• •
KHSRP通过激活JAK/STAT信号通路对结直肠癌细胞生物学行为的影响
李宏丽1,王梦瑶2,刘洋洋2,张卉3,李丽2( ),韦海涛2(
),韦海涛2( )
)
- 1.河南大学淮河医院肿瘤科,河南 开封 475099
2.河南大学护理与健康学院,河南 开封 475004
3.河南大学淮河医院消化科,河南 开封 475099
Effect of KHSRP on biological behavior of colorectal cancer cells through activation of JAK/STAT signaling pathway
Hongli LI1,Mengyao WANG2,Yangyang LIU2,Hui ZHANG3,Li LI2( ),Haitao WEI2(
),Haitao WEI2( )
)
- 1.Department of Oncology,Huaihe Hospital,Henan University,Kaifeng 475099,China
2.Department of,School of Nursing and Health,Henan University,Kaifeng 475004,China
3.Department of Gastroenterology,Huaihe Hospital,Henan University,Kaifeng 475099,China
摘要:
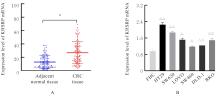
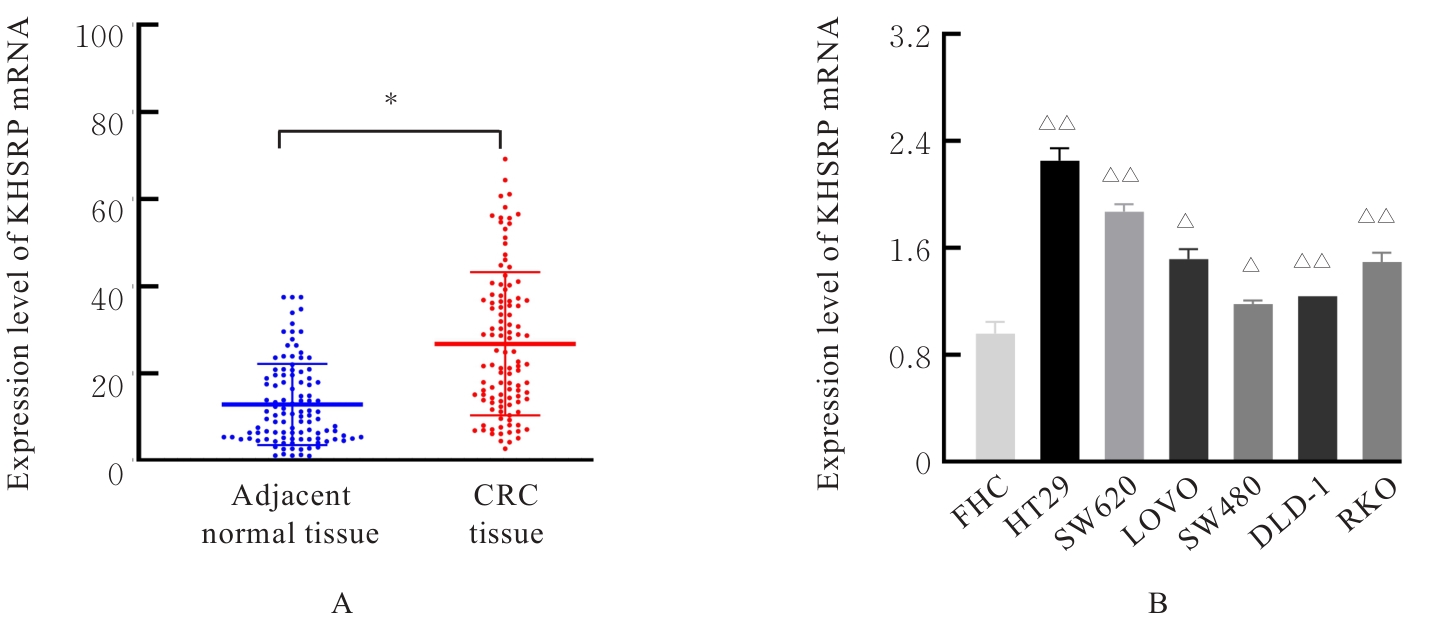
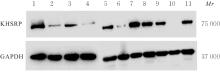
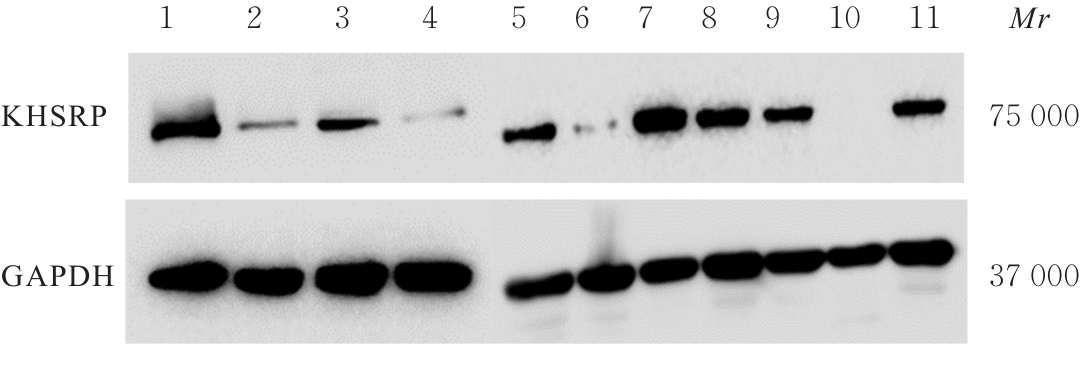
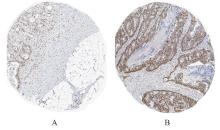
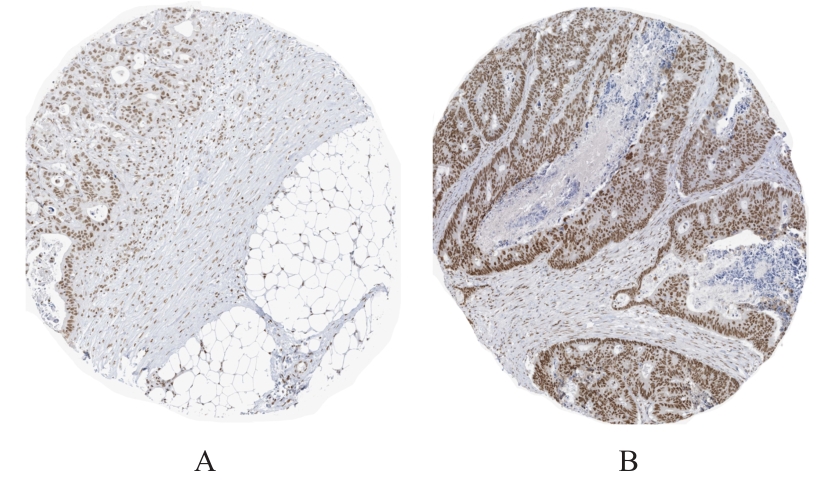
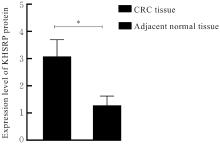
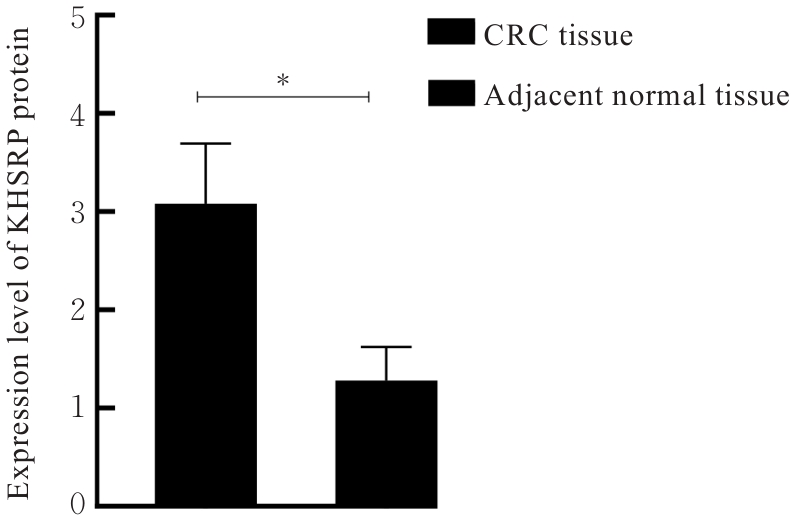
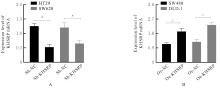
