, 2024, 96(7): e29796.
|
| [7] |
DIWATE S, YADAV P D, YADAV J, et al. Enterovirus Coxsackie A16 detected in hand, foot, and mouth disease outbreak among children in western Uttar pradesh, India, may to June 2022[J]. Asia Pac J Public Health, 2024, 36(1): 143-145.
|
| [8] |
NOISUMDAENG P, PUTHAVATHANA P. Molecular evolutionary dynamics of enterovirus A71, coxsackievirus A16 and coxsackievirus A6 causing hand, foot and mouth disease in Thailand, 2000-2022[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 17359.
|
| [9] |
LI R Q, LIN C Y, DONG S B, et al. Phylogenetics and phylogeographic characteristics of coxsackievirus A16 in hand foot and mouth disease and herpangina cases collected in Beijing, China from 2019 to 2021[J]. J Med Virol, 2023, 95(8): e28991.
|
| [10] |
YUAN X L, LIU Z W, WAN L, et al. Recent advances in anti-coxsackievirus A16 viral drug research[J]. Future Med Chem, 2023, 15(1): 97-117.
|
| [11] |
YANG D D, LIU W M, WANG W P, et al. Analysis of the impact of inactivated A71 vaccine on the incidence of hand-foot-mouth disease in Pudong new area, Shanghai[J]. Vaccines, 2024, 12(9): 962.
|
| [12] |
TAN X H, CHONG W L, LEE V S, et al. Substitution of coxsackievirus A16 VP1 BC and EF loop altered the protective immune responses in chimera enterovirus A71[J]. Vaccines, 2023, 11(8): 1363.
|
| [13] |
YI E J, KIM Y I, KIM S Y, et al. A bivalent inactivated vaccine prevents enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 infections in the Mongolian gerbil[J]. Biomol Ther, 2023, 31(3): 350-358.
|
| [14] |
YI E J, KIM Y I, SONG J H, et al. Potential of a bivalent vaccine for broad protection against enterovirus 71 and Coxsackie virus 16 infections causing hand, foot, and mouth disease[J]. Vaccine, 2023, 41(41): 6055-6063.
|
| [15] |
ZHANG G B, HU B, HUO Y Q, et al. Amino acid substitutions in VP2, VP1, and 2C attenuate a Coxsackievirus A16 in mice[J]. Microb Pathog, 2021, 150: 104603.
|
| [16] |
ZHAO Z L, LI Z L, HUAN C, et al. SAMHD1 inhibits multiple enteroviruses by interfering with the interaction between VP1 and VP2 proteins[J]. J Virol, 2021, 95(13): e00620-21.
|
| [17] |
DE COLIBUS L, WANG X X, TIJSMA A, et al. Structure elucidation of coxsackievirus A16 in complex with GPP3 informs a systematic review of highly potent capsid binders to enteroviruses[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2015, 11(10): e1005165.
|
| [18] |
宋亚荣, 王 杰, 李 杰. HBV母婴传播的分子病毒学机制[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(11): 2168-2172.
|
| [19] |
刘希佳, 何小华, 刘万红. 一种新的柯萨奇病毒A组16型中国湖北分离株(CV-A16WH16)全基因组序列测定及分析[J]. 中国病毒病杂志, 2015, 5(2): 96-103.
|
| [20] |
MA Z L, ZHA J. Characterization of VP1 gene of coxsackievirus A16 prevalent among hand foot mouth disease suffered children in Taizhou, P. R. China, between 2010 and 2013[J]. J Med Virol, 2016, 88(2): 202-210.
|
| [21] |
赵言龙, 郑浩然. 基于代谢分析的SARS-CoV-2药物靶点预测方法[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2023, 40(11): 1433-1440.
|
| [22] |
张彩霞, 叶黎文, 黄春艳. 病原体靶向测序技术在疑似肺部感染患者中的应用价值分析[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2024, 49(9): 1022-1028.
|
| [23] |
SHI J P, HUANG X L, LIU Q W, et al. Identification of conserved neutralizing linear epitopes within the VP1 protein of coxsackievirus A16[J]. Vaccine, 2013, 31(17): 2130-2136.
|
| [24] |
POROWIŃSKA D, WUJAK M, ROSZEK K, et al. Prokaryotic expression systems[J]. Postepy Hig Med Dosw, 2013, 67: 119-129.
|
| [25] |
MURAKAMI M, MURAKAMI A M, ITAGAKI S. A dual prokaryotic (E.coli) expression system (pdMAX)[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(10): e0258553.
|
| [26] |
李 丹, 宋浩志, 高维崧, 等. 小反刍兽疫病毒H蛋白的原核表达及免疫原性测定[J]. 生物技术进展, 2021, 11(6): 770-776.
|
| [27] |
张喜文, 鲁绍芳, 李盼盼, 等. 鸭坦布苏病毒NS1蛋白的原核表达与多克隆抗体制备[J]. 养殖与饲料, 2023(4): 19-25.
|
| [28] |
张树军, 狄建军, 张国文. 大肠杆菌yfiF基因原核表达系统构建、表达条件优化及蛋白纯化[J]. 生物技术, 2016, 26(3): 229-233.
|
| [29] |
梁志鹏, 刘 静, 刘闰栀, 等. 三源重组H9N2亚型禽流感病毒NA蛋白原核表达及多克隆抗体制备[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2024, 19(6): 625-630.
|
| [30] |
KIELKOPF C L, BAUER W, URBATSCH I L. Purification of polyhistidine-tagged proteins by immobilized metal affinity chromatography[J]. Cold Spring Harb Protoc, 2020, 2020(6): 102194.
|
| [31] |
ZHOU B, XU L F, ZHU R, et al. A bispecific broadly neutralizing antibody against enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 with therapeutic potential[J]. Antiviral Res, 2019, 161: 28-35.
|
| [32] |
GAO E Y, WU S W, XU Q, et al. Enterovirus type 71-immunized chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin has cross antiviral activity against coxsackievirus A16 in vitro [J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(1): 332-341.
|
 )
)
 )
)