吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1251-1259.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250511
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
新型甜味剂赤藓糖醇对ICR小鼠糖脂代谢的影响及肝脏代谢物的代谢组学分析
- 1.海军第九七一医院超声诊断科,山东 青岛 266000
2.海军军医大学第二附属医院儿科,上海 200003
3.海军第九七一医院崂山医疗区外科,山东 青岛 266000
4.中国人民解放军海军特色医疗中心消化内科,上海 200003
5.海军第九七一医院消化内科,山东 青岛 266000
Effects of novel sweetener erythritol on glycolipid metabolism and metabonomic analysis of hepatic metabolites in ICR mice
Zhen DONG1,Yueming WU2,Bin GAO3,Kewei GAO4,Haitao YU5( )
)
- 1.Department of Ultrasound Diagnosis,971st Hospital of Navy,Qingdao 266000,China
2.Department of Pediatrics,Second Affiliated Hospital,Naval Medical University,Shanghai 200003,China
3.Department of Surgery,Laoshan Medical District,971st Hospital of Navy,Qingdao 266000,China
4.Department of Gastroenterology,Navy Medical Center,People’s Liberation Army of China,Shanghai 200082,China
5.Department of Gastroenterology,971st Hospital of Navy,Qingdao 266000,China
摘要:
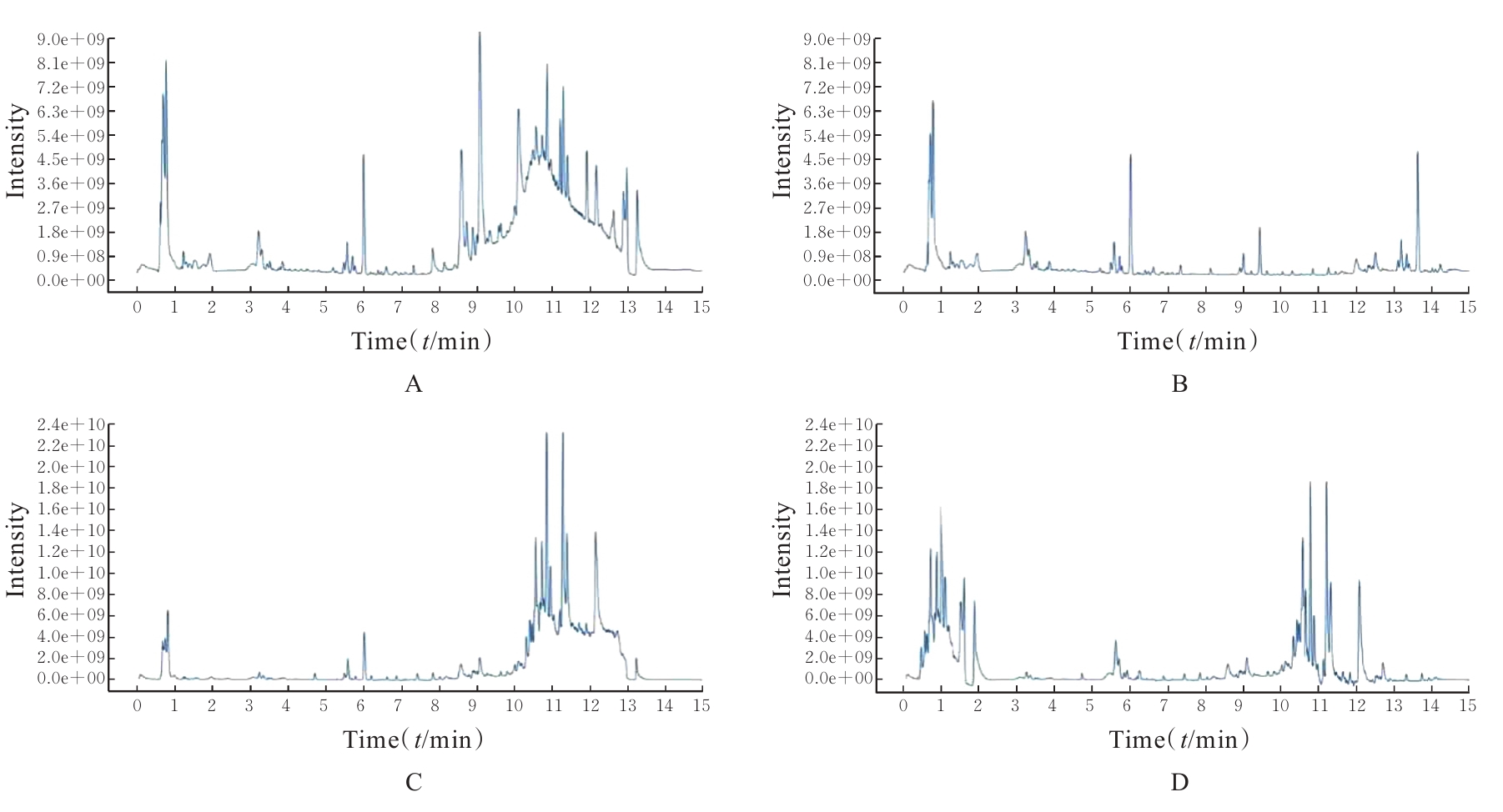
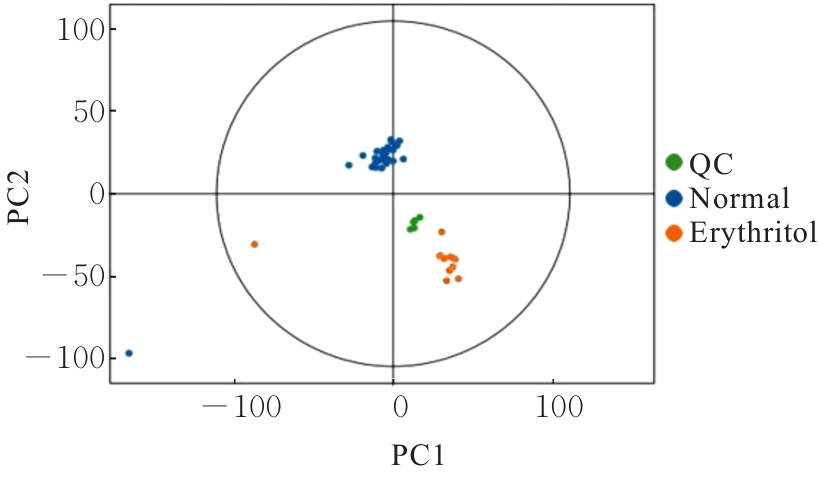
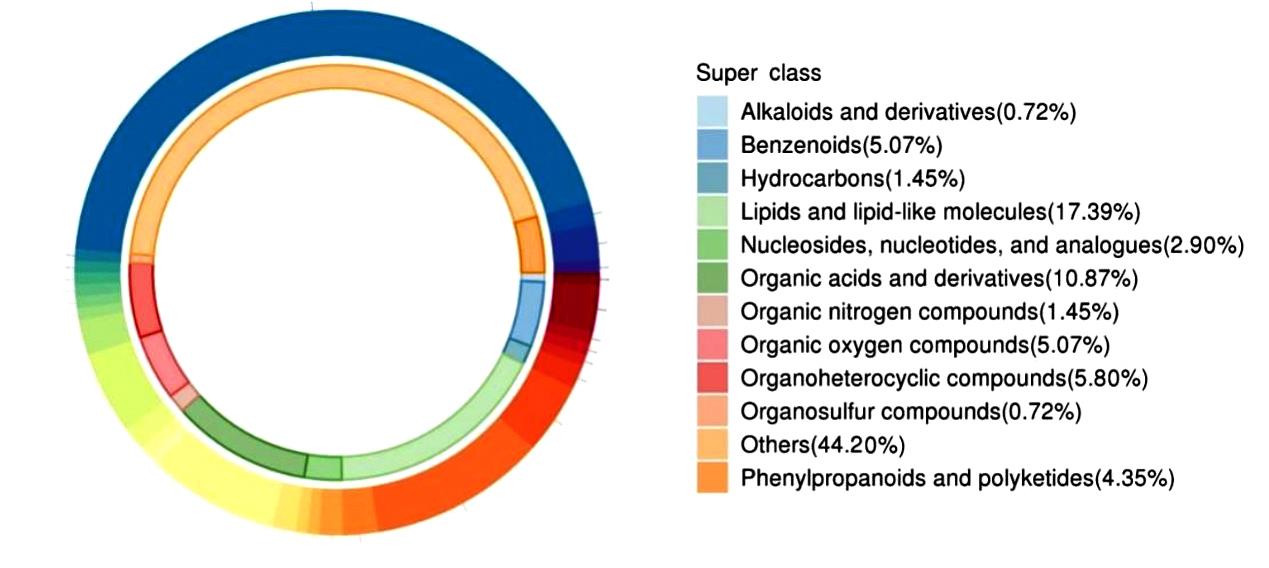