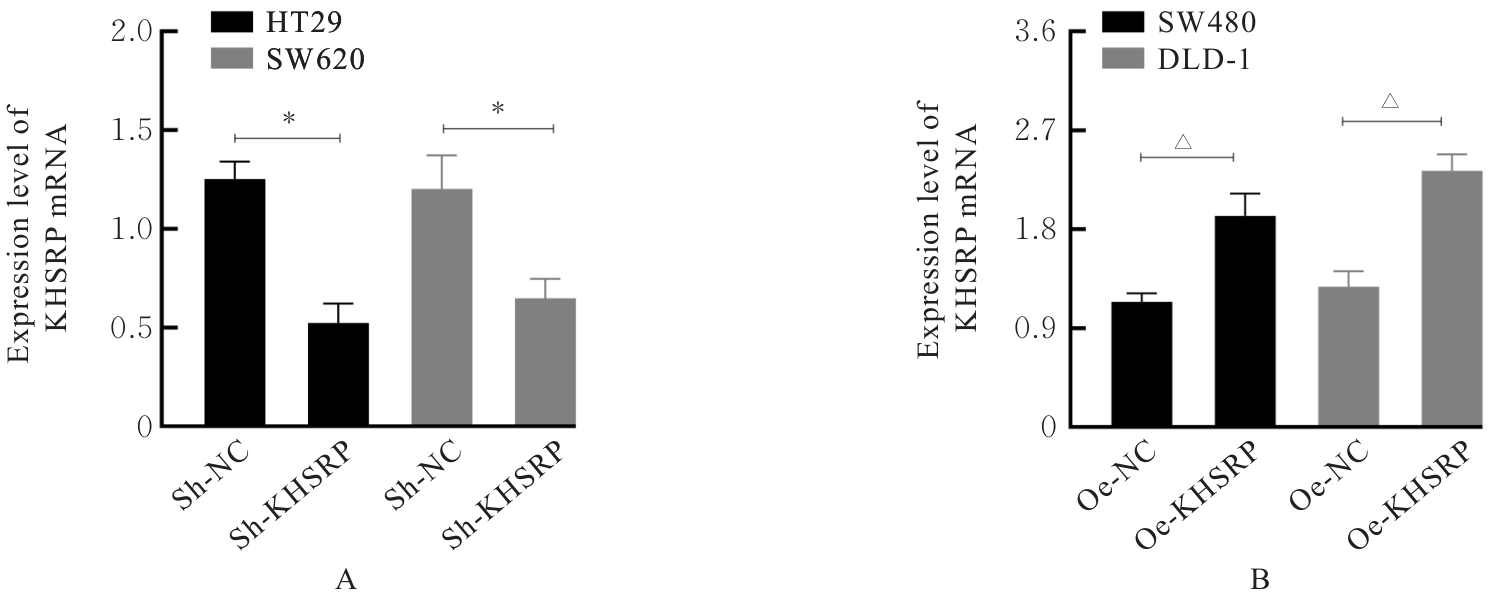
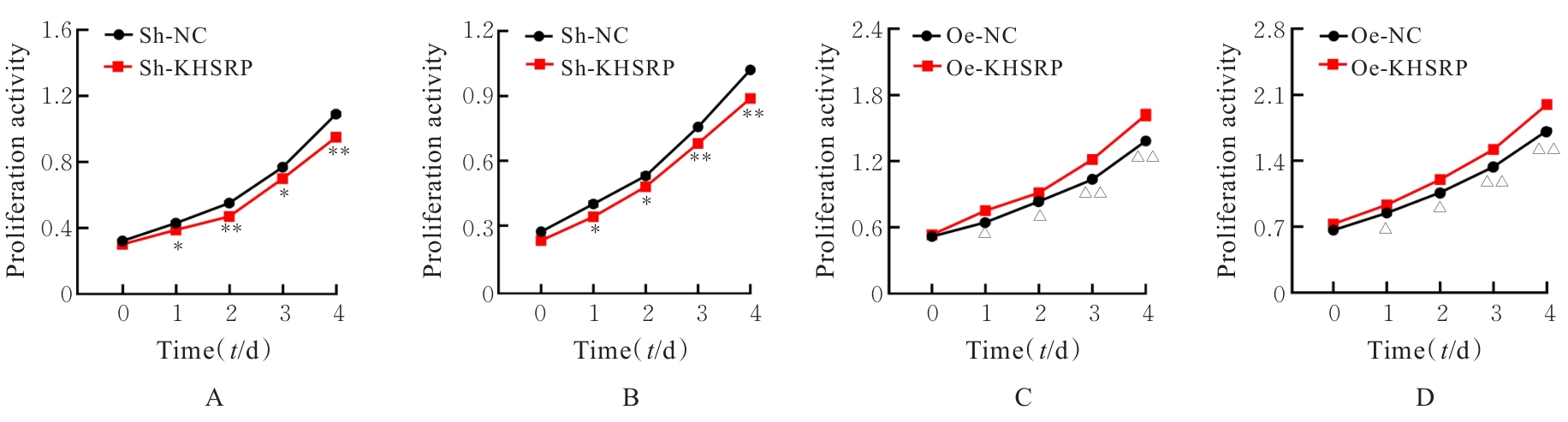
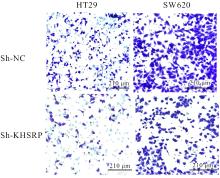
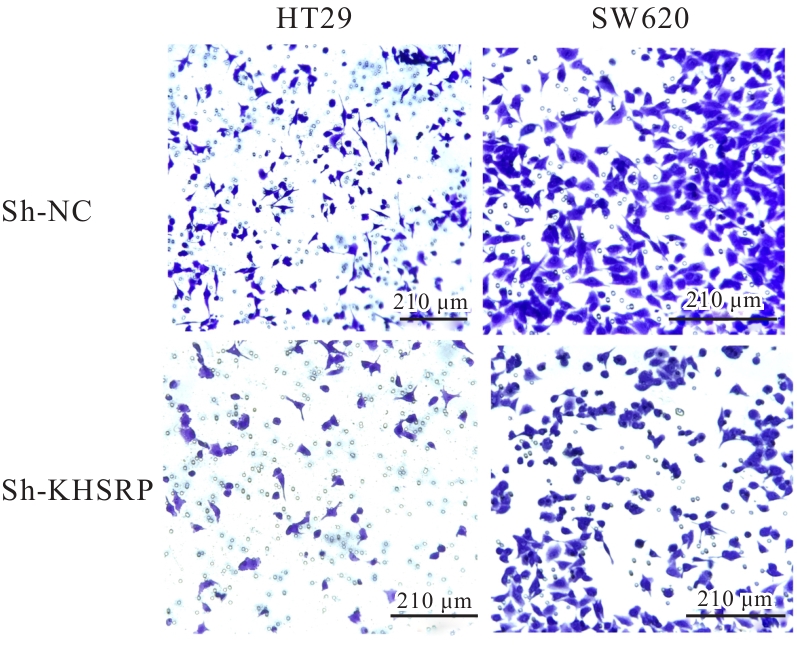
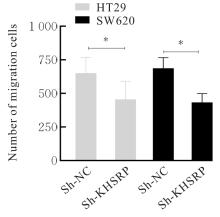
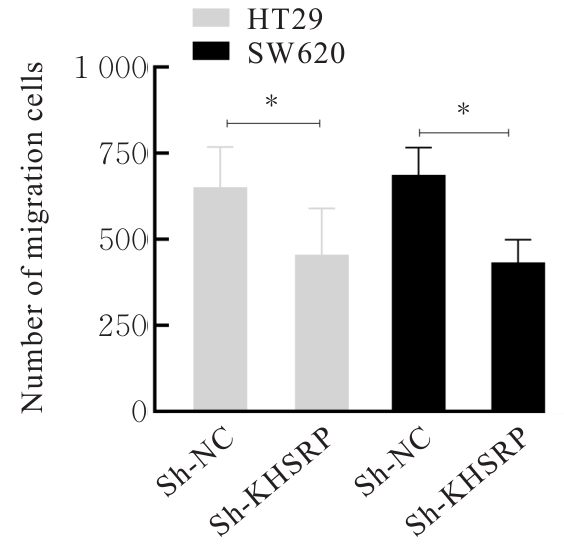
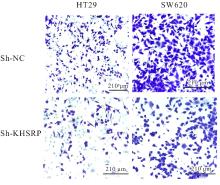
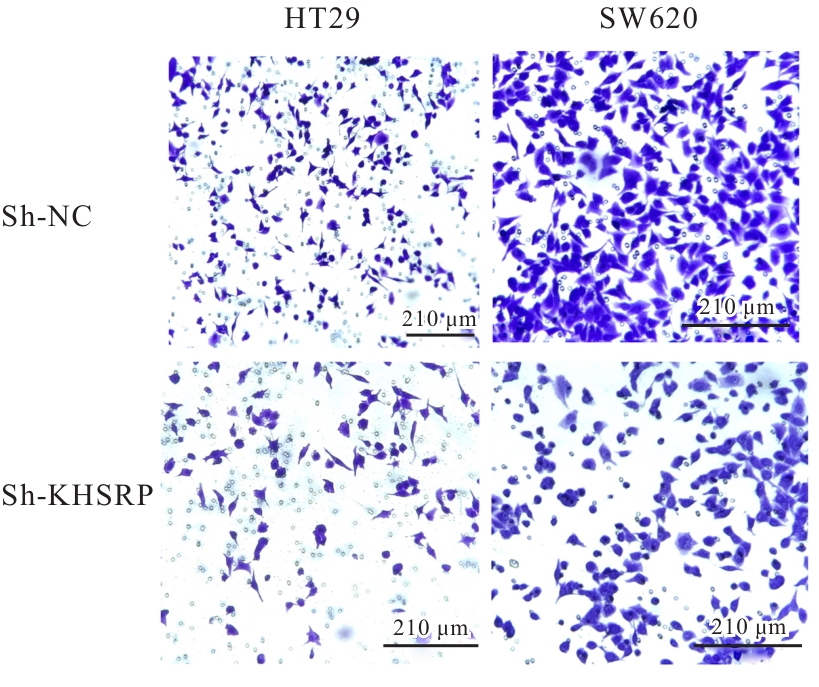
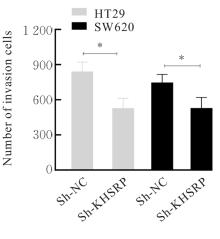
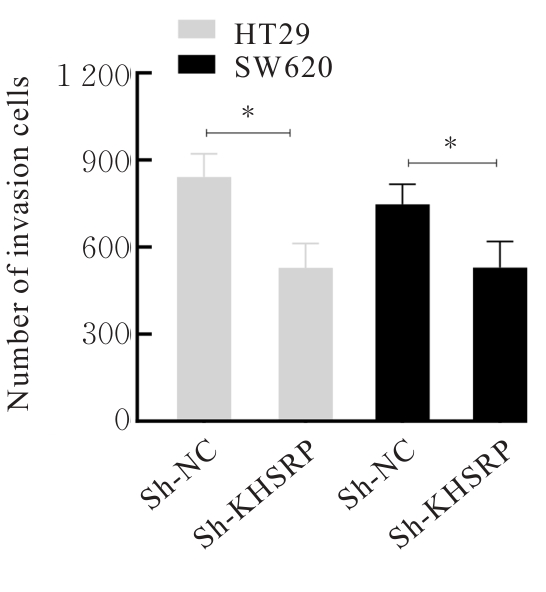
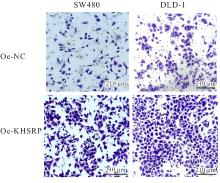
