吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1026-1034.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240417
SENP-1/HIF-1α通路对慢性间歇性低氧诱导大鼠血管内皮损伤的影响
- 南华大学衡阳医学院附属第二医院呼吸与危重症医学科,湖南 衡阳 421001
Effect of SENP-1/HIF-1α pathway on vascular endothelial injury in rats with chronic intermittent hypoxia
Yuanhang JIA,Yixia JIANG,Zhenhua HE,Lin CHEN,Fang ZHOU( )
)
- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hengyang Medical School,University of South China,Hengyang 421001,China
摘要:
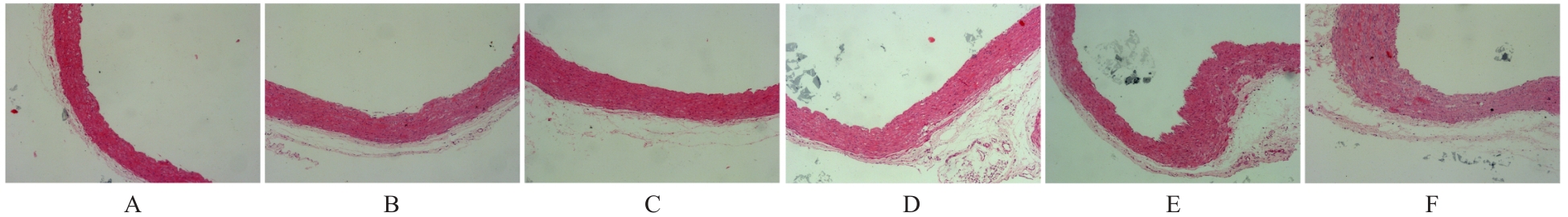
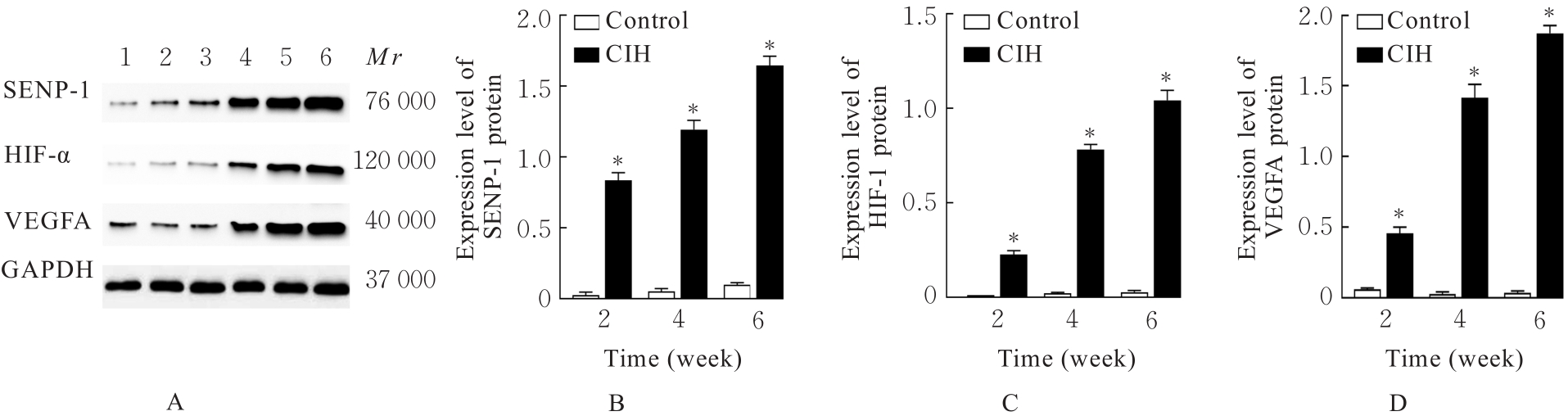
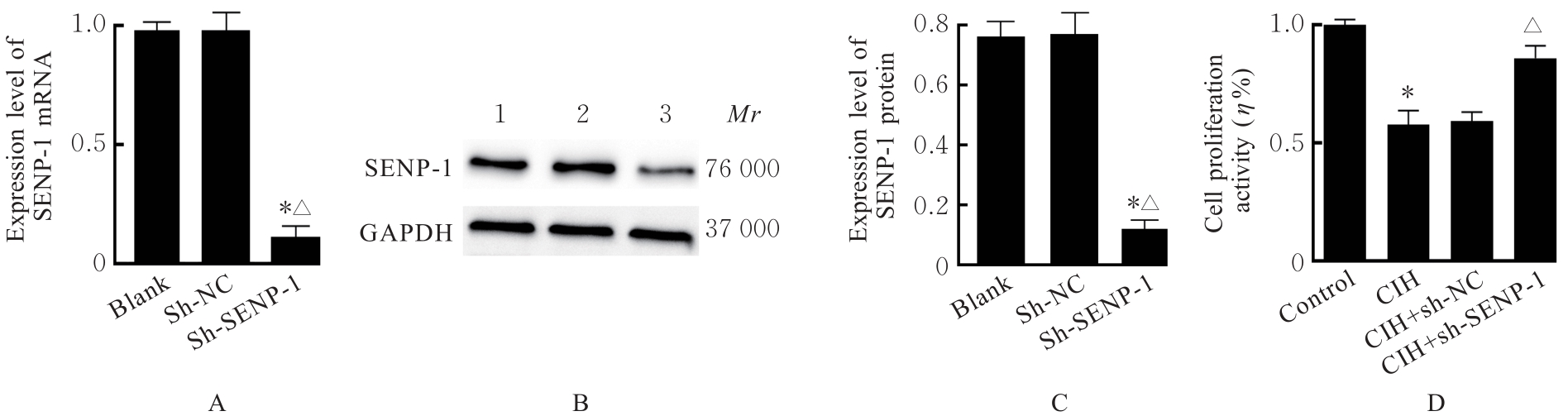
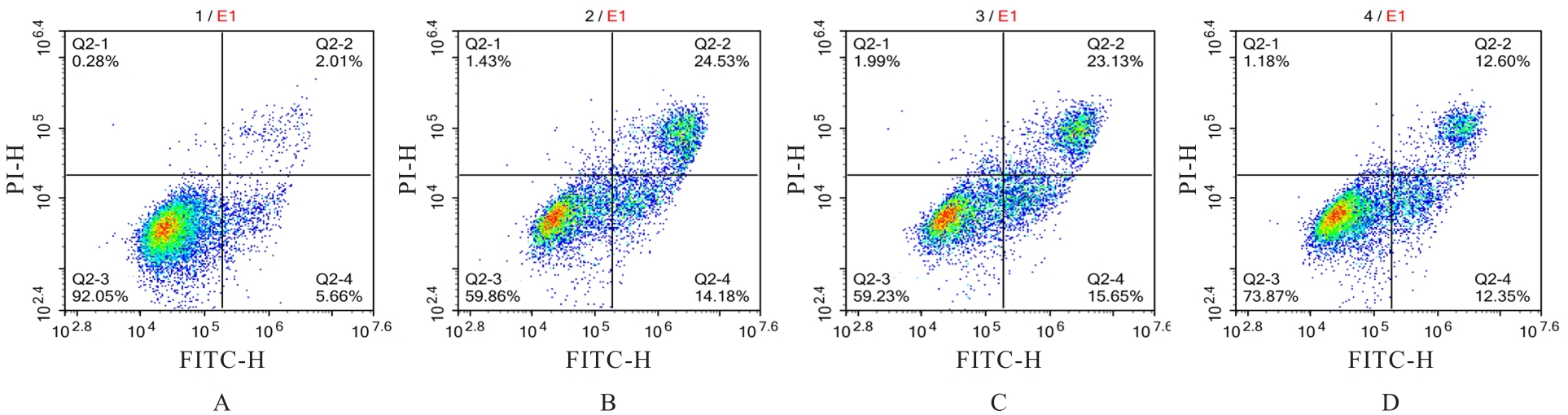
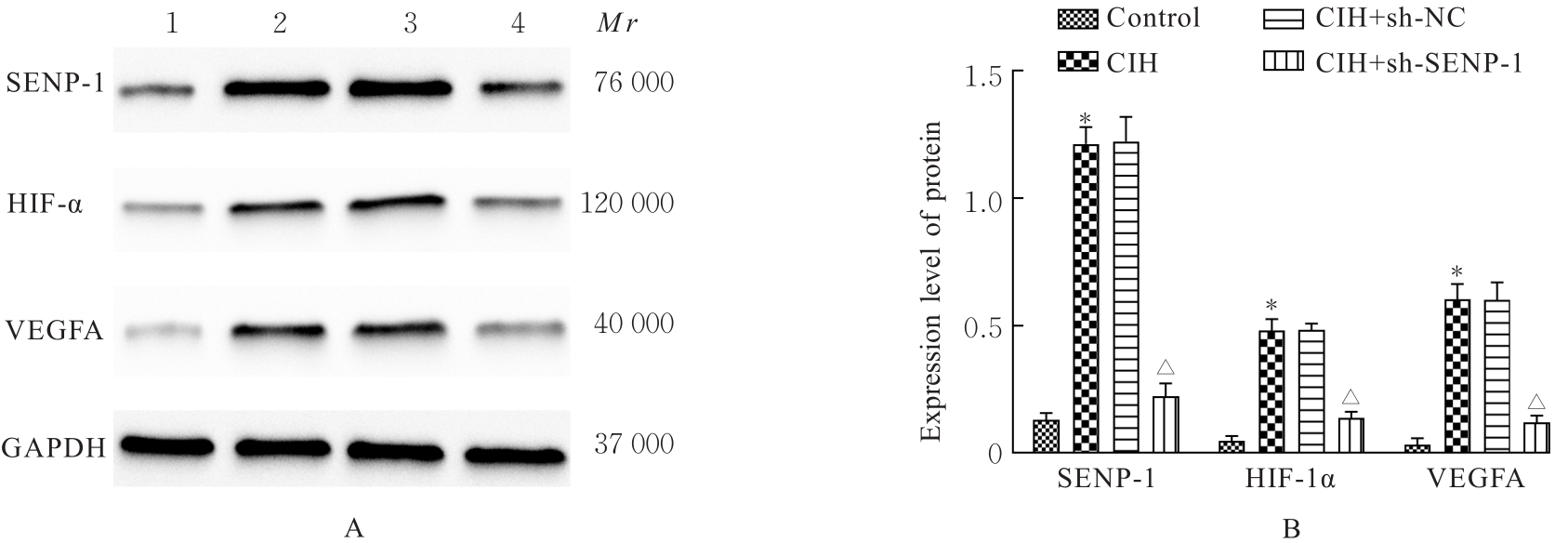