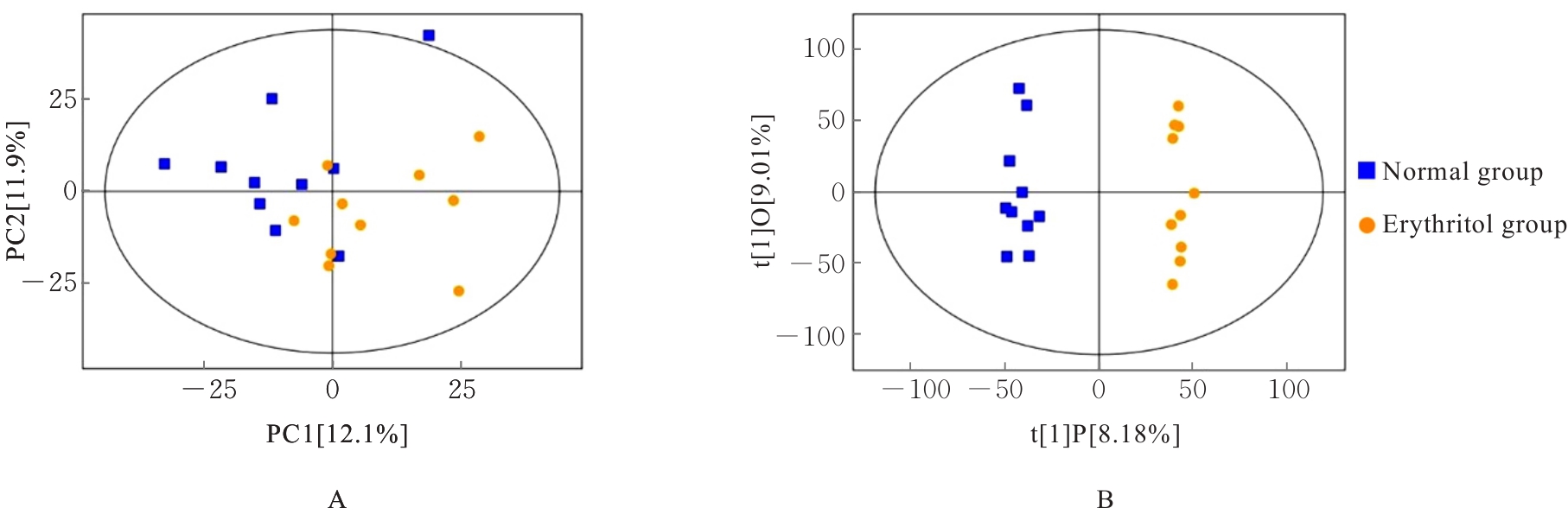
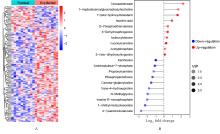
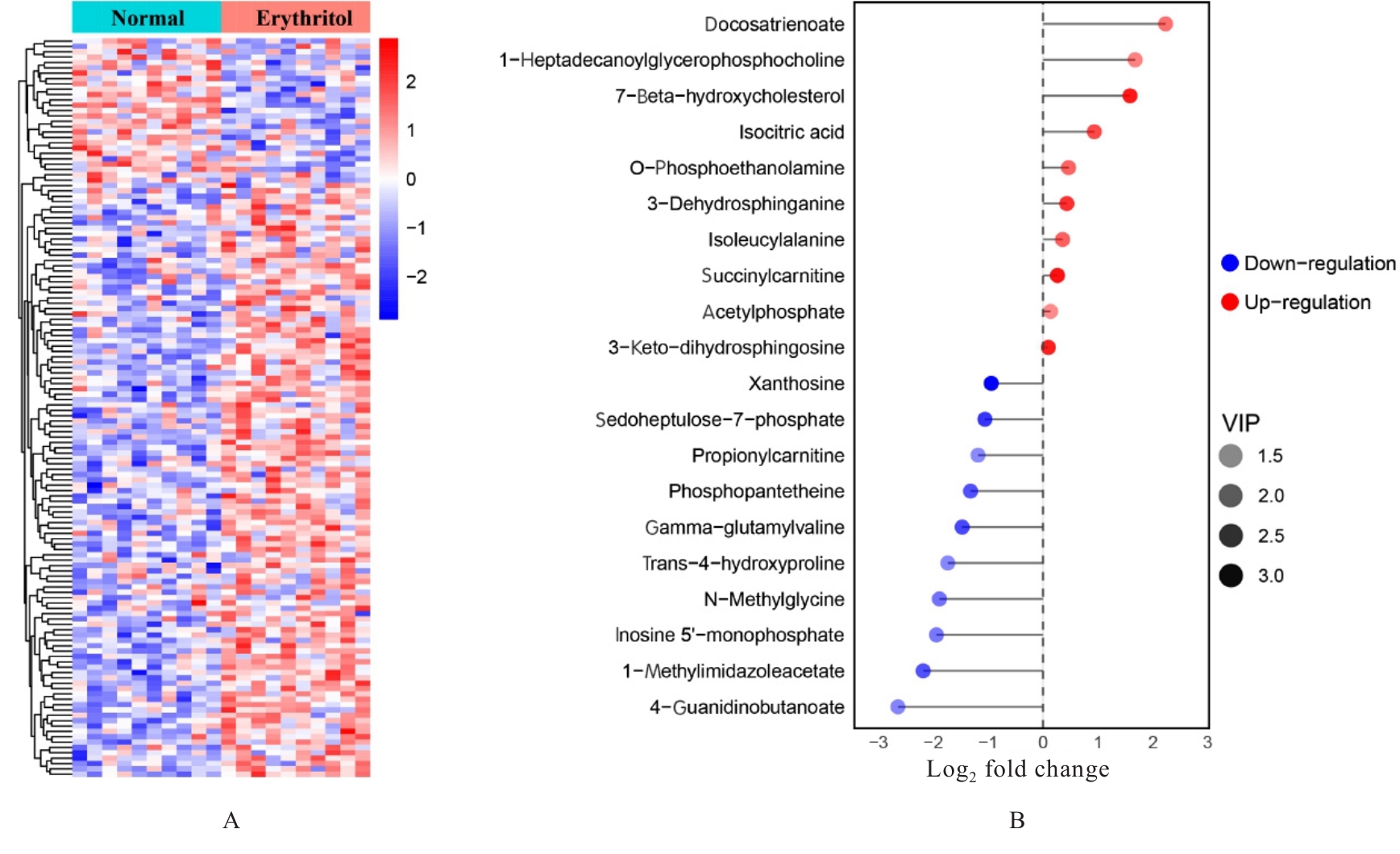
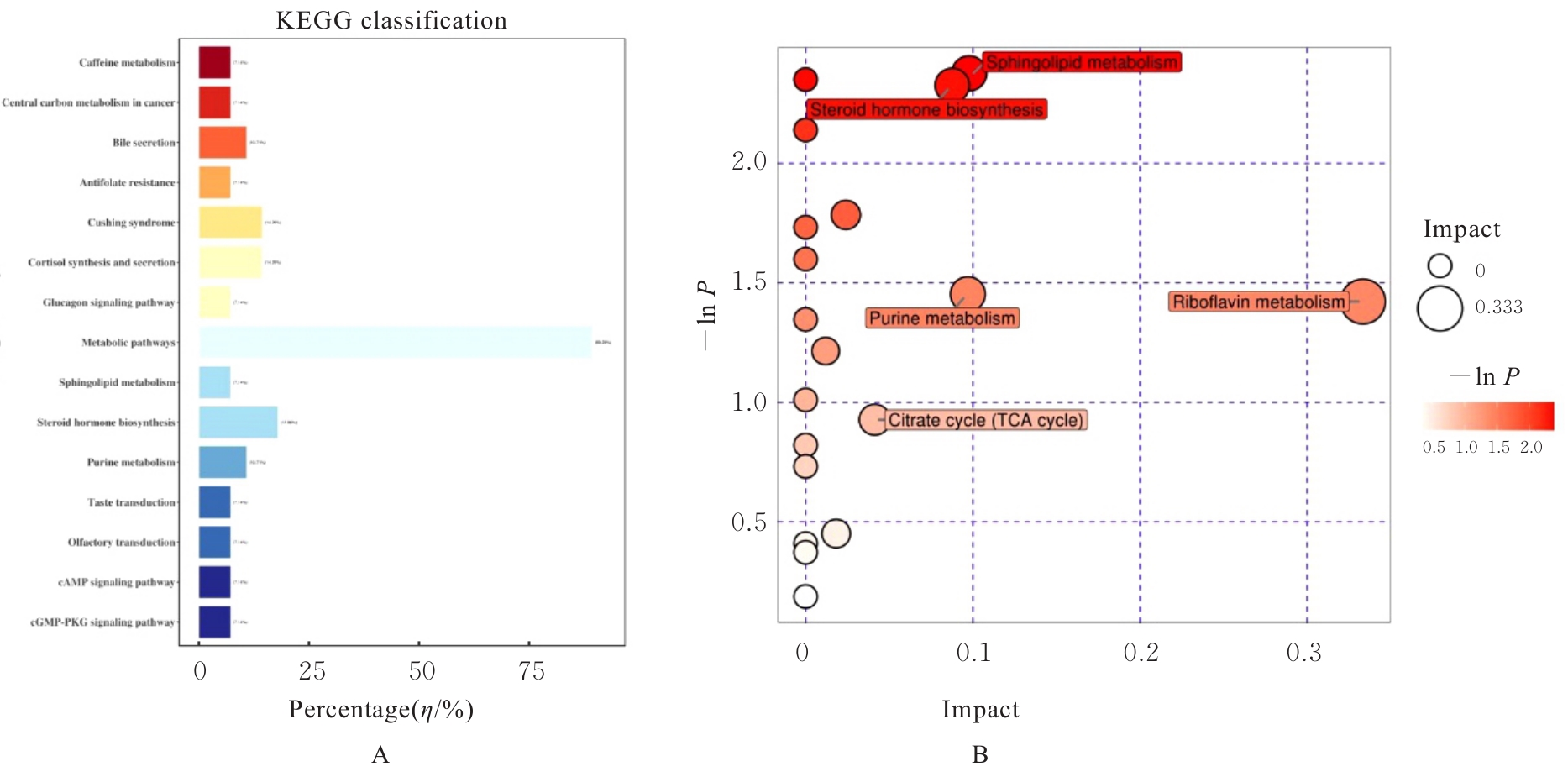
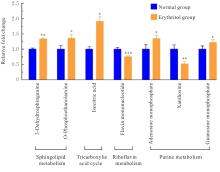
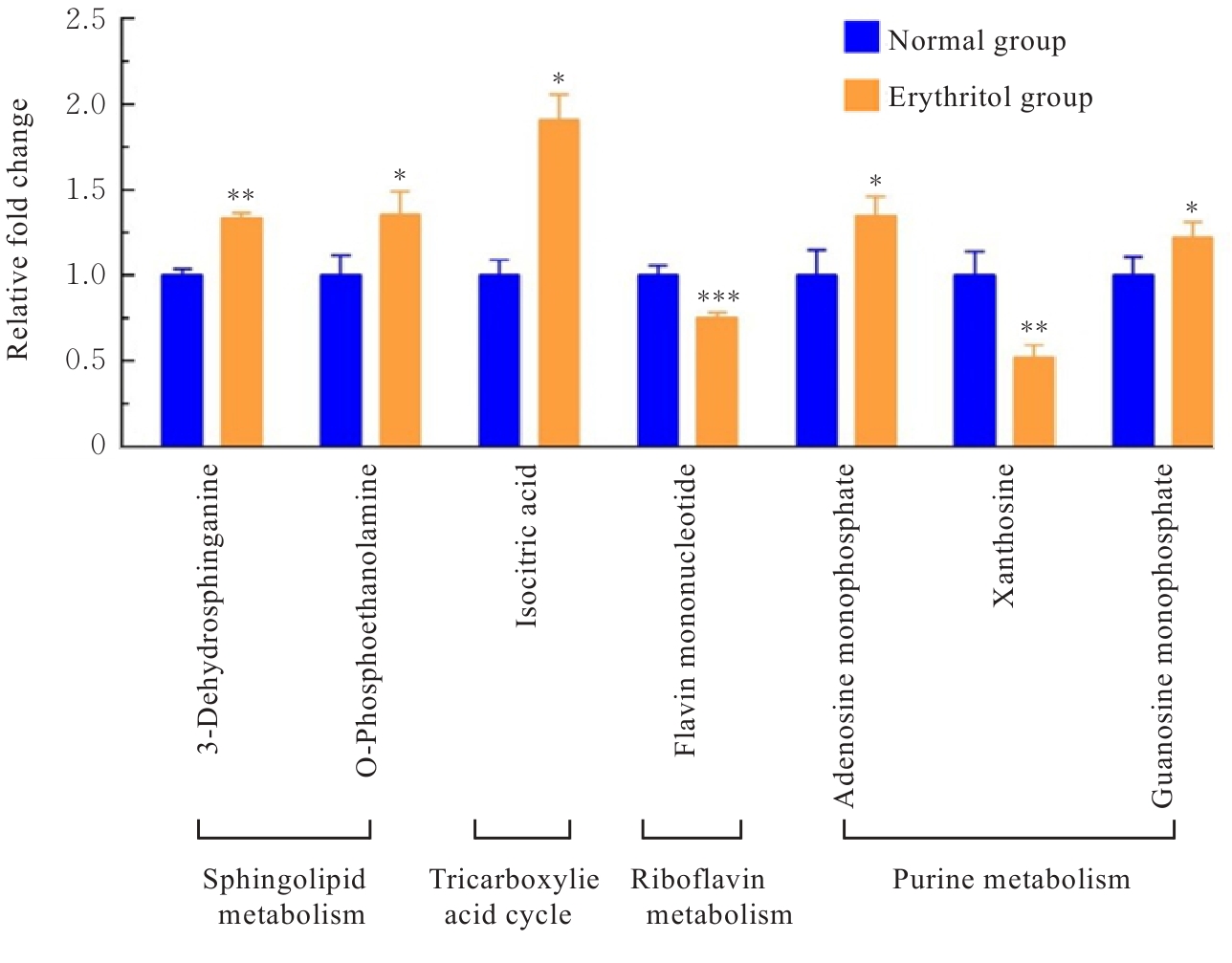
目的 探讨赤藓糖醇对机体糖脂代谢的影响,并基于代谢组学研究赤藓糖醇影响肝脏代谢的作用机制。 方法 雄性ICR小鼠随机分为正常组、蔗糖组(2%蔗糖)、低剂量赤藓糖醇(1%赤藓糖醇)组、中剂量赤藓糖醇(2%赤藓糖醇)组和高剂量赤藓糖醇(4%赤藓糖醇)组,每组10只。