• •
动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血患者发生急性脑积水的危险因素分析
- 吉林大学第一医院神经血管病外科,吉林 长春 130021
Analysis of risk factors for the development of acute hydrocephalus in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
Jiahui FENG,Renjie LIU,Xuan CHEN( )
)
- Department of Neurovascular Disease,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
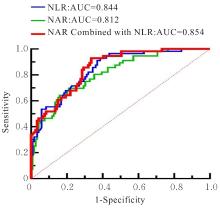
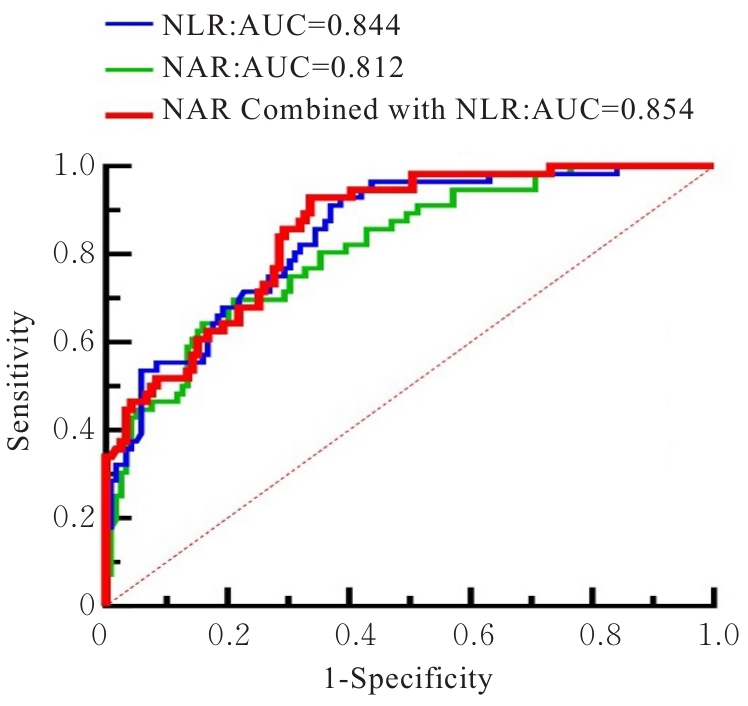
目的 探讨与动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血(aSAH)并发急性脑积水(aHCP)相关的危险因素,为该类患者的早期识别及干预提供临床参考。 方法 回顾性分析175例aSAH患者的临床资料和实验室指标,根据发病后是否出现aHCP的情况将患者分为aHCP组(n=56)和非aHCP组(n=119)。采用单因素分析和二元Logistic回归分析aSAH患者发生aHCP的危险因素,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和曲线下面积(AUC)评价分析结果对aSAH患者发生aHCP的预测价值。 结果 纳入的175例aSAH患者中,共计56例(32.0%)在发病后出现aHCP。与非aHCP组比较,aHCP组患者的中性粒细胞计数、血糖、中性粒细胞与白蛋白比值(NAR)、血小板与淋巴细胞比值(PLR)、中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(NLR)、单核细胞与淋巴细胞比值(MLR)、全身免疫炎症指数(SII)、系统炎症反应指数(SIRI)和全身炎症综合指数(AISI)水平明显升高(P<0.05),淋巴细胞计数明显降低(P<0.05),Hunt-Hess分级和改良Fisher分级更高(P<0.05),脑室积血情况更多(P<0.05)。二元Logistic回归分析,NAR升高(OR=2.237,95%CI:1.063~4.708,P=0.034)和NLR升高(OR=1.210,95%CI:1.095~1.337,P<0.01)是aSAH后aHCP发生的独立危险因素。ROC曲线分析,NAR 的AUC 为0.812(95%CI:0.745~0.878,P<0.001),NLR的AUC为0.844(95%CI:0.785~0.903,P<0.001),NAR与NLR联合AUC为0.854(95%CI:0.798~0.910,P<0.001)。 结论 NAR和NLR是aSAH患者发生aHCP的独立危险因素。
中图分类号:
- R651.1