吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1240-1250.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250510
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
防脱育发液对毛发生长的促进作用及其机制
牟燕鸿1,2,李英娜1,2,刘建增3,罗春红4,孙立伟2( ),姜锐2(
),姜锐2( )
)
- 1.长春中医药大学药学院中药化学系,吉林 长春 130117
2.长春中医药大学附属医院中医药研究中心,吉林 长春 130021
3.长春中医药大学东北亚中医药研究中心,吉林 长春 130117
4.广州白云美湾检测有限公司,广东 广州 510000
Promotional effect of CHAaHGS on hair growth and its mechanism
Yanhong MU1,2,Yingna LI1,2,Jianzeng LIU3,Chunhong LUO4,Liwei SUN2( ),Rui JIANG2(
),Rui JIANG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Tradional Chinese Medicine Chemistry,School of Pharmacy,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
2.Research Center of Chinese Medicine,Affiliated Hospital,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130021,China
3.North East Asian Center for Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changchun University of Chinese Medicine,Changchun 130117,China
4.Guangzhou Baiyun Meiyan Inspection Co,Ltd,Guangzhou 510000,China
摘要:
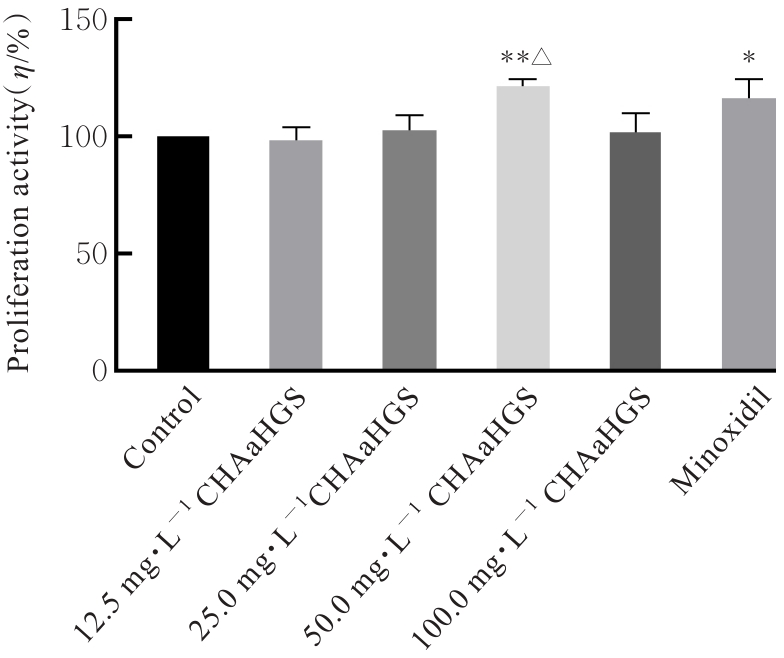
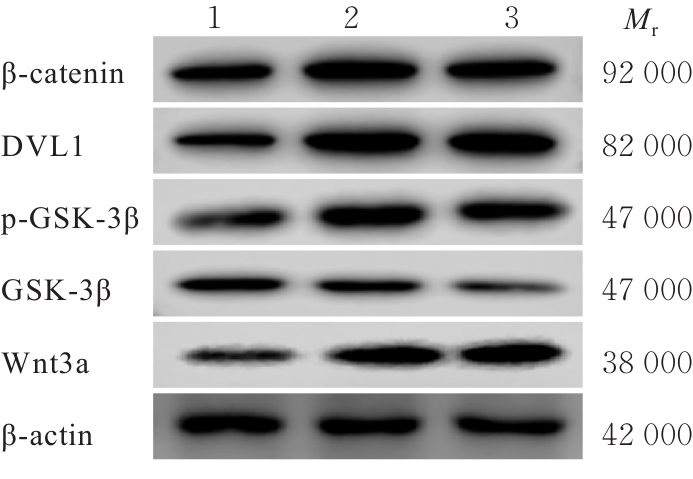
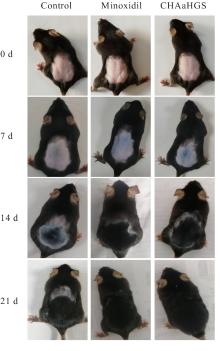
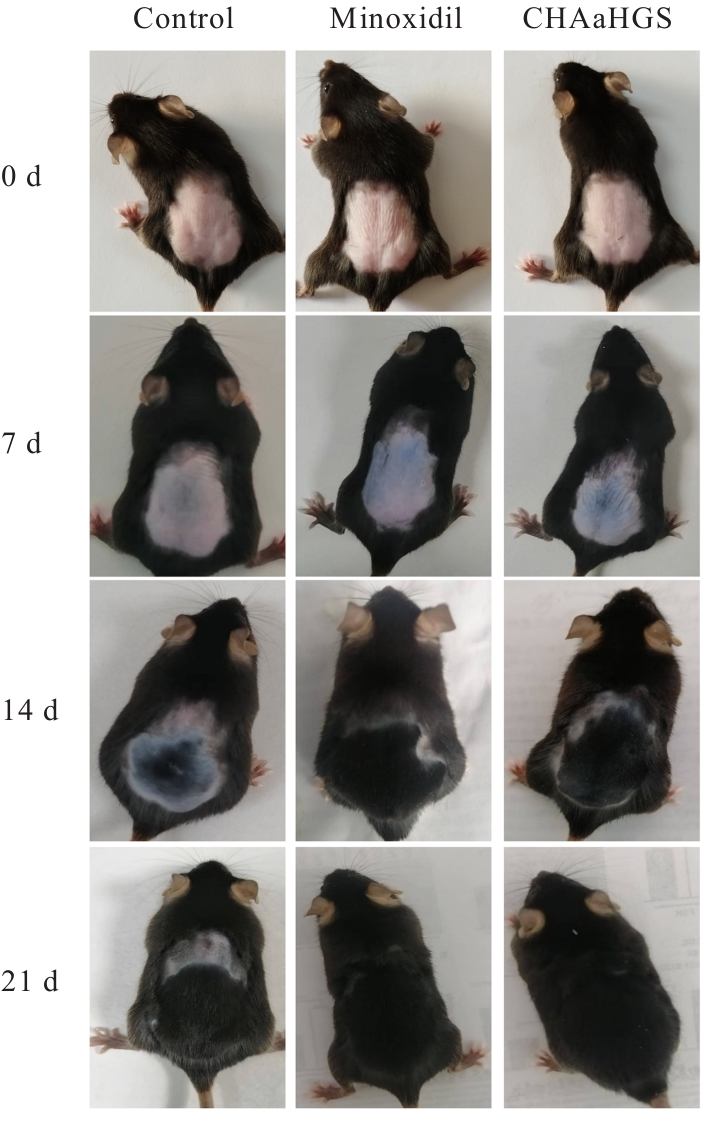
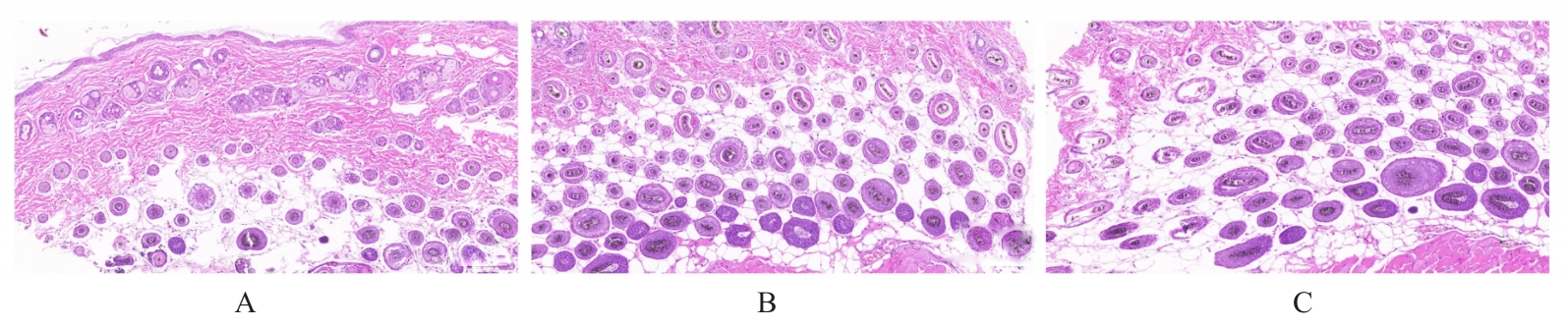
目的 通过人真皮毛乳头细胞(HDPCs)体外实验、C57BL/6小鼠体内实验和人体功效测试,探讨防脱育发液(CHAaHGS)对毛发生长的影响,阐明其潜在作用机制。 方法 将HDPCs分为对照组、CHAaHGS组和米诺地尔组。采用MTT法检测各组HDPCs增殖活性,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测各组HDPCs上清液中血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)、肝细胞生长因子(HGF)、胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)和转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