配制相应浓度蔗糖和赤藓糖醇溶液并置于水瓶中,小鼠可自由饮用和进食,连续观察12周,测定各组小鼠体质量、进食量和饮水量。采用试剂盒检测各组小鼠血清甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)和血糖水平,计算小鼠肝脏指数。采用超高效液相色谱-轨道阱高分辨质谱(UPLC-OE-MS)非靶标代谢组学检测正常组和高剂量赤藓糖醇组小鼠肝脏代谢物,采用生物信息学以变量重要性投影(VIP) >1且校正后P<0.05为条件筛选2组小鼠肝脏差异代谢物,利用京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)信号通路富集分析探讨肝脏差异代谢物的功能作用。 结果 与正常组比较,其他各组小鼠体质量、进食量、肝脏指数和血脂水平差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),高剂量赤藓糖醇组小鼠血糖水平明显升高(P<0.01)。 2组小鼠肝脏代谢组学分析共鉴定1 144个代谢物, 主要包括脂质和脂类小分子(17.39%)、有机酸及衍生物(10.87%)、有机杂环化合物(5.80%)和有机氧化合物(5.07%)等。与正常组比较,高剂量赤藓糖醇组小鼠共有138个肝脏差异代谢物,其中112个代谢物上调,26个代谢物下调。KEGG信号通路富集分析,差异代谢物主要富集于代谢、类固醇激素生物合成、皮质醇合成与代谢和库欣综合征等通路;进一步对代谢通路进行拓扑分析,差异代谢物主要涉及鞘脂代谢、三羧酸循环、核黄素代谢、类固醇激素生物合成和嘌呤代谢等信号通路。 结论 长期摄入高剂量赤藓糖醇可引起小鼠血糖水平升高,其机制可能是通过干扰核黄素代谢影响三羧酸循环和干扰鞘脂代谢,导致血糖控制系统受损。
中图分类号:
- R151.2