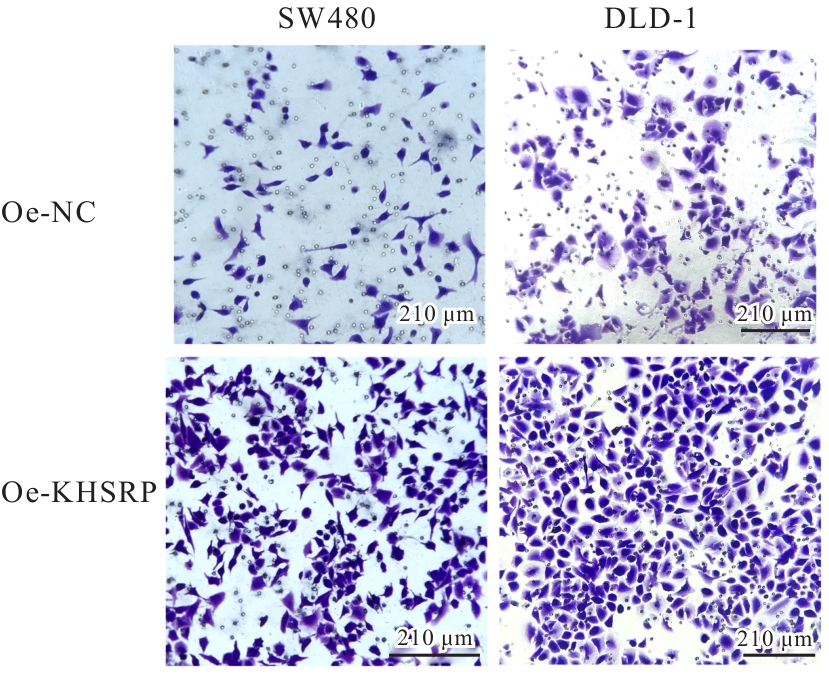
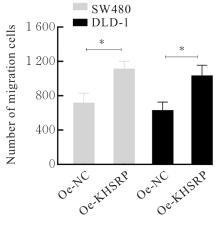
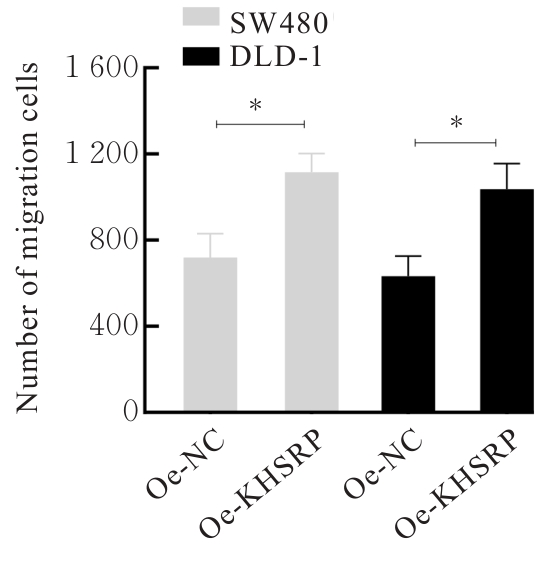
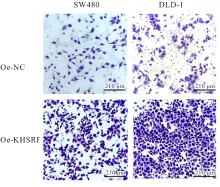
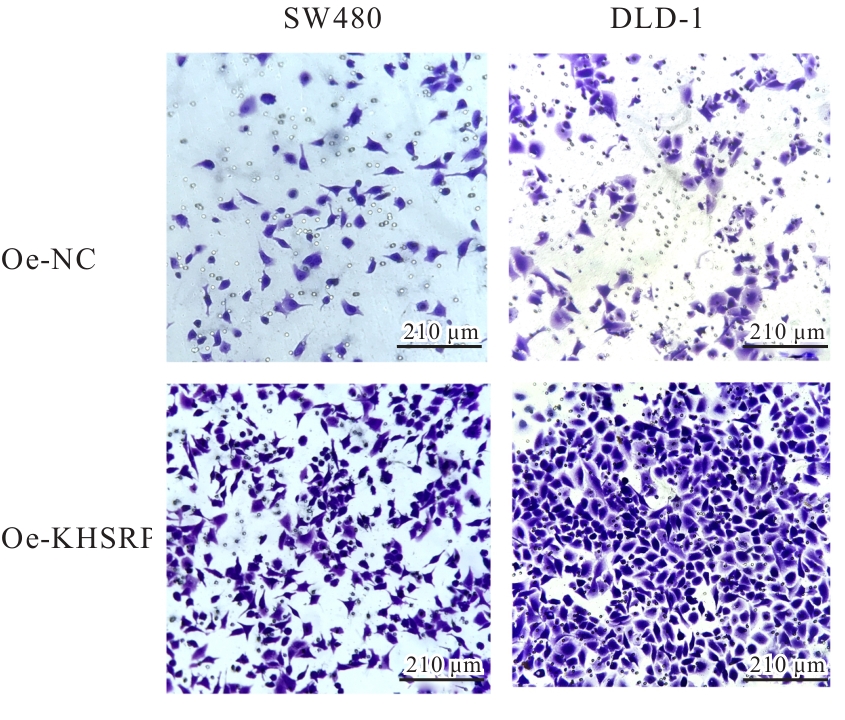
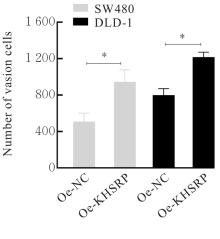
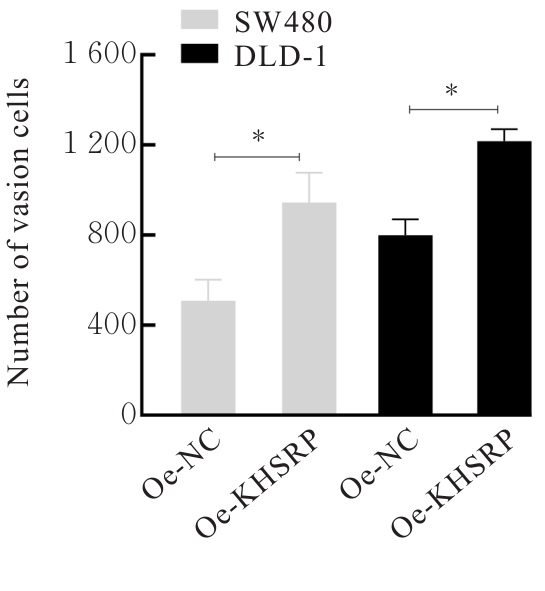
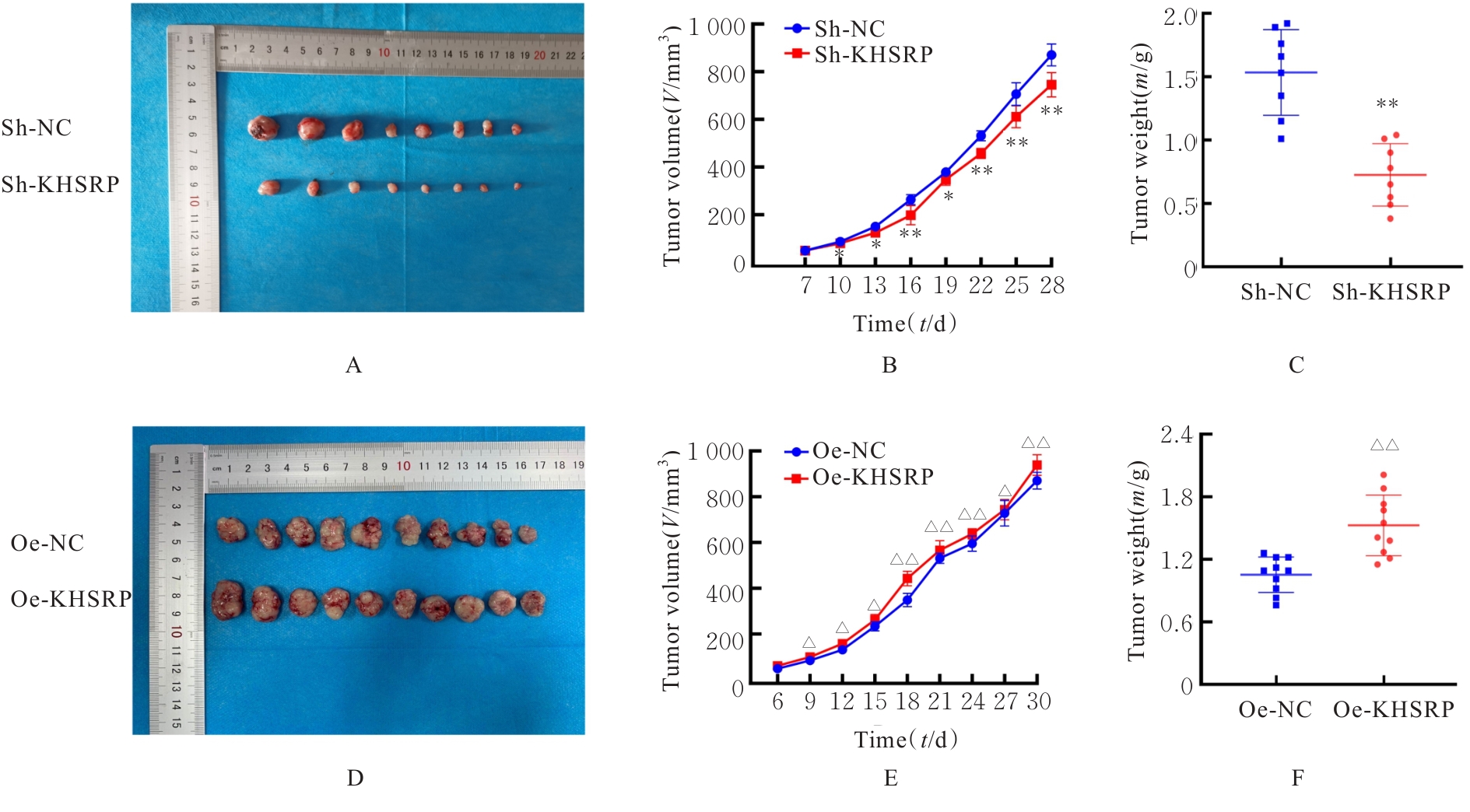
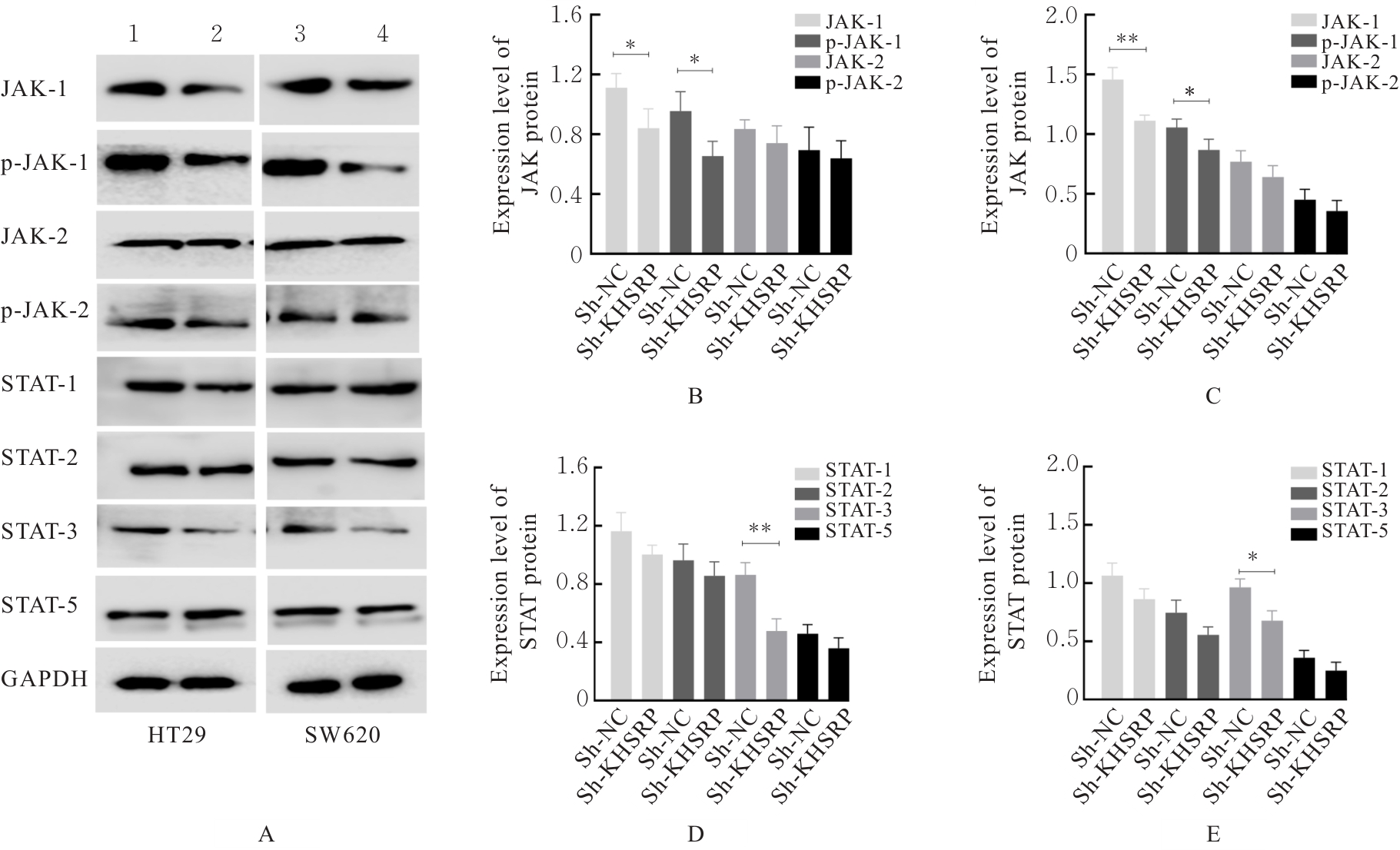
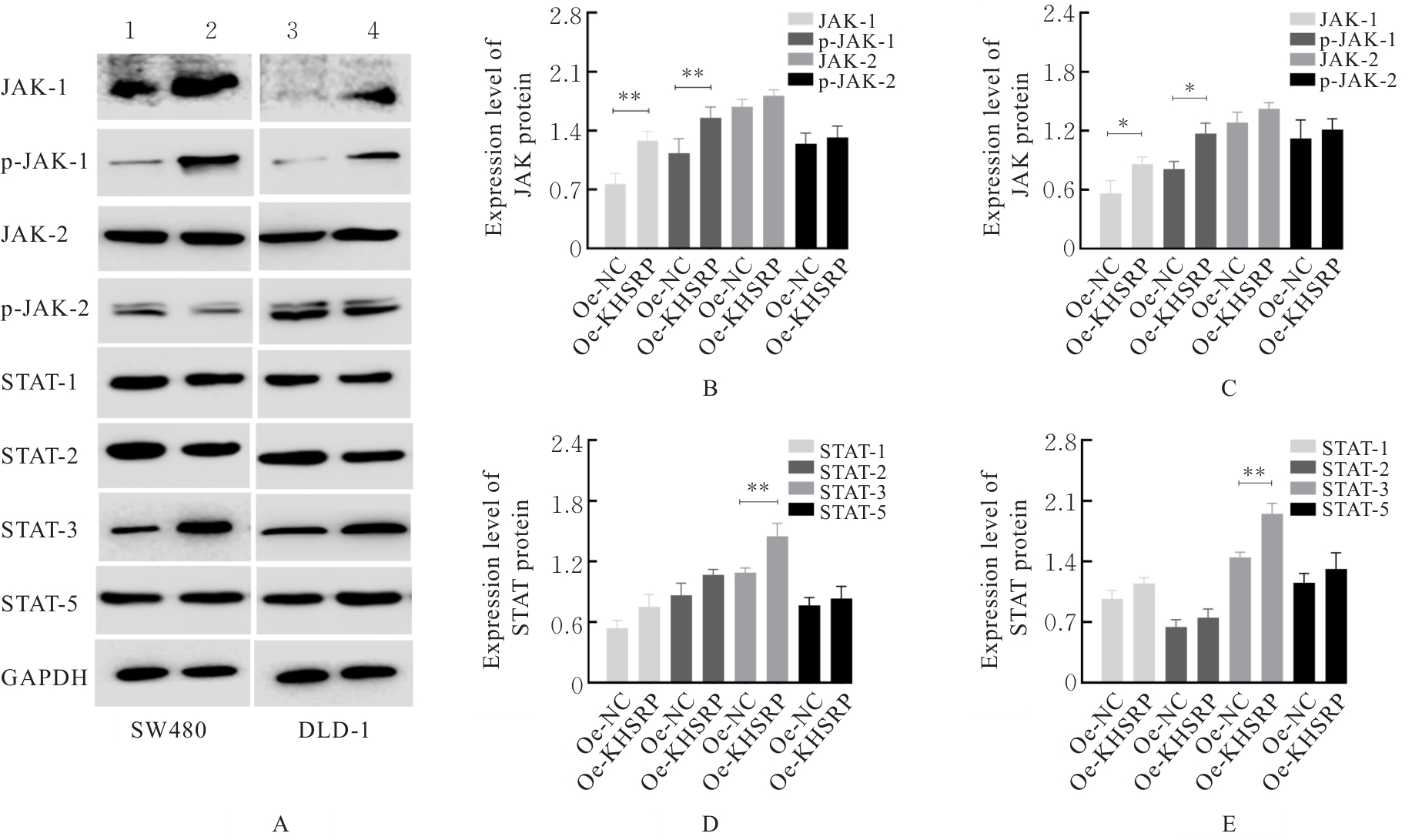
目的 探讨KH型剪切调节蛋白(KHSRP)激活Janus激酶(JAK)/信号转导与转录激活因子(STAT)信号通路对结直肠癌(CRC)恶性生物学行为的影响,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 