吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (3): 809-817.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220332
• 方法学 • 上一篇
海藻酸钠-角豆胶互穿聚合物网络水凝胶药物缓释体系的制备及评价
- 1.吉林大学口腔医院病理科 吉林省牙发育及颌骨重塑与再生重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学化学学院高分子科学系, 吉林 长春 130021
Preparation and evaluation of sodium alginate-locust bean gum interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel drug sustained-release system
Da LI1,Yanhong JIA1,Zebing ZHANG1( ),Xiufeng HAO2(
),Xiufeng HAO2( )
)
- 1.Department of Pathology,Stomatology Hospital,Jilin University,Jilin Provincial Key Laboratory of Tooth Development,Jaw Bone Remodeling and Regeneration,Changchun 130021,China
2.Department of Polymer Science,School of Chemistry,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
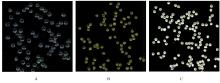
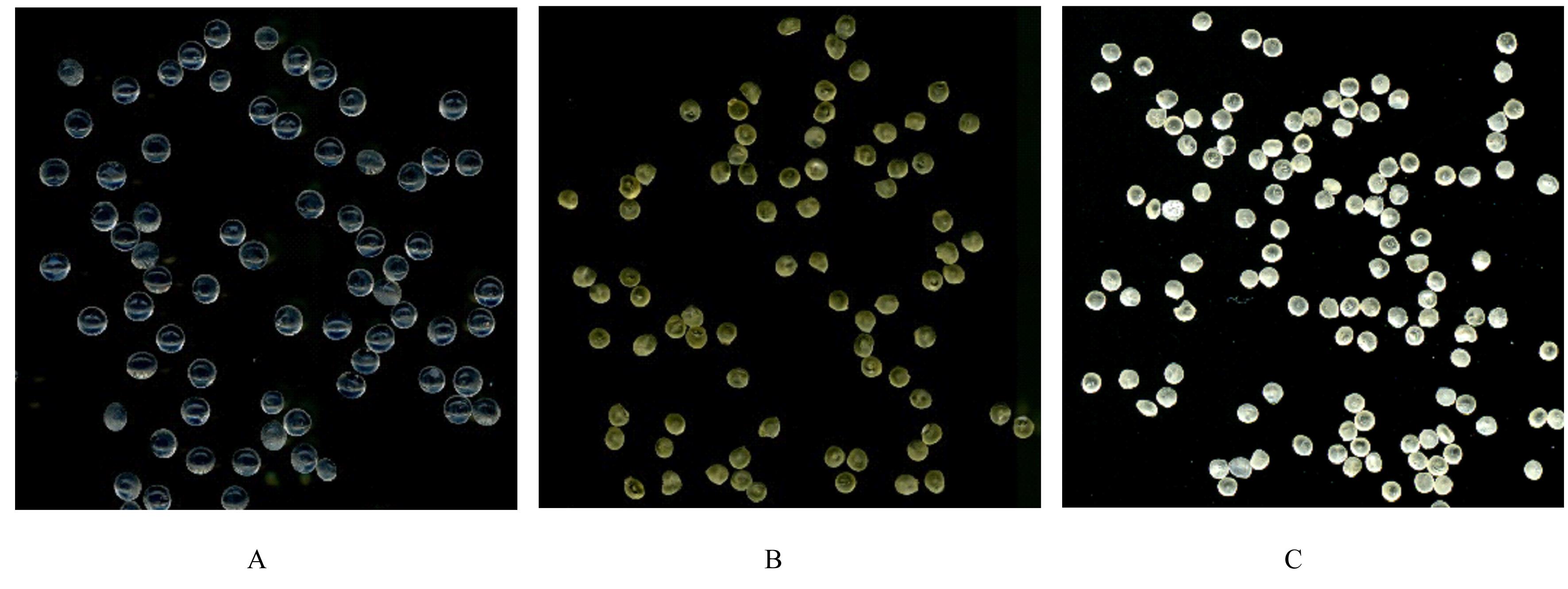
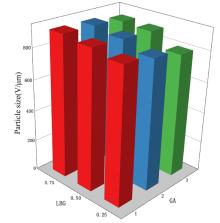
