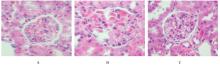
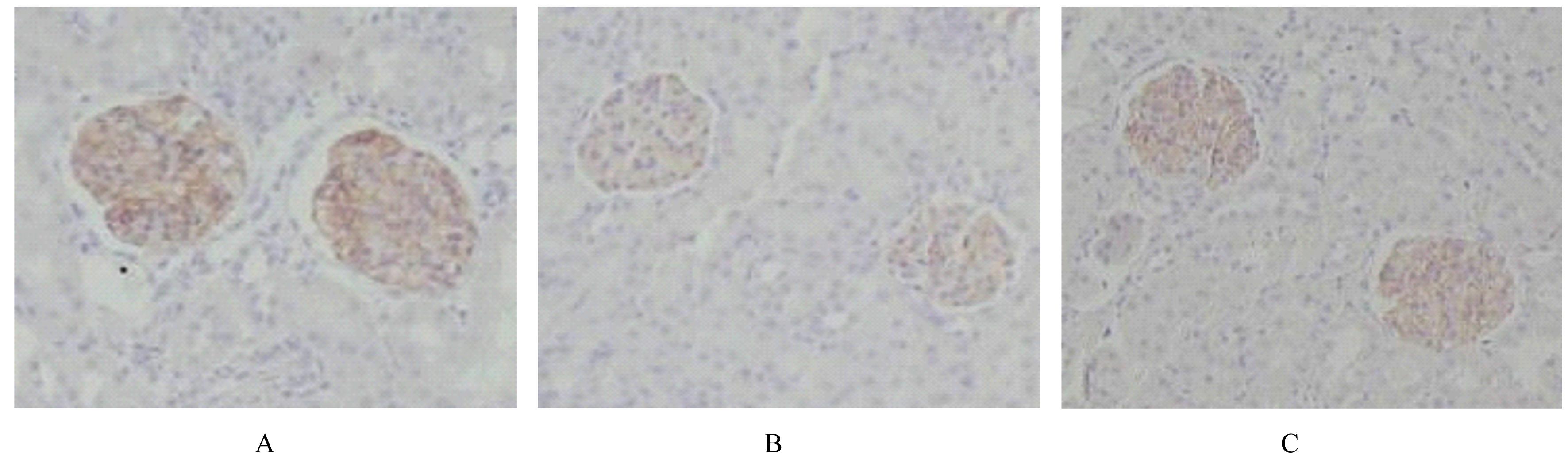
| 1 |
LIANG R, WANG M, FU C, et al. Liraglutide protects against high-fat diet-induced kidney injury by ameliorating apoptosis[J]. Endocr Connect,2020,9(9): 946-954.
|
| 2 |
KORNELIUS E, LI H H, PENG C H, et al. Liraglutide protects against glucolipotoxicity-induced RIN-m5F β-cell apoptosis through restoration of PDX1 expression[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(1): 619-629.
|
| 3 |
BAI F, ZHANG L H, ZHANG W W, et al. Conservation of glucagon like peptide-1 level with liraglutide and linagilptin protects the kidney against angiotensin Ⅱ-induced tissue fibrosis in rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 867: 172844.
|
| 4 |
LI J, LI N, YAN S, et al. Liraglutide protects renal mesangial cells against hyperglycemia mediated mitochondrial apoptosis by activating the ERK Yap signaling pathway and upregulating Sirt3 expression[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(4): 2849-2860.
|
| 5 |
ZHANG S S, WU Z, ZHANG Z, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts to prevent podocyte apoptosis induced by advanced oxidative protein products[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017,482(4):1413-1419.
|
| 6 |
CHEN P, SHI X, XU X, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates early renal injury by the activation of renal FoxO1 in a type 2 diabetic kidney disease rat model[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 137: 173-182.
|
| 7 |
祁冰雪,马 彦,张艺献,等.利拉鲁肽对高糖诱导足细胞损伤后相关蛋白mRNA和蛋白表达的影响及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2021,288(2):275-283.