目的 探讨小泛素样修饰特异性蛋白酶1(SENP-1)/低氧诱导因子1α(HIF-1α)通路对慢性间歇性低氧(CIH)诱导大鼠血管内皮损伤的影响,阐明其相关作用机制。 方法 SD大鼠随机分为对照组和CIH组,再将每组分为2、4和6周3个时间点亚组,每亚组8只。CIH组大鼠暴露于CIH舱中进行CIH诱导,制备阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征(OSAHS)模型,对照组大鼠暴露于常氧环境中。于各时间点收集各组大鼠血清和胸主动脉组织。HE染色观察各组大鼠胸主动脉血管损伤情况,采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠血清中一氧化氮(NO)、内皮素1(ET-1)、血管性血友病因子(vWF)和血栓调节蛋白(TM)水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠胸主动脉组织中SENP-1、HIF-1α和血管内皮生长因子A(VEGFA)蛋白表达水平。体外培养大鼠主动脉内皮细胞(rAECs),经SENP-1 shRNA腺病毒(sh-SENP-1)感染构建SENP-1基因低表达的rAECs 细胞株,采用 CIH 诱导建立血管内皮细胞损伤模型,分为 CIH 组、CIH+sh-NC 组和 CIH+sh-SENP-1组,另设对照组。CCK-8检测各组细胞增殖活性,ELISA法检测各组细胞培养上清中乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性及细胞中NO、ET-1、丙二醛(MDA)水平和超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性,流式细胞术检测各组细胞凋亡率,Western blotting法检测各组细胞中SENP-1、HIF-1α和VEGFA蛋白表达水平。 结果 随着CIH诱导时间的延长,与对照组比较,CIH组大鼠胸主动脉内膜逐渐粗糙并明显增厚,血清中NO水平逐渐减低(P<0.05),血清中ET-1、vWF和TM水平及胸主动脉组织中SENP-1、HIF-1α和VEGFA蛋白表达水平逐渐升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,CIH组细胞增殖活性降低(P<0.05),细胞培养上清中LDH活性及细胞中ET-1、MDA水平和细胞凋亡率升高(P<0.05),细胞中NO水平和SOD活性降低(P<0.05),SENP-1、HIF-1α和VEGFA蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与CIH组比较,CIH+sh-SENP-1组细胞增殖活性升高(P<0.05),细胞培养上清中LDH活性及细胞中ET-1、MDA水平和细胞凋亡率降低(P<0.05),细胞中NO水平和SOD活性升高(P<0.05),SENP-1、HIF-1α和VEGFA蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 SENP-1/HIF-α通路在CIH诱导的大鼠胸主动脉损伤组织中高度活化,沉默SENP-1表达可减轻CIH诱导的血管内皮细胞损伤,其作用机制可能与下调SENP-1/HIF-α通路活化水平有关。
中图分类号:
- R364.4