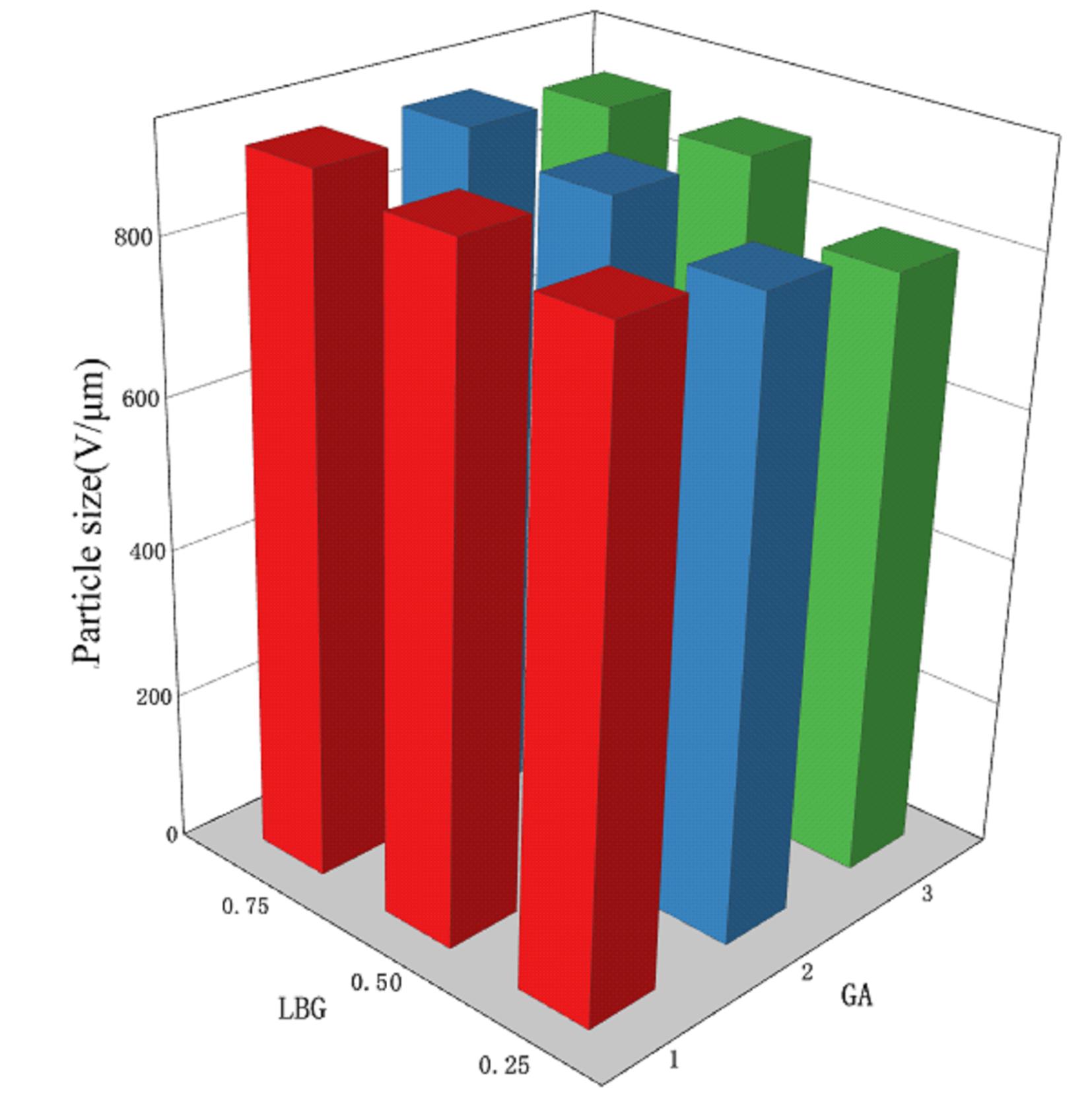
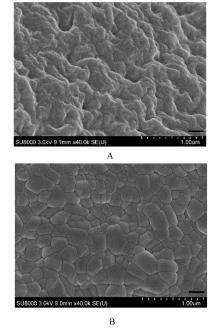
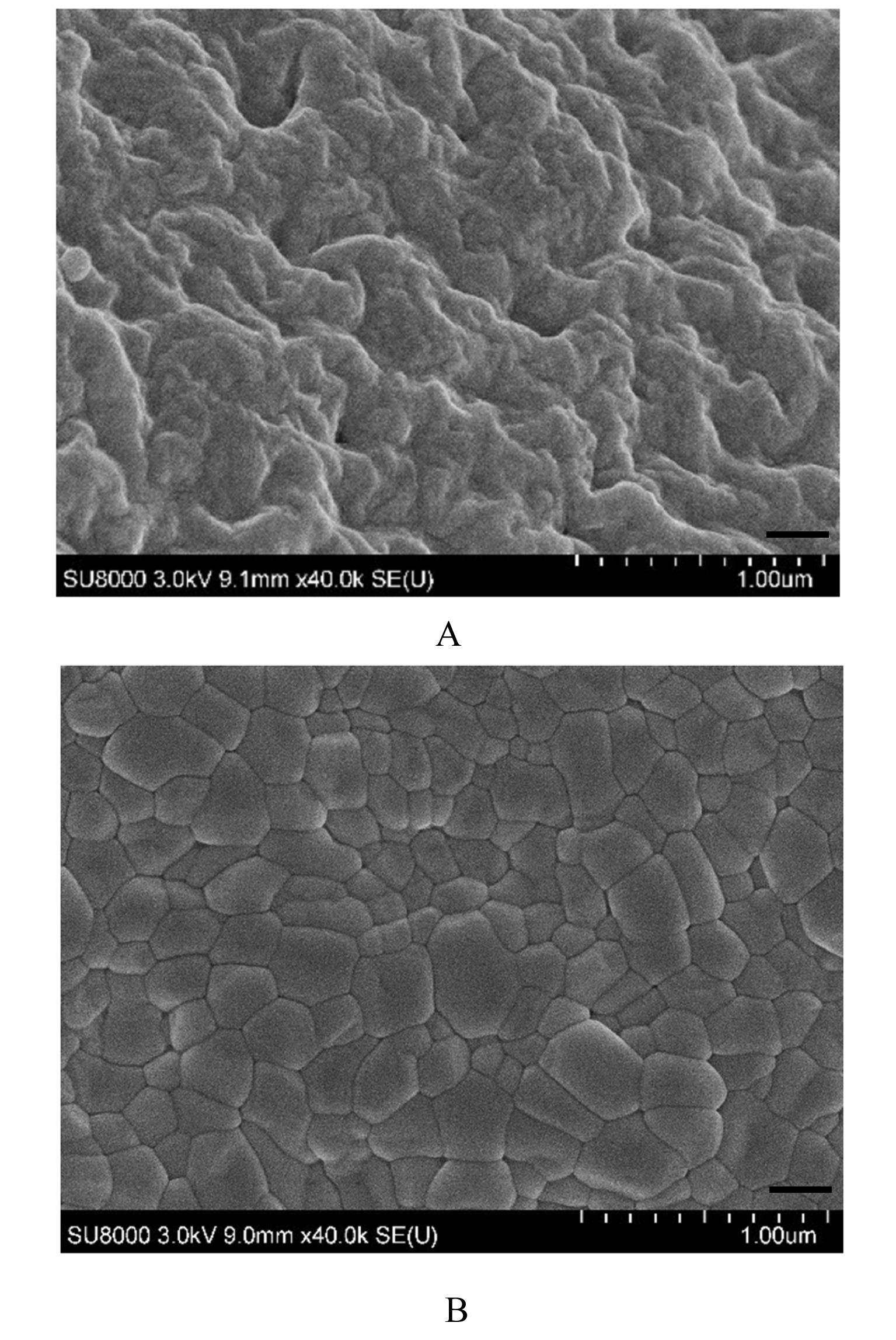
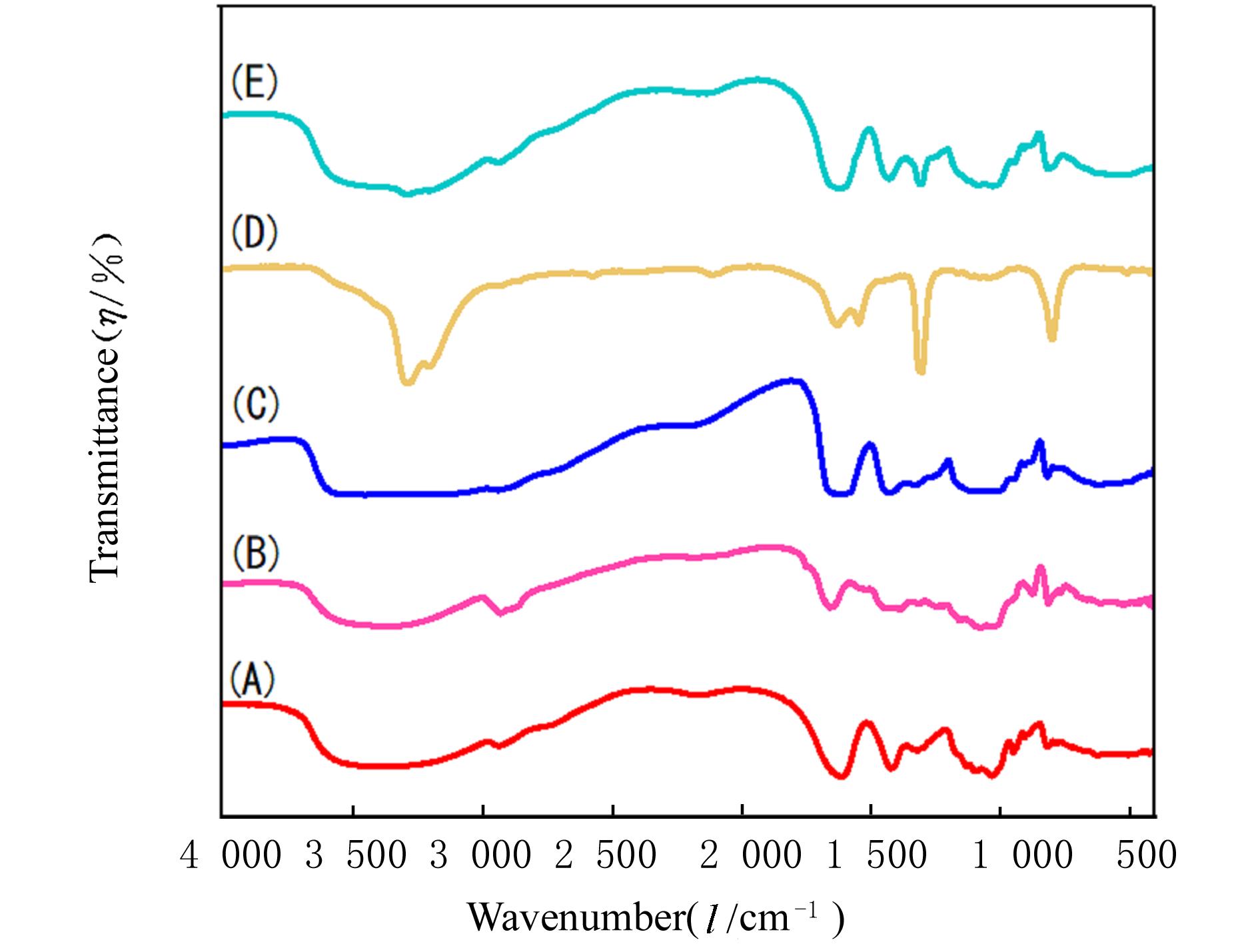
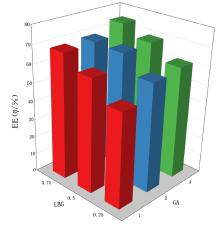
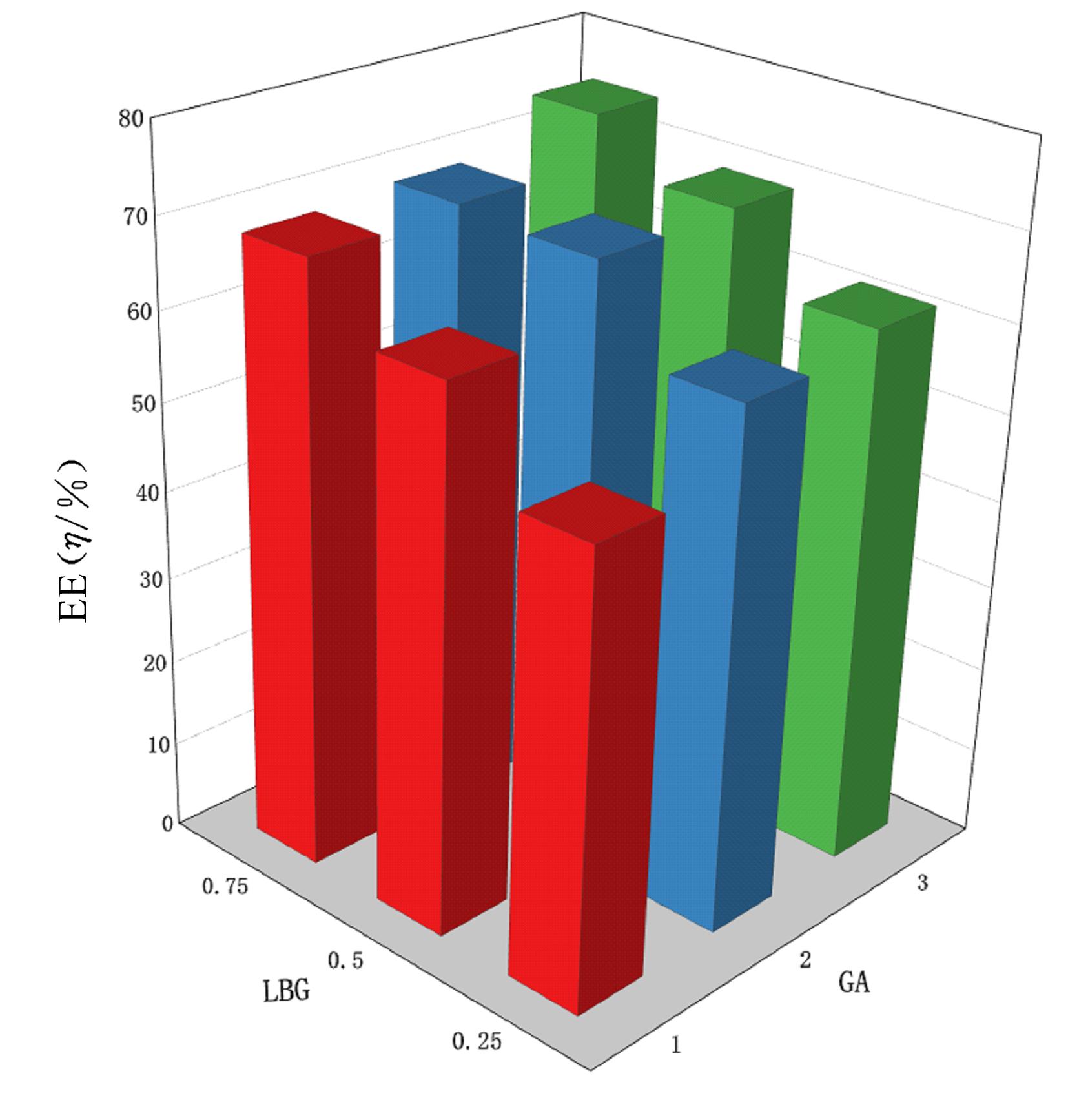
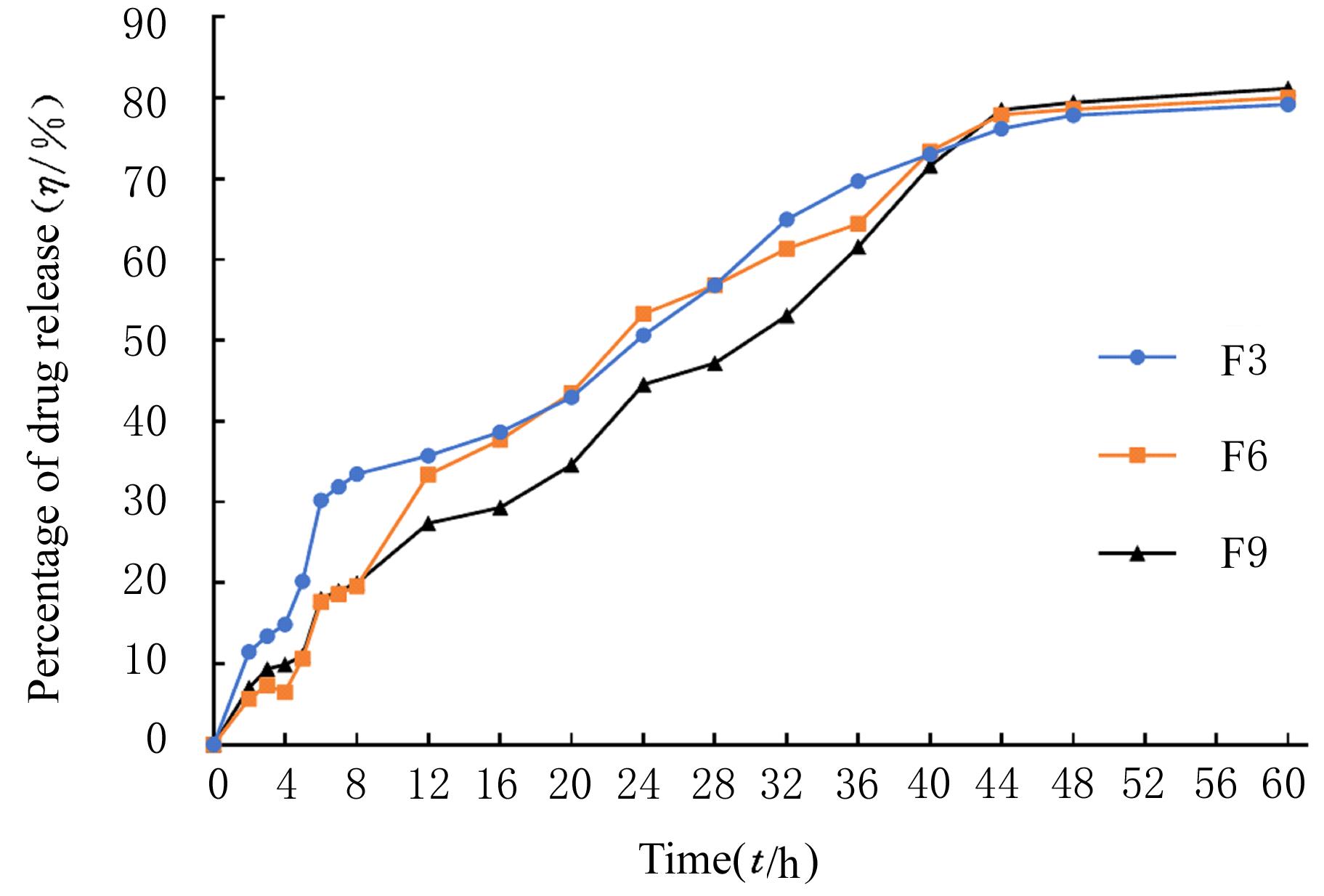
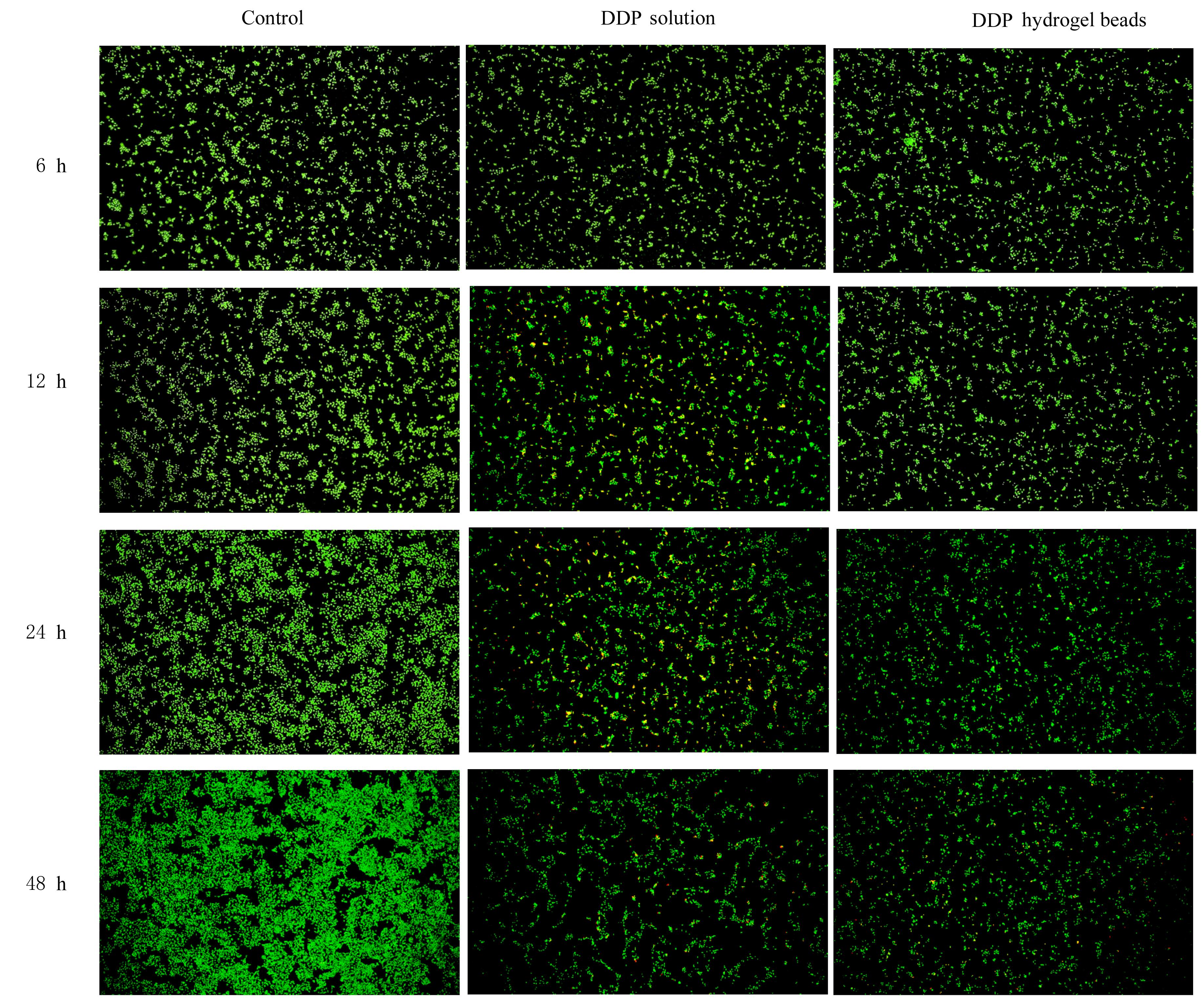