|
| 8 |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)(上)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2021,41(8):668-695.
|
| 9 |
AN X, ZHANG L, YUAN Y, et al. Hyperoside pre-treatment prevents glomerular basement membrane damage in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting podocyte heparanase expression[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1):6413.
|
| 10 |
MAEZAWA Y, TAKEMOTO M, YOKOTE K. Cell biology of diabetic nephropathy: Roles of endothelial cells,tubulointerstitial cells and podocytes[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2015, 6(1): 3-15.
|
| 11 |
DAI H R, LIU F, QIU X P, et al. Alleviation by Mahuang Fuzi and Shenzhuo decoction in high glucose-induced podocyte injury by inhibiting the activation of wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, resulting in activation of podocyte autophagy[J]. Evid Based Complement Altern Med, 2020, 2020: 7809427.
|
| 12 |
YOSHIBAYASHI M, KUME S, YASUDA-YAMAHARA M, et al. Protective role of podocyte autophagy against glomerular endothelial dysfunction in diabetes[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 525(2): 319-325.
|
| 13 |
HONG Q, ZHANG L, DAS B, et al. Increased podocyte Sirtuin-1 function attenuates diabetic kidney injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2018, 93(6): 1330-1343.
|
| 14 |
YAMADA T, WAKABAYASHI M, BHALLA A,et al.Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with SGLT-2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2021, 20(1): 14.
|
| 15 |
HERRERA COMOGLIO R, VIDAL GUITART X. Cardiovascular outcomes, heart failure and mortality in type 2 diabetic patients treated with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs): a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational cohort studies[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2020, 74(9): e13553.
|
| 16 |
HABIB H A, HEEBA G H, KHALIFA M M A. Effect of combined therapy of mesenchymal stem cells with GLP-1 receptor agonist, exenatide, on early-onset nephropathy induced in diabetic rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 892: 173721.
|
| 17 |
CUI J, SHANG A, WANG W, et al. Rational design of a GLP-1/GIP/Gcg receptor triagonist to correct hyperglycemia, obesity and diabetic nephropathy in rodent animals[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 260: 118339.
|
| 18 |
MUSKIET M H A, TONNEIJCK L, SMITS M M, et al. GLP-1 and the kidney: from physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2017, 13(10): 605-628.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU X, HUANG C H, LAO J, et al. Acute hemodynamic and renal effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 analog and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in rats[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2015, 14: 29.
|
| 20 |
DRUCKER D J. The cardiovascular biology of glucagon-like peptide-1[J]. Cell Metab, 2016, 24(1): 15-30.
|
| 21 |
HUANG L, LIN T, SHI M, et al. Liraglutide suppresses production of extracellular matrix proteins and ameliorates renal injury of diabetic nephropathy by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2020, 319(3): F458-F468.
|
| 22 |
RAMZY M M, ABDALLA A M, ZENHOM N M,et al.Therapeutic effect of liraglutide on expression of CTGF and BMP-7 in induced diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(10): 17512-17519.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU S J, BAI L, LV L, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates renal injury in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats by activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity via the downregulation of the nuclear factor κB pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 10(5): 2587-2594.
|
| 24 |
NIU B, LI C, SU H, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exendin-4 protects against interleukin-1β-mediated inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by mouse insulinoma β cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(3): 2671-2676.
|
| 25 |
NIE Y S, FU C X, ZHANG H M, et al. Celastrol slows the progression of early diabetic nephropathy in rats via the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. BMC Complementary Med Ther, 2020, 20(1): 1-14.
|
| 26 |
HUANG G, LV J, LI T, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 ameliorates podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 38(4): 1179-1189.
|
| 27 |
ZHANG Y, CHEN X, YUAN L, et al. Down-regulation of IRAK1 attenuates podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 506(3): 529-535.
|
 )
)
 )
)