吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 765-769.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230327
残余胆固醇水平对急性冠脉综合征患者发病的预测价值
- 1.承德医学院附属医院急诊医学科,河北 承德 067000
2.承德医学院病理生理学教研室,河北 承德 067000
3.吉林大学第一医院老年病科,吉林 长春 130021
Predictive value of residual cholesterol in occurrence of patients with acute coronary syndrome
Mingfei JU1,Chao LIU1,Zhigang MA1,Juan ZHAO2,Tu WANG2,Zhihao WANG3( )
)
- 1.Department of Emergency Medicine,Affiliated Hospital,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
2.Department of Pathophysiology,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
3.Department of Geriatrics,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
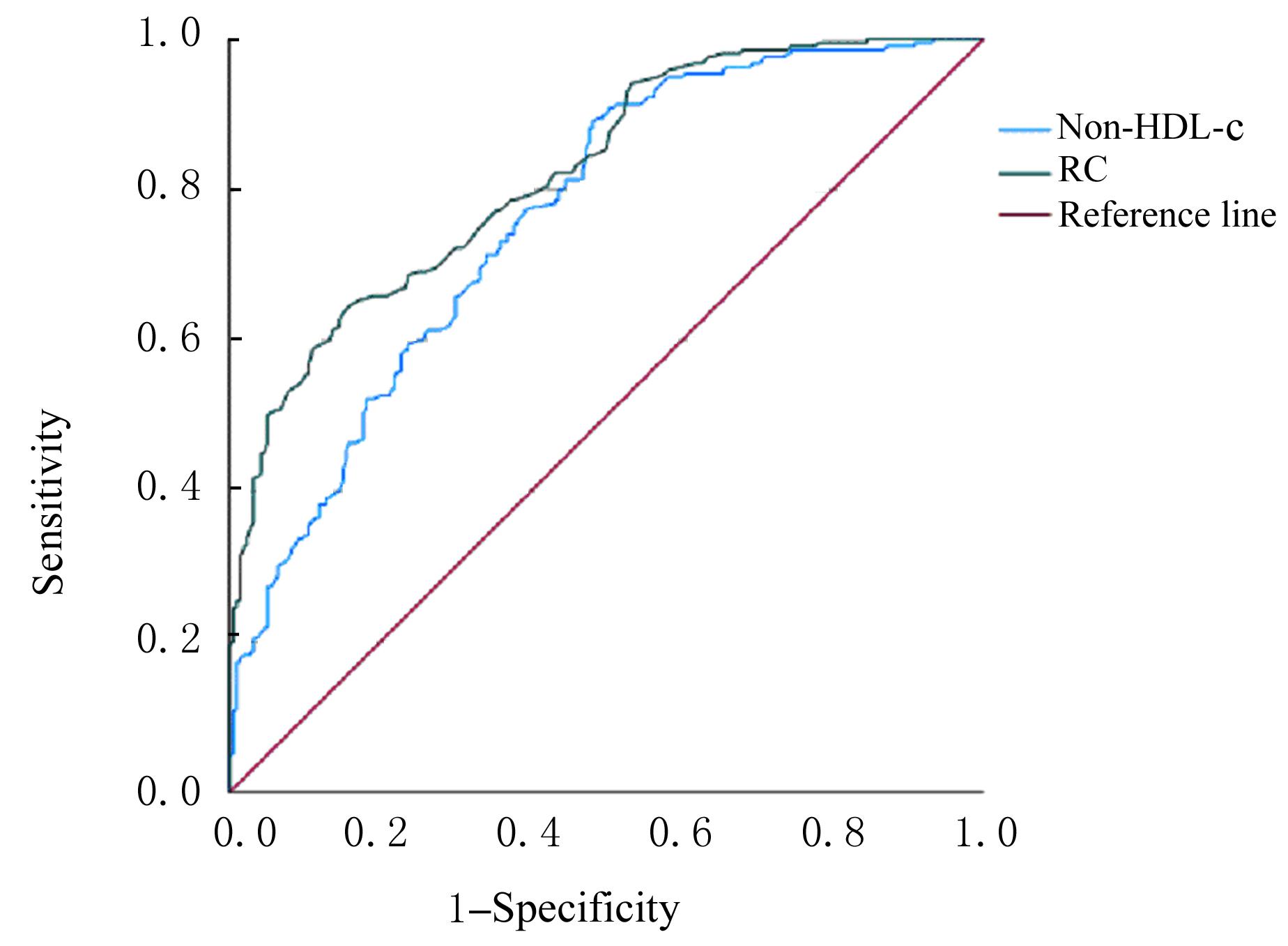
目的 分析急性冠脉综合征(ACS)患者胆固醇水平的变化,探讨残余胆固醇(RC)水平对ACS发病的预测价值。 方法 选取ACS患者220例作为ACS组,选取同期健康体验者220名作为对照组。收集2组研究对象的一般资料,包括血清总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)水平,计算血清中非HDL-c(non-HDL-c)和RC水平。采用Logistic回归分析ACS患者的危险因素及其与各血脂成分水平的相关性,采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线和曲线下面积(AUC)评价各血脂成分对ACS发病的预测价值。 结果 单因素分析,与对照组比较,ACS组患者高血压和吸烟者所占百分率明显升高(P<0.01),血清中TC、RC、LDL-c和non-HDL-c水平明显升高(P<0.01),HDL-c水平明显降低(P<0.01)。多因素Logistic回归分析,高血压(OR=0.496,P=0.005)、吸烟(OR=0.458,P=0.002)、RC水平(OR=24.051,P<0.01)和non-HDL-c水平(OR=1.711,P<0.01)是ACS发病的独立危险因素。ROC曲线分析,与non-HDL-c水平比较,RC水平的AUC较大,对ACS患者发病的预测价值更高。 结论 RC水平是ACS发病的独立危险因素,对ACS发病具有一定预测价值。
中图分类号:
- R543.3