摘要: 探讨不同配比的海藻酸钠(SA)-角豆胶(LBG)互穿聚合物网络(IPN)水凝胶的载药和释药性能,评价包裹顺铂(DDP)的IPN水凝胶对口腔鳞状细胞癌CAL-27细胞的持续性杀伤作用及其机制。 将不同配比SA和LBG溶于去离子水,以戊二醛(GA)和氯化钙(CaCl2)为交联剂,采用离子凝胶法制备不同配方的IPN水凝胶,扫描电镜(SEM)和傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)表征水凝胶的物理化学结构,紫外分光光度分析法测定水凝胶的包封率(EE)并绘制药物释放曲线。三维柱状图展示不同配比LBG和GA条件下水凝胶珠的粒径及药物EE。结合EE和药物释放曲线选用优化配方包裹DDP制备DDP凝胶珠。CAL-27细胞分为对照组、DDP药液组和DDP凝胶珠组,MTS法和AO/PI 荧光染色法观察不同时间点各组CAL-27细胞的存活率和凋亡情况。 SEM观察,干燥的凝胶珠表面粗糙甚至凹凸不平,出现褶皱现象。三维柱状图观察,粒径随LBG水平的升高而增大,随GA水平的升高而减小。随着LBG和GA水平的升高,水凝胶的EE均升高。FTIR检测,IPN水凝胶成功包封药物DDP。当SA和LBG的配比为2.25∶0.75,GA水平为3%,CaCl2浓度为3%时,水凝胶药物EE为76.8%,药物缓释时间达48 h。MTS法检测,6和12 h后,DDP凝胶珠组CAL-27细胞存活率高于DDP药液组(P<0.05);在24和48 h时,DDP凝胶珠组细胞存活率低于DDP药液组(P<0.05)。6~48 h,对照组CAL-27细胞生长状态良好,增殖后的CAL-27细胞被染色为绿色;在6和12 h,DDP药液组和DDP凝胶珠组CAL-27细胞数量均少于对照组,DDP凝胶珠组存活细胞数略多于药物组;在24 h后,DDP凝胶珠组细胞生长速度变缓, CAL-27存活细胞数少于DDP药液组。 成功制备并优化了可缓释DDP的DDP-IPN水凝胶,其对口腔鳞状细胞癌CAL-27细胞具有持续杀伤作用,有望开发成一种新型药物缓释系统。
中图分类号:
- R739.8