吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (2): 377-383.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20210217
雷公藤多苷对慢性肾脏病大鼠血管内皮损伤的保护作用及其机制
- 1.河北医科大学第一医院肾内一科,河北 石家庄 050001
2.河北医科大学第二医院肾内科,河北 石家庄 050000
Protective effect of multiglycoside of tripterygium wilfordii on vascular endothelial injury in rats with chronic kidney disease and its mechanism
Baozhen XU1,Meijuan WU2,Xiuhong HU1,Tao WANG1,Yuwei GAO1( )
)
- 1.Department of Nephrology,First Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050001,China
2.Department of Nephrology,Second Hospital,Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050000,China
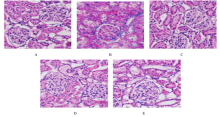
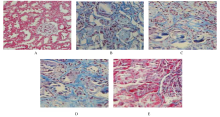
摘要: 探讨雷公藤多苷(GTW)对慢性肾脏病(CKD)大鼠血管内皮损伤的保护作用,并阐明其作用机制。 将60只大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组和低、中及高剂量GTW组,每组12只。采用腺嘌呤诱导CKD大鼠模型。低、中和高剂量GTW组大鼠分别灌胃给予3.0、6.0和9.0 mg·kg-1 GTW,对照组和模型组大鼠给予等体积生理盐水。给药4周后检测各组大鼠血清尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(Scr)水平。采用HE和Masson染色观察各组大鼠血清肾脏组织病理及纤维化改变。采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组大鼠血清内皮素1(ET-1)、一氧化氮(NO)、血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)、肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)和转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)水平。 与对照组比较,模型组大鼠血清中BUN、Scr、ET-1、AngⅡ、TNF-α、IL-6和TGF-β1水平明显升高(P<0.05),NO水平明显降低(P<0.05),肾组织纤维化程度明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量GTW组大鼠血清中BUN、Scr、ET-1、AngⅡ、TNF-α、IL-6和TGF-β1水平明显降低(P<0.05),NO水平明显升高(P<0.05),肾组织纤维化程度明显降低(P<0.05)。HE染色,对照组大鼠肾组织中肾小球和肾小管结构完整,细胞排列整齐;模型组大鼠肾组织肾小球和肾小管出现水肿,球囊粘连,有炎症细胞浸润;低、中和高剂量GTW组大鼠肾组织均有不同程度水肿和炎症细胞浸润,损伤程度较模型组轻。 GTW通过下调ET-1和AngⅡ水平、上调NO水平,降低血清炎性因子水平,对CKD大鼠血管内皮损伤起到改善作用。
中图分类号:
- R692.6