吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1287-1291.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210529
原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进并发甲状腺乳头状癌伴中度贫血1例报告及文献复习
韩慧1,于婷婷2,王野弛3,洪士萍1,王培松1,孟伟1( ),毕铭4(
),毕铭4( )
)
- 1.吉林大学第一医院甲状腺外科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科,吉林 长春 130021
3.吉林大学第一医院病理科,吉林 长春 130021
4.吉林大学口腔医院综合科,吉林 长春 130021
Primary hyperparathyrodism combined with papillary thyroid carcinoma and moderate anemia: A case report and literature reviewHAN Hui1,YU Tingting2,WANG Yechi3,HONG Shiping1,WANG Peisong1,MENG Wei1,BI Ming4(1.Department of Thyroid Surgery, First Hospital, Jilin University,Changchun 130021, China; 2. Department of Otolaryngology and Head-Neck Surgery,First Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China; 3. Department of Pathology, First Hospital,Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China;4. Department of General Dentistry, Stomatology Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China)
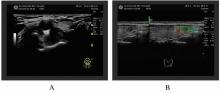
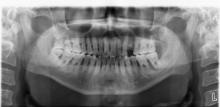
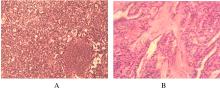
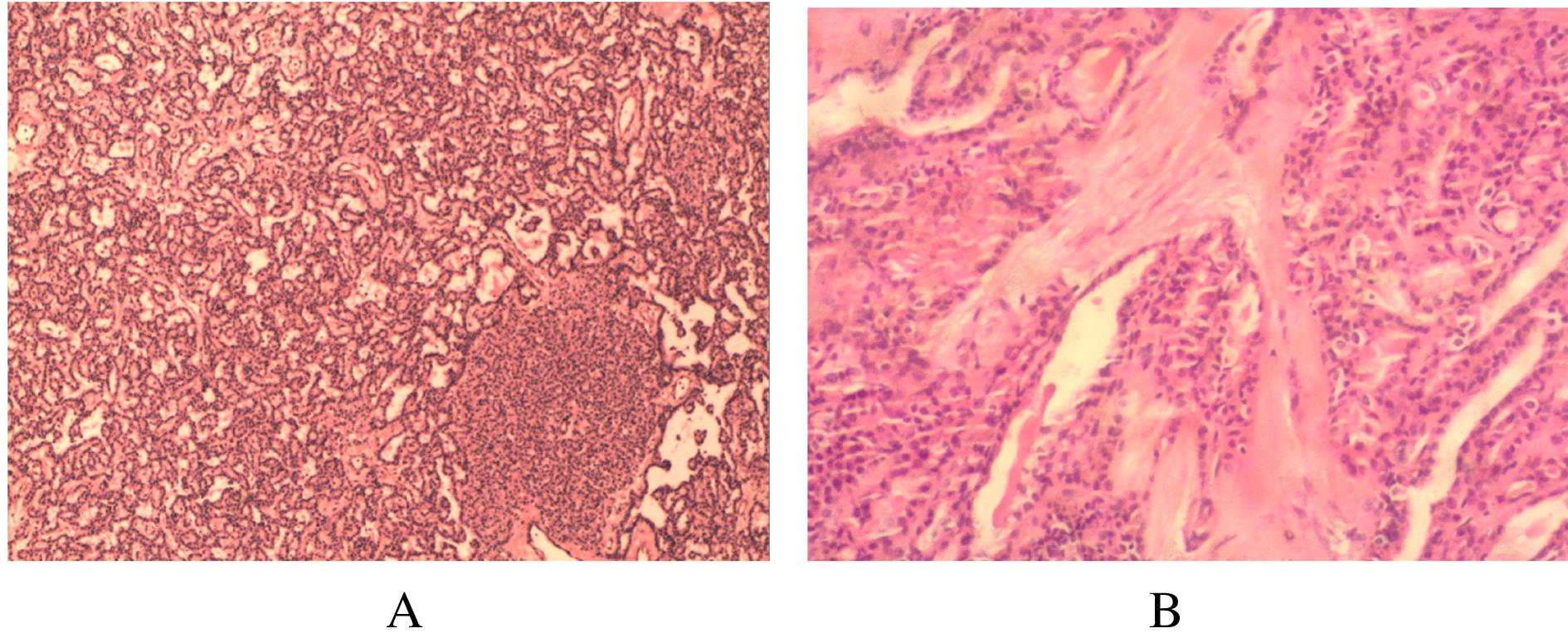
摘要: 分析原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进(PHPT)并发甲状腺乳头状癌(PTC)伴中度贫血患者的临床诊治方法,加强临床医生对此类疾病的认识,减少误诊及漏诊。 收集1例PHPT并发PTC伴中度贫血患者的临床资料,并结合文献复习,探讨其临床特征、影像学表现、诊断和手术方法。 患者,女性,42岁,因肾结石15年,PHPT 1个月,伴恶心无呕吐,伴心慌乏力,伴咀嚼不适及饮食减少,1个月内体质量减轻10 kg,贫血貌。 实验室检查,高钙,低钠和低钾,中度贫血,低蛋白血症及甲状旁腺激素升高。甲状腺超声,甲状腺左叶小结节,甲状腺影像报告和数据系统分类与描述(TI-RADS)4a级;右颈前结节,甲状旁腺来源可能性大;甲状旁腺显影,甲状腺右叶上极背侧水平放射性增高区,不除外甲状旁腺功能亢进组织。 腹部超声,胆泥淤积,左肾积水,双肾结石。 临床诊断为甲状旁腺肿物,PHPT,甲状腺肿物(性质待定),肾结石,中度贫血和慢性牙周炎。 纠正患者离子紊乱及贫血状态后,于全麻下行甲状旁腺腺瘤切除术,甲状腺癌根治术,术后给予补钙等对症治疗,治愈出院。 PHPT患者血钙升高,经久不愈导致肾结石、离子紊乱等临床症状,重者可出现贫血;对多次出现肾结石和离子紊乱及中度贫血的患者应考虑PHPT的可能,且存在并发PTC可能;此类病例罕见且易漏诊,为避免二次手术,术前应完善检查明确诊断。
中图分类号:
- R653