)水平,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组HDPCs中VEGF、HGF、IGF-1、TGF-β1和碱性磷酸酶(ALP)mRNA表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组HDPCs中β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)、蓬乱蛋白1(DVL1)、糖原合成酶激酶3β(GSK-3β)、磷酸化GSK-3β(p-GSK-3β)和无翅型MMTV整合位点家族蛋白(Wnt)家族成员3a(Wnt3a)蛋白表达水平。取18只小鼠随机分为对照组、CHAaHGS组和米诺地尔组,每组6只。采用脱毛膏建立小鼠脱毛模型,脱毛后立即给予相应药物处理。检测第21天各组小鼠新生毛发长度和毛发质量,采用HE染色观察各组小鼠第7天背部脱毛区皮肤毛囊形态表现,ELISA法检测各组小鼠背部脱毛区皮肤组织中VEGF、HGF、IGF-1和TGF-β1水平。将60名受试者随机分成对照组和CHAaHGS组,每组30名。检测第0、4、8和12周各组受试者脱发数量和毛发密度。 结果 MTT法,与对照组比较,50 mg·L-1 CHAaHGS组细胞增殖活性明显升高(P<0.01)。ELISA法,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组细胞上清液中VEGF、HGF和IGF-1水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),TGF-β1水平明显降低(P<0.01)。RT-qPCR法,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组细胞中VEGF、HGF、IGF-1和ALP mRNA表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),TGF-β1 mRNA表达水平明显降低(P<0.01);Western blotting法,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组细胞中β-catenin、DVL1、p-GSK-3β和Wnt3a蛋白表达水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),GSK-3β蛋白表达水平明显降低(P<0.05)。动物实验,第21天时,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组小鼠新生毛发长度明显增长(P<0.05),毛发质量明显增加(P<0.01)。第7天时,HE染色,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组小鼠毛囊间距明显减少(P<0.05),毛囊数量明显增加(P<0.01);ELISA法,与对照组比较,CHAaHGS组小鼠脱毛区皮肤组织中VEGF、HGF和IGF-1水平明显升高(P<0.05或P<0.01),TGF-β1水平明显降低(P<0.05)。人体功效试验测试,与对照组比较,第12周时CHAaHGS组受试者脱发数量明显减少(P<0.01),局部毛发密度增加(P<0.05)。 结论 CHAaHGS对毛发生长具有促进作用,其机制可能与其增加HDPCs增殖活性,诱导VEGF、HGF和IGF-1分泌及激活Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5