选取64例CRC患者的CRC组织和癌旁正常组织,体外培养人CRC HT29、SW620、SW480、DLD-1、LOVO和RKO细胞及人正常结直肠黏膜FHC细胞,提取CRC组织和组细胞中总RNA,采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测CRC组织癌旁正常组织和各种细胞中KHSRP mRNA表达水平。将HT29和SW620细胞分为sh-NC组(无相关性的核苷酸序列插入慢病毒质粒)和sh-KHSRP组(转染敲降KHSRP慢病毒);SW480和DLD-1细胞分为oe-NC组(无相关性的核苷酸序列插入慢病毒质粒)和oe-KHSRP组(转染过表达KHSRP慢病毒)。采用免疫组织化学(IHC)染色法分析CRC组织和癌旁正常组织中KHSRP蛋白表达情况,细胞计数试剂盒8(CCK-8)法检测各组CRC细胞增殖活性,Transwell小室实验检测各组CRC细胞的迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数,Western blotting法检测各组CRC细胞中KHSRP、JAK1、磷酸化JAK1(p-JAK1)、JAK2、磷酸化JAK2(p-JAK2)、STAT1、STAT2、STAT3和STAT5蛋白表达水平,裸鼠皮下移植瘤实验检测各组小鼠肿瘤质量和肿瘤体积。 结果 与癌旁正常组织比较,CRC组织中KHSRP mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.01);与人正常结直肠黏膜FHC细胞比较,CRC细胞中KHSRP mRNA表达水平均升高(P<0.05),后续实验选择HT29和SW620细胞进行KHSRP敲降,选择SW480和DLD-1细胞进行 KHSRP过表达。Western blotting法检测,CRC组织和细胞中KHSRP蛋白表达量高于癌旁正常组织和FHC细胞。IHC染色法分析,与癌旁正常组织比较,CRC组织中KHSRP蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.01)。