吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 469-476.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210228
可控型心脏死亡后器官捐献术中应用乌司他丁预处理对肾移植受体术后肾功能的影响
- 1.吉林大学第一医院麻醉科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院神经内科,吉林 长春 130021
Effect of ulinastatin pretreatment on postoperative recipients’ renal function in operation of donation after controllable cardiac death
Yangyang SONG1,Tingting LIN1,Qianyan HE2,Huanqiu LIU1( ),Yanhua FENG1(
),Yanhua FENG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Anesthesiology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Neurology,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
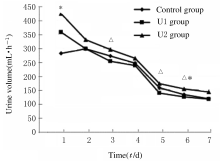
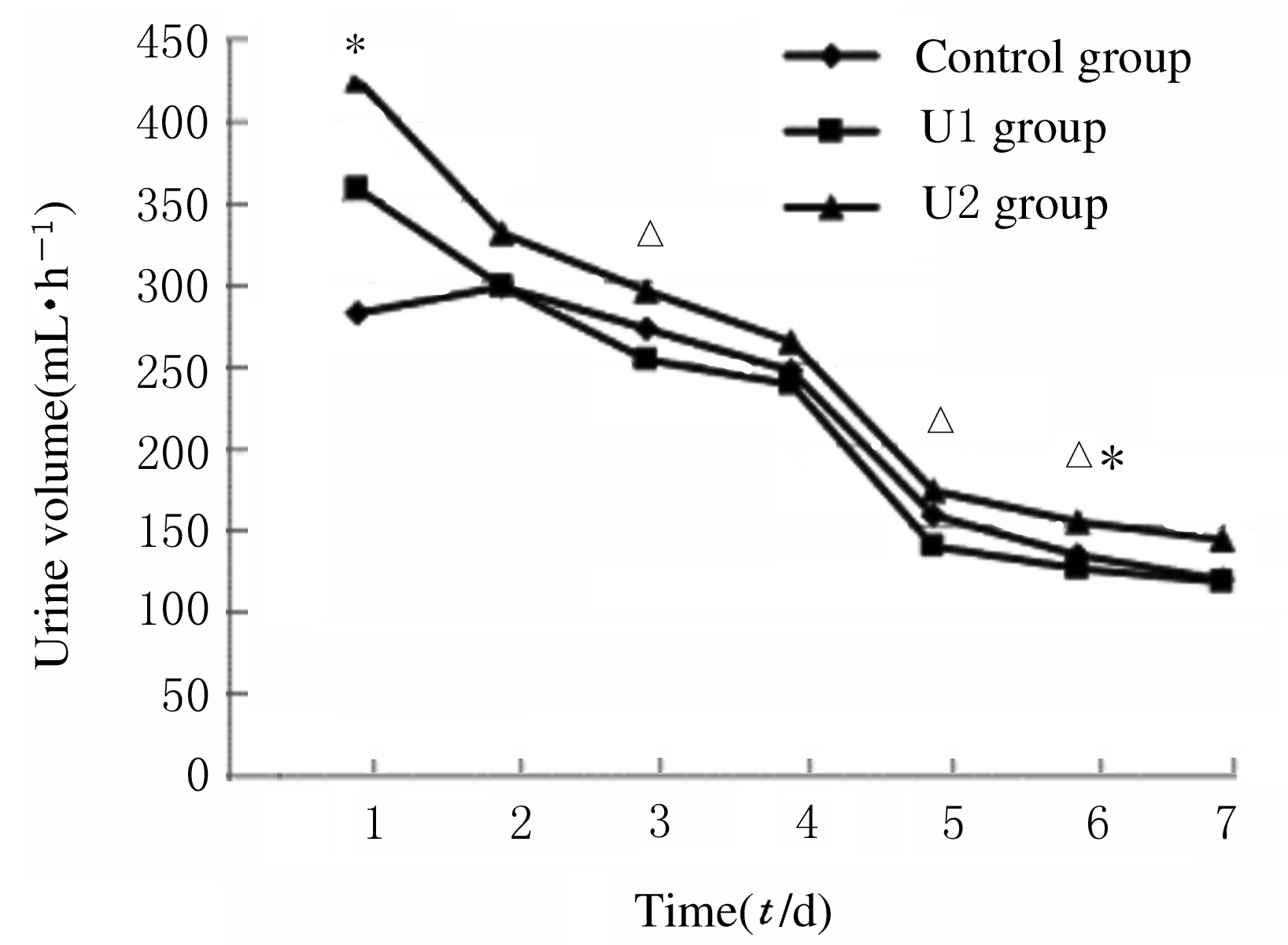
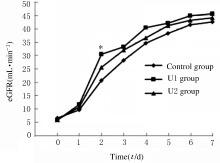
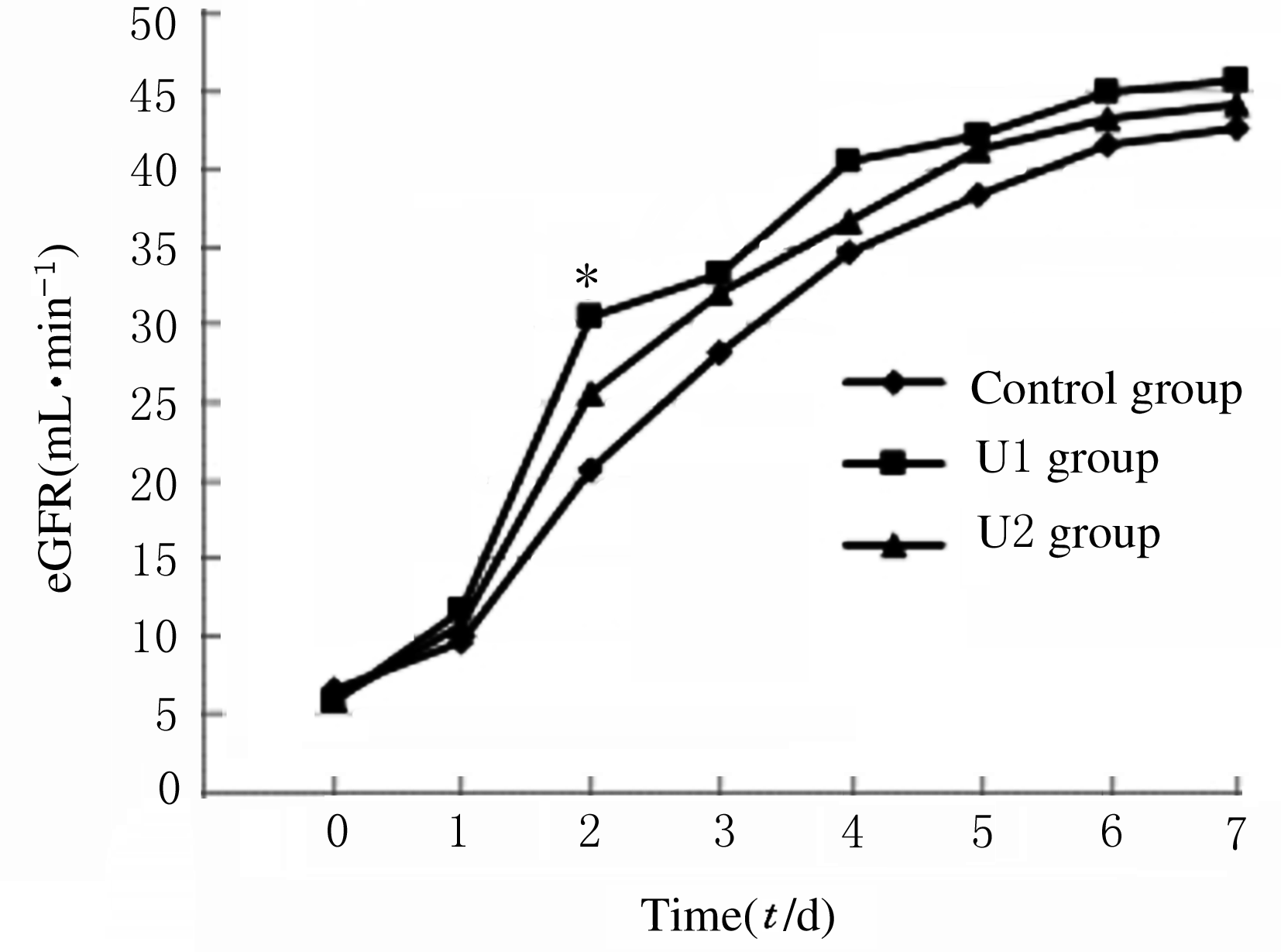
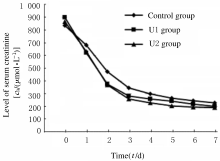
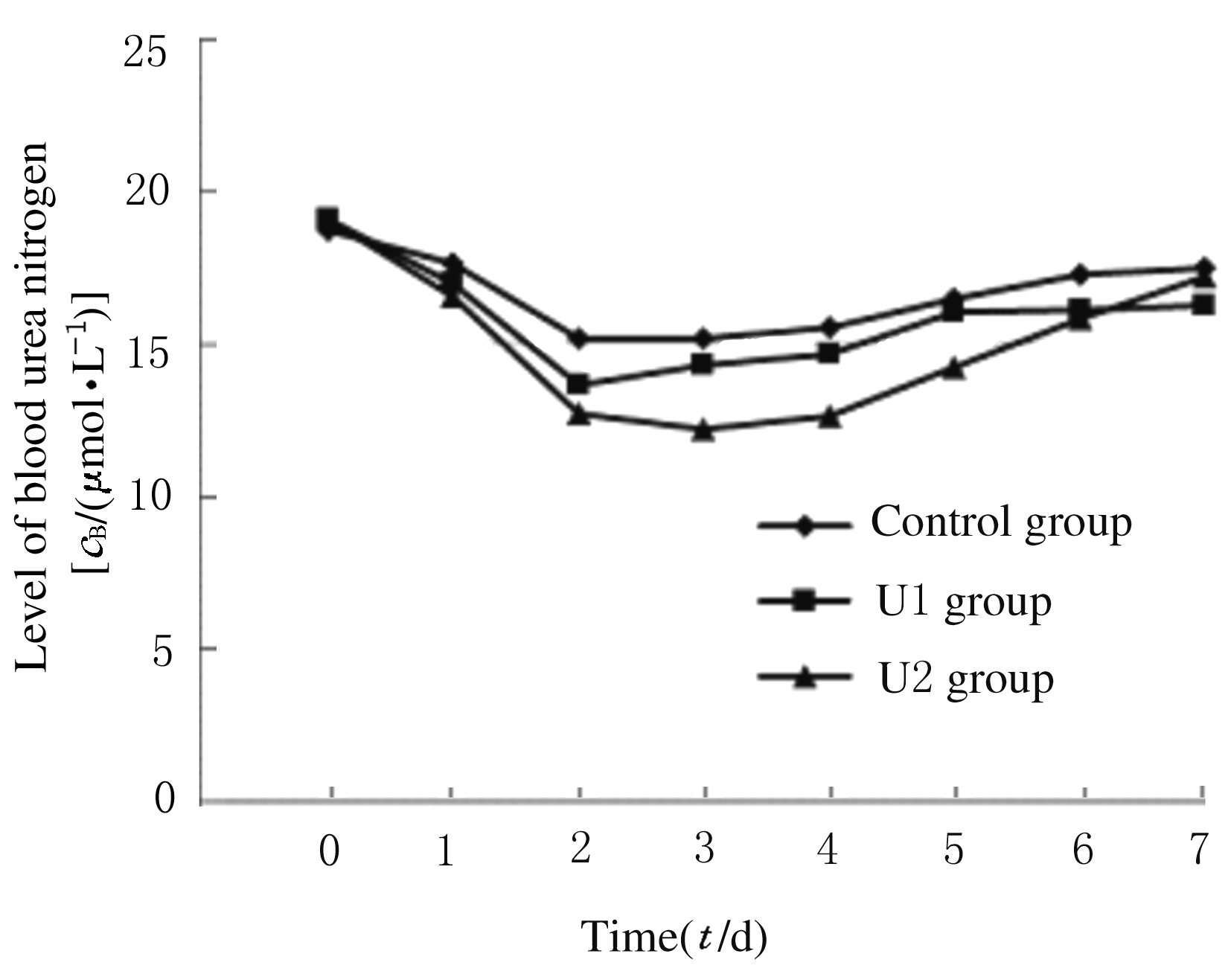
摘要: 在可控型心脏死亡器官捐献(DCD)术中应用不同剂量的乌司他丁预处理,观察其对肾移植受体术后肾功能的影响。 可控型DCD供体90例,肾移植受体174例。将供体随机分为3组,U1组术中使用乌司他丁5 000 U·kg-1;U2组术中使用乌司他丁10 000 U·kg-1;对照组术中不使用乌司他丁,给予等量的生理盐水。检测受体术前及术后1~7 d的血肌酐和血尿素氮水平,计算估算肾小球滤过率(eGFR),记录每小时尿量,计算术后移植物功能延迟恢复 (DGF)发生率。 3组受体术后7 d的每小时尿量呈现下降的趋势。术后第1天,U1组和U2组受体每小时尿量高于对照组(P<0.05)。术后第3天,U2组受体每小时尿量高于U1组(P<0.05)。术后第5天,U2组每小时尿量高于U1组(P<0.05)。术后第6天,U2组受体每小时尿量高于U1组和对照组(P<0.05)。其余各天3组受体每小时尿量比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后7 d内U1组和U2组受体eGFR均高于对照组,术后第2天U1组受体eGFR高于对照组(P<0.05),其余时间3组受体eGFR比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。3组受体术后7 d内血肌酐水平均明显降低,U1组和U2组受体血肌酐水平较对照组下降幅度更低,但3组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。3组受体血尿素氮水平均降低后又升高,U1组和U2组受体血尿素氮水平较对照组下降幅度更大,但3组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。对照组、U1组和U2组受体术后DGF发生率分别为10.5%、8.5%和6.9%,U1组和U2组受体术后DGF发生率低于对照组,但3组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 乌司他丁预处理可控型DCD,可促进肾移植受体术后尿量早期恢复,对肾功能有一定的保护作用。
中图分类号:
- R617