RT-qPCR法检测,与sh-NC组比较,sh-KHSRP组CRC HT29和SW620细胞中KHSRP mRNA表达水平降低(P<0.01);与oe-NC组比较,oe-KHSRP组SW480和DLD-1细胞中KHSRP mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.01),提示细胞转染成功。CCK-8法检测,与sh-NC组比较,敲降KHSRP后,sh-KHSRP组HT29和SW620细胞增殖活性降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与oe-NC组比较,过表达KHSRP后,oe-KHSRP组SW480和DLD-1细胞增殖活性升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与sh-NC组比较,敲降KHSRP后,sh-KHSRP组HT29和SW620细胞的迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数减少(P<0.05);与oe-NC组比较,过表达KHSRP后,oe-KHSRP组SW480和DLD-1细胞的迁移细胞数和侵袭细胞数增多(P<0.05)。敲降KHSRP后,oe-KHSRP组小鼠肿瘤体积和质量小于sh-NC组(P<0.05或P<0.01);过表达KHSRP后,oe-KHSRP组小鼠肿瘤体积和质量大于oe-NC组(P<0.05或P<0.01)。与sh-NC组比较,sh-KHSRP组CRC细胞中JAK1、p-JAK-1和STAT3蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与oe-NC组比较,oe-KHSRP组CRC细胞中JAK1、p-JAK-1和STAT3蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01)。 结论 KHSRP高表达可促进CRC细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭,促进小鼠CRC细胞皮下移植瘤的生长,其机制可能与其激活JAK1/STAT3信号通路有关联。
中图分类号:
- R735.3